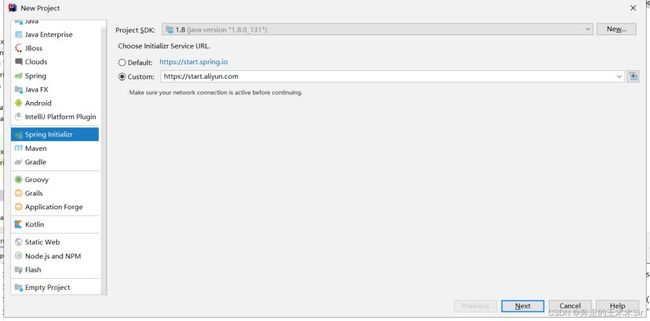
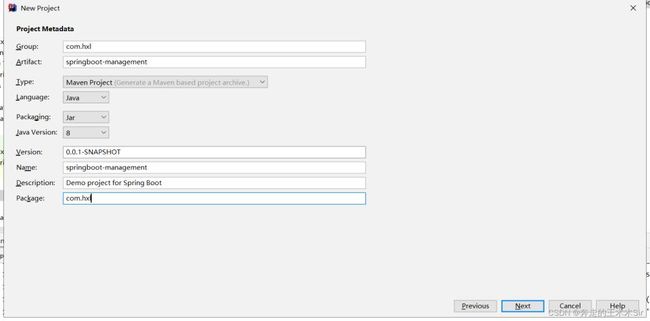
准备工作
1.新建一个项目
next之后选择SpringWeb和Thymeleaf,然后直接next,Finish即可。
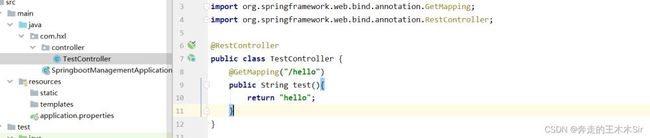
之后我们进行测试,看是否搭建成功
ok,我们已经项目创建好了。
2.导入静态资源
根据下方的图片展示将资源导入
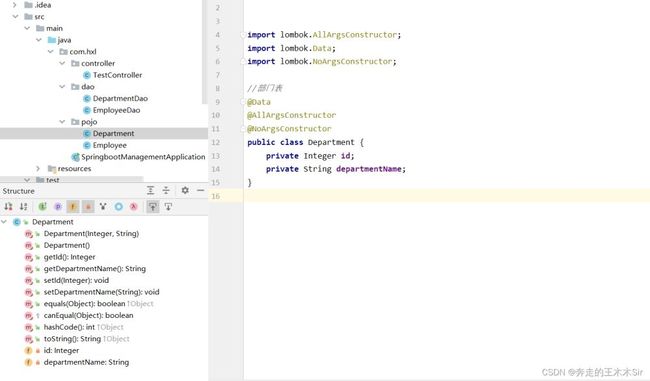
3.创建实体类
首先我们先导入lombok
org.projectlombok lombok 1.18.20
创建pojo的包,在其下创建两个实体类Department和Employee
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
//部门表
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
}
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.Date;
//员工表
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String employeeName;
private String email;
private Integer gender; //0:女 1:男
private Department department;
private Date birth;
}
遇到的问题:有些人会遇到这个问题,为什么我的lombok导入了,也用将其方法生成了,但是最后不能用,就像下面的情况
其实不要你以为写了那三行就是有了,我们打开structure看一下,发现虽然写了,但是还是没有方法。这又是为什么呢?
