人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.15
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架
工具库:OmniXAI - 可解释AI开发库
tags: [AI,可解释]
‘OmniXAI: A Library for Explainable AI - OmniXAI: A Library for eXplainable AI’ by Salesforce
GitHub: https://github.com/salesforce/OmniXAI
工具库:WeTTS - 产品级端到端文本语音合成工具包
tags: [语音合成,端到端]
‘WeTTS - Production First and Production Ready End-to-End Text-to-Speech Toolkit’ by WeNet Open Source Community
GitHub: https://github.com/wenet-e2e/wetts
工具库:Honor of Kings Game Environment - 腾讯lab出品支持强化学习研究的王者荣耀游戏环境
tags: [强化学习,王者荣耀,环境]
包括1v1游戏核心、强化学习框架和基于训练框架的PPO算法实现
‘Honor of Kings Game Environment’ by tencent-ailab
GitHub: https://github.com/tencent-ailab/hok_env
工具库:Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART) - Python机器学习安全库/对抗性鲁棒性工具箱
‘Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART) v1.5 - Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART) - Python Library for Machine Learning Security - Evasion, Poisoning, Extraction, Inference’ by Trusted-AI
GitHub: https://github.com/Trusted-AI/adversarial-robustness-toolbox
工具语言:rulex - 一种新的可移植正则表达式语言
tags: [正则表达式,可移植,语言]
‘rulex - A new, portable, regular expression language’
GitHub: https://github.com/rulex-rs/rulex
工具:Tasqueue - Go语言实现的一个简单可定制的分布式作业/worker
tags: [Go,分布式,job/worker]
‘Tasqueue - A simple, customizable distributed job/worker in Go’ by Lakshay Kalbhor
GitHub: https://github.com/kalbhor/Tasqueue
2.项目&代码
项目:bytetrack-opencv-onnxruntime - 目标跟踪项目部署
tags: [目标跟踪,bytetrack,opencv]
分别使用OpenCV、ONNXRuntime部署YOLOX+ByteTrack目标跟踪,包含C++和Python两个版本的程序
GitHub: https://github.com/hpc203/bytetrack-opencv-onnxruntime
3.博文&分享
免费书籍:《强化学习导论(第二版)》最新版
《Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction》by Richard S. Sutton, Andrew G. Barto
Link:http://www.incompleteideas.net/book/the-book.html
pdf: http://www.incompleteideas.net/book/RLbook2020.pdf
4.数据&资源
资源:大数据算法基础课程笔记集锦
《Sketching Algorithms for Big Data | Sketching Algorithms》
Link: https://www.sketchingbigdata.org/fall17/lec/
5.研究&论文
可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:Recurrent Video Restoration Transformer with Guided Deformable Attention
论文标题:Recurrent Video Restoration Transformer with Guided Deformable Attention
论文时间:5 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Deblurring,Denoising,Super-Resolution,Video Restoration,Video Super-Resolution,去模糊,去噪,超分辨率,视频修复,视频超分辨率
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02146
代码实现:https://github.com/jingyunliang/rvrt
论文作者:Jingyun Liang, Yuchen Fan, Xiaoyu Xiang, Rakesh Ranjan, Eddy Ilg, Simon Green, JieZhang Cao, Kai Zhang, Radu Timofte, Luc van Gool
论文简介:Specifically, RVRT divides the video into multiple clips and uses the previously inferred clip feature to estimate the subsequent clip feature. / 具体来说,RVRT 将视频分成多个片段,并使用之前推断的片段特征来估计后续片段特征。
论文摘要:Video restoration aims at restoring multiple high-quality frames from multiple low-quality frames. Existing video restoration methods generally fall into two extreme cases, i.e., they either restore all frames in parallel or restore the video frame by frame in a recurrent way, which would result in different merits and drawbacks. Typically, the former has the advantage of temporal information fusion. However, it suffers from large model size and intensive memory consumption; the latter has a relatively small model size as it shares parameters across frames; however, it lacks long-range dependency modeling ability and parallelizability. In this paper, we attempt to integrate the advantages of the two cases by proposing a recurrent video restoration transformer, namely RVRT. RVRT processes local neighboring frames in parallel within a globally recurrent framework which can achieve a good trade-off between model size, effectiveness, and efficiency. Specifically, RVRT divides the video into multiple clips and uses the previously inferred clip feature to estimate the subsequent clip feature. Within each clip, different frame features are jointly updated with implicit feature aggregation. Across different clips, the guided deformable attention is designed for clip-to-clip alignment, which predicts multiple relevant locations from the whole inferred clip and aggregates their features by the attention mechanism. Extensive experiments on video super-resolution, deblurring, and denoising show that the proposed RVRT achieves state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets with balanced model size, testing memory and runtime.
