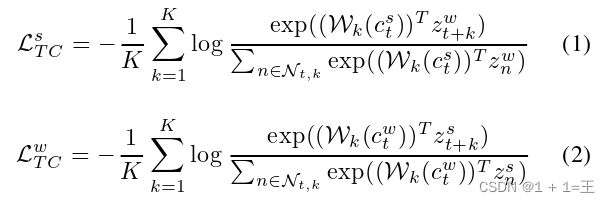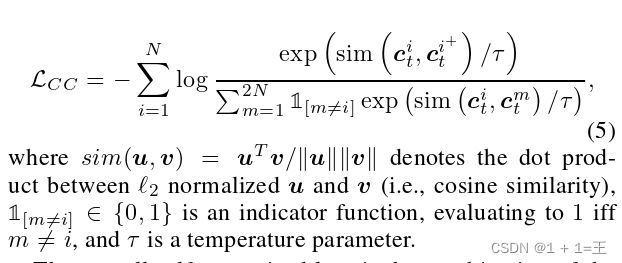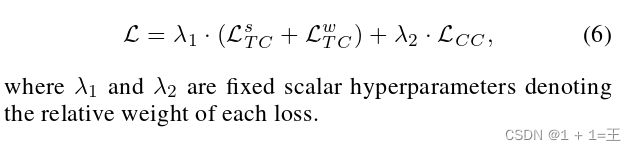- Python学习日记------def __init__( ):函数
Canliays
学习python
在Python中,__init__方法是类的构造函数,用于在创建对象时进行初始化。它可以接受参数也可以不接受参数,具体的选择取决于你是否希望在创建对象时传入初始值。无参数的__init__方法无参数的__init__方法通常在类定义时使用默认值来初始化属性,而不需要在创建对象时传入任何参数。classStudent:def__init__(self):self.name="Unknown"#默认值
- AI人工智能深度学习算法:搭建可拓展的深度学习模型架构
AI天才研究院
大数据AI人工智能AI大模型企业级应用开发实战大厂Offer收割机面试题简历程序员读书硅基计算碳基计算认知计算生物计算深度学习神经网络大数据AIGCAGILLMJavaPython架构设计Agent程序员实现财富自由
AI人工智能深度学习算法:搭建可拓展的深度学习模型架构作者:禅与计算机程序设计艺术/ZenandtheArtofComputerProgramming1.背景介绍1.1问题的由来随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,深度学习作为其主要驱动力之一,已经在各个领域取得了显著的成果。然而,随着模型规模的不断扩大,如何高效地搭建、训练和部署深度学习模型,成为一个亟待解决的问题。传统的单机训练方式在计算资源有限的情况
- 【Matlab高端绘图SCI绘图模板】第006期 对比绘柱状图 (只需替换数据)
小熊科研路(同名GZH)
可视化matlab信息可视化开发语言
1.简介柱状图作为科研论文中常用的实验结果对比图,本文采用了3组实验对比的效果展示图,代码已调试好,只需替换数据即可生成相关柱状图,为科研加分。通过获得Nature配色的柱状图,让你的论文看起来档次更高,让你的科研更快地进行成果产出。用户能够生成既美观又精确的数据可视化图表。代码涵盖了从数据准备到最终图像输出的全过程,包括文件读取、颜色自定义、图形界面设置、数据可视化以及图像导出等关键步骤。适合数
- 手把手教你怎么用chatgpt写毕业论文和学术小论文
洛白白
chatgptchatgpt学习方法经验分享笔记学习
以下是50个学术论文指令的目录,当然,用完了复制的时候.千万记得删除指令。一、学术角色预设指令(2个)二、论文撰写指令(8个)三、学术润色指令(20个)·四、中英翻译指令(5个)·五、论文查重指令(1个)·六、参考文献指令(2个)·七、投稿审稿指令(2个)·八、其他学术指令(11个)一、学术角色预设论文中无论是润色,语法检查还是降重,都要先进行角色预设,先给定一个身份。有些学术GPT是自带提示词的
- ignoring return value of ‘scanf’怎么解决
Nate Hillick
算法数据结构c++c语言开发语言
这个警告是说,scanf函数的返回值被忽略了。scanf函数的返回值表示成功读入的项目数,因此在程序中忽略它可能会导致错误。要解决这个警告,可以使用以下方法之一:将scanf函数的返回值存储在变量中,并在后续代码中使用该变量:intret=scanf("%d",&num);if(ret!=1){//处理错误}
- python 只用opencv吗,python – OpenCV:使用solvePnP来确定单应性
weixin_39934296
python只用opencv吗
在过去的几周里,我尝试学习纠正图像,并在这里的人们的帮助下,我已经设法更好地理解它.大约一个星期前,我设置了一个我想要纠正的测试示例(从上面查看图像).这很好(原始:http://sitedezign.net/original.jpg和纠正:http://sitedezign.net/rectified.jpg)功能T=cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(UV_cp,XYZ_g