其实是因为你的IDEA里面没有Lombok的插件,只需要在Setting->Plugins->搜索lombok->Install->重新启动idea
最后看下成果
4.编写dao层
同样建包dao,并在其下创建DepartmentDao和EmployeeDao
import com.hxl.pojo.Department;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
//部门dao
//注册到IOC容器中
@Repository
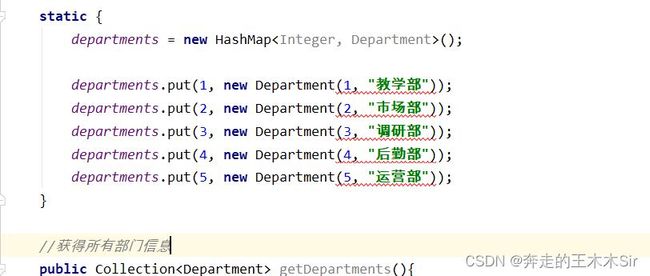
public class DepartmentDao {
//模拟数据库中的数据
private static Map departments = null;
static {
departments = new HashMap();
departments.put(1, new Department(1, "教学部"));
departments.put(2, new Department(2, "市场部"));
departments.put(3, new Department(3, "调研部"));
departments.put(4, new Department(4, "后勤部"));
departments.put(5, new Department(5, "运营部"));
}
//获得所有部门信息
public Collection getDepartments(){
return departments.values();
}
//通过id得到部门
public Department getDepartmentById(Integer id){
return departments.get(id);
}
}
import com.hxl.pojo.Department;
import com.hxl.pojo.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
//员工dao
//注册到IOC容器中
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
//模拟数据库中的数据
static private Map employees = null;
//员工所属的部门
@Autowired
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
static {
employees = new HashMap();//创建一个员工表
employees.put(1, new Employee(1, "hxl", "[email protected]", 1, new Department(1, "教学部"), new Date()));
employees.put(2, new Employee(2, "zmc", "[email protected]", 1, new Department(2, "市场部"), new Date()));
employees.put(3, new Employee(3, "kwb", "[email protected]", 0, new Department(3, "调研部"), new Date()));
employees.put(4, new Employee(4, "lqs", "[email protected]", 1, new Department(4, "后勤部"), new Date()));
employees.put(5, new Employee(5, "wjr", "[email protected]", 1, new Department(5, "运营部"), new Date()));
}
//主键自增
private static Integer initialId = 6;
//增加一个员工
public void addEmployee(Employee employee) {
if (employee.getId() == null) {
employee.setId(initialId++);
