人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.17
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架
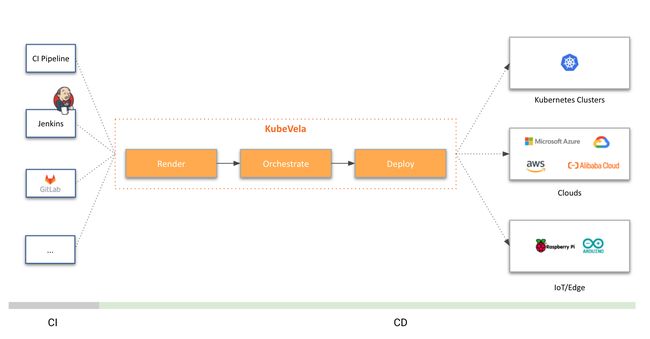
工具平台:KubeVela - 现代应用代码编译部署平台
tags: [部署,应用,平台]
‘KubeVela - The Modern Application Platform.’
GitHub: https://github.com/kubevela/kubevela
工具库:SsciBERT - 社会科学文本的预训练语言模型
tags: [社会科学,文本,预训练模型]
‘SsciBERT: A pretrained language model for social scientific text’ by S-T-Full-Text-Knowledge-Mining
GitHub: https://github.com/S-T-Full-Text-Knowledge-Mining/SSCI-BERT
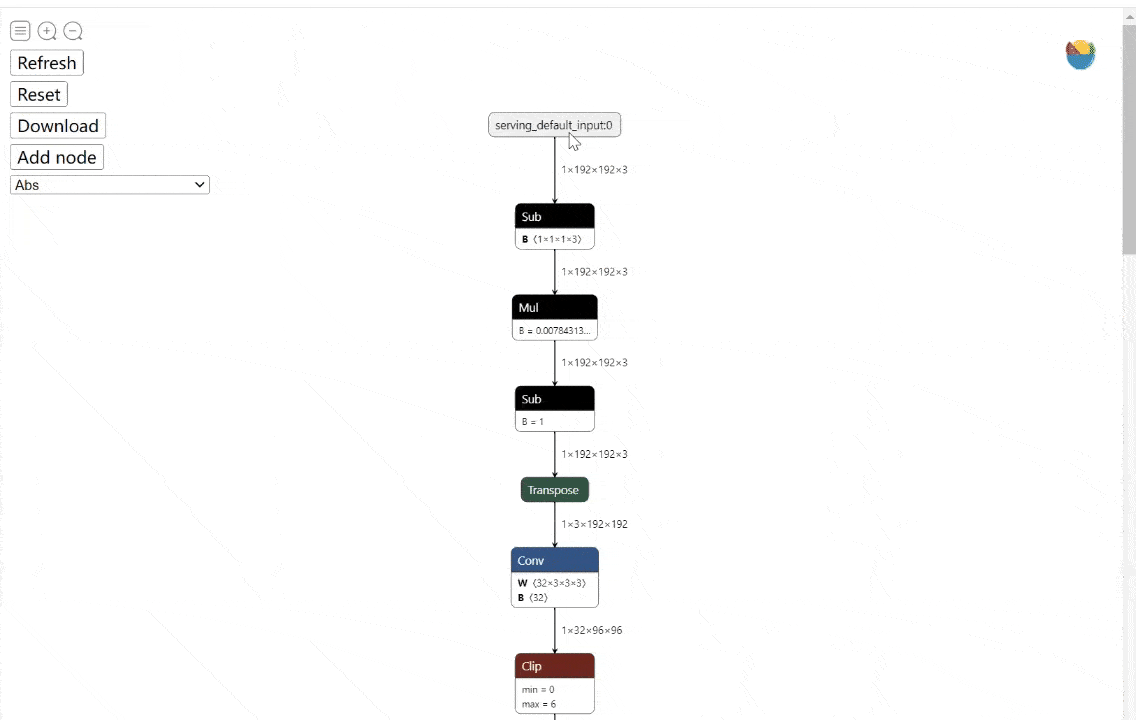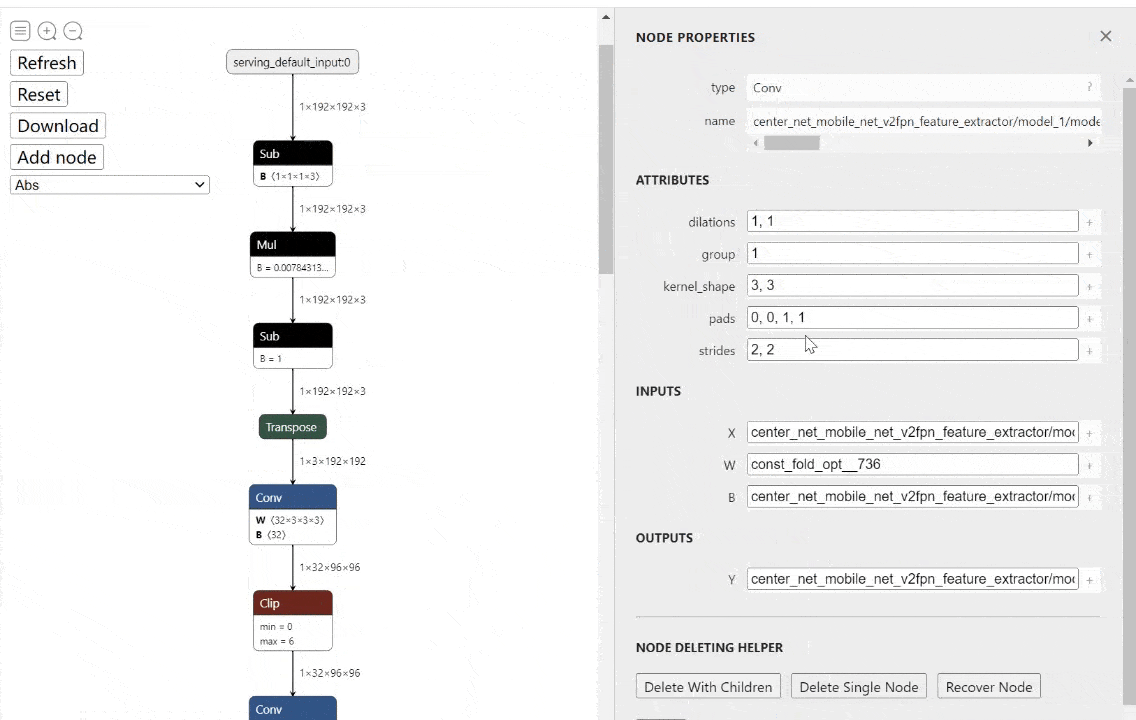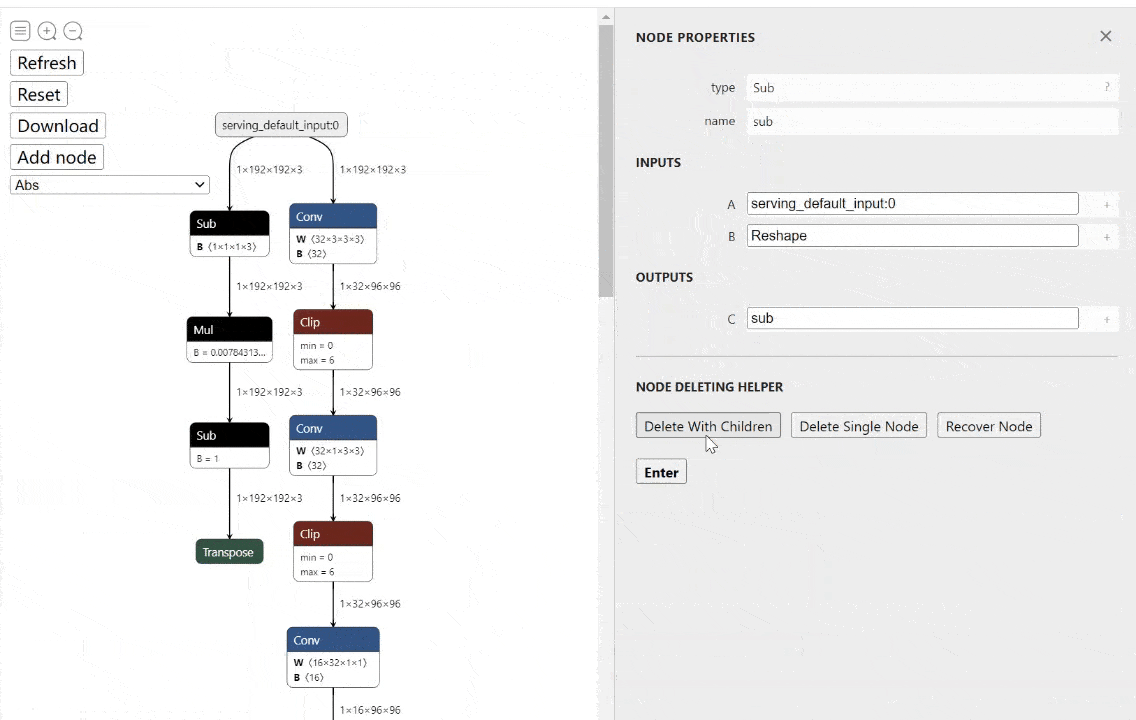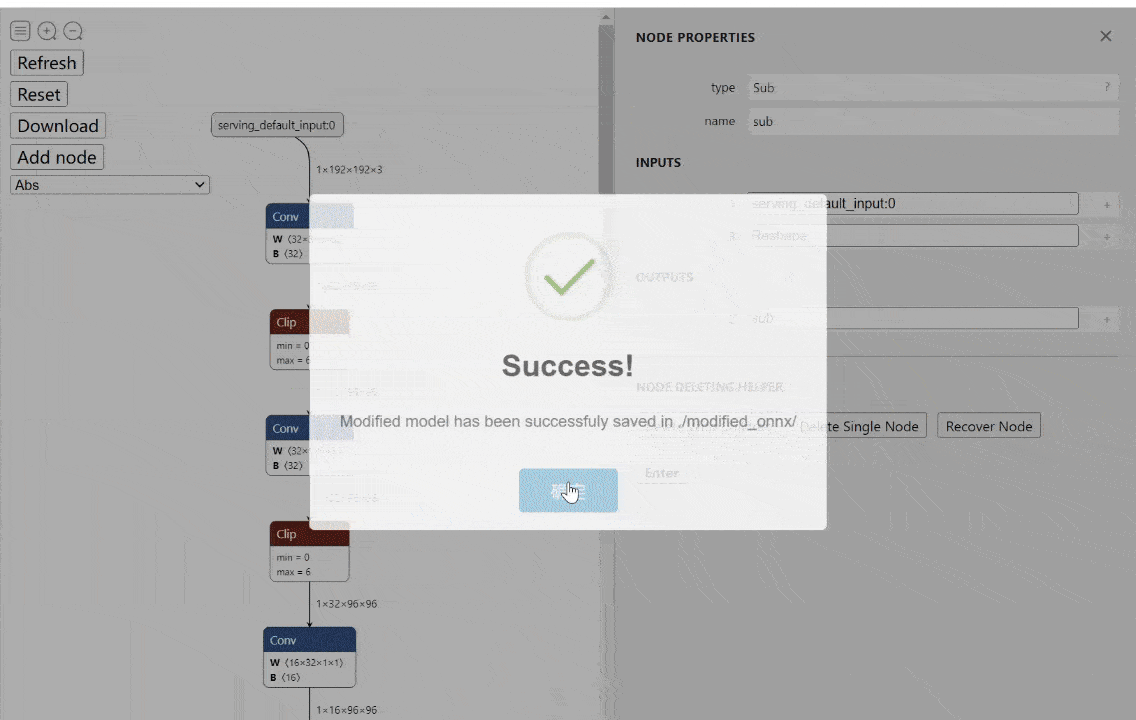
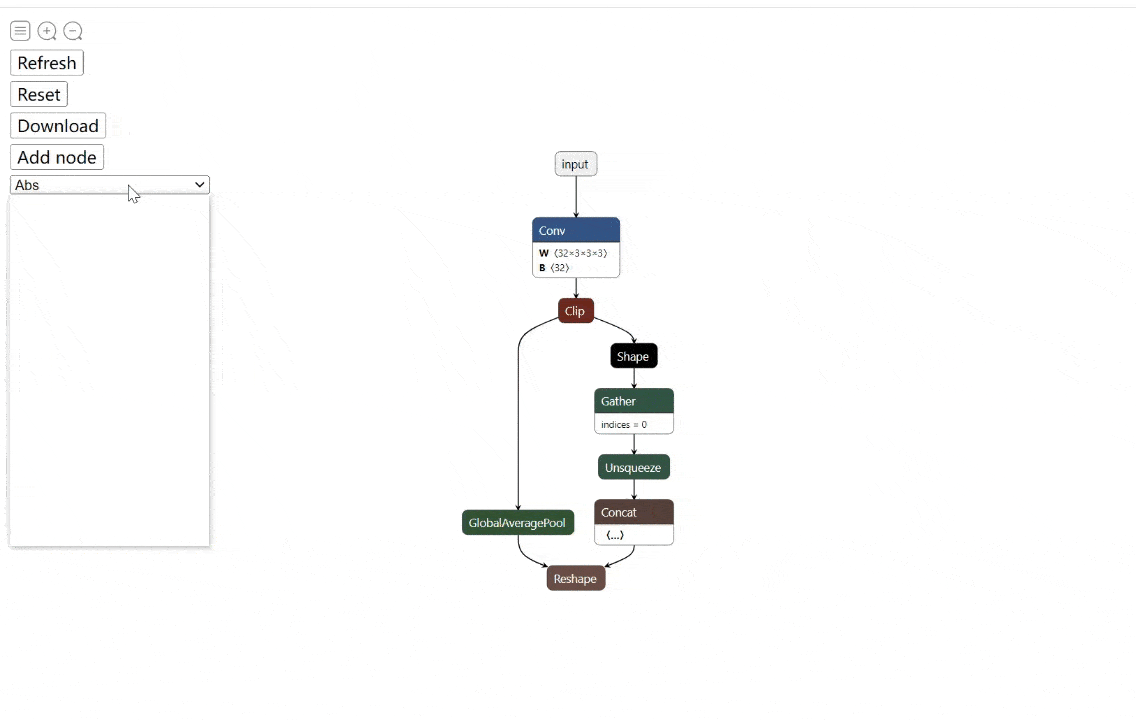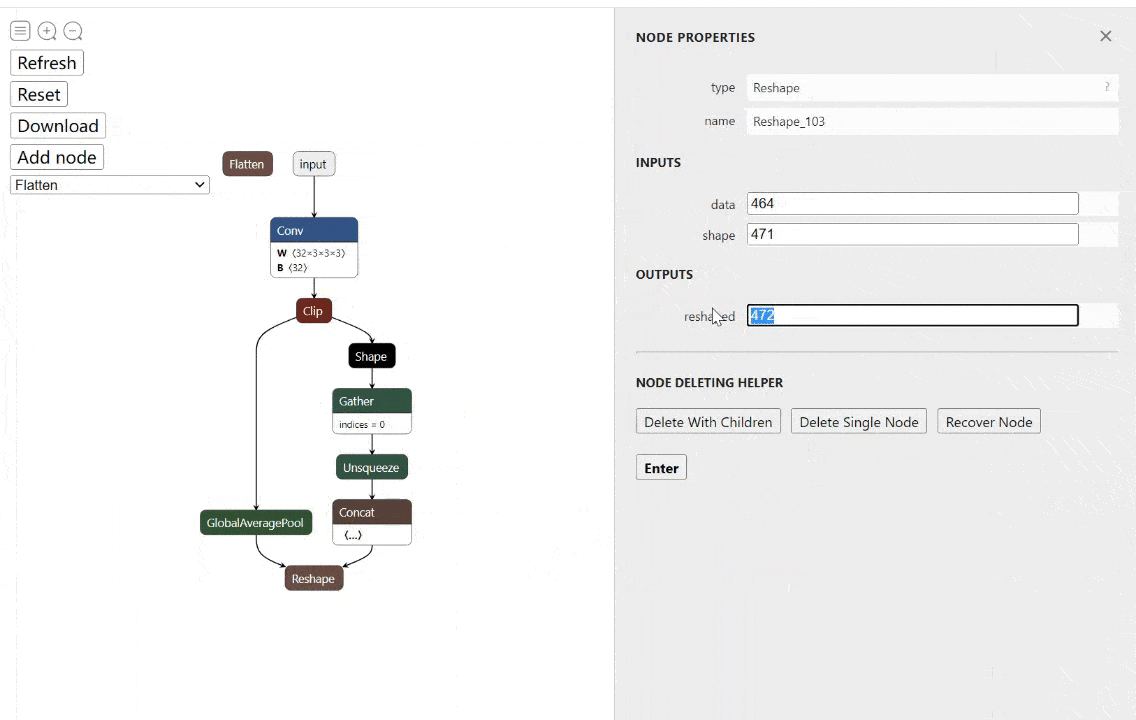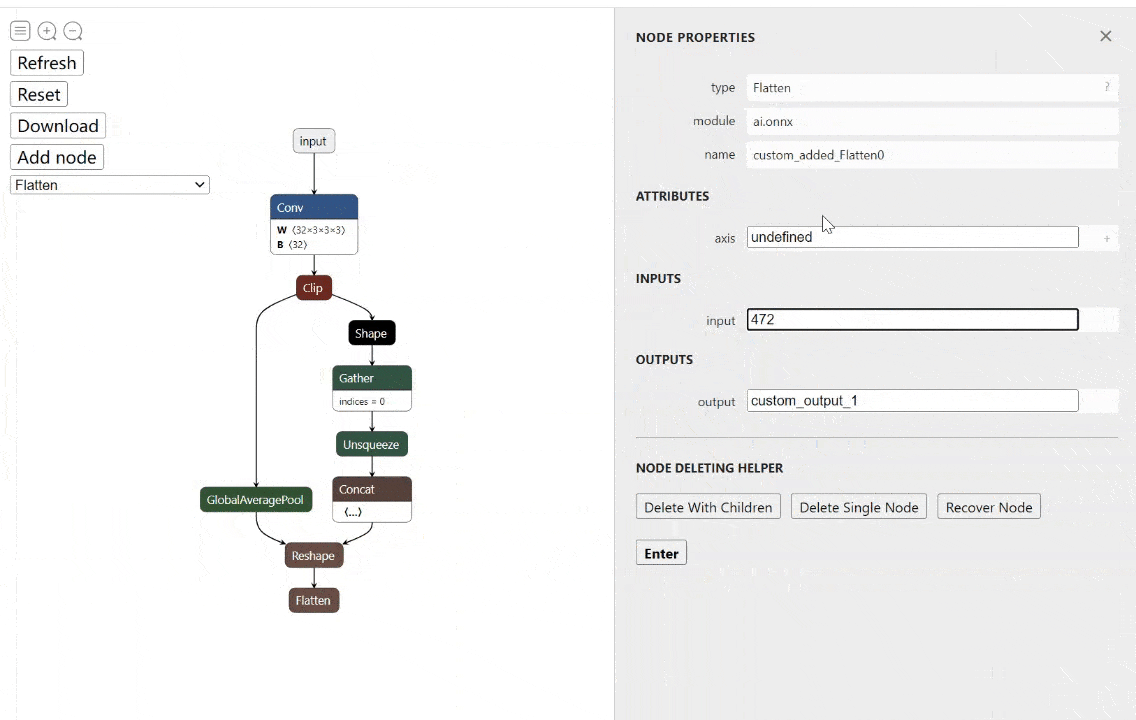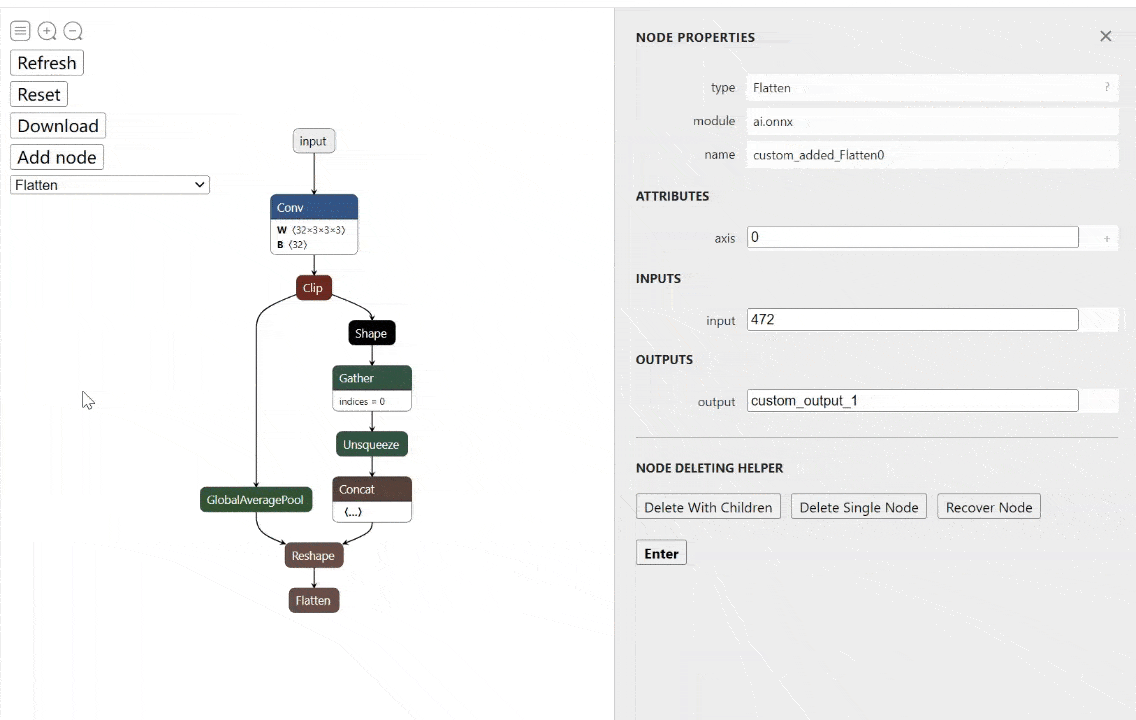
工具:onnx-modifier - ONNX模型实时可视化编辑工具
tags: [ONNX,可视化,模型编辑]
‘onnx-modifier - A tool to modify onnx models in a visualization fashion, based on Netron and flask.’ by Zhang Ge
GitHub: https://github.com/ZhangGe6/onnx-modifier
MulimgViewer:多图像浏览器,在一个界面显示多个图像,方便图像的比较、筛选
tags: [图像浏览器,多图像,图像比较,图像筛选]
‘MulimgViewer - a multi-image viewer that can open multiple images in one interface, which is convenient for image comparison and image stitching.’ by Jiawei Liu
GitHub: https://github.com/nachifur/MulimgViewer
工具库:SwissArmyTransformer - 可用来开发Transformer新变体的开发库
tags: [Transformer,变体,开发]
‘SwissArmyTransformer - a flexible and powerful library to develop your own Transformer variants.’ by THUDM
GitHub: https://github.com/THUDM/SwissArmyTransformer
工具:opera - 目标感知与应用统一工具箱,支持检测、分割、姿态估计等
tags: [目标检测,图像分割,姿态估计,工具箱]
‘opera - A Unified Toolbox for Object Perception & Application’ by Hikvision Research Institute
GitHub: https://github.com/hikvision-research/opera
3.博文&分享
资源分享:Python3面试准备参考
‘Python3 interview prep cheatsheet and examples’ by peterlamar
GitHub: https://github.com/peterlamar/python-cp-cheatsheet
博文:广义视觉语言模型
《Generalized Visual Language Models》by Lilian Weng
Link: https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2022-06-09-vlm/
4.数据&资源
资源列表:高效论文写作相关参考资料集
‘awesome-scholarly-productivity’ by OpenMindClub
GitHub: https://github.com/OpenMindClub/awesome-scholarly-productivity/blob/main/README.zh-cn.md
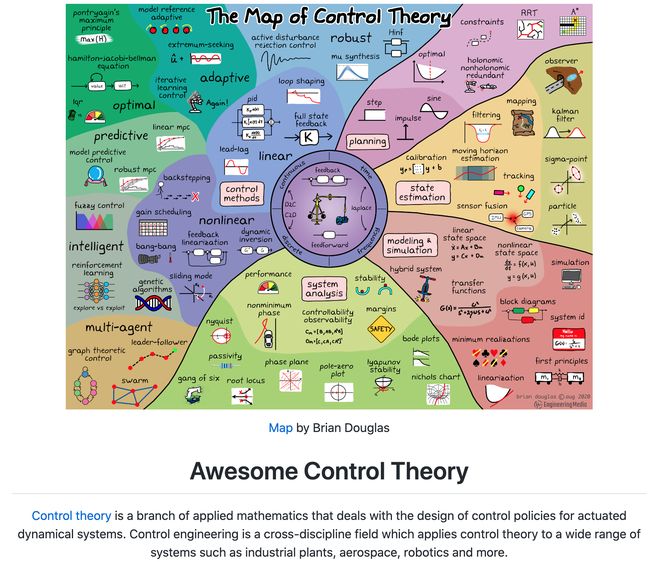
资源列表:控制论相关资源列表
‘Awesome Control Theory - Awesome resources for learning control theory’ by A-make