- Monorepo 在网易的工程改造实践
若川视野
前端javascriptnpmvue.js开发语言
大家好,我是若川。我持续组织了近一年的源码共读活动,感兴趣的可以点此扫码加我微信lxchuan12参与,每周大家一起学习200行左右的源码,共同进步。同时极力推荐订阅我写的《学习源码整体架构系列》包含20余篇源码文章。历史面试系列。另外:目前建有江西|湖南|湖北籍前端群,可加我微信进群。背景目前云音乐内有多个RN收银台场景分布在不同的工程,比如页面收银台,浮层收银台,个性收银台等,后续可能还会有别
- # 第一章:认识chatgpt
出门喝奶茶
chatgptchatgpt
chatgpt发展背景详细介绍一、基础理论背景人工智能和自然语言处理的兴起早期理论:20世纪中期,人工智能(AI)初见端倪,目标是模拟人类智能。自然语言处理作为AI的重要分支,致力于让机器理解和生成人类语言。关键里程碑:1980年代的统计方法和2000年代的神经网络技术,使NLP实现了从规则驱动到数据驱动的转变。神经网络与深度学习2010年代,深度学习的兴起极大推动了NLP的发展。基于大规模语料库
- 机器学习&深度学习目录
UQI-LIUWJ
各专栏目录深度学习人工智能1024程序员节
机器学习模型机器学习笔记:Transformer_刘文巾的博客-CSDN博客attention相关机器学习笔记:attention_UQI-LIUWJ的博客-CSDN博客机器学习笔记:ELMOBERT_UQI-LIUWJ的博客-CSDN博客机器学习笔记:ViT(论文AnImageIsWorth16X16Words:TransformersforImageRecognitionatScale)_UQ
- 医院服务总线常见架构比较:面向服务架构与事件驱动架构
登山看云海
医院信息集成平台架构系统架构
随着医疗信息化的快速发展,医院系统的集成需求日益增长。电子病历(EMR)、临床信息系统(CIS)、实验室信息系统(LIS)等各类系统之间的数据交换和协同工作,要求信息系统能够实现高效、稳定、可扩展的架构设计。在这种背景下,企业服务总线(ESB,EnterpriseServiceBus)成为关键的集成解决方案。本文将重点对比两种常见架构——面向服务架构(SOA,Service-OrientedArc
- RAG系列(二):如何优化索引
东临碣石82
kotlinandroid开发语言
上篇文章总览了RAG的各个环节,这篇我们接着讲第一个环节也就是“索引”环节如何做优化。具体细节“人人都是产品经理”的这篇文章里有非常详细的说明,不过我对微软体系搜索优化了解的多些,看到过的一些优化方法这里没有提到,比如微软的AISearch还有DataverseSemanticSearch里用到一些优化方法这里就没看到。知识搜索是一个可以扣出很多细节的领域,这里做个备考、补充学习过程中的一些体会并
- chatgpt赋能Python-python_pyomo
atest166
ChatGptpythonchatgpt开发语言
PythonPyomo:优化问题解决利器PythonPyomo是一个开源的Python优化建模语言工具箱。它提供了一种简单灵活的方法来描述优化问题,并在可行性、线性、非线性、混合整数和二次规划等方面提供广泛的建模和求解功能。优点灵活:Pyomo可以通过对象导向编程方式来描述优化问题,而无需使用特定的语法或格式。它提供了一种比传统表格方式更灵活的方式来表示问题。可扩展:Pyomo的建模框架可以很容易
- 【练习】PAT 乙 1024 科学计数法
柠石榴
PAT题解输入输出c++开发语言字符串
