LeetCode刷题——单链表(详细图解)
题目目录
- 1.反转链表
-
- 方法一:暴力改链表方向
- 方法二:迭代法
- 2.链表的中间结点
-
- 方法一:暴力解法
- 方法二:快慢指针
- 3.链表中倒数第k个节点
- 4.回文链表
- 5.合并两个有序链表
- 6.分割链表
- 7.相交链表
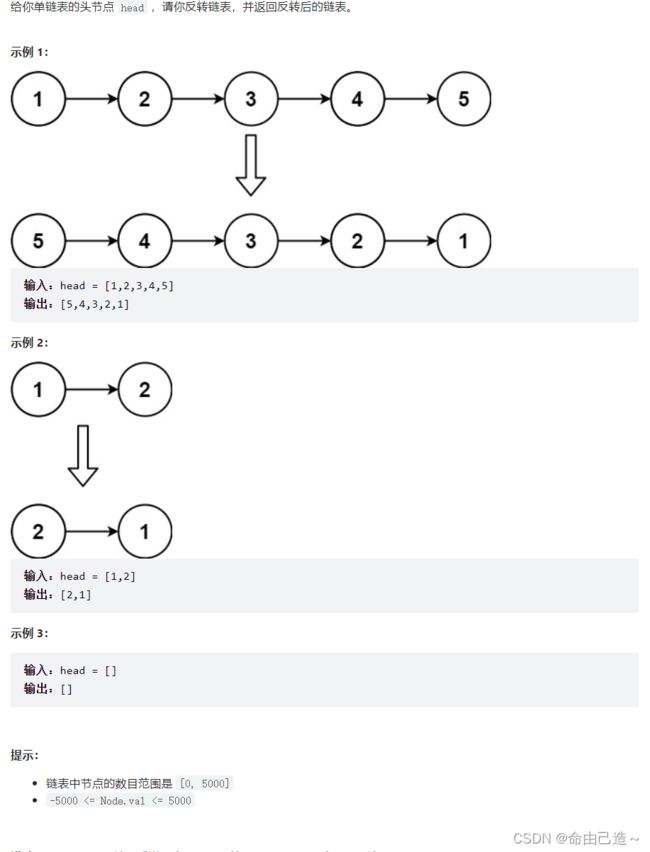
1.反转链表
方法一:暴力改链表方向
思路就是直接把箭头全改为反向
要注意的是要三个结构体指针n1(要改的前一个), n2(要改的), n3(要改的后面一个),依次向后遍历就能完成。
代码如下 :
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL;
struct ListNode* n2 = head;
struct ListNode* n3 = head->next;
while(n3 != NULL)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
n3 = n3->next;
}
n2->next = n1;
return n2;
}
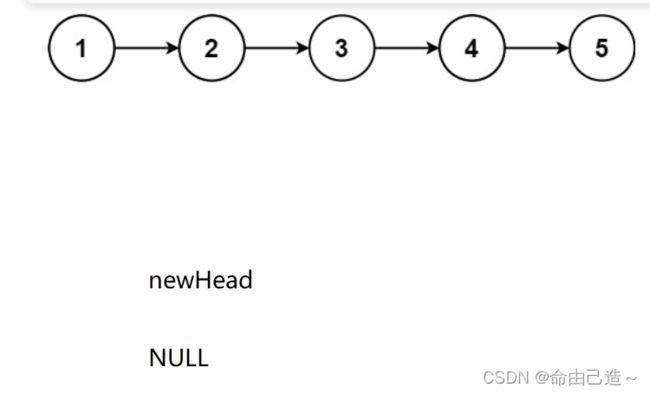
方法二:迭代法
用尾插的方法迭代:
创建一个新的尾(NULL),原链表从左向右依次插入新链表就能完成反转,如图:
开始
结束
要注意的是newHead的位置要改变到新链表头部,以返回新链表。
代码如下 :
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
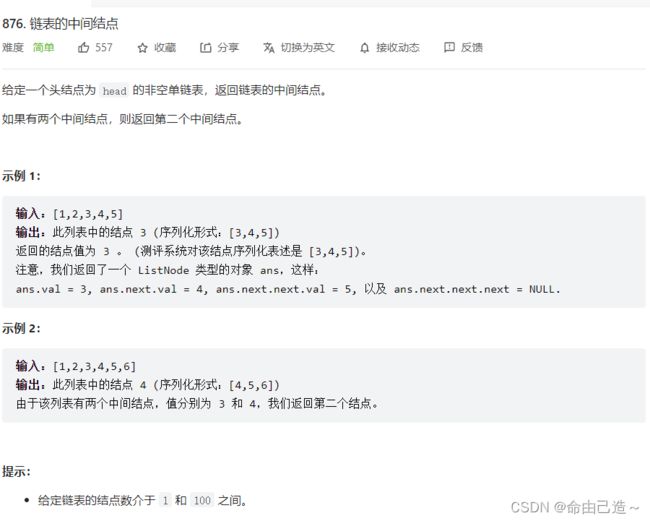
2.链表的中间结点
方法一:暴力解法
遍历链表计算总共数目,结果 /2 就为中间值,再遍历到这个位置
代码如下 :
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
int count = 0;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
count++;
cur = cur->next;
}
count = count/2;
