【2021】Andriod(安卓)开发(持续更新)
开发零基础入门
- 1.工程结构介绍
-
- 总目录
- app目录
-
- src目录
-
- Main 目录
- 2.控件介绍
-
- TextView
-
- 1.TextView组件
- 2.带阴影的TextView
- 3.实现跑马灯的效果的TextView
- button
-
- 1.StateListDrawable
- E.g 登录页面实例
-
- activity_main.xml
- MainActivity.java
- string.xml
- color.xml
- 五种常用布局
-
- 布局的通用属性
- TableLayout表格布局
- Framelayout帧布局
- ConstraintLayout约束布局
- Activity(活动)
-
- 重要:
- 掌握:
- 了解:
-
- 生命周期的结构图:
- 生命周期状态
- Intent介绍
-
- 显式意图:
- 隐式意图:
- E.g. Activity(活动组件的使用和intent的使用)
-
- MainActivity.java
- activity_main.xml
- SecondActivity.java
- activity_second.xml
- AndriodManifest.xml
- 效果图:
- 代码图:
- 创建类和布局的两种方法
-
- 1.使用Andriod Studio的默认
- 2.分别进行创建
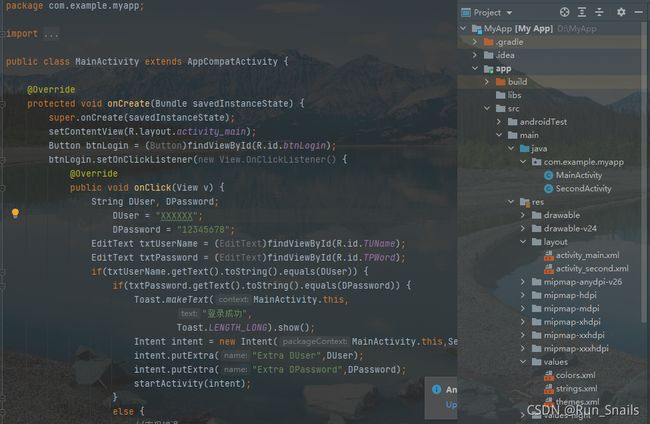
1.工程结构介绍
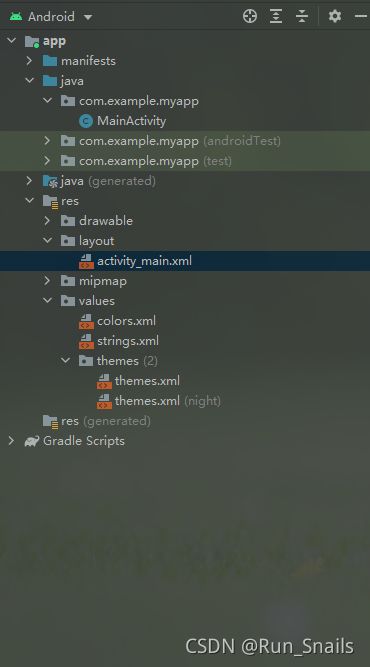
总目录
.gradle和.Idea是Andriod studio 自动生成的文件,而且不用手动去编辑,打包时会将其删除。
App文件夹是代码和资源等一些东西,工作的核心目录。
Gradle是一个构建器,里面还会有相应的版本。
.gitignore是一个版本控制的时候,可以将一些版本和目录排除在外,像git的时候可以将部分代码排除到外。
Build.gradle是项目gradle全局的构建脚本,一般该文件夹是不用修改的。
Gradle.properties是项目的全局的gradle配置文件。
Gradlew和gradlew.bet 是用来编写gradle命令的,是操作系统有关的,E.g. Gradlew是linux和max系统上的而gradlew.bet是window 系统中实现的。
Local.porperties是sdk的路径,都会自动生成,也可以进行更改sdk的路径。
Sttings.gradle是我们项目中所有的引路的路径。
External.libraries是第三方的库文件。(libraries文件)
app目录
Build是在Andriod Studio中的build的make project 的部署下生成的目录文件夹。
Libs是第三方的jar包都要放在这个目录。
Gitignore是管理app内部的版本文件夹。
Build.gradle是项目app全局的构建脚本。
src目录
AndroidTest是测试andriod的引用的
Main 目录
AndriodManifest.xml是app的清单文件,一般会有我们使用的组件。(app的权限和图标等)

Main中的java是java文件的地方
Com.example.myapplication是包名(app)
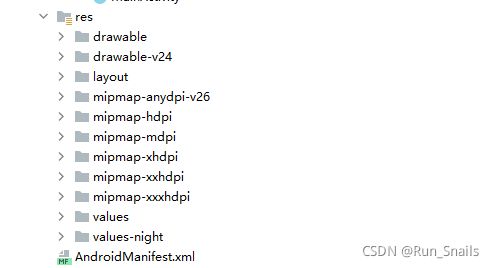
Res中的文件比较多,都是关于app的布局文件。
Drawable是关于图片的文件夹。
Layout是我们app的布局文件。
Mipmap是图标的放置,后缀不同——屏幕的适配。
Values是用来放颜色,字符串,主题文件的。
工程文件夹目录介绍结束。
2.控件介绍
TextView
1.TextView组件
- layout. _width:组件的宽度
- layout_ height:组件的高度
- id:为TextView设置一个组件id
- text:设置显示的文本内容
- textColor:设置字体颜色
- textStyle::设置字体风格,三个可选值: normal(无效果), bold(加粗), italic(斜体)
- textSize:字体大小,单位一般是用sp
- background:控件的背景颜色,可以理解为填充整个控件的颜色,可以是图片
- gravity:设置控件中内容的对齐方向,TextVlew中是文字, ImageView中是图片等等。
Andriod Studio 自带的Activity_main.xml