题目科学计数法是科学家用来表示很大或很小的数字的一种方便的方法,其满足正则表达式[±][1-9]”.”[0-9]+E[±][0-9]+,即数字的整数部分只有1位,小数部分至少有1位,该数字及其指数部分的正负号即使对正数也必定明确给出。现以科学计数法的格式给出实数A,请编写程序按普通数字表示法输出A,并保证所有有效位都被保留。输入格式每个输入包含1个测试用例,即一个以科学计数法表示的实数A。该数字的
- 【用Java学习数据结构系列】初识泛型
Gu Gu Study
【用Java学习数据结构系列】java数据结构机器学习人工智能
看到这句话的时候证明:此刻你我都在努力加油陌生人br/>个人主页:GuGuStudy专栏:用Java学习数据结构系列喜欢的一句话:常常会回顾努力的自己,所以要为自己的努力留下足迹喜欢的话可以点个赞谢谢了。作者:小闭前言好久没有更新文章了,大概断更了20天,想着今天就写一下文章吧!最近也是又温习了一下数据结构,其实之前我写过关于数据结构的一个专栏那个专栏是写了顺序表,链表,栈和队列,但是那时是用C语
- 软件测试中的AI-为什么它在软件自动化测试中很重要?
测试界霄霄
软件测试人工智能功能测试自动化测试软件测试程序人生职场和发展
通俗地说,人工智能(AI)是计算机科学的一个领域,它专注于使机器“智能化”。所谓智能,就是使系统能够像人类一样学习和做出决策。因此,人工智能机器将能够学习如何在特定情况下做出反应,然后根据其学习情况在未来场景中做出决策。人工智能(AI)在大多数领域的应用仍处于早期阶段,想要完美运行还需要很长时间。今天的人工智能(AI)技术可以帮助我们完成许多不需要复杂思考的重复性日常任务。接下来,让我们讨论软件测
- 【AI论文】FilmAgent: 一个用于虚拟3D空间中端到端电影制作自动化的多智能体框架
东临碣石82
自动化运维
摘要:虚拟电影制作涉及复杂的决策过程,包括剧本编写、虚拟摄影以及演员的精确定位和动作设计。受近期基于语言智能体社会的自动化决策领域进展的启发,本文提出了FilmAgent,这是一个新颖的、基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体协作框架,旨在实现我们构建的3D虚拟空间中的端到端电影制作自动化。FilmAgent模拟了各种剧组成员角色,包括导演、编剧、演员和摄影师,并涵盖了电影制作工作流程的关键阶段:(
- GitLab/GitHub上传项目时忽略文件规则
满眼清香
#Git#Windows操作系统gitWindows
平时使用idea或者eclipse时总会有一些自动生成的文件,比如日志文件、编译文件,但是项目上传的时候这些文件是不需要的,而且浪费空间导致项目非常大,所以这些没有用的文件上传的时候需要通过.ignore过滤掉,接下来说一下过滤规则。git对于.ignore配置文件是按行从上到下进行规则匹配的,意味着如果前面的规则匹配的范围更大,则后面的规则将不会生效;以斜杠“/”开头表示目录;以星号“*”通配多
- 高效向量搜索RAG解决方案(Canopy)
deepdata_cn
RAGRAG
Canopy利用Pinecone在高效向量搜索方面的专业知识,提供强大且可扩展的RAG(Retrieval-AugmentedGeneration)解决方案。包括与Pinecone向量数据库的紧密集成,支持流处理和实时更新,先进的查询处理和重新排序功能,以及管理知识库和版本控制的工具。一、基本原理1.向量嵌入:Canopy首先会将文本数据转换为向量表示,通常使用预训练的语言模型等技术,将文本映射到
- 遥感深度学习过程中图像分割的尺寸对模型训练结果的影响
司南锤
深度学习遥感深度学习人工智能
1.计算资源与显存占用大尺寸图像:需要更高的显存和计算资源,可能限制训练时的批大小(batchsize),甚至导致无法训练。解决方案:通常将大图裁剪为小尺寸的补丁(patches),例如256x256或512x512。小尺寸图像:显存占用低,但可能丢失全局上下文信息(如大面积地物分布),影响模型对复杂场景的理解。2.模型感受野与上下文信息小尺寸输入:模型感受野受限,可能无法捕捉大范围地物(如河流、
- 使用小尺寸的图像进行逐像素语义分割训练,出现样本不均衡训练效果问题