GitHub: https://github.com/A-make/awesome-control-theory
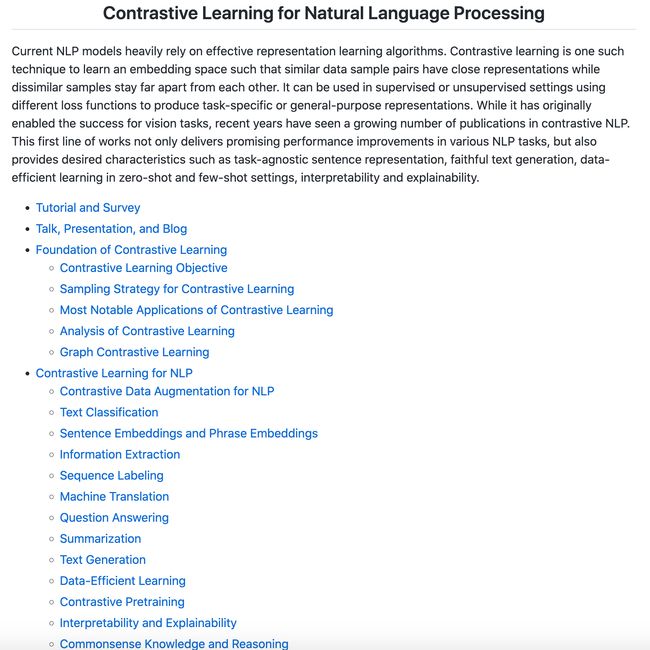
资源大全:对比学习自然语言处理相关资源大列表
‘Contrastive-Learning-NLP-Papers - Paper List for Contrastive Learning for Natural Language Processing’ by Rui Zhang
GitHub: https://github.com/ryanzhumich/Contrastive-Learning-NLP-Papers
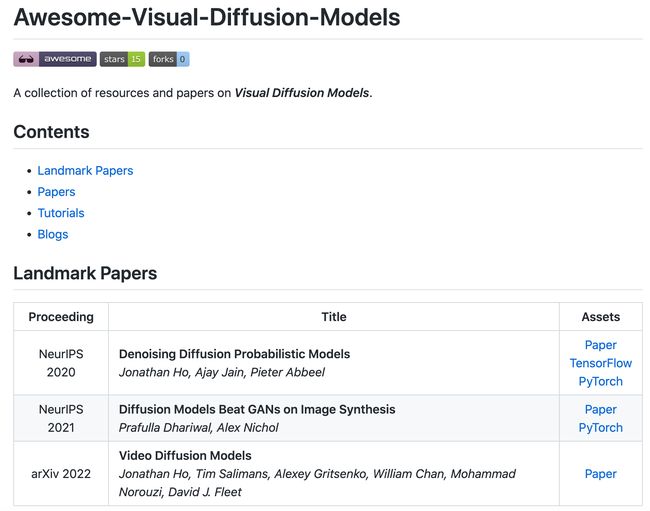
资源大全:视觉扩散模型相关资源大列表
‘Awesome-Visual-Diffusion-Models - A collection of resources and papers on Visual Diffusion Models.’ by Xiefan Guo
GitHub: https://github.com/Xiefan-Guo/Awesome-Visual-Diffusion-Models
5.研究&论文
可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
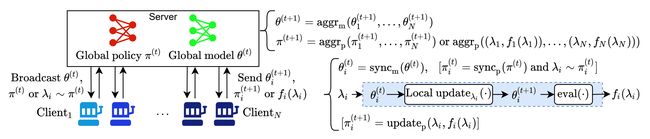
论文:FedHPO-B: A Benchmark Suite for Federated Hyperparameter Optimization
论文标题:FedHPO-B: A Benchmark Suite for Federated Hyperparameter Optimization
论文时间:8 Jun 2022
所属领域:联邦学习
对应任务:Federated Learning,Hyperparameter Optimization,联邦学习,超参数优化
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.03966
代码实现:https://github.com/alibaba/federatedscope
论文作者:Zhen Wang, Weirui Kuang, Ce Zhang, Bolin Ding, Yaliang Li
论文简介:Due to this uniqueness, existing HPO benchmarks no longer satisfy the need to compare HPO methods in the FL setting. / 由于这种独特性,现有的 HPO 基准不再满足在 FL 设置中比较 HPO 方法的需要。
论文摘要:Hyperparameter optimization (HPO) is crucial for machine learning algorithms to achieve satisfactory performance, whose progress has been boosted by related benchmarks. Nonetheless, existing efforts in benchmarking all focus on HPO for traditional centralized learning while ignoring federated learning (FL), a promising paradigm for collaboratively learning models from dispersed data. In this paper, we first identify some uniqueness of HPO for FL algorithms from various aspects. Due to this uniqueness, existing HPO benchmarks no longer satisfy the need to compare HPO methods in the FL setting. To facilitate the research of HPO in the FL setting, we propose and implement a benchmark suite FedHPO-B that incorporates comprehensive FL tasks, enables efficient function evaluations, and eases continuing extensions. We also conduct extensive experiments based on FedHPO-B to benchmark a few HPO methods. We open-source FedHPO-B at https://github.com/alibaba/FederatedScope/tree/master/benchmark/FedHPOB