struct ListNode* curr = head;
while(count--)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
return curr;
}
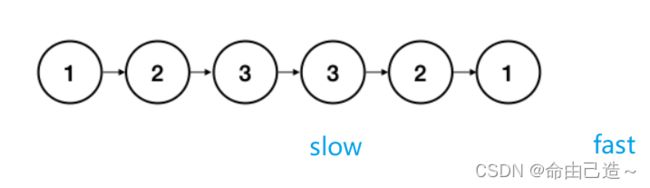
方法二:快慢指针
这里的快慢不是指速度,而是指针移动的距离大小。
我们可以用两个指针
fast:一次移动2位
slow:一次移动1位
当fast移动完slow就会移动到中间。
如图:
开始

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)//顺序不能变
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
这里要注意while的判断部分顺序不能变,不然会对空指针引用(偶数的情况下)
3.链表中倒数第k个节点
这道题其实就是上面一道题的进阶也是用快慢指针的方法。k为快指针比慢指针多走的位数。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* getKthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int k){
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while(k--)
{
if(fast == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast != NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
4.回文链表
我们可以发现这道题是前几个题的总和。
1️⃣先用快慢指针找到位置
2️⃣在旋转后边的
3️⃣最后进行比较
最后两个同时遍历比较就好了
代码如下 :
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
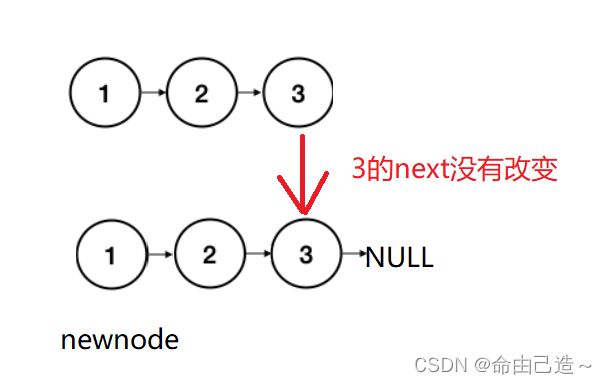
//旋转后半部分
//尾插
struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;