司南锤
深度学习遥感计算机视觉人工智能机器学习
在使用小尺寸图像进行逐像素语义分割训练时,确实可能出现样本不均衡问题,且这种问题可能比大尺寸图像更显著。1.小尺寸图像如何加剧样本不均衡?(1)局部裁剪导致类别分布偏差问题:遥感图像中某些类别(如道路、建筑)可能稀疏分布。小尺寸裁剪后,部分训练样本可能完全不含某些类别(例如一块纯农田的补丁),导致模型对这些类别缺乏学习机会。示例:原图中“道路”占比5%,若裁剪为256x256的小图,部分小图中可能
- 如何解决小尺寸图像分割中的样本不均衡问题
司南锤
深度学习遥感笔记深度学习
1.生成对抗数据增强(Copy-PasteAugmentation)原理:将稀有目标的像素块复制粘贴到其他图像中,低成本生成平衡数据。适用场景:小目标(如车辆、船只)或极端稀疏类别(如灾害损毁区域)。PyTorch实现:importrandomdefcopy_paste_augment(image,mask,paste_image,paste_mask):#从粘贴数据中随机选择一个目标实例obj_
- 读书笔记--分布式服务架构对比及优势
一望无际的大草原
读书笔记服务中心后端读书笔记分布式架构共享服务
本篇是在上一篇的基础上,主要对共享服务平台建设所依赖的分布式服务架构进行学习,主要记录和思考如下,供大家学习参考。随着企业各业务数字化转型工作的推进,之前在传统的单一系统(或单体应用)模式中,每个系统都要做这些公共的功能或模块,比如用户管理,权限认证,日志,邮件,财务等等,随着企业各大应用系统的不断扩展,各垂直业务板块逐步沉淀形成各自的核心业务的数字化能力,提出了基于SOA理念的分布式服务架构,S
- 06-机器学习-数据预处理
不会打代码呜呜呜呜
机器学习机器学习人工智能
数据清洗数据清洗是数据预处理的核心步骤,旨在修正或移除数据集中的错误、不完整、重复或不一致的部分,为后续分析和建模提供可靠基础。以下是数据清洗的详细流程、方法和实战示例:一、数据清洗的核心任务问题类型表现示例影响缺失值数值型字段为空(NaN)模型无法处理缺失值,导致训练中断或偏差异常值年龄=200岁,房价=-100万扭曲统计指标(如均值),降低模型泛化性重复数据两行记录完全相同导致模型过拟合,降低
- Linux学习笔记(复习版day008)
ccnnlxc
Liux学习复习笔记linux学习笔记
1.僵尸进程僵尸进程(ZombieProcess)是指那些已经终止(即完成执行)的进程,但其父进程尚未读取其退出状态信息的进程。简单来说,僵尸进程的生命周期已经结束,但它的进程描述符仍然存在于系统中,以便父进程能够获取其退出状态。处理:1.top命令查询是否有僵尸进程,此处1zombie表示有一个僵尸进程2.ps-aux|grepZ查询僵尸进程的pid,STAT状态为Z+的即为僵尸进程。3.pst
- 从零推导线性回归:最小二乘法与梯度下降的数学原理
Echo-Nie
机器学习机器学习线性回归人工智能梯度下降数学推导
欢迎来到我的主页:【Echo-Nie】本篇文章收录于专栏【机器学习】本文所有内容相关代码都可在以下仓库中找到:Github-MachineLearning1线性回归1.1什么是线性回归线性回归是一种用来预测和分析数据之间关系的工具。它的核心思想是找到一条直线(或者一个平面),让这条直线尽可能地“拟合”已有的数据点,通过这条直线,我们可以预测新的数据。eg:假设你想预测房价,你知道房子的大小(面积)
- 机器视觉python+opencv函数库:一
二师弟_k
opencvpython
对此图片进行操作:代码部分:第一步:importcv2#导入opencv函数库img_test=cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\12044\Desktop\test.png")#读取图像,img_test为原图名称cv2.imshow("image",img_test)#显示图像,引号中的内容为图像显示窗口的名称,即“image”cv2.waitKey(0)#等待事件触发,参数0表示永
