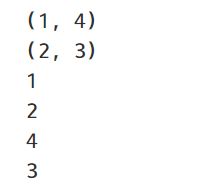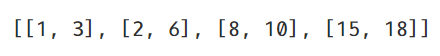Leetcode刷题技巧总结篇(python版)
持续更新……
1 求字符差值
python不可以直接进行字符减运算。当需要进行字符之间的减运算时,我们可以用ord()函数。ord()是python自带的函数,无需导入。
print(ord('b')-ord('a'))
2 字符串反转
string='leetcode'
print(string[::-1])
3 数组元素计数
import collections
li=[1,2,2,4,5,5]
cnt = collections.Counter(li)
print(cnt)
4 字典遍历
cnt={1:4,2:3}
# 遍历键值对
for item in cnt.items():
print(item)
# 遍历键
for item in cnt.keys():
print(item)
# 遍历值
for item in cnt.values():
print(item)
5 初始化全0数组
# 第一种
li=[0]*length
# 第二种
li=[0 for i in range(length)]
# 二维数组
li = [[0] * 3 for i in range(4)]
6 Counter计数
from collections import Counter
colors = ['red', 'blue', 'red', 'green', 'blue', 'blue']
c = Counter(colors)
print(c)
print(dict(c))
c = Counter(a=3, b=1)
d = Counter(a=1, b=2)
c + d # 相加
#Counter({'a': 4, 'b': 3})
6 bisect的用法
bisect是python内置模块,用于有序序列的插入和查找。
查找: bisect(array, item)
插入: insort(array,item)
import bisect
a = [1,2,2,5,8]
position = bisect.bisect(a,7)#找到插入位置
print(position)
# 4
bisect.insort(a,4)#找到位置插入
print(a)
# [1, 2, 2, 4, 5, 8]
bisect.bisect_left(a,2)#插到左侧
# 1
bisect.bisect_right(a,2)#插到右侧
# 3
7 列表去重
l1 = [1,4,4,2,3,4,5,6,1]
l2 = list(set(l1))
print(l2) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
8 列表转化成字符串
li=['a','b','c']
print(' '.join(str(i) for i in li))
9 map函数
map(function, iterable, …)
返回的是一个迭代器对象。
def square(x): # 计算平方数
return x**2
a = list(map(square, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])) # 计算列表各个元素的平方
b = list(map(lambda x: x**2, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])) # 使用 lambda 匿名函数
print(a, b)
10 collections.deque
deque是双端队列(double-ended queue)的缩写,由于两端都能编辑,deque既可以用来实现栈(stack)也可以用来实现队列(queue)。
from collections import deque
# que = collections.deque()
a=deque([1,2,3])
a.pop()
# [1,2]
a.append(4)
# [1,2,4]
a.popleft()
# [2,4]
a.appendleft(0)
# [0,2,4]
相比于list实现的队列,deque实现拥有更低的时间和空间复杂度。list实现出队(pop)和插入(insert)时的空间复杂度大约为O(n),deque在出队(pop)和入队(append)时的时间复杂度是O(1)。
11 PriorityQueue
from queue import PriorityQueue
Q=PriorityQueue()
Q.put(3)
Q.put(2)
Q.put(1)
Q.get()
优先级队列,默认是从小到大排序的。
12 二维list按某一列的值排序
li = [[1,3],[8,10],[2,6],[15,18]]
li.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])
li
13 f-string的用法
name = 'Runoob'
>>> f'Hello {name}' # 替换变量
'Hello Runoob'
14 zip函数的用法
teams = ['Barcelona', 'Bayern Munich', 'Chelsea']
leagues = ['La Liga', 'Bundesliga', 'Premiere League']
countries = ['Spain', 'Germany', 'UK']
for team, league, country in zip(teams, leagues, countries):
print(f'{team} plays in {league}. Country: {country}')
15 利用get()方法获取字典value
person = {'name': 'John', 'age': 20}
print('Name: ', person.get('name'))
print('Age: ', person.get('age'))
print('Salary: ', person.get('salary'))
16 collections.OrderedDict有序字典
from collections import OrderedDict
mydict=OrderedDict({'a':2,'b':1,'c':0})
for key,value in mydict.items():
print(key,value)
17 取字典最大value值对应key
nums=[1,2,2,2,3,4,4]
from collections import Counter
cnt=Counter(nums)
print(max(cnt.keys(),key=cnt.get))
18 @lru_cache装饰器用法
一个为函数提供缓存功能的装饰器,直接用于一个用户自定义函数,在下次以相同参数调用时直接返回上一次的结果。
lru_cache maxsize 参数默认值 为128。如果 设为 None,缓存可无限增长。
@lru_cache(maxsize=None)
def fib(n):
if n < 2:
return n
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
19 字典的排序
# 字典排序
a = {'a': 3, 'c': 89, 'b': 0, 'd': 34}
# 按照字典的值进行排序
a1 = sorted(a.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])
# 按照字典的键进行排序
a2 = sorted(a.items(), key=lambda x: x[0])
print('按值排序后结果', a1)
print('按键排序后结果', a2)
print('结果转为字典格式', dict(a1))
print('结果转为字典格式', dict(a2))