超参数优化(HPO)对于机器学习算法获得令人满意的性能至关重要,相关基准测试推动了其进展。尽管如此,现有的基准测试工作都集中在传统集中式学习的 HPO 上,而忽略了联邦学习 (FL),这是一种从分散数据中协作学习模型的有前途的范式。在本文中,我们首先从各个方面确定了 FL 算法的 HPO 的一些独特性。由于这种独特性,现有的 HPO 基准不再满足在 FL 设置中比较 HPO 方法的需要。为了促进 FL 环境中 HPO 的研究,我们提出并实施了一个基准套件 FedHPO-B,该套件包含了全面的 FL 任务,实现了高效的功能评估,并简化了持续扩展。我们还基于 FedHPO-B 进行了广泛的实验,以对一些 HPO 方法进行基准测试。我们在 https://github.com/alibaba/FederatedScope/tree/master/benchmark/FedHPOB 开源 FedHPO-B。
![]()
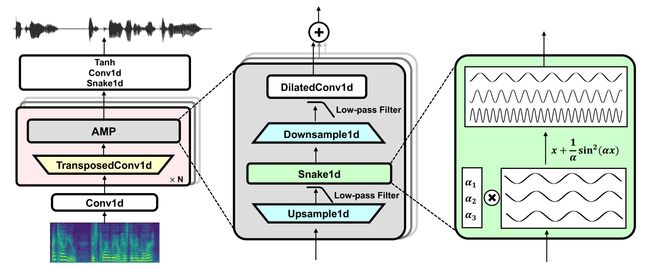
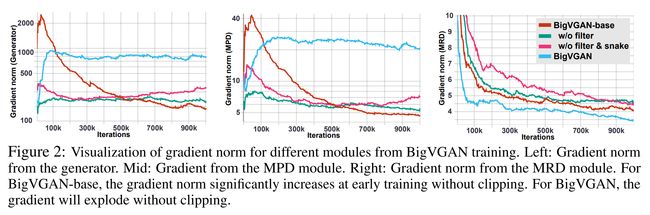
论文:BigVGAN: A Universal Neural Vocoder with Large-Scale Training
论文标题:BigVGAN: A Universal Neural Vocoder with Large-Scale Training
论文时间:9 Jun 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04658
代码实现:https://github.com/nvidia/bigvgan
论文作者:Sang-gil Lee, Wei Ping, Boris Ginsburg, Bryan Catanzaro, Sungroh Yoon
论文简介:Despite recent progress in generative adversarial network(GAN)-based vocoders, where the model generates raw waveform conditioned on mel spectrogram, it is still challenging to synthesize high-fidelity audio for numerous speakers across varied recording environments. / 尽管最近在基于生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的声码器方面取得了进展,其中模型生成以梅尔频谱图为条件的原始波形,但在不同的录音环境中为众多扬声器合成高保真音频仍然具有挑战性。
论文摘要:Despite recent progress in generative adversarial network(GAN)-based vocoders, where the model generates raw waveform conditioned on mel spectrogram, it is still challenging to synthesize high-fidelity audio for numerous speakers across varied recording environments. In this work, we present BigVGAN, a universal vocoder that generalizes well under various unseen conditions in zero-shot setting. We introduce periodic nonlinearities and anti-aliased representation into the generator, which brings the desired inductive bias for waveform synthesis and significantly improves audio quality. Based on our improved generator and the state-of-the-art discriminators, we train our GAN vocoder at the largest scale up to 112M parameters, which is unprecedented in the literature. In particular, we identify and address the training instabilities specific to such scale, while maintaining high-fidelity output without over-regularization. Our BigVGAN achieves the state-of-the-art zero-shot performance for various out-of-distribution scenarios, including new speakers, novel languages, singing voices, music and instrumental audio in unseen (even noisy) recording environments. We will release our code and model at https://github.com/NVIDIA/BigVGAN