- 超实用的 30 段 Python 案例(上)
Python之栈
python开发语言
Python是目前最流行的语言之一,它在数据科学、机器学习、web开发、脚本编写、自动化方面被许多人广泛使用。它的简单和易用性造就了它如此流行的原因。如果你正在阅读本文,那么你或多或少已经使用过Python或者对Python感兴趣。在本文中,我们将会介绍30个简短的代码片段,你可以在30秒或更短的时间里理解和学习这些代码片段。1.检查重复元素下面的方法可以检查给定列表中是否有重复的元素。它使用了s
- cv python_python里面cv是什么意思
weixin_40004659
cvpython
OpenCV(OpenSourceComputerVisionLibrary)开放源代码计算机视觉库,主要算法涉及图像处理、计算机视觉和机器学习相关方法。OpenCV其实就是一堆C和C++语言的源代码文件,这些源代码文件中实现了许多常用的计算机视觉算法。OpenCV由一系列C函数和C++类构成,它有C,C++,Python和java接口,当前SDK(SoftwareDevelopmentKit软件
- Hadoop学习笔记 --- YARN执行流程与工作原理
杨鑫newlfe
数据仓库大数据挖掘与大数据应用案例YARNHadoop大数据资源调度数据仓库
一、YARN简述首先介绍一下YARN在Hadoop2.0版本引进的资源管理系统,直接从MapReduceV1演化而来(由于引擎的功能缺陷);原因是将MapReduce1中的JobTracker的资源管理和作业调度两个功能分开,分别由ResourceManager和ApplicationMaster进行实现;ResourceManager:负责整个集群的资源管理和调度ApplicationMaste
- 使用 rasterstats 库进行栅格与矢量数据的空间分析
xyt556_CUMT
人工智能
在地理信息系统(GIS)领域,栅格数据和矢量数据是两类常见的数据类型。栅格数据通常代表像素网格,如遥感影像或土地利用图,而矢量数据则通常表示具体的地理实体,如行政区划或土地边界。如何有效地结合这两类数据进行空间分析是许多地理研究中的关键问题。rasterstats是一个用于处理栅格和矢量数据的Python库,提供了便捷的工具来实现栅格统计、空间叠加分析等。本文将介绍如何使用rasterstats库
- java杨辉三角
3213213333332132
java基础
package com.algorithm;
/**
* @Description 杨辉三角
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-1-22上午10:10:59
*/
public class YangHui {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化二维数组长度
int[][] y
- 《大话重构》之大布局的辛酸历史
白糖_
重构
《大话重构》中提到“大布局你伤不起”,如果企图重构一个陈旧的大型系统是有非常大的风险,重构不是想象中那么简单。我目前所在公司正好对产品做了一次“大布局重构”,下面我就分享这个“大布局”项目经验给大家。
背景
公司专注于企业级管理产品软件,企业有大中小之分,在2000年初公司用JSP/Servlet开发了一套针对中
- 电驴链接在线视频播放源码
dubinwei
源码电驴播放器视频ed2k
本项目是个搜索电驴(ed2k)链接的应用,借助于磁力视频播放器(官网:
http://loveandroid.duapp.com/ 开放平台),可以实现在线播放视频,也可以用迅雷或者其他下载工具下载。
项目源码:
http://git.oschina.net/svo/Emule,动态更新。也可从附件中下载。
项目源码依赖于两个库项目,库项目一链接:
http://git.oschina.