视频恢复旨在从多个低质量帧中恢复多个高质量帧。现有的视频恢复方法一般分为两种极端情况,要么并行恢复所有帧,要么以循环的方式逐帧恢复视频,这将导致不同的优点和缺点。通常,前者具有时间信息融合的优势。但是,它存在模型尺寸大和内存消耗大的问题;后者的模型尺寸相对较小,因为它跨帧共享参数;但是,它缺乏远程依赖建模能力和并行性。在本文中,我们试图通过提出一种循环视频恢复转换器,即 RVRT 来整合这两种情况的优点。 RVRT 在全局循环框架内并行处理局部相邻帧,可以在模型大小、有效性和效率之间实现良好的权衡。具体来说,RVRT 将视频划分为多个剪辑,并使用之前推断的剪辑特征来估计后续剪辑特征。在每个剪辑中,不同的帧特征通过隐式特征聚合联合更新。在不同的剪辑中,引导的可变形注意力被设计用于剪辑到剪辑的对齐,它从整个推断的剪辑中预测多个相关位置,并通过注意机制聚合它们的特征。视频超分辨率、去模糊和去噪的大量实验表明,所提出的 RVRT 在具有平衡模型大小、测试内存和运行时间的基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
论文:PIDNet: A Real-time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired from PID Controller
论文标题:PIDNet: A Real-time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired from PID Controller
论文时间:4 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,Semantic Segmentation,实时语义分割,语义分割
论文地址:(https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02066
代码实现:https://github.com/XuJiacong/PIDNet
论文作者:Jiacong Xu, Zixiang Xiong, Shankar P. Bhattacharyya
论文简介:However, direct fusion of low-level details and high-level semantics will lead to a phenomenon that the detailed features are easily overwhelmed by surrounding contextual information, namely overshoot in this paper, which limits the improvement of the accuracy of existed two-branch models. / 但是,低层细节和高层语义的直接融合会导致细节特征容易被周围的上下文信息淹没的现象,即本文中的overshoot,这限制了现有两分支模型的准确性提升。
论文摘要:Two-branch network architecture has shown its efficiency and effectiveness for real-time semantic segmentation tasks. However, direct fusion of low-level details and high-level semantics will lead to a phenomenon that the detailed features are easily overwhelmed by surrounding contextual information, namely overshoot in this paper, which limits the improvement of the accuracy of existed two-branch models. In this paper, we bridge a connection between Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller and reveal that the two-branch network is nothing but a Proportional-Integral (PI) controller, which inherently suffers from the similar overshoot issue. To alleviate this issue, we propose a novel three-branch network architecture: PIDNet, which possesses three branches to parse the detailed, context and boundary information (derivative of semantics), respectively, and employs boundary attention to guide the fusion of detailed and context branches in final stage. The family of PIDNets achieve the best trade-off between inference speed and accuracy and their test accuracy surpasses all the existing models with similar inference speed on Cityscapes, CamVid and COCO-Stuff datasets. Especially, PIDNet-S achieves 78.6% mIOU with inference speed of 93.2 FPS on Cityscapes test set and 81.6% mIOU with speed of 153.7 FPS on CamVid test set.
双分支网络架构在实时语义分割任务中显示了其效率和有效性。然而,低层细节和高层语义的直接融合会导致细节特征容易被周围的上下文信息淹没的现象,即本文中的overshoot,这限制了现有双分支模型准确率的提高。在本文中,我们在卷积神经网络 (CNN) 和比例积分微分 (PID) 控制器之间建立了联系,并揭示了双分支网络只不过是比例积分 (PI) 控制器,它固有地受到类似的过冲问题。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了一种新颖的三分支网络架构:PIDNet,它拥有三个分支来分别解析细节、上下文和边界信息(语义的导数),并采用边界注意力来指导细节和上下文的融合最后阶段的分支。 PIDNet 系列在推理速度和准确度之间实现了最佳平衡,其测试准确度超过了在 Cityscapes、CamVid 和 COCO-Stuff 数据集上具有相似推理速度的所有现有模型。特别是,PIDNet-S 在 Cityscapes 测试集上以 93.2 FPS 的推理速度实现了 78.6% 的 mIOU,在 CamVid 测试集上以 153.7 FPS 的速度实现了 81.6% 的 mIOU。
论文:SNAKE: Shape-aware Neural 3D Keypoint Field
论文标题:SNAKE: Shape-aware Neural 3D Keypoint Field
论文时间:3 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Keypoint Detection,关键点检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01724
代码实现:https://github.com/zhongcl-thu/snake
论文作者:Chengliang Zhong, Peixing You, Xiaoxue Chen, Hao Zhao, Fuchun Sun, Guyue Zhou, Xiaodong Mu, Chuang Gan, Wenbing Huang
论文简介:Detecting 3D keypoints from point clouds is important for shape reconstruction, while this work investigates the dual question: can shape reconstruction benefit 3D keypoint detection? / 从点云中检测 3D 关键点对于形状重建很重要,而这项工作研究了对偶问题:形状重建是否有利于 3D 关键点检测?