while(slow)
{
struct ListNode* tmp = slow;
slow = slow->next;
tmp->next = newnode;
newnode = tmp;
}
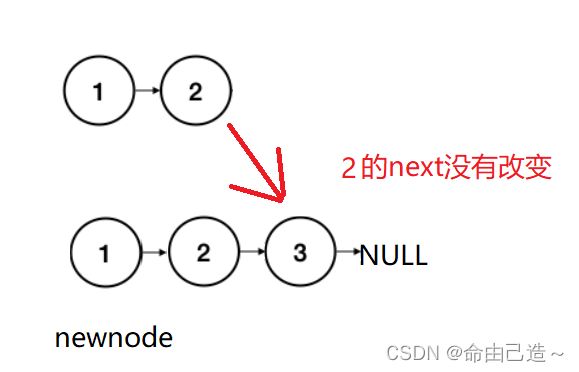
//比较
//奇数个中间的前一个的next没变
struct ListNode* hcur = head, *ncur = newnode;
while(hcur && ncur)
{
if(hcur->val != ncur->val)
{
return false;
}
else
{
hcur = hcur->next;
ncur = ncur->next;
}
}
return true;
}
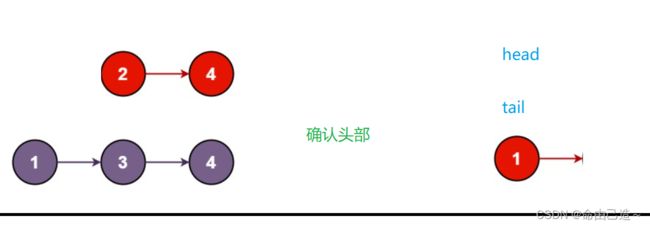
5.合并两个有序链表
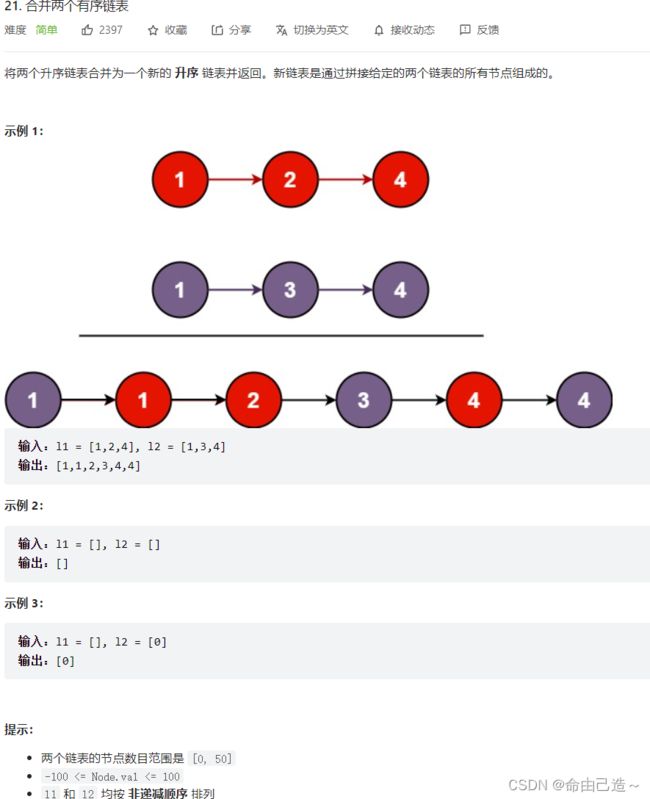
先设置个新的头部取两个链表的最小值放进去,然后依次比较两条链表的较小值尾插到新链表。
如图:
开始

代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if(list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
struct ListNode* head = NULL, *tail = NULL;
//先取最小的当头节点
if(list1->val < list2->val)
{
head = tail = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
head = tail = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
//尾插
while(list1 && list2)
{
if(list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
if(list1 == NULL)
{
tail->next = list2;
}
else
{
tail->next = list1;
}
return head;
}