- Javascript中函数的toString()方法
周凡杨
JavaScriptjstoStringfunctionobject
简述
The toString() method returns a string representing the source code of the function.
简译之,Javascript的toString()方法返回一个代表函数源代码的字符串。
句法
function.
- struts处理自定义异常
g21121
struts
很多时候我们会用到自定义异常来表示特定的错误情况,自定义异常比较简单,只要分清是运行时异常还是非运行时异常即可,运行时异常不需要捕获,继承自RuntimeException,是由容器自己抛出,例如空指针异常。
非运行时异常继承自Exception,在抛出后需要捕获,例如文件未找到异常。
此处我们用的是非运行时异常,首先定义一个异常LoginException:
/**
* 类描述:登录相
- Linux中find常见用法示例
510888780
linux
Linux中find常见用法示例
·find path -option [ -print ] [ -exec -ok command ] {} \;
find命令的参数;
- SpringMVC的各种参数绑定方式
Harry642
springMVC绑定表单
1. 基本数据类型(以int为例,其他类似):
Controller代码:
@RequestMapping("saysth.do")
public void test(int count) {
}
表单代码:
<form action="saysth.do" method="post&q
- Java 获取Oracle ROWID
aijuans
javaoracle
A ROWID is an identification tag unique for each row of an Oracle Database table. The ROWID can be thought of as a virtual column, containing the ID for each row.
The oracle.sql.ROWID class i
- java获取方法的参数名
antlove
javajdkparametermethodreflect
reflect.ClassInformationUtil.java
package reflect;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javassist.CtMethod;
import javassist.Modifier;
import javassist.bytecode.CodeAtt
- JAVA正则表达式匹配 查找 替换 提取操作
百合不是茶
java正则表达式替换提取查找
正则表达式的查找;主要是用到String类中的split();
String str;
str.split();方法中传入按照什么规则截取,返回一个String数组
常见的截取规则:
str.split("\\.")按照.来截取
str.
- Java中equals()与hashCode()方法详解
bijian1013
javasetequals()hashCode()
一.equals()方法详解
equals()方法在object类中定义如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
很明显是对两个对象的地址值进行的比较(即比较引用是否相同)。但是我们知道,String 、Math、I
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(4)使用SQL语句
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
--工资级别表
create table SALGRADE
(
GRADE NUMBER(10),
LOSAL NUMBER(10,2),
HISAL NUMBER(10,2)
)
insert into SALGRADE values(1,0,100);
insert into SALGRADE values(2,100,200);
inser
- 【Nginx二】Nginx作为静态文件HTTP服务器
bit1129
HTTP服务器
Nginx作为静态文件HTTP服务器
在本地系统中创建/data/www目录,存放html文件(包括index.html)
创建/data/images目录,存放imags图片
在主配置文件中添加http指令
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name
- kafka获得最新partition offset
blackproof
kafkapartitionoffset最新
kafka获得partition下标,需要用到kafka的simpleconsumer
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.
- centos 7安装docker两种方式
ronin47
第一种是采用yum 方式
yum install -y docker
- java-60-在O(1)时间删除链表结点
bylijinnan
java
public class DeleteNode_O1_Time {
/**
* Q 60 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
* 给定链表的头指针和一个结点指针(!!),在O(1)时间删除该结点
*
* Assume the list is:
* head->...->nodeToDelete->mNode->nNode->..