论文摘要:Detecting 3D keypoints from point clouds is important for shape reconstruction, while this work investigates the dual question: can shape reconstruction benefit 3D keypoint detection? Existing methods either seek salient features according to statistics of different orders or learn to predict keypoints that are invariant to transformation. Nevertheless, the idea of incorporating shape reconstruction into 3D keypoint detection is under-explored. We argue that this is restricted by former problem formulations. To this end, a novel unsupervised paradigm named SNAKE is proposed, which is short for shape-aware neural 3D keypoint field. Similar to recent coordinate-based radiance or distance field, our network takes 3D coordinates as inputs and predicts implicit shape indicators and keypoint saliency simultaneously, thus naturally entangling 3D keypoint detection and shape reconstruction. We achieve superior performance on various public benchmarks, including standalone object datasets ModelNet40, KeypointNet, SMPL meshes and scene-level datasets 3DMatch and Redwood. Intrinsic shape awareness brings several advantages as follows. (1) SNAKE generates 3D keypoints consistent with human semantic annotation, even without such supervision. (2) SNAKE outperforms counterparts in terms of repeatability, especially when the input point clouds are down-sampled. (3) the generated keypoints allow accurate geometric registration, notably in a zero-shot setting. Codes are available at https://github.com/zhongcl-thu/SNAKE
从点云中检测 3D 关键点对于形状重建很重要,而这项工作研究了对偶问题:形状重建是否有利于 3D 关键点检测?现有方法要么根据不同阶数的统计寻找显着特征,要么学习预测对变换不变的关键点。然而,将形状重建结合到 3D 关键点检测中的想法尚未得到充分探索。我们认为这受到以前的问题表述的限制。为此,提出了一种名为 SNAKE 的新型无监督范式,它是 shape-aware 神经 3D 关键点场的简称。与最近基于坐标的辐射或距离场类似,我们的网络将 3D 坐标作为输入,同时预测隐式形状指标和关键点显著性,从而自然地纠缠 3D 关键点检测和形状重建。我们在各种公共基准测试中实现了卓越的性能,包括独立对象数据集 ModelNet40、KeypointNet、SMPL 网格和场景级数据集 3DMatch 和 Redwood。内在形状感知带来以下几个优点: (1) SNAKE 生成与人类语义注释一致的 3D 关键点,即使没有这样的监督。 (2) SNAKE 在可重复性方面优于同行,尤其是在对输入点云进行下采样时。 (3) 生成的关键点允许精确的几何配准,尤其是在零样本场景。
论文:What Are Expected Queries in End-to-End Object Detection?
论文标题:What Are Expected Queries in End-to-End Object Detection?
论文时间:2 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Instance Segmentation,Object Detection,Semantic Segmentation,实例分割,目标检测,语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01232
代码实现:https://github.com/jshilong/ddq
论文作者:Shilong Zhang, Xinjiang Wang, Jiaqi Wang, Jiangmiao Pang, Kai Chen
论文简介:As both sparse and dense queries are imperfect, then \emph{what are expected queries in end-to-end object detection}? / 由于稀疏查询和密集查询都不完美,那么端到端目标检测中的预期查询是什么?