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#CF2861"
android:backgroundTint="#009688"
android:backgroundTintMode="src_in"
android:foregroundTint="#CDDC39"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="42dp"
android:autoSizeMaxTextSize="60sp"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textColor="#FFEB3B"
android:textColorHighlight="#DC396D"
android:textColorLink="#9C27B0"
android:textSize="48sp"
android:visibility="visible"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.497"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.32999998"
tools:ignore="TextContrastCheck" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
学属性最好的方式就是将代码写到程序中
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_one"
android:text="TextView学习"
android:textColor="#ffff0000"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textSize="36sp"
android:background="#55ff0000"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_width="225dp"
android:layout_height="224dp">
TextView>
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout 是个容器(布局)
android:textColor="#ffff0000"由8个字符构成,前两为透明度,后面6位为颜色。
android:textStyle="bold"有三种选择。
android:textSize="36sp"有三种基本选择,也可以用数字表示,单位为“sp”。
package com.example.myapplication;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView tv_one = findViewById(R.id.tv_one);
tv_one.setText("leo");
}
}
其中的Id是写到.ava文件中
tv_one.setText("leo");
会影响用行的结果,正规的项目一般都在values文件夹的string.xml中写。
2.带阴影的TextView
- android:shadowColor:设置阴影颜色需要与shadowRadius一起使用
- android:shadowRadius:设置阴影的模糊程度设为0.1就变 成字体颜色了建议使用3.0
- android:shadowDx:设置阴影在水平方向的偏移,就是水平方向阴影开始的横坐标位置
- android:shadowDy:设置阴影在竖直方向的偏移,就是竖直方向阴影开始的纵坐标位置
3.实现跑马灯的效果的TextView
- android:singleLine:内容单行显示
- android:focusable:是否可以获取焦点
- android:focuablelnTouchMode:用于控制视图在触摸模式下是否可以聚焦
- android:ellipsize:在哪里省略文本
- android:marqueeRepestima:字幕动面重复的次数
button
1.StateListDrawable
StateListDrawable是Drowable资源的一种,可以根据不同的状态,设置不同的图片效果,关键节点,我们只需要将Button的background属性设置为该drawable资源即可轻松实现,按下按钮时不同的按钮颜色或背景
7. drawable:引用的Drawable位图
8. state_focused:是否获得焦点
9. state_pressed:控件是否被按下
