旷世开源yolox的目标检测使用
如何使用yolox训练自己的目标检测模型
1. 源码的下载,及网络模型的选择
1.1 源码下载
在github官网上搜索yolox,链接
pycharm下yolox的目录结构
1.2 docker下yolox环境的配置
作者做的yolox实验是在docker环境下进行的,想要安装yolox环境可转至:如何使用docker制作深度学习镜像,并参考官方源码中的环境配置自行安装。
2. yolox对数据集的处理
由于yolox和传统的yolo系列算法不同,yolox可以支持VOC格式的数据。所以此次训练针对于VOC格式数据的训练。
2.1 代码中数据需要处理的部分
-
选取网络模型
在yolox官网上,我们可以看到yolox有多个网络模型,我们可以根据自己的需要选取自己的网络模型。作者不关心检测的速率问题,只关注与检测的准确问题,所以此次实验采用的是YOLOX-x。
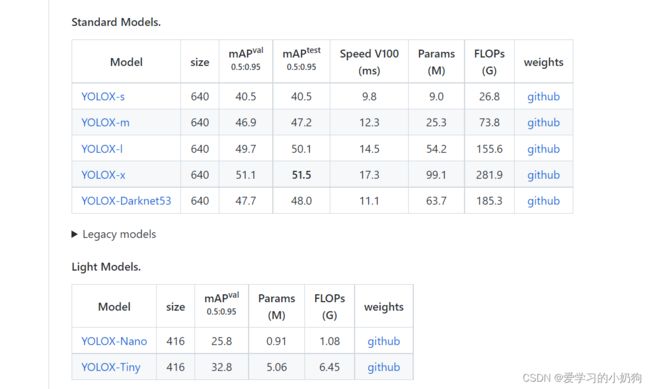
在项目的exps/example/yolox_voc目录下,复制yolox_voc_s.py并重新命名为yolox_voc_x.py。
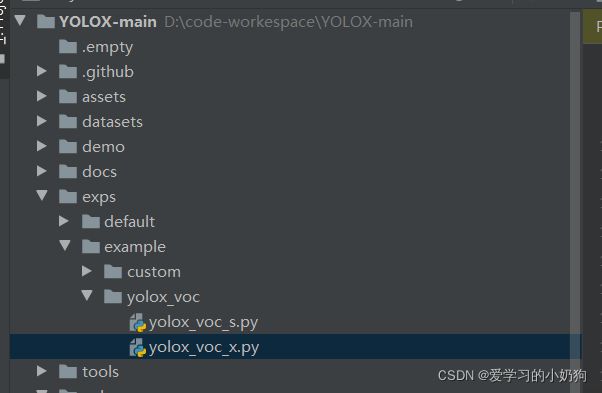
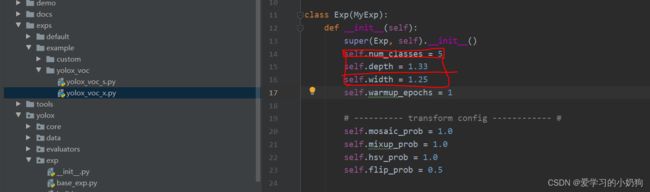
修改yolox_voc_x.py中的num_class、self.depth、self.width:,三个参数其中:- num_class: 为当前训练所需要的类别数
- self.depth:为当前网络模型的深度
- self.width:为当前网络模型的宽度(也不知道对不对,反正就这样吧)。
注意: 修改self.depth、self.width时请参考exps/default下的yolox_x.py
修改完成后的模样如下所示: 注意:num_classes一定要修改为自己的类别数目。
-
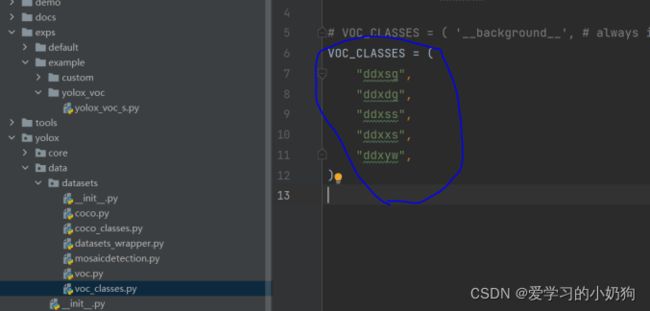
训练类别标签的修改
在项目yolox/data/datasets/voc_classes.py中修改数据集类别,将当前的类别改为自己数据集的类别标签。
-
数据集查找的代码部分修改。
在第一步中我们给出了数据集的格式和目录结构,在此步骤中需要将这个目录结构填写到代码中,告诉代码数据集的路径。
train路径的修改: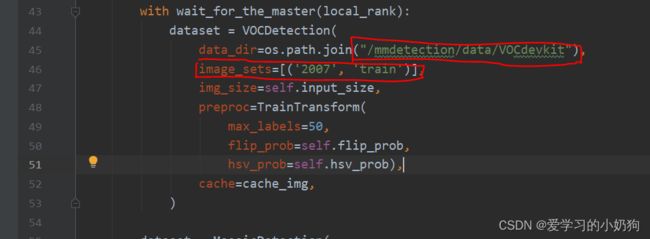
- 先修改data_dir:此处的修改只针对于个人项目的路径。
- 修改image_sets
test路径的修改:
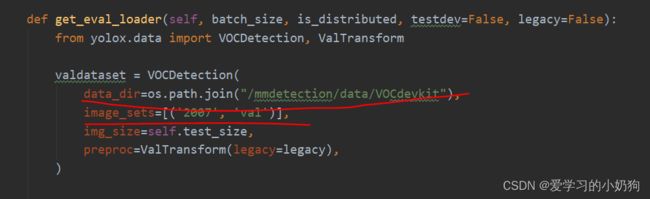