- nginx利用proxy_cache来缓存文件
cfyme
cache
user zhangy users;
worker_processes 10;
error_log /var/vlogs/nginx_error.log crit;
pid /var/vlogs/nginx.pid;
#Specifies the value for ma
- [JWFD开源工作流]JWFD嵌入式语法分析器负号的使用问题
comsci
嵌入式
假如我们需要用JWFD的语法分析模块定义一个带负号的方程式,直接在方程式之前添加负号是不正确的,而必须这样做:
string str01 = "a=3.14;b=2.71;c=0;c-((a*a)+(b*b))"
定义一个0整数c,然后用这个整数c去
- 如何集成支付宝官方文档
dai_lm
android
官方文档下载地址
https://b.alipay.com/order/productDetail.htm?productId=2012120700377310&tabId=4#ps-tabinfo-hash
集成的必要条件
1. 需要有自己的Server接收支付宝的消息
2. 需要先制作app,然后提交支付宝审核,通过后才能集成
调试的时候估计会真的扣款,请注意
- 应该在什么时候使用Hadoop
datamachine
hadoop
原帖地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-301743-id-3925358.html
存档,某些观点与我不谋而合,过度技术化不可取,且hadoop并非万能。
--------------------------------------------万能的分割线--------------------------------
有人问我,“你在大数据和Hado
- 在GridView中对于有外键的字段使用关联模型进行搜索和排序
dcj3sjt126com
yii
在GridView中使用关联模型进行搜索和排序
首先我们有两个模型它们直接有关联:
class Author extends CActiveRecord {
...
}
class Post extends CActiveRecord {
...
function relations() {
return array(
'
- 使用NSString 的格式化大全
dcj3sjt126com
Objective-C
格式定义The format specifiers supported by the NSString formatting methods and CFString formatting functions follow the IEEE printf specification; the specifiers are summarized in Table 1. Note that you c
- 使用activeX插件对象object滚动有重影
蕃薯耀
activeX插件滚动有重影
使用activeX插件对象object滚动有重影 <object style="width:0;" id="abc" classid="CLSID:D3E3970F-2927-9680-BBB4-5D0889909DF6" codebase="activex/OAX339.CAB#
- SpringMVC4零配置
hanqunfeng
springmvc4
基于Servlet3.0规范和SpringMVC4注解式配置方式,实现零xml配置,弄了个小demo,供交流讨论。
项目说明如下:
1.db.sql是项目中用到的表,数据库使用的是oracle11g
2.该项目使用mvn进行管理,私服为自搭建nexus,项目只用到一个第三方 jar,就是oracle的驱动;
3.默认项目为零配置启动,如果需要更改启动方式,请
- 《开源框架那点事儿16》:缓存相关代码的演变
j2eetop
开源框架
问题引入
上次我参与某个大型项目的优化工作,由于系统要求有比较高的TPS,因此就免不了要使用缓冲。
该项目中用的缓冲比较多,有MemCache,有Redis,有的还需要提供二级缓冲,也就是说应用服务器这层也可以设置一些缓冲。
当然去看相关实现代代码的时候,大致是下面的样子。
[java]
view plain
copy
print
?
public vo
- AngularJS浅析
kvhur
JavaScript
概念
AngularJS is a structural framework for dynamic web apps.
了解更多详情请见原文链接:http://www.gbtags.com/gb/share/5726.htm
Directive
扩展html,给html添加声明语句,以便实现自己的需求。对于页面中html元素以ng为前缀的属性名称,ng是angular的命名空间
- 架构师之jdk的bug排查(一)---------------split的点号陷阱
nannan408
split
1.前言.
jdk1.6的lang包的split方法是有bug的,它不能有效识别A.b.c这种类型,导致截取长度始终是0.而对于其他字符,则无此问题.不知道官方有没有修复这个bug.