论文摘要:End-to-end object detection is rapidly progressed after the emergence of DETR. DETRs use a set of sparse queries that replace the dense candidate boxes in most traditional detectors. In comparison, the sparse queries cannot guarantee a high recall as dense priors. However, making queries dense is not trivial in current frameworks. It not only suffers from heavy computational cost but also difficult optimization. As both sparse and dense queries are imperfect, then \emph{what are expected queries in end-to-end object detection}? This paper shows that the expected queries should be Dense Distinct Queries (DDQ). Concretely, we introduce dense priors back to the framework to generate dense queries. A duplicate query removal pre-process is applied to these queries so that they are distinguishable from each other. The dense distinct queries are then iteratively processed to obtain final sparse outputs. We show that DDQ is stronger, more robust, and converges faster. It obtains 44.5 AP on the MS COCO detection dataset with only 12 epochs. DDQ is also robust as it outperforms previous methods on both object detection and instance segmentation tasks on various datasets. DDQ blends advantages from traditional dense priors and recent end-to-end detectors. We hope it can serve as a new baseline and inspires researchers to revisit the complementary between traditional methods and end-to-end detectors. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/jshilong/DDQ
端到端目标检测在 DETR 出现后迅速发展。 DETR 使用一组稀疏查询来替换大多数传统检测器中的密集候选框。相比之下,稀疏查询不能保证作为密集先验的高召回率。但是,在当前框架中,使查询变得密集并非易事。它不仅计算成本高,而且优化困难。由于稀疏和密集查询都不完美,那么端到端目标检测中的预期查询是什么?本文表明预期的查询应该是密集的不同查询(DDQ)。具体来说,我们将密集先验引入框架以生成密集查询。对这些查询应用重复查询删除预处理,以便它们彼此区分开来。然后迭代处理密集的不同查询以获得最终的稀疏输出。我们展示了 DDQ 更强大、更健壮且收敛更快。它在 MS COCO 检测数据集上仅用 12 个 epoch 就获得了 44.5 AP。 DDQ 也很强大,因为它在各种数据集上的对象检测和实例分割任务上都优于以前的方法。 DDQ 融合了传统密集先验和最近的端到端检测器的优势。我们希望它可以作为一个新的基线,并让研究人员重新审视传统方法和端到端检测器之间的互补性。源代码在 https://github.com/jshilong/DDQ 上公开
论文:YOLO-Pose: Enhancing YOLO for Multi Person Pose Estimation Using Object Keypoint Similarity Loss
论文标题:YOLO-Pose: Enhancing YOLO for Multi Person Pose Estimation Using Object Keypoint Similarity Loss
论文时间:14 Apr 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Multi-Person Pose Estimation,Object Detection,Pose Estimation,多人姿态估计,目标检测,姿态估计
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06806
代码实现:https://github.com/texasinstruments/edgeai-yolov5 , https://github.com/texasinstruments/edgeai-yolox
论文作者:Debapriya Maji, Soyeb Nagori, Manu Mathew, Deepak Poddar
论文简介:All experiments and results reported in this paper are without any test time augmentation, unlike traditional approaches that use flip-test and multi-scale testing to boost performance. / 与使用翻转测试和多尺度测试来提高性能的传统方法不同,本文报告的所有实验和结果都没有任何测试时间增加。
论文摘要:We introduce YOLO-pose, a novel heatmap-free approach for joint detection, and 2D multi-person pose estimation in an image based on the popular YOLO object detection framework. Existing heatmap based two-stage approaches are sub-optimal as they are not end-to-end trainable and training relies on a surrogate L1 loss that is not equivalent to maximizing the evaluation metric, i.e. Object Keypoint Similarity (OKS). Our framework allows us to train the model end-to-end and optimize the OKS metric itself. The proposed model learns to jointly detect bounding boxes for multiple persons and their corresponding 2D poses in a single forward pass and thus bringing in the best of both top-down and bottom-up approaches. Proposed approach doesn’t require the postprocessing of bottom-up approaches to group detected keypoints into a skeleton as each bounding box has an associated pose, resulting in an inherent grouping of the keypoints. Unlike top-down approaches, multiple forward passes