注意: 作者在文章目标检测-数据处理常用脚本文件已经说明了:非比赛项目,基本不使用test数据,所有的数据因划分为train和val两部分。所以在test环节中我们直接使用val集代替。此处修改的train和val是对应我们的train.txt和val.txt文件。 -
其他需要修改的地方
打开yolox/data/datasets/voc.py,这里面有个错误。画框位置,将大括号的“%s”去掉,否则验证的时候一直报找不到文件的错误。
2.2 配置文件的修改
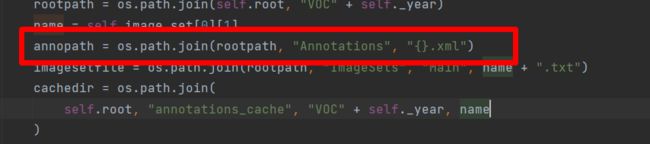
- 图像resize尺寸的修改
在yolox/exp/yolox_base.py做如下修改: 如果修改了train的图像size,那么val的图像size也要做相应修改。
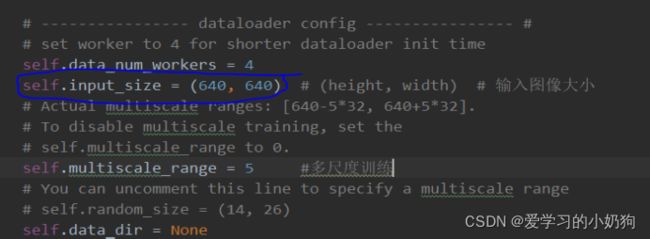
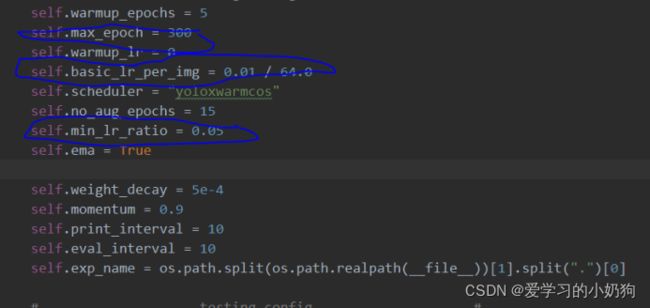
- 关于学习率和训练轮次epoch的修改:在yolox/exp/yolox_base.py做如下修改:
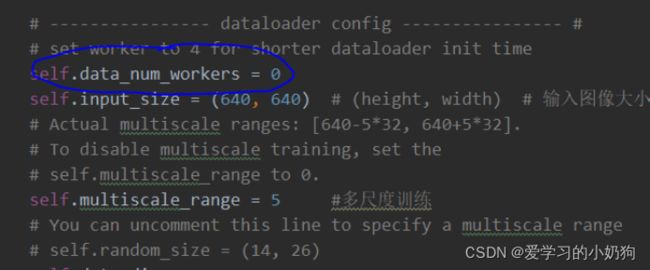
- 关于训练过程中容易出错的多线程修改:在yolox/exp/yolox_base.py中将 data_num_workers修改为0。
- 预训练权重的下载:在官网上根据自己所选取的网络模型,下载对应的预训练权重。
3. docker容器的挂载
Docker run --runtime=nvidia --name=容器的名字
-v yolox代码的路径/:/挂载到容器中的名字(自己起)
-v 数据集的路径/:/挂载到容器中的名字(自己起)/data/ VOCdevkit/VOC2007
-i -t 镜像的id /bin/bash
如: docker run --runtime=nvidia --name=test01 -v yolox/:/yolox_test -v datasets/:/yolox_test/data/VOCdevkit/VOC2007 -i -t 123456 /bin/bash
4. 多gpu训练
Python toos/train.py -f exps/example/yolox_voc_x.py -d 8 -b 64 –fp16 -c checkpoints/yolox_x.pth
其中: -d:为gpu训练数量
-f :为需要训练的网络路径
-b: 为网络训练的bathsize
-c: 为预训练权重的路径
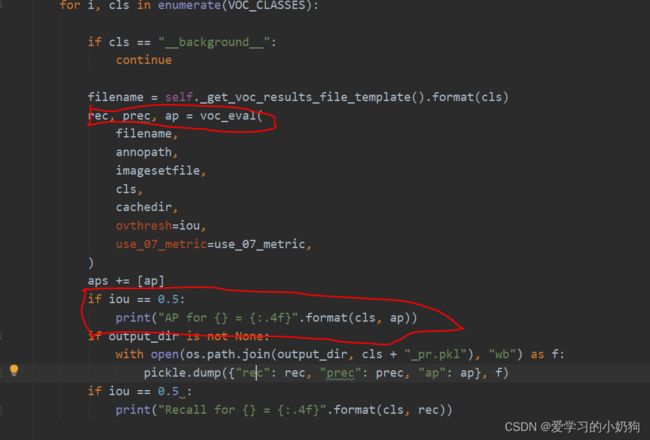
注意:作者在训练的时候发现,源代码只能够输出模型验证的ap指标,并没有输出recall,我们可以在 yolox/data/datasets/voc.py
的_do_python_eval函数中(预计在313行中)自己手动打印recall,如下图所示:
5. 模型的测试
解释说明: 作者通过观察源码发现,yolox官方源码封装较好,并没有给出如何测试多张图片的demo脚本,如果需要测试多张图片需要自己根据源码中的测试单张图片的demo修改,作者自己根据这个脚本修改出一个测试多张图片的脚本,如下所示:
测试命令:python tools/test_mutil_jpg.py image -f exps/default/yolox_s.py -c checkpoints/yolox_s.pth --conf 0.3 --nms 0.65 --tsize 640 --device gpu
-f :为算法模型
-c:为权重所在路径
--conf 0.3
--nms 0.65
--tsize 640 :为图片需要resize的大小,需要跟自己训练时的大小一致
--device gpu : 是否使用gpu测试
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Copyright (c) Megvii, Inc. and its affiliates.
'''
测试命令: python tools/test_mutil_jpg.py image -f exps/default/yolox_s.py -c checkpoints/yolox_s.pth --conf 0.3 --nms 0.65 --tsize 640 --device gpu
其中:
-f :为算法模型
-c:为权重所在路径
--conf 0.3
--nms 0.65
--tsize 640 :为图片需要resize的大小,需要跟自己训练时的大小一致
--save_result : 测试完成是否需要保存图片
--device gpu : 是否使用gpu测试
以下代码需要修改的地方:
1. 测试图片输入的地方:
2. 测试图片输出的地方:
'''
import argparse
import os
import time
from loguru import logger
import cv2
import torch
from yolox.data.data_augment import ValTransform
from yolox.data.datasets import COCO_CLASSES
from yolox.exp import get_exp
from yolox.utils import fuse_model, get_model_info, postprocess, vis
IMAGE_EXT = [".jpg", ".jpeg", ".webp", ".bmp", ".png"]
def make_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("YOLOX Demo!")