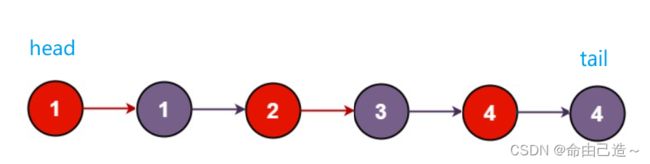
6.分割链表
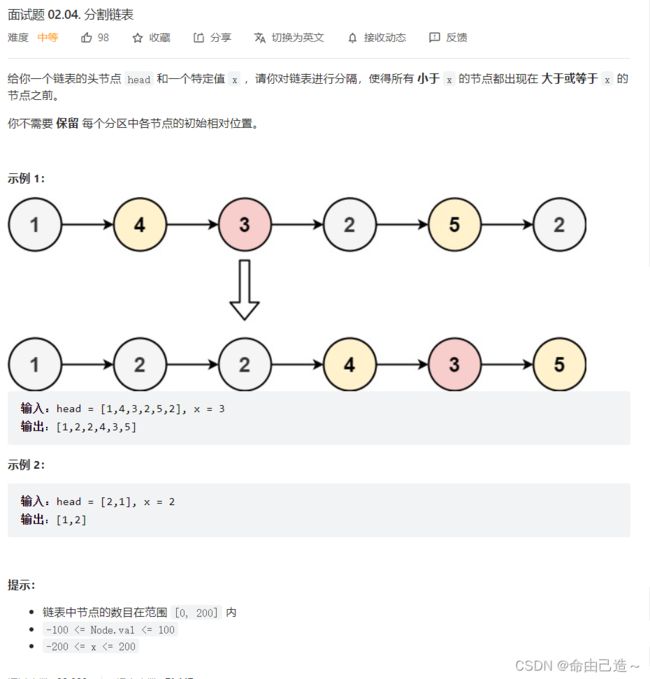
要我们分割链表,我们可以把小于x的节点放到 smallnode 链表里,把大于等于x的节点放到 largenode 链表里再把两个链表相连返回即可。
如图:
开始
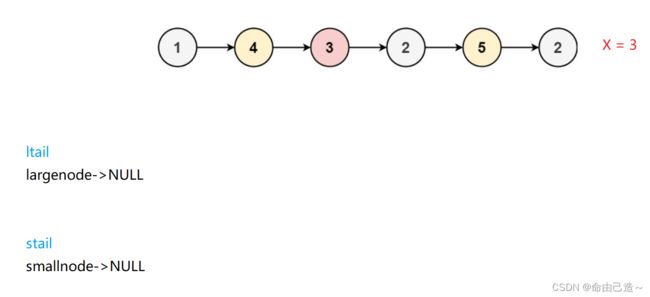
过程
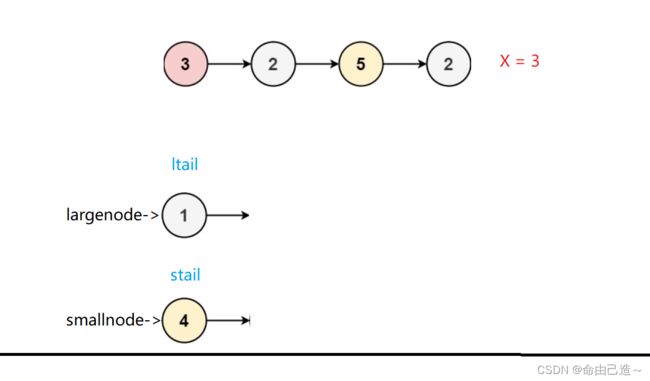
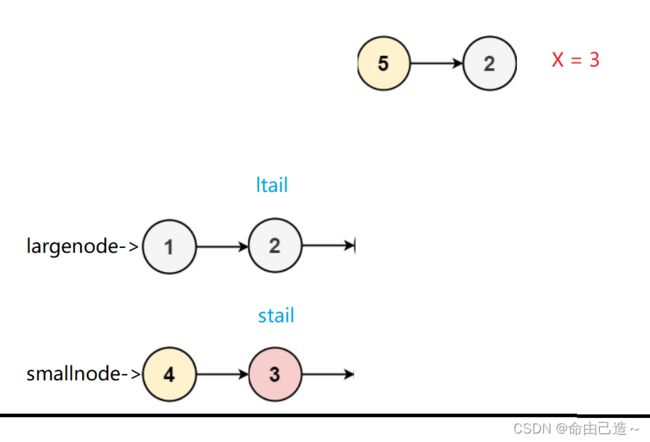
结束
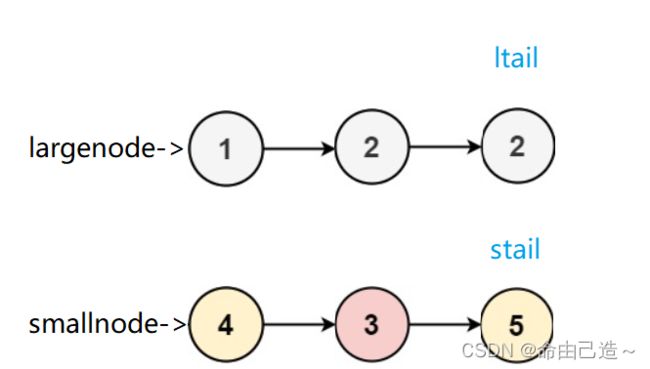
连接
代码如下 :
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){
if(head == NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode* largenode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
largenode->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* smallnode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
smallnode->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* ltail = largenode, *stail = smallnode;
while(head)
{
if(head->val < x)
{
stail->next = head;
stail = stail->next;
}
else
{
ltail->next = head;
ltail = ltail->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
stail->next = largenode->next;