are done away with since all persons are localized along with their pose in a single inference. YOLO-pose achieves new state-of-the-art results on COCO validation (90.2% AP50) and test-dev set (90.3% AP50), surpassing all existing bottom-up approaches in a single forward pass without flip test, multi-scale testing, or any other test time augmentation. All experiments and results reported in this paper are without any test time augmentation, unlike traditional approaches that use flip-test and multi-scale testing to boost performance. Our training codes will be made publicly available at https://github.com/TexasInstruments/edgeai-yolov5 and https://github.com/TexasInstruments/edgeai-yolox
我们介绍了 YOLO-pose,一种基于流行的 YOLO的新型无热图方法,用于联合检测以及目标检测框架的图像中的 2D 多人姿势估计。现有的基于热图的两阶段方法是次优的,因为它们不是端到端可训练的,并且训练依赖于和最大化评估指标不等价的surrogate L1 损失,即对象关键点相似度 (OKS)。我们的框架允许我们端到端地训练模型并优化 OKS 指标本身。所提出的模型学习在单次前向传递中联合检测多人的边界框及其相应的 2D 姿势,从而引入自上而下和自下而上的最佳方法。所提出的方法不需要自下而上方法的后处理来将检测到的关键点分组到骨架中,因为每个边界框都有一个相关的姿势,从而导致关键点的固有分组。与自上而下的方法不同,无需多个前向传递,因为所有的人都与他们的姿势一起被定位在一个单一的推理中。 YOLO-pose 在 COCO 验证 (90.2% AP50) 和测试开发集 (90.3% AP50) 上取得了新的最先进的结果,在没有翻转测试的单次前向传递中超越了所有现有的自下而上方法,多尺度测试,或任何其他测试时间增加。与使用翻转测试和多尺度测试来提高性能的传统方法不同,本文报告的所有实验和结果都没有任何测试时间增加。
论文:On Bridging Generic and Personalized Federated Learning for Image Classification
论文标题:On Bridging Generic and Personalized Federated Learning for Image Classification
论文时间:ICLR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Federated Learning,Image Classification,Personalized Federated Learning,联邦学习,图像分类,个性化联邦学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.00778
代码实现:https://github.com/TsingZ0/PFL-Non-IID
论文作者:Hong-You Chen, Wei-Lun Chao
论文简介:On the one hand, we introduce a family of losses that are robust to non-identical class distributions, enabling clients to train a generic predictor with a consistent objective across them. / 一方面,我们引入了一系列对不同类别分布具有鲁棒性的损失,使客户端能够训练具有一致目标的通用预测器。
论文摘要:Federated learning is promising for its capability to collaboratively train models with multiple clients without accessing their data, but vulnerable when clients’ data distributions diverge from each other. This divergence further leads to a dilemma: “Should we prioritize the learned model’s generic performance (for future use at the server) or its personalized performance (for each client)?” These two, seemingly competing goals have divided the community to focus on one or the other, yet in this paper we show that it is possible to approach both at the same time. Concretely, we propose a novel federated learning framework that explicitly decouples a model’s dual duties with two prediction tasks. On the one hand, we introduce a family of losses that are robust to non-identical class distributions, enabling clients to train a generic predictor with a consistent objective across them. On the other hand, we formulate the personalized predictor as a lightweight adaptive module that is learned to minimize each client’s empirical risk on top of the generic predictor. With this two-loss, two-predictor framework which we name Federated Robust Decoupling (Fed-RoD), the learned model can simultaneously achieve state-of-the-art generic and personalized performance, essentially bridging the two tasks.
联邦学习有望在不访问其数据的情况下与多个客户端协作训练模型,但当客户端的数据分布彼此不同时,它很容易受到攻击。这种分歧进一步导致了一个困境:“我们应该优先考虑学习模型的通用性能(以供将来在服务器上使用)还是其个性化性能(针对每个客户端)?”这两个看似相互竞争的目标已将社区划分为专注于其中一个,但在本文中,我们表明可以同时实现这两个目标。具体来说,我们提出了一种新颖的联邦学习框架,它明确地将模型的双重职责与两个预测任务解耦。一方面,我们引入了一系列对不同类别分布具有鲁棒性的损失,使客户端能够训练具有一致目标的通用预测器。另一方面,我们将个性化预测器制定为一个轻量级的自适应模块,该模块被学习以最小化每个客户在通用预测器之上的经验风险。有了这个我们称之为联合鲁棒解耦 (Fed-RoD) 的双损失、双预测框架,学习模型可以同时实现最先进的通用和个性化性能,本质上是桥接这两个任务。
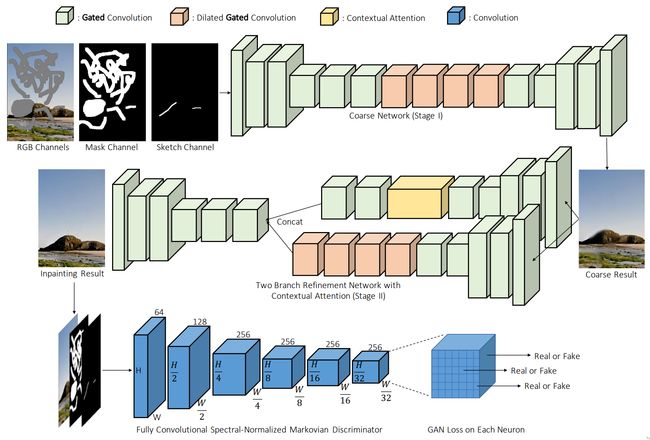
论文:Free-Form Image Inpainting with Gated Convolution
论文标题:Free-Form Image Inpainting with Gated Convolution