10. state_enabled:控件是否可用
11. state_selected:控件是否被选择,针对有滚轮的情况
12. state_checked:控件是否被勾选
13. state_checkable:控件可否被勾选eg:checkbox
14. state_window_focused:是否获得窗口焦点
15. state_gactive:控件是否处于活动状态.eg:slidingTab
16. state_single:控件包含多个子控件时,确定是否只显示一个子控件
17. state_first:控件包含多个子控件时,确定第一个子控件是否处于显示状态
18. state_middle:控件包含多个子控件时,确定中间一个子控件是否处于显示状态
19. state_last:控件包含多个子控件时,确定最后一个子控件是否处于显示状态
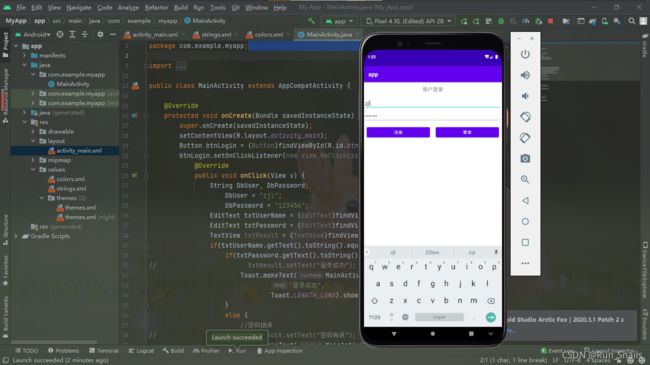
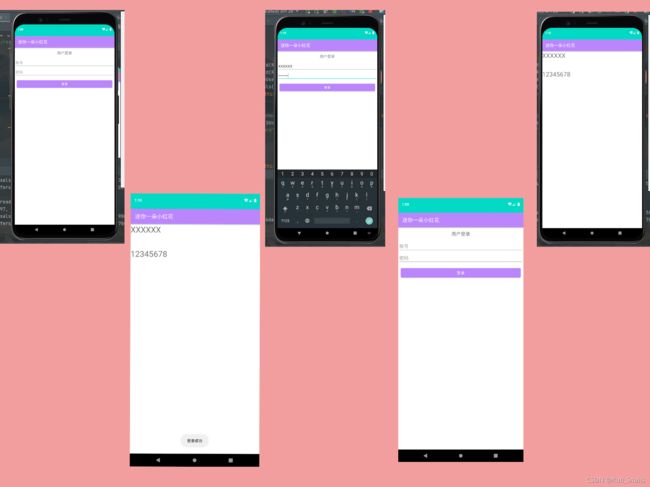
2021.09.03继续更新做的第一个登录页面
E.g 登录页面实例
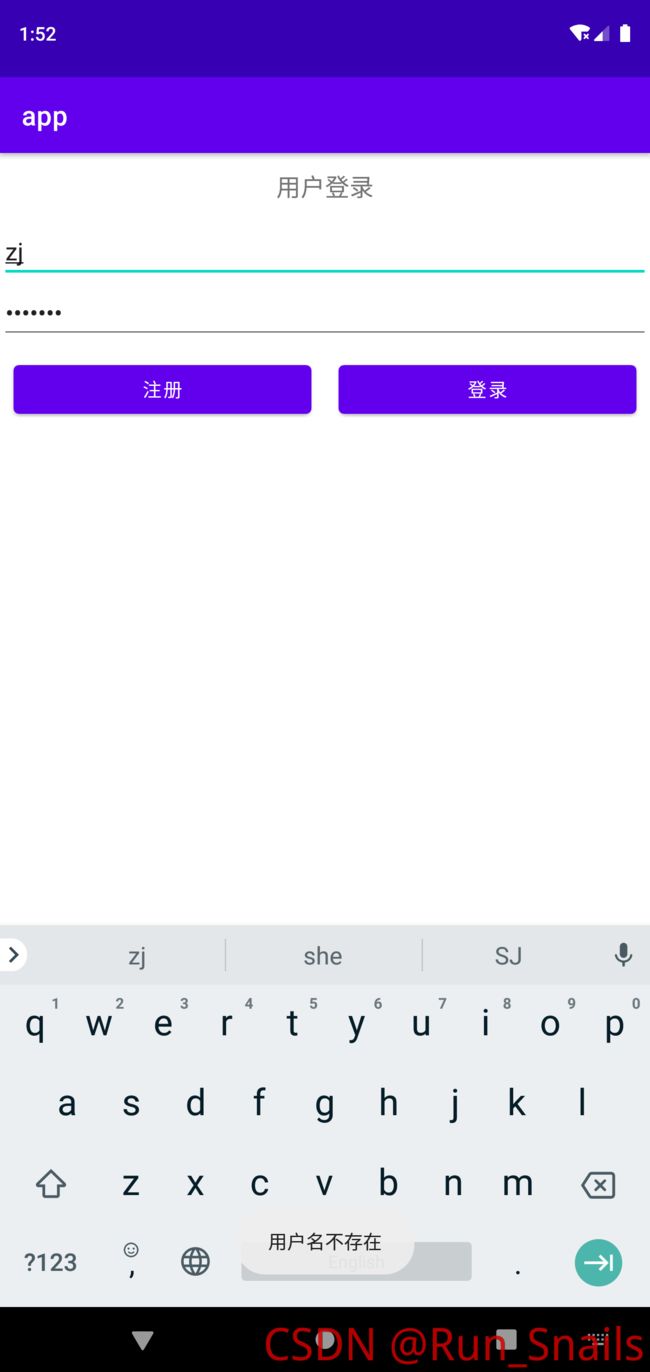
当用户名和密码正确时,会弹出登录成功。
当用户名不正确时,会弹出用户名不存在。
当密码不正确是,会弹出用密码错误。
下面时app的目录示意图:
activity_main.xml
主界面的布局设计
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/LblLogin"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/txtUserName"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="@string/LblUserName"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/txtPassword"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="@string/LblPassword"
android:inputType="textPassword" />
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/zhuce"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/zhuce"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
tools:ignore="DuplicateIds" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnLogin"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="@string/LblBtnLogin" />
RadioGroup>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtResult"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="@android:color/holo_red_light" />
LinearLayout>
注:LinearLayout为线性布局
orientation=“vertical”(方向:这里时垂直)
orientation=“horizontal”(方向:这里时水平)
MainActivity.java
package com.example.myapp;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.appcompat.widget.ButtonBarLayout;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btnLogin = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnLogin);
btnLogin.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String DbUser, DbPassword;
DbUser = "zjl";
DbPassword = "123456";