}
employee.setDepartment(departmentDao.getDepartmentById(employee.getDepartment().getId()));
employees.put(employee.getId(), employee);
}
//查询全部员工信息
public Collection getAllEmployees() {
return employees.values();
}
//通过id查询员工
public Employee getEmployeeById(Integer id) {
return employees.get(id);
}
//通过id删除员工
public void deleteEmployeeById(int id) {
employees.remove(id);
}
}
至此我们的准备工作就完成了。
首页实现
首先我们像之前创建一个config的包用来存放自定义的配置
创建一个MyMvcConfig的配置类,进行首页的视图跳转
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
//添加一个,打了"/",然后让他去index
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("index.html").setViewName("index");
}
}
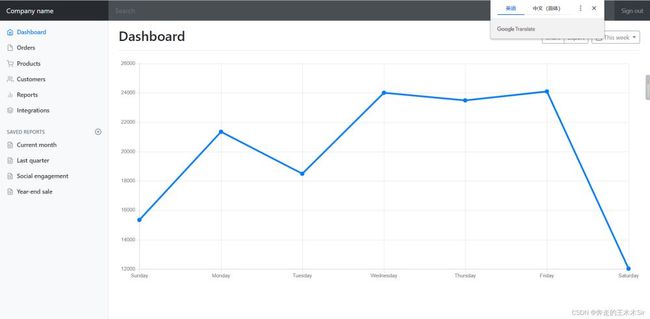
启动程序,进行测试访问localhost:8080/或者locahost:8080/index.html出现下面的界面就ok了
在这块中,我们发现仅有一些文字,样式图片等都没有加载出来,这是因为我们之前导入的静态资源的html,没有使用Thymeleaf的的语法。我们的模板引擎为Thymeleaf。
我们将之前导入的html里面的都改为thymeleaf语法。
注意所有html都需要引入Thymeleaf命名空间
然后修改所有页面静态资源的引入,使用@{...} 链接表达式(只要是自己本地的链接资源,都需要根据这个语法来修改)
在标签前增加th:
以index.html为例
注意:第一个/代表项目的classpath,也就是这里的resources目录
修改之后我们再次运行
中英文切换
首先我们要保证我们的编码是UTF-8
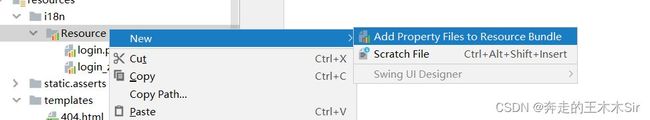
Properties编写
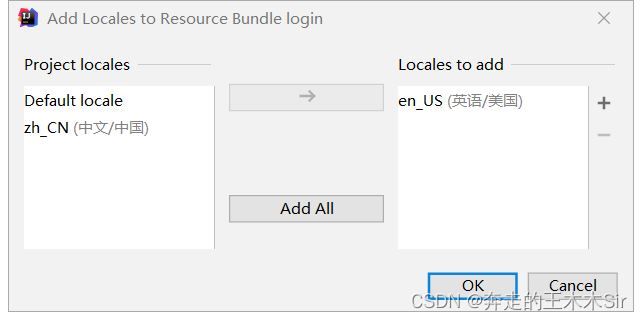
接下来我们进行配置编写,在resources目录下创建一个文件夹i18n,然后在其下创建一个login.properties和login_zh_CN.properties创建完成后发现他们两个合并了。
这样我们就有了默认配置和中文的配置,接下来再创建一个英语的,来看步骤:
这样我们就有了三个文件。展示操作的时候到了
首先点击这里,可以让我们拥有可视化操作。没有可视化选项的兄弟下载插件Flagiarism然后重启就可以了
接下来将我们的内容一次创建
直接点击+号,创建文件名和输入内容即可。
之后我们就会发现这里也会增加内容。
接下来按照图片一次进行创建
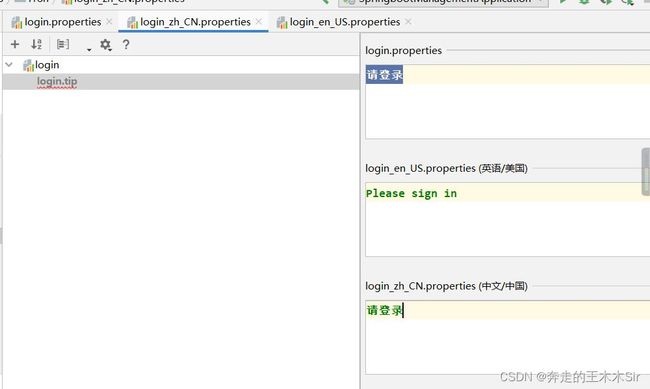
这里展示一个内容
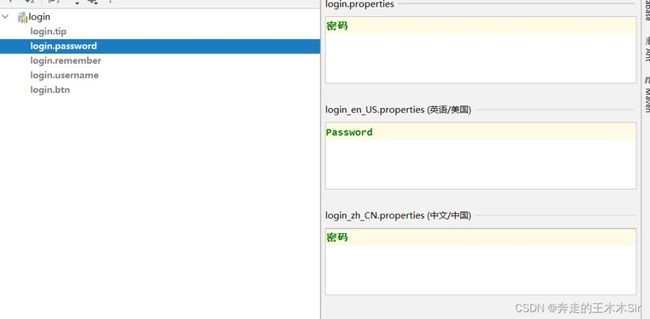
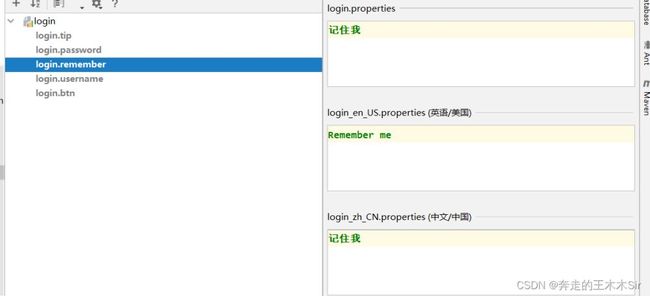
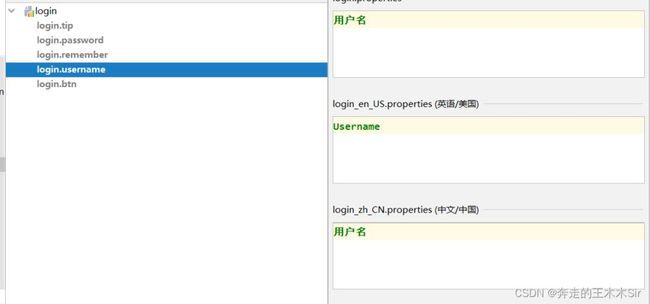
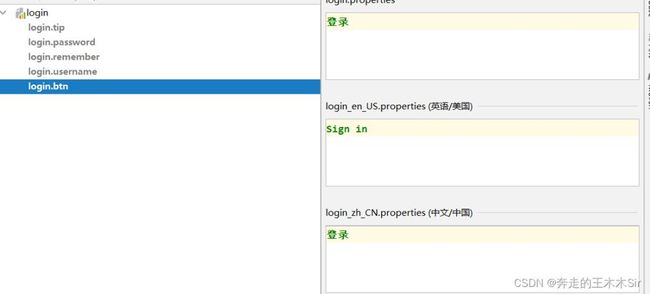
login.properties
login.btn=登录 login.password=密码 login.remember=记住我 login.tip=请登录 login.username=用户名
login_en_US.properties
login.btn=Sign in login.password=Password login.remember=Remember me login.tip=Please sign in login.username=Username