尽管最近在基于生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的声码器方面取得了进展,其中模型生成以 mel 频谱图为条件的原始波形,但在不同的录音环境中为众多扬声器合成高保真音频仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了 BigVGAN,这是一种通用声码器,可以在零样本设置中的各种看不见的条件下很好地泛化。我们在发生器中引入了周期性非线性和抗锯齿表示,这为波形合成带来了所需的感应偏置,并显着提高了音频质量。基于我们改进的生成器和最先进的判别器,我们以高达 112M 参数的最大规模训练我们的 GAN 声码器,这在文献中是前所未有的。特别是,我们识别并解决了特定于这种规模的训练不稳定性,同时保持高保真输出而不会过度正则化。我们的 BigVGAN 为各种分布式场景(包括新扬声器、新语言、歌声、音乐和看不见(甚至嘈杂)录音环境中的乐器音频)实现了最先进的零样本模型性能。我们将在以下位置发布我们的代码和模型:https://github.com/NVIDIA/BigVGAN
论文:Meta Optimal Transport
论文标题:Meta Optimal Transport
论文时间:10 Jun 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.05262
代码实现:https://github.com/facebookresearch/meta-ot
论文作者:Brandon Amos, samuel cohen, Giulia Luise, Ievgen Redko
论文简介:We study the use of amortized optimization to predict optimal transport (OT) maps from the input measures, which we call Meta OT. / 我们研究使用摊销优化去预测输入的最优传输 (OT) 图,我们称之为 Meta OT。
论文摘要:We study the use of amortized optimization to predict optimal transport (OT) maps from the input measures, which we call Meta OT. This helps repeatedly solve similar OT problems between different measures by leveraging the knowledge and information present from past problems to rapidly predict and solve new problems. Otherwise, standard methods ignore the knowledge of the past solutions and suboptimally re-solve each problem from scratch. Meta OT models surpass the standard convergence rates of log-Sinkhorn solvers in the discrete setting and convex potentials in the continuous setting. We improve the computational time of standard OT solvers by multiple orders of magnitude in discrete and continuous transport settings between images, spherical data, and color palettes. Our source code is available at http://github.com/facebookresearch/meta-ot
我们研究使用摊销优化预测输入度量的最优传输 (OT) 图,我们称之为 Meta OT。这有助于通过利用过去问题中的知识和信息来快速预测和解决新问题,从而重复解决不同措施之间的类似 OT 问题。否则,标准方法会忽略过去解决方案的知识,并以次优方式从头开始解决每个问题。 Meta OT 模型在离散设置中超过了 log-Sinkhorn 求解器的标准收敛速度,在连续设置中超过了凸势。在图像、球形数据和调色板之间的离散和连续传输设置中,我们将标准 OT 求解器的计算时间提高了多个数量级。我们的源代码位于 http://github.com/facebookresearch/meta-ot
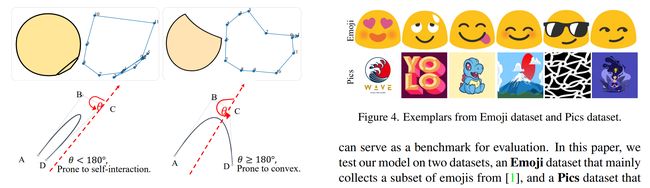
论文:Towards Layer-wise Image Vectorization
论文标题:Towards Layer-wise Image Vectorization
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:图像矢量化
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04655