2.代码
String[] paths = "object.object2.prop11".split("'");
System.ou
- 如何对10亿数据量级的mongoDB作高效的全表扫描
quentinXXZ
mongodb
本文链接:
http://quentinXXZ.iteye.com/blog/2149440
一、正常情况下,不应该有这种需求
首先,大家应该有个概念,标题中的这个问题,在大多情况下是一个伪命题,不应该被提出来。要知道,对于一般较大数据量的数据库,全表查询,这种操作一般情况下是不应该出现的,在做正常查询的时候,如果是范围查询,你至少应该要加上limit。
说一下,
- C语言算法之水仙花数
qiufeihu
c算法
/**
* 水仙花数
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 10
int main()
{
int x,y,z;
for(x=1;x<=N;x++)
for(y=0;y<=N;y++)
for(z=0;z<=N;z++)
if(x*100+y*10+z == x*x*x
- JSP指令
wyzuomumu
jsp
jsp指令的一般语法格式: <%@ 指令名 属性 =”值 ” %>
常用的三种指令: page,include,taglib
page指令语法形式: <%@ page 属性 1=”值 1” 属性 2=”值 2”%>
include指令语法形式: <%@include file=”relative url”%> (jsp可以通过 include
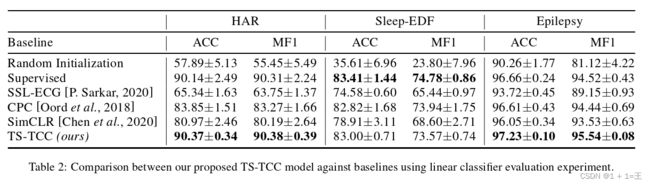
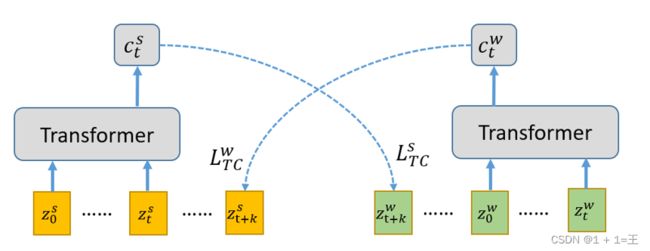
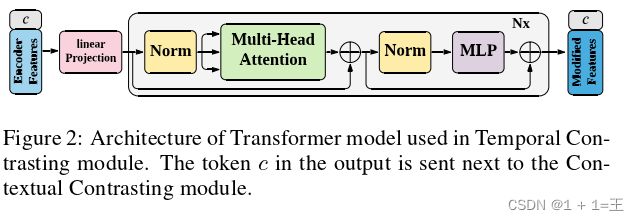
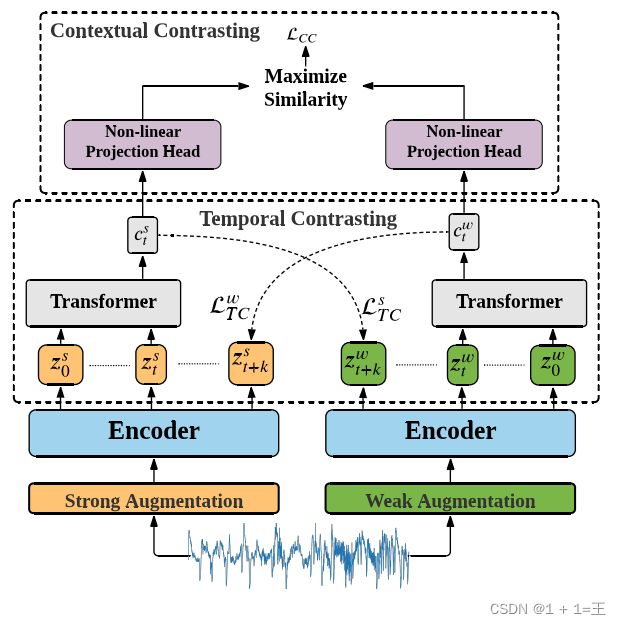
 2. 介绍实验细节
2. 介绍实验细节