我们设置完之后,该怎么让我们的项目识别呢。需要在我们的application.properties下进行绑定
# 我们的配置文件的真实位置 spring.messages.basename=i18n.login
源码分析:
我们去MessageSourceAutoConfiguration这个类下,查看messageSource该方法
public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties);
可以看到,他的参数是一个MessageSourceProperties对象,我们继续查看,它首先是一个属性basename,默认值为message
- 如果你不在springboot配置文件中指定以
.分隔开的国际化资源文件名称的话 - 它默认会去类路径下找messages.properties作为国际化资源文件
这也就是我们为什么要在配置文件中进行配置。
后面好了,那么我们的html页面该怎么进行呢。查阅资料发现Thymeleaf中取值需要进行使用到#{}例如
根据上述步骤将其他的几处也进行修改
最后的效果
接下来就是可以中英文进行切换,此时需要加一个组件
在我们的首页界面中可以看到我们的两个中英文标签
此时我们需要对其加上跳转链接同时加上参数,原来我们的参数是?现在不需要,用的是()。
自定义地区的解析器组件
在spring中,有两个关于国际化的类,一个是代表地区的Locale,每一个对象都代表了特定的区域,还有一个关于地区解析器LocaleResolver。
首先搜索WebMvcAutoConfiguration,可以在其中找到关于一个方法localeResolver()
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale")
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
//如果用户配置了,则使用用户配置好的,容器中没有就自己配,有就用用户的
if (this.mvcProperties.getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
}
//用户没有配置,则使用默认的,接收头 国际化分解
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}
该方法就是获取LocaleResolver地区对象解析器:
- 如果用户配置了则使用用户配置的地区解析器;
- 如果用户没有配置,则使用默认的地区解析器
可以发现它继承了LocaleResolver接口,实现了地区解析
因此我们想要实现上述自定义的国际化资源生效,只需要编写一个自己的地区解析器,继承LocaleResolver接口,重写其方法即可
在config包下新建一个MyLocaleResolver
package com.hxl.config;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Locale;
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
//获取请求中的国际化参数
String language = httpServletRequest.getParameter("l");
//默认的地区
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
//如果请求的链接参数不为空,携带了国际化参数
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)) {
String[] split = language.split("_");//zh_CN(语言_地区)
locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Locale locale) {
}
}
完成组件后,需要在MvcConfig配置类下添加上我们的Bean
//自定义的国际化组件生效