代码实现:https://github.com/picsart-ai-research/live-layerwise-image-vectorization
论文作者:Xu Ma, Yuqian Zhou, Xingqian Xu, Bin Sun, Valerii Filev, Nikita Orlov, Yun Fu, Humphrey Shi
论文简介:Image rasterization is a mature technique in computer graphics, while image vectorization, the reverse path of rasterization, remains a major challenge. / 图像光栅化是计算机图形学中的一项成熟技术,而图像矢量化(光栅化的逆向路径)仍然是一项重大挑战。
论文摘要:Image rasterization is a mature technique in computer graphics, while image vectorization, the reverse path of rasterization, remains a major challenge. Recent advanced deep learning-based models achieve vectorization and semantic interpolation of vector graphs and demonstrate a better topology of generating new figures. However, deep models cannot be easily generalized to out-of-domain testing data. The generated SVGs also contain complex and redundant shapes that are not quite convenient for further editing. Specifically, the crucial layer-wise topology and fundamental semantics in images are still not well understood and thus not fully explored. In this work, we propose Layer-wise Image Vectorization, namely LIVE, to convert raster images to SVGs and simultaneously maintain its image topology. LIVE can generate compact SVG forms with layer-wise structures that are semantically consistent with human perspective. We progressively add new bezier paths and optimize these paths with the layer-wise framework, newly designed loss functions, and component-wise path initialization technique. Our experiments demonstrate that LIVE presents more plausible vectorized forms than prior works and can be generalized to new images. With the help of this newly learned topology, LIVE initiates human editable SVGs for both designers and other downstream applications. Codes are made available at https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/LIVE-Layerwise-Image-Vectorization
图像光栅化是计算机图形学中一项成熟的技术,而图像矢量化(光栅化的逆向路径)仍然是一项重大挑战。最近先进的基于深度学习的模型实现了矢量图的矢量化和语义插值,并展示了生成新图形的更好拓扑结构。然而,深度模型不能轻易地推广到域外测试数据。生成的 SVG 还包含复杂和冗余的形状,不太方便进一步编辑。具体来说,图像中关键的分层拓扑和基本语义仍然没有得到很好的理解,因此没有得到充分的探索。在这项工作中,我们提出了逐层图像矢量化,即 LIVE,将光栅图像转换为 SVG,同时保持其图像拓扑。 LIVE 可以生成紧凑的 SVG 表单,其分层结构在语义上与人类视角一致。我们逐步添加新的贝塞尔路径,并使用逐层框架、新设计的损失函数和逐组件路径初始化技术优化这些路径。我们的实验表明,LIVE 呈现出比以前的作品更合理的矢量化形式,并且可以推广到新图像。在这种新学习的拓扑的帮助下,LIVE 为设计师和其他下游应用程序启动了人工可编辑的 SVG。代码可在 https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/LIVE-Layerwise-Image-Vectorization