EditText txtUserName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtUserName);
EditText txtPassword = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtPassword);
TextView txtResult = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.txtResult);
if(txtUserName.getText().toString().equals(DbUser)) {
if(txtPassword.getText().toString().equals(DbPassword)) {
// txtResult.setText("登录成功");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"登录成功",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
else {
//密码错误
// txtResult.setText("密码有误");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"密码有误",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
else{
//用户名不存在
// txtResult.setText("用户名不存在");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"用户名不存在",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
});
}
}
实现弹窗效果。
string.xml
<resources>
<string name="app_name">appstring>
<string name="LblLogin">用户登录string>
<string name="LblUserName">用户姓名string>
<string name="LblPassword">用户密码string>
<string name="zhuce">注册string>
<string name="LblBtnLogin">登录string>
resources>
布局文件使用
color.xml
<resources>
<color name="purple_200">#FFBB86FCcolor>
<color name="purple_500">#FF6200EEcolor>
<color name="purple_700">#FF3700B3color>
<color name="teal_200">#FF03DAC5color>
<color name="teal_700">#FF018786color>
<color name="black">#FF000000color>
<color name="white">#FFFFFFFFcolor>
resources>
完成以后就和上面的实例图一样了。
五种常用布局
(线性布局最为常用,这里跳过。)
| 线性布局 | 特点:以水平或永直方向排列 |
| 相对布局 | 特点:通过相对定位排列 |
| 帧布局 | 特点:开辟空白区域,帧里的控件(层}叠加 |
| 表格布局 | 特点:表格形式排列 |
| 约束布局 | 特点:可视化的方式编写布局 |
布局的通用属性
- Android系统提供的五i种常用布局直接或者间接继承自
ViewGroup,因此它们也支持在ViewGroup中定义的属性,这些
属性听以看作是布局的通用属性。
| 属性名称 | 功能描述 |
| android:id | 设置布局的标识 |
| androld:layout :width | 设置布局的宽度 |
| android:layout :helight | 设置布局的宽度 |
| androld:background | 设置布局的背景 |
| android:layout_margin | 设置当前布局与屏幕边界或与周围控件的距高 |
| android:padding | 设置当前布局与该布局中控件的距离 |
RelativeLayout相对布度
- 相对布局( RelativeLayout)是通过相对定位的方式指定子控件
位置,即以其它控件或父容器为参照物,摆放控件位置。 - 定义格式:
<RclativeLayout>
| 控件属性 | 功能描述 |
| android:layout_centerlnParent | 设置当前控件位于父布局的中央位置 |