论文时间:ICCV 2019
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:feature selection,Image Inpainting,特征选择,图像修复
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.03589
代码实现:https://github.com/JiahuiYu/generative_inpainting , https://github.com/avalonstrel/GatedConvolution_pytorch , https://github.com/avalonstrel/GatedConvolution , https://github.com/csqiangwen/DeepFillv2_Pytorch , https://github.com/zuruoke/watermark-removal
论文作者:Jiahui Yu, Zhe Lin, Jimei Yang, Xiaohui Shen, Xin Lu, Thomas Huang
论文简介:We present a generative image inpainting system to complete images with free-form mask and guidance. / 我们提出了一种生成式图像修复系统,以使用自由形式的掩码和引导来完成图像。
论文摘要:We present a generative image inpainting system to complete images with free-form mask and guidance. The system is based on gated convolutions learned from millions of images without additional labelling efforts. The proposed gated convolution solves the issue of vanilla convolution that treats all input pixels as valid ones, generalizes partial convolution by providing a learnable dynamic feature selection mechanism for each channel at each spatial location across all layers. Moreover, as free-form masks may appear anywhere in images with any shape, global and local GANs designed for a single rectangular mask are not applicable. Thus, we also present a patch-based GAN loss, named SN-PatchGAN, by applying spectral-normalized discriminator on dense image patches. SN-PatchGAN is simple in formulation, fast and stable in training. Results on automatic image inpainting and user-guided extension demonstrate that our system generates higher-quality and more flexible results than previous methods. Our system helps users quickly remove distracting objects, modify image layouts, clear watermarks and edit faces. Code, demo and models are available at https://github.com/JiahuiYu/generative_inpainting
我们提出了一种生成式图像修复系统,以使用自由形式的掩码和引导来完成图像。该系统基于从数百万张图像中学习的门控卷积,无需额外的标记工作。所提出的门控卷积解决了将所有输入像素视为有效像素的普通卷积问题,通过为跨所有层的每个空间位置的每个通道提供可学习的动态特征选择机制来推广部分卷积。此外,由于自由形式的掩模可能出现在任何形状的图像中,为单个矩形掩模设计的全局和局部 GAN 不适用。因此,我们还提出了一种基于补丁的 GAN 损失,称为 SN-PatchGAN,通过在密集图像补丁上应用频谱归一化鉴别器。 SN-PatchGAN 公式简单,训练速度快且稳定。自动图像修复和用户引导扩展的结果表明,我们的系统比以前的方法产生更高质量和更灵活的结果。我们的系统可帮助用户快速移除分散注意力的对象、修改图像布局、清除水印和编辑面部。
论文:The GatedTabTransformer. An enhanced deep learning architecture for tabular modeling
论文标题:The GatedTabTransformer. An enhanced deep learning architecture for tabular modeling
论文时间:1 Jan 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.00199
代码实现:https://github.com/radi-cho/gatedtabtransformer
论文作者:Radostin Cholakov, Todor Kolev
论文简介:There is an increasing interest in the application of deep learning architectures to tabular data. / 人们越来越关注将深度学习架构应用于结构化(表格)数据。
论文摘要:There is an increasing interest in the application of deep learning architectures to tabular data. One of the state-of-the-art solutions is TabTransformer which incorporates an attention mechanism to better track relationships between categorical features and then makes use of a standard MLP to output its final logits. In this paper we propose multiple modifications to the original TabTransformer performing better on binary classification tasks for three separate datasets with more than 1% AUROC gains. Inspired by gated MLP, linear projections are implemented in the MLP block and multiple activation functions are tested. We also evaluate the importance of specific hyperparameters during training.
人们越来越关注将深度学习架构应用于结构化(表格)数据。 最先进的解决方案之一是 TabTransformer,它结合了注意力机制来更好地跟踪分类特征之间的关系,然后利用标准 MLP 输出其最终 logits。 在本文中,我们建议对原始 TabTransformer 进行多项修改,使其在三个独立数据集的二元分类任务上表现更好,AUROC 增益超过 1%。 受门控 MLP 的启发,在 MLP 模块中实现了线性投影,并测试了多个激活函数。 我们还评估了训练期间特定超参数的重要性。
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处 - 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~