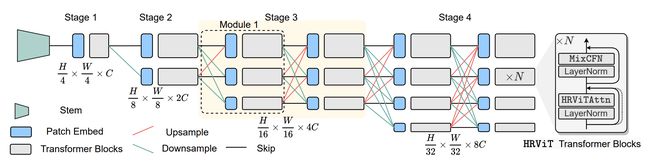
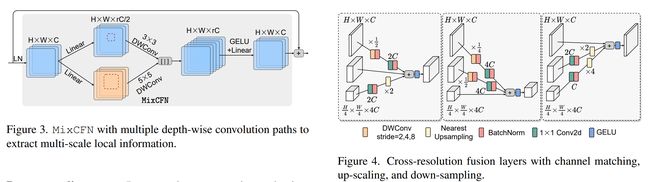
论文:Multi-Scale High-Resolution Vision Transformer for Semantic Segmentation
论文标题:Multi-Scale High-Resolution Vision Transformer for Semantic Segmentation
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Classification,Representation Learning,Semantic Segmentation,图像分类,表示学习,语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.01236
代码实现:https://github.com/facebookresearch/HRViT
论文作者:Jiaqi Gu, Hyoukjun Kwon, Dilin Wang, Wei Ye, Meng Li, Yu-Hsin Chen, Liangzhen Lai, Vikas Chandra, David Z. Pan
论文简介:Therefore, we propose HRViT, which enhances ViTs to learn semantically-rich and spatially-precise multi-scale representations by integrating high-resolution multi-branch architectures with ViTs. / 因此,我们提出 HRViT,它通过将高分辨率多分支架构与 ViT 集成,增强 ViT 以学习语义丰富和空间精确的多尺度表示。
论文摘要:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have emerged with superior performance on computer vision tasks compared to convolutional neural network (CNN)-based models. However, ViTs are mainly designed for image classification that generate single-scale low-resolution representations, which makes dense prediction tasks such as semantic segmentation challenging for ViTs. Therefore, we propose HRViT, which enhances ViTs to learn semantically-rich and spatially-precise multi-scale representations by integrating high-resolution multi-branch architectures with ViTs. We balance the model performance and efficiency of HRViT by various branch-block co-optimization techniques. Specifically, we explore heterogeneous branch designs, reduce the redundancy in linear layers, and augment the attention block with enhanced expressiveness. Those approaches enabled HRViT to push the Pareto frontier of performance and efficiency on semantic segmentation to a new level, as our evaluation results on ADE20K and Cityscapes show. HRViT achieves 50.20% mIoU on ADE20K and 83.16% mIoU on Cityscapes, surpassing state-of-the-art MiT and CSWin backbones with an average of +1.78 mIoU improvement, 28% parameter saving, and 21% FLOPs reduction, demonstrating the potential of HRViT as a strong vision backbone for semantic segmentation.