| android:layout_ceanterVertical | 设置当前控件位于父布局的垂直居中位置 |
| android:lagyout_centerHorizontal | 设置当前控件位于父控件的水平居中位置 |
| android:layoat_above | 设置当前控件位于某控件上方 |
| android:layout_below | 设置当前控件位于某控件下方 |
| android:layouat_toLeftOf | 设置当前控件位于某控件左侧 |
| android:layout_toRightOf | 设置当前控件位于某控件右侧 |
| android:layout_alignParentTop | 设置当前控件是否与父控件顶端对齐 |
| android:layout_alimParentLeft | 设置当前控件是否与父控件左对齐 |
| android: layout_alignParcentRight | 设置当前控件是否与父控件右对齐 |
| android:l layout_alignParcntBottom | 设置当前控件是否与父控件底端对齐 |
| android:layout_salignTop | 设置当前控件的,上边界与某控件的上边界对齐 |
| android:layout_slignBottom | 设置当前控件的下边界与某控件的下边界对齐 |
| android:lagout_alignLeft | 设置当前控件的左边界与某控件的左边界对齐 |
| android:layout_alignRight | 设置当前控件的右边界与某控件的右边界对齐 |
TableLayout表格布局
- 采用行、列的形式来管理控件,它不雷要明确声明包含多少行、多少列,而是通过在TableLayout布局中添加TableRow布局来控制表格的行数,通过在TableRow布局中添加控件来控制表格的列数。
<TableRow>
UI控件
TablcRow>
TableLayout>
| 布局属性 | 功能描述 |
| android:strctcColumns | 设置读列被拉伸 |
| android:shrinkColumns | 设置该列被收缩 |
| android:collepscColumns | 设置该列被隐藏 |
| 控件属性 | 功能描述 |
| Android:layout_column | 设置该单元显示位置 |
| Android:layout_span | 设置该单元格占据几行,默认为1行 |
Framelayout帧布局
-
帧布局(FrameLayout) 用于在屏幕上创建一 块空白区域,添加到该区域中的每个子控件占一帧,这些帧会-一个一个叠加在一起,后加入的控件会叠加在上一个控件上层
-
所有控件都默认显示在屏幕左上角。
-
定义格式:
FrameLayout>
ConstraintLayout约束布局
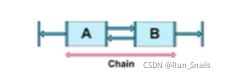
- Chain(链)是一种特殊的约束,他使我们能够对一-组水平或竖 直方向互相关联的控件进行统一管理。一组控件通过一个双向的约束关系链接起来,就能形成一个Chain。
Activity(活动)
重要:
Intent与IntentFilter
Acitvity之间的跳转
Activity的启动模式
掌握:
Activity生命周期
Activity的创建配置和关闭
了解:
使用Fragment
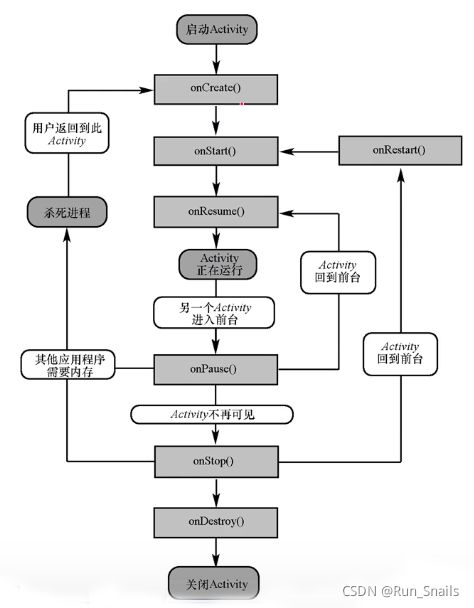
生命周期的结构图:
生命周期状态
启动状态: 当Activity启动之后便会进入下一状态。
运行状态: Activity处于屏幕最前端,可与用户进行交互。
暂停状态: Activity仍然可见,但无法获取焦点,用户对他操作没有响应。
停止状态: Activity完全不可见,系统内存不足时会销毁该Activity。
销毁状态: Activity将被清理出内存。
Intent介绍
- Intent被称为意图,是程序中各组件进行交互的一种重要 方式,他不仅可以指定当前组件要执行的动作,还可以在不同组件之间进行数据传递。
- 一般用于启动Activity、 Service以及发送广播等。根据开启目标组件的方式不同,Intent被分为两种类型显示意图和隐式意图。
显式意图:
显式意图可以直接通过名称开启指定的目标组件。
Intent intent = new Intent(this, SecondActivity.c lass );
注:
创建一个Intent对象,其中第1个参数为Context表示当前的Activity对象,第2个参数表示要 启动的目标Activity.