parser.add_argument(
"demo", default="image", help="demo type, eg. image, video and webcam"
)
parser.add_argument("-expn", "--experiment-name", type=str, default=None)
parser.add_argument("-n", "--name", type=str, default=None, help="model name")
#测试图片输入入口,更改default值
parser.add_argument(
"--path", default="./assets/dog.jpg", help="path to images or video"
)
parser.add_argument("--camid", type=int, default=0, help="webcam demo camera id")
#测试图片输出入口,更改default值
parser.add_argument(
"--save_result",
default="./result",
action="store_true",
help="whether to save the inference result of image/video"
)
# exp file
parser.add_argument(
"-f",
"--exp_file",
default=None,
type=str,
help="pls input your experiment description file",
)
parser.add_argument("-c", "--ckpt", default=None, type=str, help="ckpt for eval")
parser.add_argument(
"--device",
default="cpu",
type=str,
help="device to run our model, can either be cpu or gpu",
)
parser.add_argument("--conf", default=0.3, type=float, help="test conf")
parser.add_argument("--nms", default=0.3, type=float, help="test nms threshold")
parser.add_argument("--tsize", default=None, type=int, help="test img size")
parser.add_argument(
"--fp16",
dest="fp16",
default=False,
action="store_true",
help="Adopting mix precision evaluating.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--legacy",
dest="legacy",
default=False,
action="store_true",
help="To be compatible with older versions",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--fuse",
dest="fuse",
default=False,
action="store_true",
help="Fuse conv and bn for testing.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--trt",
dest="trt",
default=False,
action="store_true",
help="Using TensorRT model for testing.",
)
return parser
def get_image_list(path):
image_names = []
for maindir, subdir, file_name_list in os.walk(path):
for filename in file_name_list:
apath = os.path.join(maindir, filename)
ext = os.path.splitext(apath)[1]
if ext in IMAGE_EXT:
image_names.append(apath)
return image_names
class Predictor(object):
def __init__(
self,
model,
exp,
cls_names=COCO_CLASSES,
trt_file=None,
decoder=None,
device="cpu",
fp16=False,
legacy=False,
):
self.model = model
self.cls_names = cls_names
self.decoder = decoder
self.num_classes = exp.num_classes
self.confthre = exp.test_conf
self.nmsthre = exp.nmsthre
self.test_size = exp.test_size
self.device = device
self.fp16 = fp16
self.preproc = ValTransform(legacy=legacy)
if trt_file is not None:
from torch2trt import TRTModule
model_trt = TRTModule()
model_trt.load_state_dict(torch.load(trt_file))
x = torch.ones(1, 3, exp.test_size[0], exp.test_size[1]).cuda()
self.model(x)
self.model = model_trt
def inference(self, img):
img_info = {"id": 0}
if isinstance(img, str):
img_info["file_name"] = os.path.basename(img)
img = cv2.imread(img)
else:
img_info["file_name"] = None
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img_info["height"] = height
img_info["width"] = width
img_info["raw_img"] = img
ratio = min(self.test_size[0] / img.shape[0], self.test_size[1] / img.shape[1])
img_info["ratio"] = ratio
img, _ = self.preproc(img, None, self.test_size)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0)
img = img.float()
if self.device == "gpu":
img = img.cuda()
if self.fp16:
img = img.half() # to FP16
with torch.no_grad():
t0 = time.time()
outputs = self.model(img)
if self.decoder is not None:
outputs = self.decoder(outputs, dtype=outputs.type())
outputs = postprocess(
outputs, self.num_classes, self.confthre,
self.nmsthre, class_agnostic=True
)
logger.info("Infer time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - t0))
return outputs, img_info
def visual(self, output, img_info, cls_conf=0.35):
ratio = img_info["ratio"]
img = img_info["raw_img"]
if output is None:
return img
output = output.cpu()