与基于卷积神经网络 (CNN) 的模型相比,视觉Transformers (ViTs) 在计算机视觉任务上的表现更为出色。然而,ViTs 主要设计用于生成单尺度低分辨率表示的图像分类,这使得 ViTs 的语义分割等密集预测任务具有挑战性。因此,我们提出 HRViT,它通过将高分辨率多分支架构与 ViT 集成来增强 ViT 以学习语义丰富和空间精确的多尺度表示。我们通过各种分支块协同优化技术来平衡 HRViT 的模型性能和效率。具体来说,我们探索异构分支设计,减少线性层中的冗余,并通过增强的表现力来增加注意力块。正如我们对 ADE20K 和 Cityscapes 的评估结果所示,这些方法使 HRViT 将语义分割的性能和效率的帕累托前沿推向了一个新的水平。 HRViT 在 ADE20K 上实现了 50.20% mIoU,在 Cityscapes 上实现了 83.16% mIoU,超过了最先进的 MiT 和 CSWin 主干,平均提升了 +1.78 mIoU,节省了 28% 的参数,减少了 21% 的 FLOPs,证明了HRViT 作为语义分割的强大视觉骨干。
论文:A Normalized Gaussian Wasserstein Distance for Tiny Object Detection
论文标题:A Normalized Gaussian Wasserstein Distance for Tiny Object Detection
论文时间:26 Oct 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Object Detection,Small Object Detection,物体检测,小物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13389
代码实现:https://github.com/jwwangchn/NWD , https://github.com/bhyun-kim/NWD
论文作者:Jinwang Wang, Chang Xu, Wen Yang, Lei Yu
论文简介:To alleviate this, we propose a new evaluation metric using Wasserstein distance for tiny object detection. / 为了缓解这种情况,我们提出了一种新的评估指标,使用 Wasserstein 距离进行微小物体检测。
论文摘要:Detecting tiny objects is a very challenging problem since a tiny object only contains a few pixels in size. We demonstrate that state-of-the-art detectors do not produce satisfactory results on tiny objects due to the lack of appearance information. Our key observation is that Intersection over Union (IoU) based metrics such as IoU itself and its extensions are very sensitive to the location deviation of the tiny objects, and drastically deteriorate the detection performance when used in anchor-based detectors. To alleviate this, we propose a new evaluation metric using Wasserstein distance for tiny object detection. Specifically, we first model the bounding boxes as 2D Gaussian distributions and then propose a new metric dubbed Normalized Wasserstein Distance (NWD) to compute the similarity between them by their corresponding Gaussian distributions. The proposed NWD metric can be easily embedded into the assignment, non-maximum suppression, and loss function of any anchor-based detector to replace the commonly used IoU metric. We evaluate our metric on a new dataset for tiny object detection (AI-TOD) in which the average object size is much smaller than existing object detection datasets. Extensive experiments show that, when equipped with NWD metric, our approach yields performance that is 6.7 AP points higher than a standard fine-tuning baseline, and 6.0 AP points higher than state-of-the-art competitors.