startActivity(intent);
注:
调用Activity的startActivity方法启动目标组件。
隐式意图:
隐式意图通过指定action和category等属性,系统根据这些信息进行分析后寻找目标Activity。
<activity android:name= "cn.itcast.Activity02">
<intent- filter>
<action android:name "cn.itcast.START ACTIVIT Y"/>
<category android:nane="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<intent- filter>
activity>
注:
设置action动作,当代码中的action与该action相匹配时启动该组件。
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent. setAction("cn.itcast.START ACTIVITY");
startA ctivity( intent):
注:
设置action动作,当与清单文件中的action相匹配时启动目标组件。
E.g. Activity(活动组件的使用和intent的使用)
MainActivity.java
package com.example.myapp;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.appcompat.widget.ButtonBarLayout;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btnLogin = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnLogin);
btnLogin.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String DUser, DPassword;
DUser = "XXXXXXX";
DPassword = "12345678";
EditText txtUserName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.TUName);
EditText txtPassword = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.TPWord);
if(txtUserName.getText().toString().equals(DUser)) {
if(txtPassword.getText().toString().equals(DPassword)) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "登录成功",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("Extra DUser",DUser);
intent.putExtra("Extra DPassword",DPassword);
startActivity(intent);
}
else {//密码错误
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"密码有误",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
else{//用户名不存在
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"用户名不存在",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
});
}
}
注:上面的为主要的活动MainActivity.java
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/LblLogin"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/TUName"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="@string/LblUserName"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/TPWord"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="@string/LblPassword"
android:inputType="textPassword" />
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnLogin"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/LblBtnLogin" />