bboxes = output[:, 0:4]
# preprocessing: resize
bboxes /= ratio
cls = output[:, 6]
scores = output[:, 4] * output[:, 5]
vis_res = vis(img, bboxes, scores, cls, cls_conf, self.cls_names)
return vis_res
def image_demo(predictor, vis_folder, path, current_time, save_result):
if os.path.isdir(path):
files = get_image_list(path)
else:
files = [path]
files.sort()
for image_name in files:
outputs, img_info = predictor.inference(image_name)
result_image = predictor.visual(outputs[0], img_info, predictor.confthre)
# if save_result:
# save_folder = os.path.join(
# vis_folder, time.strftime("%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S", current_time)
# )
# os.makedirs(save_folder, exist_ok=True)
# save_file_name = os.path.join(save_folder, os.path.basename(image_name))
# logger.info("Saving detection result in {}".format(save_file_name))
# cv2.imwrite(save_file_name, result_image)
save_folder =vis_folder
os.makedirs(save_folder, exist_ok=True)
save_file_name = os.path.join(save_folder, os.path.basename(image_name))
logger.info("Saving detection result in {}".format(save_file_name))
cv2.imwrite(save_file_name, result_image)
ch = cv2.waitKey(0)
if ch == 27 or ch == ord("q") or ch == ord("Q"):
break
def imageflow_demo(predictor, vis_folder, current_time, args):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(args.path if args.demo == "video" else args.camid)
width = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH) # float
height = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT) # float
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
save_folder = os.path.join(
vis_folder, time.strftime("%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S", current_time)
)
os.makedirs(save_folder, exist_ok=True)
if args.demo == "video":
save_path = os.path.join(save_folder, args.path.split("/")[-1])
else:
save_path = os.path.join(save_folder, "camera.mp4")
logger.info(f"video save_path is {save_path}")
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(
save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (int(width), int(height))
)
while True:
ret_val, frame = cap.read()
if ret_val:
outputs, img_info = predictor.inference(frame)
result_frame = predictor.visual(outputs[0], img_info, predictor.confthre)
if args.save_result:
vid_writer.write(result_frame)
ch = cv2.waitKey(1)
if ch == 27 or ch == ord("q") or ch == ord("Q"):
break
else:
break
def main(exp, args):
if not args.experiment_name:
args.experiment_name = exp.exp_name
file_name = os.path.join(exp.output_dir, args.experiment_name)
os.makedirs(file_name, exist_ok=True)
print("======================")
vis_folder = args.save_result
# if args.save_result:
# vis_folder = os.path.join(file_name, "vis_res")
os.makedirs(vis_folder, exist_ok=True)
if args.trt:
args.device = "gpu"
logger.info("Args: {}".format(args))
if args.conf is not None:
exp.test_conf = args.conf
if args.nms is not None:
exp.nmsthre = args.nms
if args.tsize is not None:
exp.test_size = (args.tsize, args.tsize)
model = exp.get_model()
logger.info("Model Summary: {}".format(get_model_info(model, exp.test_size)))
if args.device == "gpu":
model.cuda()
if args.fp16:
model.half() # to FP16
model.eval()
if not args.trt:
if args.ckpt is None:
ckpt_file = os.path.join(file_name, "best_ckpt.pth")
else:
ckpt_file = args.ckpt
logger.info("loading checkpoint")
ckpt = torch.load(ckpt_file, map_location="cpu")
# load the model state dict
model.load_state_dict(ckpt["model"])
logger.info("loaded checkpoint done.")
if args.fuse:
logger.info("\tFusing model...")
model = fuse_model(model)
if args.trt:
assert not args.fuse, "TensorRT model is not support model fusing!"
trt_file = os.path.join(file_name, "model_trt.pth")
assert os.path.exists(
trt_file
), "TensorRT model is not found!\n Run python3 tools/trt.py first!"