检测微小物体是一个非常具有挑战性的问题,因为一个微小的物体只包含几个像素大小。我们证明,由于缺乏外观信息,最先进的检测器在微小物体上无法产生令人满意的结果。我们的主要观察结果是,基于交并比 (IoU) 的度量(例如 IoU 本身及其扩展)对微小物体的位置偏差非常敏感,并且在用于基于锚的检测器时会大大降低检测性能。为了缓解这种情况,我们提出了一种新的评估指标,使用 Wasserstein 距离进行微小物体检测。具体来说,我们首先将边界框建模为 2D 高斯分布,然后提出一种称为归一化 Wasserstein 距离 (NWD) 的新度量,通过它们对应的高斯分布计算它们之间的相似性。所提出的 NWD 度量可以很容易地嵌入到任何基于锚的检测器的分配、非最大抑制和损失函数中,以取代常用的 IoU 度量。我们在用于微小对象检测 (AI-TOD) 的新数据集上评估我们的指标,其中平均对象大小远小于现有对象检测数据集。大量实验表明,当配备 NWD 指标时,我们的方法产生的性能比标准微调基线高 6.7 AP 点,比最先进的其他方法高 6.0 AP 点。
论文:Xplique: A Deep Learning Explainability Toolbox
论文标题:Xplique: A Deep Learning Explainability Toolbox
论文时间:9 Jun 2022
所属领域:模型可解释
对应任务:深度学习模型可解释,模型理解
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04394
代码实现:https://github.com/deel-ai/xplique
论文作者:Thomas Fel, Lucas Hervier, David Vigouroux, Antonin Poche, Justin Plakoo, Remi Cadene, Mathieu Chalvidal, Julien Colin, Thibaut Boissin, Louis Bethune, Agustin Picard, Claire Nicodeme, Laurent Gardes, Gregory Flandin, Thomas Serre
论文简介:Today’s most advanced machine-learning models are hardly scrutable. / 当今最先进的机器学习模型几乎难以理解。
论文摘要:Today’s most advanced machine-learning models are hardly scrutable. The key challenge for explainability methods is to help assisting researchers in opening up these black boxes, by revealing the strategy that led to a given decision, by characterizing their internal states or by studying the underlying data representation. To address this challenge, we have developed Xplique: a software library for explainability which includes representative explainability methods as well as associated evaluation metrics. It interfaces with one of the most popular learning libraries: Tensorflow as well as other libraries including PyTorch, scikit-learn and Theano. The code is licensed under the MIT license and is freely available at https://github.com/deel-ai/xplique
当今最先进的机器学习模型几乎不可考查。 可解释性方法的关键挑战是帮助研究人员打开这些黑匣子,通过揭示导致给定决策的策略、描述其内部状态或研究底层数据表示。 为了应对这一挑战,我们开发了 Xplique:一个用于可解释性的软件库,其中包括代表性的可解释性方法以及相关的评估指标。 它与最流行的学习库之一连接:Tensorflow 以及其他库,包括 PyTorch、scikit-learn 和 Theano。 该代码在 MIT 许可下获得许可,可在 https://github.com/deel-ai/xplique 上免费获得
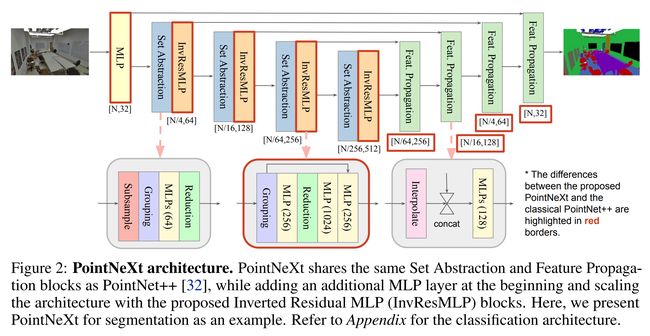
论文:PointNeXt: Revisiting PointNet++ with Improved Training and Scaling Strategies
论文标题:PointNeXt: Revisiting PointNet++ with Improved Training and Scaling Strategies
论文时间:9 Jun 2022
所属领域:点云
对应任务:3D Classification,3D Part Segmentation,3D Point Cloud Classification,Data Augmentation,Semantic Segmentation,3D分类,3D零件分割,3D点云分类,数据增强,语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04670
代码实现:https://github.com/guochengqian/pointnext
论文作者:Guocheng Qian, Yuchen Li, Houwen Peng, Jinjie Mai, Hasan Abed Al Kader Hammoud, Mohamed Elhoseiny, Bernard Ghanem
论文简介:In this work, we revisit the classical PointNet++ through a systematic study of model training and scaling strategies, and offer two major contributions. / 在这项工作中,我们通过对模型训练和缩放策略的系统研究重新审视了经典的 PointNet++,并提供了两个主要贡献。
论文摘要:PointNet++ is one of the most influential neural architectures for point cloud understanding. Although the accuracy of PointNet++ has been largely surpassed by recent networks such as PointMLP and Point Transformer, we find that a large portion of the performance gain is due to improved training strategies, i.e. data augmentation and optimization techniques, and increased model sizes rather than architectural innovations. Thus, the full potential of PointNet++ has yet to be explored. In this work, we revisit the classical PointNet++ through a systematic study of model training and scaling strategies, and offer two major contributions. First, we propose a set of improved training strategies that significantly improve PointNet++ performance. For example, we show that, without any change in architecture, the overall accuracy (OA) of PointNet++ on ScanObjectNN object classification can be raised from 77.9% to 86.1%, even outperforming state-of-the-art PointMLP. Second, we introduce an inverted residual bottleneck design and separable MLPs into PointNet++ to enable efficient and effective model scaling and propose PointNeXt, the next version of PointNets. PointNeXt can be flexibly scaled up and outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both 3D classification and segmentation tasks. For classification, PointNeXt reaches an overall accuracy of 87.7% on ScanObjectNN, surpassing PointMLP by 2.3%, while being 10× faster in inference. For semantic segmentation, PointNeXt establishes a new state-of-the-art performance with 74.9% mean IoU on S3DIS (6-fold cross-validation), being superior to the recent Point Transformer. The code and models are available at https://github.com/guochengqian/pointnext
PointNet++ 是用于点云理解的最具影响力的神经架构之一。尽管 PointNet++ 的准确性已被 PointMLP 和 Point Transformer 等最近的网络在很大程度上超越,但我们发现很大一部分性能提升是由于改进了训练策略,即数据增强和优化技术,以及增加了模型大小而不是架构创新。因此,PointNet++ 的全部潜力还有待探索。在这项工作中,我们通过对模型训练和缩放策略的系统研究重新审视了经典的 PointNet++,并提供了两个主要贡献。首先,我们提出了一组改进的训练策略,显着提高了 PointNet++ 的性能。例如,我们表明,在不改变架构的情况下,PointNet++ 在 ScanObjectNN 对象分类上的整体准确率(OA)可以从 77.9% 提高到 86.1%,甚至优于最先进的 PointMLP。其次,我们将倒置残差瓶颈设计和可分离 MLP 引入 PointNet++,以实现高效且有效的模型缩放,并提出 PointNeXt,即下一版本的 PointNets。 PointNeXt 可以灵活扩展,在 3D 分类和分割任务上都优于最先进的方法。对于分类,PointNeXt 在 ScanObjectNN 上的整体准确率达到 87.7%,超过 PointMLP 2.3%,同时推理速度快 10 倍。对于语义分割,PointNeXt 在 S3DIS(6 折交叉验证)上以 74.9% 的平均 IoU 建立了新的最先进的性能,优于最近的 Point Transformer。代码和模型在 https://github.com/guochengqian/pointnext
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处 - 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~