ltail->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* phead = smallnode->next;
free(smallnode);
free(largenode);
return phead;
}
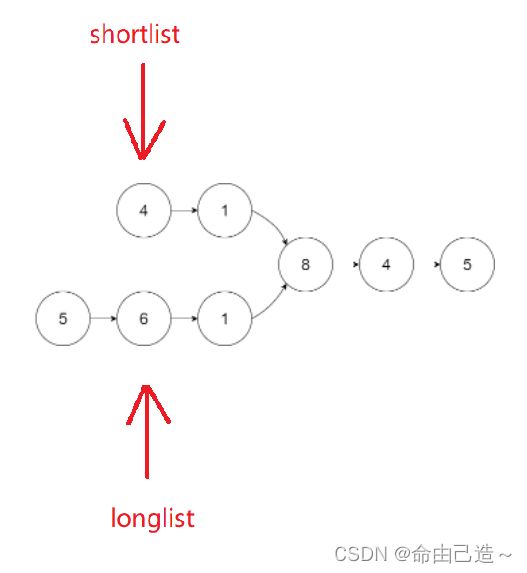
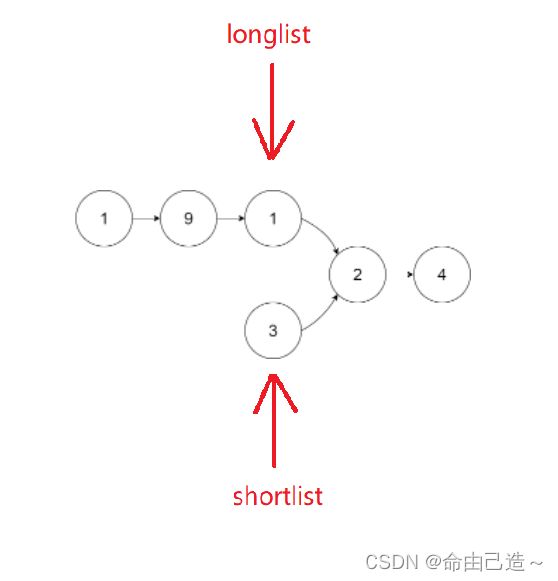
7.相交链表
首先说方法,把两个链表都遍历一遍算出长度,顺便把最后一个元素比较,如果不同,则不相交,因为只要有交点,后边的元素必全部重合。长度的差值就为长链表先走的位数,可以参考前面的快慢指针的方法,此时两个链表同时往后才有可能找到交点。
用题中所给的例子:
代码如下 :
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* curA = headA, *curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while(curA->next)
{
curA = curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB->next)
{
curB = curB->next;
lenB++;
}
if(curB != curA)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* longlist = headA, *shortlist = headB;
if(lenA < lenB)
{
longlist = headB;
shortlist = headA;
}
//长的先走gap步
//abs是绝对值的意思
int gap = abs(lenA-lenB);
while(gap--)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
}
while(longlist != shortlist)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
shortlist = shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
}