【机器学习】day4:作业一:预测PM2.5的值(李宏毅)
作业一:预测PM2.5的值
- 1. 作业描述
- 2. 代码实现
-
- 2.1 数据预处理
- 2.2 建立模型
- 2.3 模型训练
- 2.4 模型评估
- 2.5 模型预测
1. 作业描述
视频要求:李宏毅《机器学习》- 作业1 - PM2.5预测
作业描述
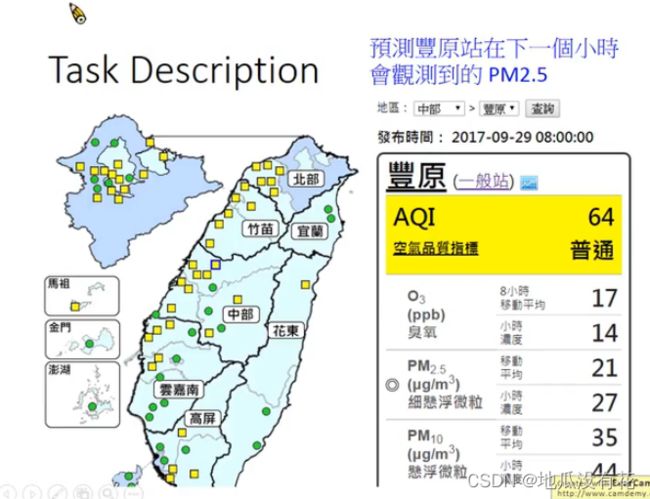
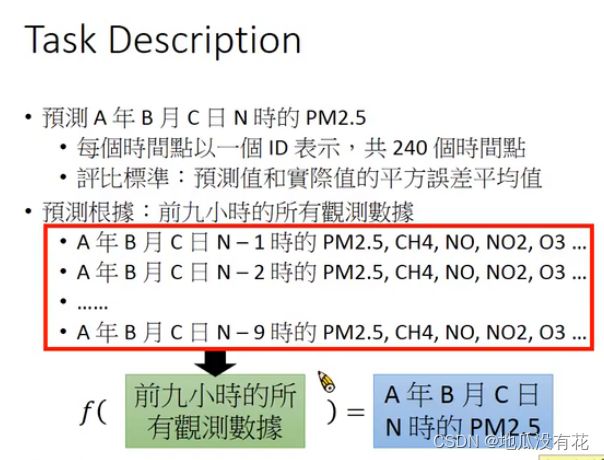
让机器预测到丰原站在下一个小时会观测到的PM2.5。
举例来说,现在是2017-09-29 08:00:00,那么要预测2017-09-29 09:00:00丰原站的PM2.5值会是多少。
2. 代码实现
代码参考:机器学习笔记-作业1
2.1 数据预处理
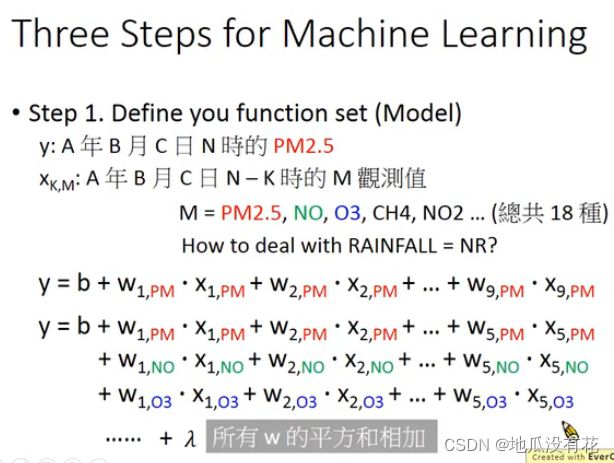
# 取出 PM2.5 的数据,训练集中一共有 240 天,每天取出 15 组 含有 9 个特征 和 1 个标签的数据,共有 240*15*9个数据
for i in range(15):
x = train.iloc[:, i:i + 9]
# notice if we don't set columns name, it will have different columns name in each iteration
x.columns = np.array(range(9))
y = train.iloc[:, i + 9]
y.columns = np.array(range(1))
train_x.append(x)
train_y.append(y)
train_x = pd.concat(train_x)
train_y = pd.concat(train_y)
# 进行标准缩放,即数据归一化
ss = StandardScaler()
# 进行数据拟合
ss.fit(train_x)
# 进行数据转换
train_x = ss.transform(train_x)
2.2 建立模型
def __init__(self):
# 初始化 Linear Regression 模型
self.coef_ = None
self.intercept_ = None
self._theta = None
def fit_normal(self, X_train, y_train):
# 根据训练数据集X_train, y_train训练Linear Regression模型
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
# 对训练数据集添加 bias
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train]) # np.hstack():横向拼接,增加特征量
self._theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train) # np.linalg.inv():矩阵求逆
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
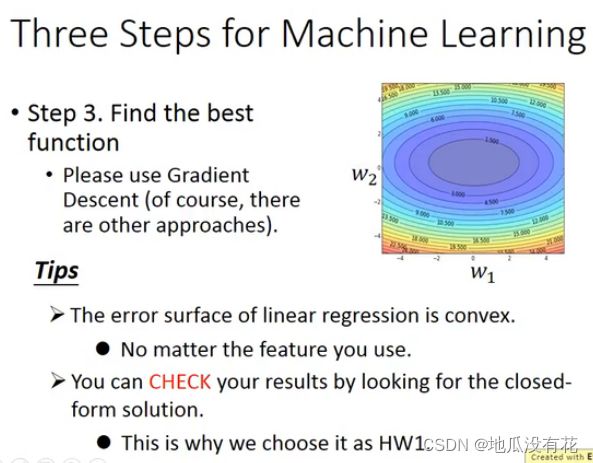
2.3 模型训练
def fit_gd(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):
'''
:param X_train: 训练集
:param y_train: label
:param eta: 学习率
:param n_iters: 迭代次数
:return: theta 模型参数
'''
# 根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
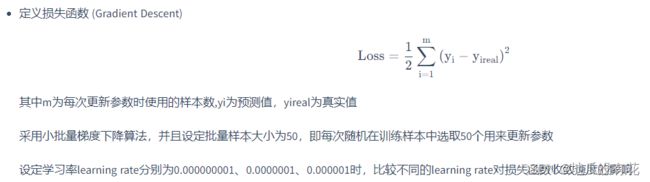
# 定义损失函数
def J(theta, X_b, y):
try:
return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(y)
except:
return float('inf')
# 对损失函数求导
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):
return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y)
def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):
'''
:param X_b: 输入特征向量
:param y: lebel
:param initial_theta: 初始参数
:param eta: 步长
:param n_iters: 迭代次数
:param epsilon: 容忍度
:return:theta:模型参数
'''
theta = initial_theta
cur_iter = 0
while cur_iter < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
# abs() 函数返回数字的绝对值。
if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):
break
cur_iter += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) # 初始化theta
self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
2.4 模型评估
# 定义评估函数
# 计算均方误差(Mean Squared Error,MSE)
# r^2 用于度量因变量的变异中 可以由自变量解释部分所占的比例 取值一般为 0~1
def r2_score(y_true, y_predict):
# 计算y_true和y_predict之间的MSE
MSE = np.sum((y_true - y_predict) ** 2) / len(y_true)
# 计算y_true和y_predict之间的R Square
return 1 - MSE / np.var(y_true)
2.5 模型预测
def predict(self, X_predict):
# 给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])
return X_b.dot(self._theta)
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
# 根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)