RadioGroup>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtResult"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="@android:color/holo_red_light" />
LinearLayout>
注:上面的为主要的活动MainActivity的页面布局activity_main.xml
SecondActivity.java
package com.example.myapp;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView textView;
private TextView textView1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_second);
Intent intent = getIntent();
String DUser = intent.getStringExtra("Extra DUser");
String DPassword = intent.getStringExtra("Extra DPassword");
Log.d("SecondActivity",DUser);
Log.d("SecondActivity",DPassword);
textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView);
textView1 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
textView.setText(DUser);
textView1.setText(DPassword);
}
}
注:上面为主要的活动SecondActivity.java
activity_second.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".SecondActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="90dp"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_weight="2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="90dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:textSize="30dp" />
LinearLayout>
注:上面的为主要的活动SecondActivity的页面布局activity_second.xml
AndriodManifest.xml
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.myapp">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.MyApp">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity">activity>
application>
manifest>
注:这为Andriod Stuido 的开发的主要页面,只有将MainActivity.java和SecondActivity.java同时注册AndriodManifest.xml中才可以进行页面的跳转(intent)。
效果图:
代码图:
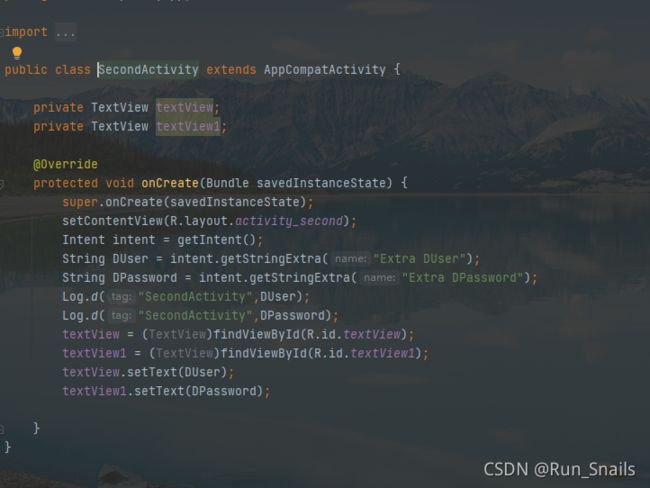
SecondActivity.java
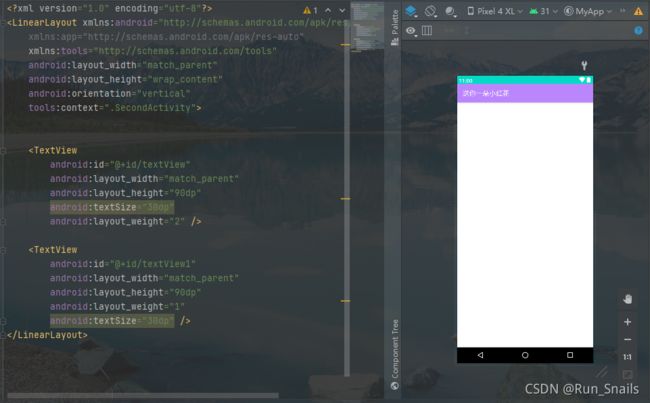
activity_main.xml
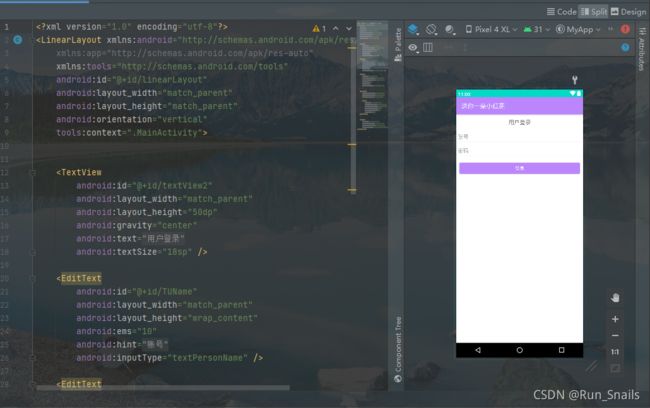
activity_second.xml
创建类和布局的两种方法
1.使用Andriod Studio的默认
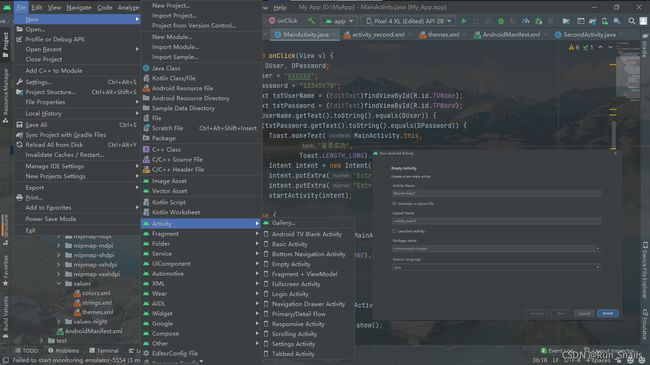
在其中带有许多的…java类,可以进行.xml自动带取,也可以在AndriodManifest.xml中自动注册。(建议使用这个方法进行测试)
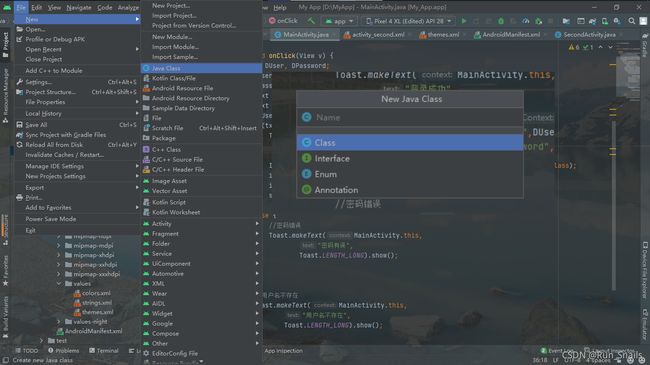
2.分别进行创建
1).先进行class(类)的创建
2).在进行页面的创建.xml
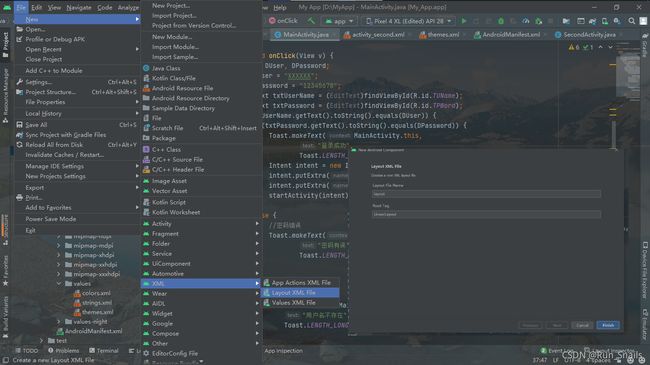
3).在AndriodManifest.xml中进行部署。(不建议第二个方法,容易发生错误)
2021.09.19 更新,上面还用到intent的传值,下期进行讲解。