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
重新启动项目,我们就可以通过点击下方的中英文来进行切换。
总结
- 我们需要配置
i18n文件 - 需要自定义一个组件
MyLocaleResolver,以便在项目中进行按钮的自动切换。 - 将自己的组件配置到spring容器中
@Bean - 取值用的是
#{}
登录功能
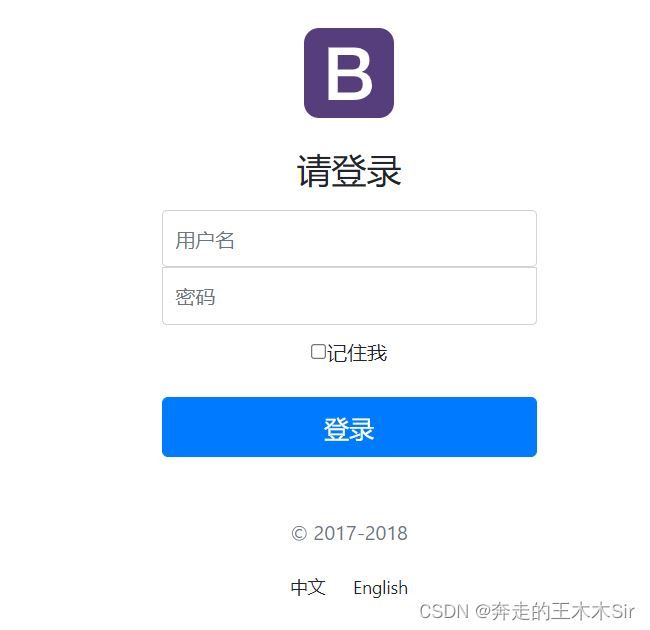
1.页面调整
我们需要将这里进行修改。
查看页面之后发现,我们点击登录按钮的时候会进入dashboard页面。
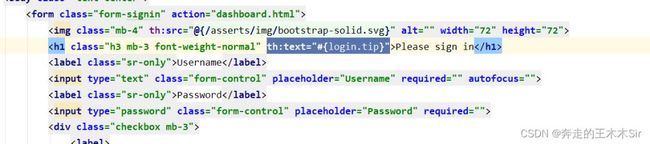
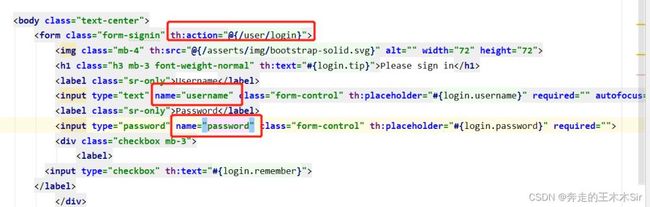
所以我们需要将这里的提交地址进行修改,以及将用户名和密码框加上属性以便传参。
2.编写LoginController
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password, Model model){
//如果用户名和密码都正确
if("wangmm".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
return "dashboard";
}else{
//如果用户名或者密码不正确
model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码不正确");
return "index";
}
}
}
我们需要在登录页面增加一个返回错误信息的标签。
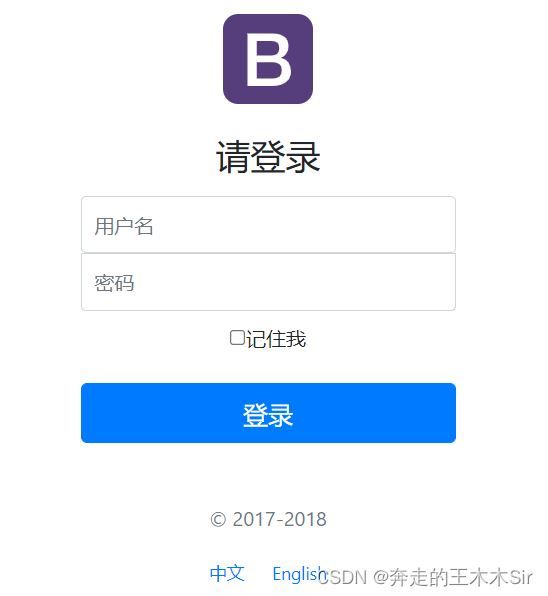
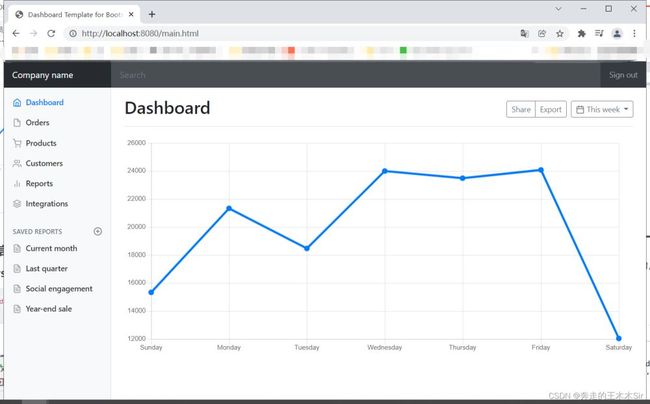
此时启动程序并访问localhost:8080。输入正确的账号密码访问我们可以看到这个页面
输入错误的账号密码会呈现
好了,我们这里已经成功了。但是当我们成功登录后我们的页面显示不全,这是因为之前提到的静态页面展示的问题,需要把我们dashboard页面下的本地静态资源都用Thymeleaf语法进行修改。修改成功后即可。
同时我们可以到浏览器页面的url暴露了我们的信息。所以我们需要进行修改。
在自定义的配置类MyMvcConfig中增加。这样我们访问main.html也就是访问了dashboard页面。
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
同时我们也要去将LoginController下的登录页面也重定向到main.html中。
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password, Model model){
//如果用户名和密码都正确
if("wangmm".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
return "redirect:/main.html";
}else{
//如果用户名或者密码不正确
model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码不正确");
return "index";
}
}
}
之后我们运行查看,浏览器上的url不再携带用户的信息。
此时出现了新的问题,就是我们不管登录不登录,通过localhost:8080/main.html都可以访问到我们的dashboard的页面。
3.登录拦截器
在config目录下,新建一个登录拦截器类LoginHandlerInterceptor
目的:用户登录成功后得到用户的信息。防止未登录用户查看页面
得到用户信息,我们需要先保存用户的信息,所以我们需要在LoginController中当用户登录成功后,存入用户信息到session中
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password, Model model, HttpSession session){
//如果用户名和密码都正确
