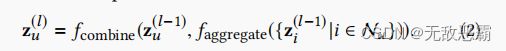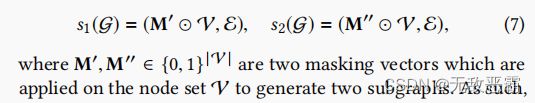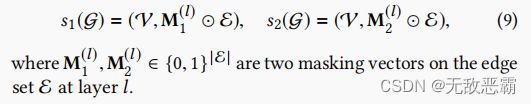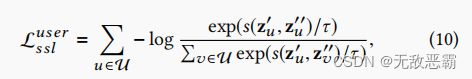Self-supervised Graph Learning for Recommendation(SIGIR2021)
原文链接Self-supervised Graph Learning for Recommendation![]() https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10783v4
https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10783v4
目录
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 目前基于GCN的推荐模型仍存在一些局限性:
1.2 自监督辅助任务:
1.3 自监督对于GCN推荐模型的补充:
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 Recap GCN
2.2 Supervised Learning Loss.
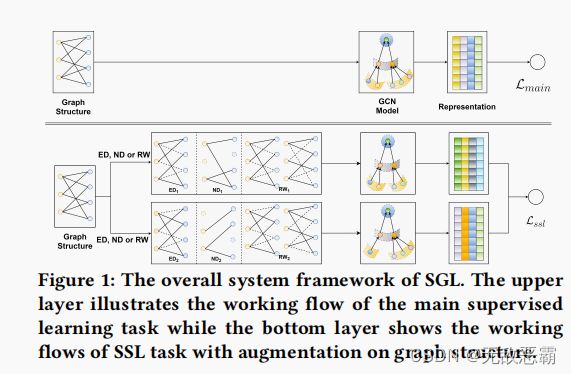
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Augmentation on Graph Structure
Node Dropout (ND).
Edge Dropout (ED).
Random Walk (RW).
3.2 Contrastive Learning
3.3 Multi-task Training
3.4 Theoretical Analyses of SGL
3.5 Complexity Analyses of SGL
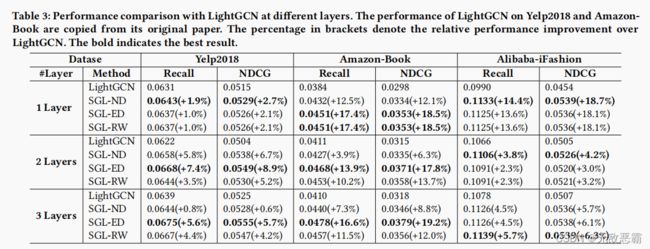
4 EXPERIMENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 目前基于GCN的推荐模型仍存在一些局限性:
①Sparse Supervision Signal---稀疏的监督信号
②Skewed Data Distribution---长尾效应
③Noises in Interactions---隐反馈常常包含噪声
为解决以上问题,引入自监督self-supervised learning (SSL) ,通过设置辅助任务从输入数据本身(特别是无标记数据)提取额外信号,从而增进下游任务的性能。
1.2 自监督辅助任务:
①data augmentation数据增广:node dropout、 edge dropout、random walk 生成多视图
②contrastive learning对比学习:which maximizes the agreement between different views of the same node, compared to that of other nodes.最大化正样本(同一结点不同视图)的一致性
1.3 自监督对于GCN推荐模型的补充:
①提供辅助监督信号,补充了原有的稀疏信号;
②增广操作特别是edge dropout减轻长尾效应: helps to mitigate the degree biases by intentionally reducing the influence of high-degree nodes;
③节点的多个视图包含不同的局部结构和邻域,增强了模型对交互噪声的鲁棒性。
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 Recap GCN
2.2 Supervised Learning Loss.
BPR损失
3 METHODOLOGY
where two stochastic selections s1 and s2 are independently applied on graph G, and establish two correlated views of nodes Z1 and Z2.
3.1 Data Augmentation on Graph Structure
Node Dropout (ND).
图中的每个节点以概率ρ被丢弃,连同其连接的边。从不同的增广视图中识别有影响的节点,并使表示学习对结构变化不那么敏感。
Edge Dropout (ED).
根据一定概率丢弃边。只有邻域内的部分连接对节点表示有贡献, 捕获节点局部结构的有用模式,并进一步赋予表示对噪声交互更强的鲁棒性。
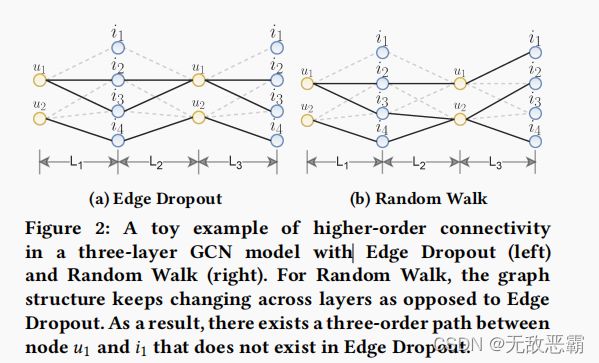
Random Walk (RW).
以上两个操作生成跨所有图卷积层共享的子图
3.2 Contrastive Learning
最大化正样本对对的一致性,最小化负样本对的一致性
3.3 Multi-task Training
还考虑了替代优化——Lssl的预训练和Lmain的微调。更多详情请参见第4.4.2节。
3.4 Theoretical Analyses of SGL
3.5 Complexity Analyses of SGL
由于SGL没有引入可训练的参数,因此空间的复杂度仍然与LightGCN相同。
时间复杂度也是相同的,包括:①邻接矩阵的归一化处理 ②自监督损失