model.head.decode_in_inference = False
decoder = model.head.decode_outputs
logger.info("Using TensorRT to inference")
else:
trt_file = None
decoder = None
predictor = Predictor(
model, exp, COCO_CLASSES, trt_file, decoder,
args.device, args.fp16, args.legacy,
)
current_time = time.localtime()
if args.demo == "image":
image_demo(predictor, vis_folder, args.path, current_time, args.save_result)
elif args.demo == "video" or args.demo == "webcam":
imageflow_demo(predictor, vis_folder, current_time, args)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("==============")
args = make_parser().parse_args()
exp = get_exp(args.exp_file, args.name)
print("=================")
main(exp, args)
6. 模型的验证
1.如果只想验证当前数据集的验证集则只需要运行一下命令:
python tools/eval.py -f exps/example/yolox_voc/yolox_voc_x.py -d 3 -b 24 --conf 0.001
-f :模型路径
-d :使用gpu数量
-b : bath_size
2.如果想使用当前模型验证其他数据集:
python tools/eval.py -f exps/example/yolox_voc/yolox_voc_x.py -d 3 -b 24 --conf 0.001
注意: 作者在做模型验证的时候发现过一些bug,当我们的验证集更改后,再进行测试文件时需要将之前测试文件的缓存给删除,不然容易报错。
7. 输出指定格式的检测结果
解释说明: 源码中输出的结果要不就是txt文件格式的、或者直接在图片上画框,作者根据自己的需求写了一个脚本文件,这个脚本文件可以将预测结果以列表的形式返回,如果想一次性测试多张图片可以采用for训练。
这个脚本需要输入的参数有: 图片名、config文件、权重路径、检测类别。
import os
import cv2
import torch
from yolox.data.data_augment import ValTransform
from yolox.exp import get_exp
from yolox.utils import postprocess
def vis_list(boxes, scores, cls_ids, conf=0.5, class_names=None): # 置性度需要自己给定,这里默认采用0.5
result_list = []
for i in range(len(boxes)):
box = boxes[i]
cls_id = int(cls_ids[i])
score = scores[i]
if score < conf:
continue
x0 = int(box[0])
y0 = int(box[1])
x1 = int(box[2])
y1 = int(box[3])
class_name = class_names[cls_id]
one_line = [str(x0), str(y0), str(x1), str(y1), class_name, str(float(score))]
result_list.append(one_line)
## 返还列表形式的检测结果 检测结果中包含score得分、类别信息、bbox坐标
return result_list
class Predictor(object):
def __init__(
self,
model,
exp,
cls_names,
device="gpu",
):
self.model = model
self.cls_names = cls_names
self.num_classes = exp.num_classes
self.confthre = exp.test_conf
self.nmsthre = exp.nmsthre
self.test_size = exp.test_size
self.device = device
self.preproc = ValTransform(legacy=False)
def inference(self, img):
img_info = {"id": 0}
if isinstance(img, str):
img_info["file_name"] = os.path.basename(img)
img = cv2.imread(img)
else:
img_info["file_name"] = None
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img_info["height"] = height
img_info["width"] = width
img_info["raw_img"] = img
ratio = min(self.test_size[0] / img.shape[0], self.test_size[1] / img.shape[1])
img_info["ratio"] = ratio
img, _ = self.preproc(img, None, self.test_size)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0)
img = img.float()
if self.device == "gpu":
img = img.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self.model(img)
outputs = postprocess(
outputs, self.num_classes, self.confthre,
self.nmsthre, class_agnostic=True
)
return outputs, img_info
def visual(self, output, img_info, cls_conf=0.35):
ratio = img_info["ratio"]
img = img_info["raw_img"]
if output is None:
return img
output = output.cpu()
bboxes = output[:, 0:4]
bboxes /= ratio
cls = output[:, 6]
scores = output[:, 4] * output[:, 5]
result_list = vis_list(bboxes, scores, cls, cls_conf, self.cls_names)
return result_list
def test(config,ckpt_file,image_name,VOC_CLASSES):
name = None
exp = get_exp(config, name)
exp.test_conf = 0.3
exp.nmsthre = 0.5
exp.test_size = (960, 960)
model = exp.get_model()
model.cuda()
model.eval()
ckpt = torch.load(ckpt_file, map_location="cpu")
# load the model state dict
model.load_state_dict(ckpt["model"])
predictor = Predictor(
model, exp, VOC_CLASSES
)
outputs,img_info= predictor.inference(image_name)
result_list = predictor.visual(outputs[0], img_info, predictor.confthre)
return result_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
config = "exps/example/yolox_voc/yolox_voc_x.py" # config文件
ckpt_file = "YOLOX_outputs/yolox_voc_x/best_ckpt.pth" # 权重路径
image_name = "./test_jpg/202011_338646.jpg" # 图片名字
VOC_CLASSES = ('xcxjpy', 'fzchy', 'fzctl', 'fzcpy', "fzcxs", "pbhxs", "zcxs") # 检测类别
test(config,ckpt_file,image_name,VOC_CLASSES)