if("wangmm".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
session.setAttribute("LoginUser", username);
return "redirect:/main.html";
}else{
//如果用户名或者密码不正确
model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码不正确");
return "index";
}
}
}
实现拦截器。需要继承HandlerInterceptor接口
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//用户登录成功拥有session
Object loginUser = request.getSession().getAttribute("LoginUser");
if(loginUser == null){
request.setAttribute("msg","用户权限不够,请登录");
//权限不够就重定向到首页
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response);
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
}
有了拦截器就需要注册到bean中,在MyMvcConfig配置类中,添加我们自定义的拦截器,注意屏蔽主页、登录相关请求、静态资源的拦截
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/index.html", "/", "/user/login", "/asserts/**");
}
注意这个地方,有些人不是在整一个文件夹中,所以需要分开写"/css/**", "/js/**", "/img/**"
测试:启动程序直接访问http://localhost:8080/main.html
之后我们登录,成功之后再重新进入之前的链接http://localhost:8080/main.html发现也是可以访问得到的。
这是因为登录之后用户的信息已经保存在了session中。拦截器自然不会拦截。
员工信息——查
实现界面中的Customers中的员工查询。
th:fragment="sidebar"th:replace="~{commons/commons::topbar}"- 如果要传递参数,可以直接使用
()传参,接收判断即可 - 列表循环展示
首先我们先将模板中的跳转链接进行跳转
同时将list.html中的代码进行修改
在templates目录下新建一个包emp用来存放员工的相关页面
之后我们编写对应的Controller
package com.hxl.controller;
import com.hxl.dao.EmployeeDao;
import com.hxl.pojo.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.Collection;
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@RequestMapping("/emps")
public String list(Model model){
Collection employees = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
model.addAttribute("emps",employees);
return "emp/list";
}
}
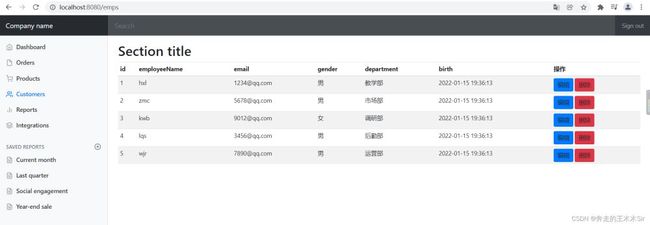
启动测试,发现是这个页面,这是由于咱们的语法有问题,和之前的一样将本地静态资源进行修改。
之后进行修改可以得到新的界面。
优化
点击员工管理之后应该是高亮的状态,但是我们发现点击之后高亮不在Customers而在Dashboard
同时我们可以将侧边栏以及顶部栏公共的部分进行提炼
提取页面的公共部分
我们可以将两个页面dashboard.html和list.html`中顶部导航栏和侧边栏的代码删除
启动测试查看:所有顶部和侧边都没有了
将公共的部分引入
在dashboard.html和list.html删除的部分插入提取出来的公共部分topbar和sidebar
解决高亮
通过观察,在页面中高亮的部分是由于class="nav-link active"属性
我们可以通过传递参数来进行判断说明自己的页面应该哪里高亮
将dashboard.html的侧边栏标签传递参数active为dashboard.html
将list.html的侧边栏标签传递参数active为list.html
我们将页面参数修改后需要在公共页面部分接收参数active
th:class="${active=='dashboard.html'?'nav-link active':'nav-link'}"
th:class="${active=='list.html'?'nav-link active':'nav-link'}"
测试:
点击Customers,Customers高亮,成功
显示员工信息
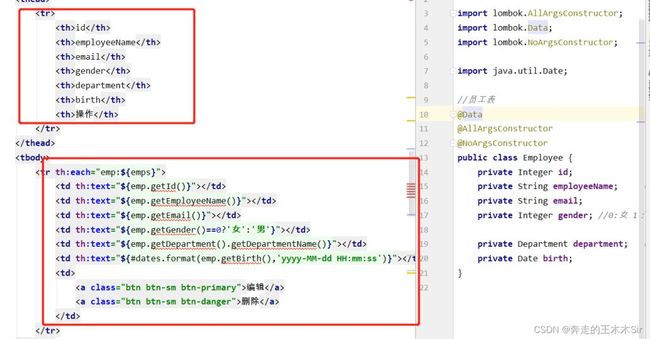
将list.html中数据进行修改,显示员工的信息,并添加编辑和删除的标签
修改成功后,测试
员工信息——增
- 按钮提交
- 跳转到添加页面
- 添加员工成功
- 返回首页
表单提交尽量用重定向:redirect,否则容易出现表单重复提交
首先增加提交按钮
在list.html中增加一个添加员工的按钮,点击按钮时发起有一个/addEmps的请求
这里去编写对应的controller,处理请求。
通过get的方式进行请求提交,所以在EmployeeController中添加一个方法addEmps用来处理list页面点击提交按钮的操作,返回到add.html添加员工页面(页面需要增加,原先没有)
注意在最开始的地方将departmentDao进行装配
@Autowired private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
@GetMapping("/addEmps")
public String add(Model model) {
//查出所有的部门信息,添加到departments中,用于前端接收
Collection departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments", departments);
return "emp/add";//返回到添加员工页面
}
创建员工界面add.html
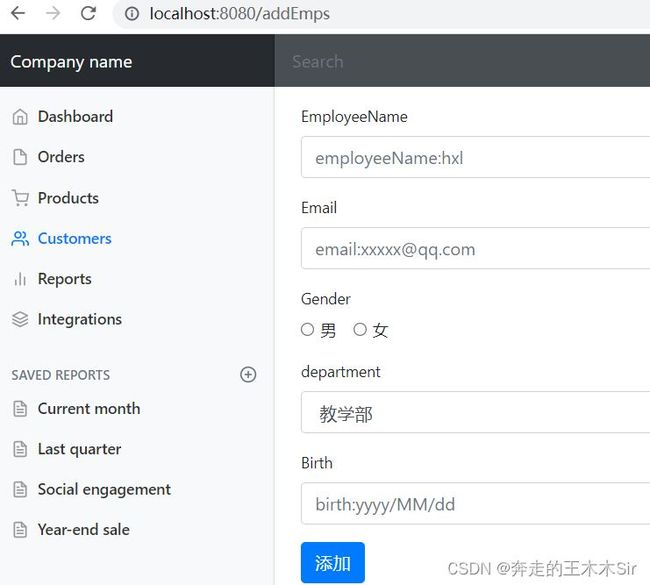
在我们的templates/emp下新建一个add.html,只需要将list.html界面进行复制,然后修改表单即可。修改内容如下:
注意下拉框中的内容应该是我们自己部门名。通过遍历得到
测试:
员工请求addEmps
在add.html页面,当我们填写完信息,点击添加按钮,应该完成添加返回到list页面,展示新的员工信息;因此在add.html点击添加按钮的一瞬间,我们同样发起一个请求/addEmps,与上述提交按钮发出的请求路径一样,但这里发出的是post请求
编写对应的controller
@PostMapping("/addEmps")
public String addEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.addEmployee(employee);//添加一个员工
return "redirect:/emps";//重定向到/emps,刷新列表,返回到list页面
}
测试:
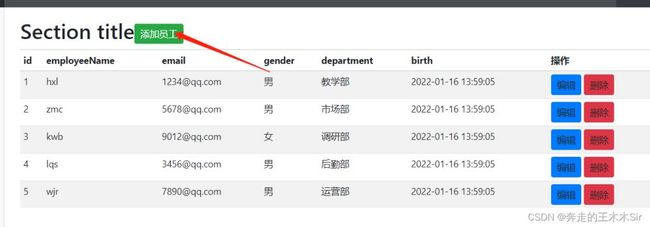
提交之后我们可以跳转到员工页面查看我们的新增加的员工
差一个添加成功的图片
同时这里需要注意:日期格式必须是yyyy/MM/dd才能正确跳转,否则就会出错。因为这是spring默认的,如果要修改日期格式,需要在application.properties中进行修改
spring.mvc.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd
这样日期格式就变了,此时原来的格式就不能用了
链接形式处理是getMapping
员工信息——改
首页编辑按钮
当我们点击编辑时,应该跳转到更新员工的页面update.html,在list.html中修改
这里进行跳转就需要GetMapping
编写对应controller,在EmployeeController中添加一个方法update用来处理list页面点击编辑按钮的操作,返回到update.html
//restful风格接收参数
@GetMapping("/update/{id}")
public String update(@PathVariable("id") int id, Model model) {
//查询指定id的员工,添加到empByID中,用于前端接收
Employee employeeByID = employeeDao.getEmployeeById(id);
model.addAttribute("empByID", employeeByID);
//查出所有的部门信息,添加到departments中,用于前端接收
Collection departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments", departments);
return "emp/update";//返回到编辑员工页面
}
更新员工的页面
复制add.html并修改
这里已经将日期格式进行了修改,没有修改之前的日期是不太正确的。
同时页面跳转的时候需要将Id携带过去。但是不能显示出来,所以需要hidden在上方已经有标注。
页面提交请求
页面编辑完成后会发起一个请求
这需要我们去controller中处理请求
@PostMapping("/update")
public String updateEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.addEmployee(employee);//添加一个员工
return "redirect:/emps";//添加完成重定向到/emps,刷新列表
}
测试:
原来的信息:
![]()
点击编辑之后:
修改之后:
?
成功将员工进行了修改。
员工信息——删
点击删除进行请求跳转:修改我们的删除标签
然后编写对应的controller,处理点击删除按钮的请求,删除指定员工,重定向到/emps请求,更新员工信息
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
employeeDao.deleteEmployeeById(id);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
测试:
删除成功
错误页面定制
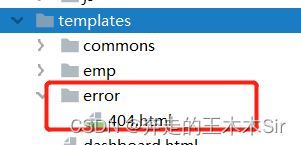
404页面定制
springboot中错误页面定制比较简单,比如说404。直接在thmplates下新建一个error文件夹,然后将404页面直接丢进去即可。
登录测试一下
注销
在我们提取出来的公共commons页面,顶部导航栏处中的标签添加href属性,实现点击发起请求/user/logout
去LoginController中编写对应的方法,清除session,并重定向到首页
@RequestMapping("/user/logout")
public String logout(HttpSession session) {
session.invalidate();
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
测试:点击右上角的Sign out就可以退出界面,访问main.html是没有权限的。
到此这篇关于Springboot-Management的项目实践的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Springboot Management内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!