Pytorch 注意力机制
Pytorch 注意力机制
0. 环境介绍
环境使用 Kaggle 里免费建立的 Notebook
教程使用李沐老师的 动手学深度学习 网站和 视频讲解
小技巧:当遇到函数看不懂的时候可以按 Shift+Tab 查看函数详解。
1. 注意力
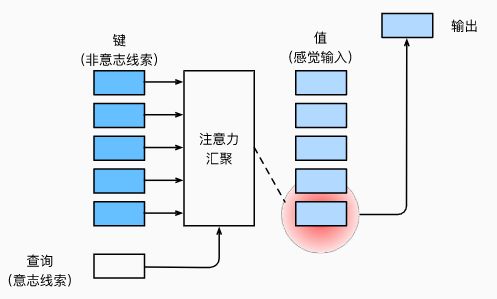
1.1 心理学
- 动物需要在复杂环境下有效关注值得注意的点
- 心理学框架:人类根据随意线索和不随意线索选择注意点
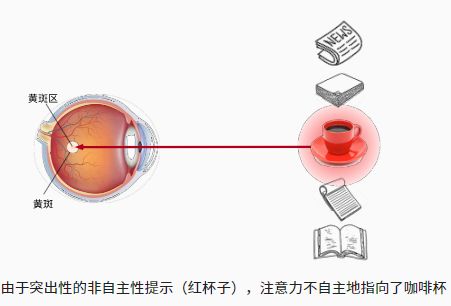
不随意线索(无意识注意):
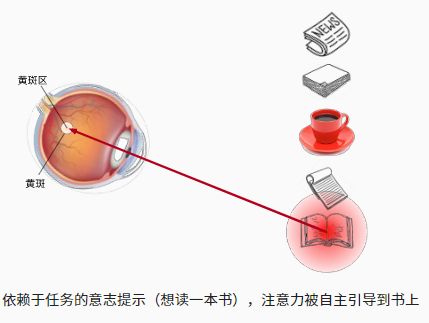
想读书:随意线索(有意识地注意)
1.2 注意力机制
- 卷积、全连接、池化层都只考虑不随意线索(无意识的)
- 注意力机制则显式的考虑随意线索(有意识的)
- 随意线索被称之为查询(Query)
- 每个输入是一个值(Value)和不随意线索(Key)的对
- 通过注意力池化(Pooling)来有偏向性的选择某些输入
1.3 非参注意力池化层
非参就是不学习参数。
- 给定数据 ( x i , y i ) , i = 1 , . . . , n (x_i, y_i), i=1,...,n (xi,yi),i=1,...,n
- 平均池化是最简单的方案:
f ( x ) = 1 n ∑ i y i f(x)=\frac{1}{n}\sum_i{y_i} f(x)=n1i∑yi - 更好的方案是 60 年代提出来的 Nadaraya-Watson 核回归
f ( x ) = ∑ i = 1 n K ( x − x i ) ∑ j = 1 n K ( x − x j ) y i f(x)=\sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{K\left(x-x_{i}\right)}{\sum_{j=1}^{n} K\left(x-x_{j}\right)} y_{i} f(x)=i=1∑n∑j=1nK(x−xj)K(x−xi)yi
x x x 表示 Query, x j , x i x_j, x_i xj,xi 表示 Key, y i y_i yi 表示 Value。
1.4 Nadaraya-Watson 核回归
- 如果 使用高斯核:
K ( u ) = 1 2 π exp ( − u 2 2 ) K(u)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} \exp \left(-\frac{u^{2}}{2}\right) K(u)=2π1exp(−2u2) - 那么:
f ( x ) = ∑ i = 1 n exp ( − 1 2 ( x − x i ) 2 ) ∑ j = 1 n exp ( − 1 2 ( x − x j ) 2 ) y i = ∑ i = 1 n softmax ( − 1 2 ( x − x i ) 2 ) y i \begin{aligned} f(x) &=\sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{\exp \left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(x-x_{i}\right)^{2}\right)}{\sum_{j=1}^{n} \exp \left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(x-x_{j}\right)^{2}\right)} y_{i} \\ &=\sum_{i=1}^{n} \operatorname{softmax}\left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(x-x_{i}\right)^{2}\right) y_{i} \end{aligned} f(x)=i=1∑n∑j=1nexp(−21(x−xj)2)exp(−21(x−xi)2)yi=i=1∑nsoftmax(−21(x−xi)2)yi
1.5 参数化的注意力机制
-
在 1.4 的基础上引入可学系的权重 w w w:
f ( x ) = ∑ i = 1 n softmax ( − 1 2 ( ( x − x i ) w ) 2 ) y i f(x)=\sum_{i=1}^{n} \operatorname{softmax}\left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(\left(x-x_{i}\right) w\right)^{2}\right) y_{i} f(x)=i=1∑nsoftmax(−21((x−xi)w)2)yi -
可以一般化写作 f ( x ) = ∑ i α ( x , x i ) y i f(x)=\sum_{i} \alpha\left(x, x_{i}\right) y_{i} f(x)=∑iα(x,xi)yi,这里 α ( x , x i ) \alpha\left(x, x_{i}\right) α(x,xi) 是注意力权重。
注意力机制关键就在于权重如何设计。
2. 代码
2.0 导包
!pip install -U d2l
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
2.1 生成数据集
考虑一个回归问题:给定成对的 “输入-输出” 数据集 { ( x 1 , y 1 ) , . . . , ( x n , y n ) } \{(x_1, y_1), ..., (x_n, y_n)\} {(x1,y1),...,(xn,yn)},如何学习 f f f 来预测任意新的输入 x x x 的输出 y ^ = f ( x ) \hat{y} = f(x) y^=f(x)?
根据下面的非线性函数生成一个人工数据集, 其中加入的噪声项为 ϵ \epsilon ϵ:
y i = 2 sin ( x i ) + x i 0.8 + ϵ y_i = 2\sin(x_i) + x_i^{0.8} + \epsilon yi=2sin(xi)+xi0.8+ϵ
其中噪声项 ϵ ∼ N ( 0 , 0. 5 2 ) \epsilon \sim N(0, 0.5^2) ϵ∼N(0,0.52)
n_train = 50 # 训练样本数
# 排序后的训练样本
x_train, _ = torch.sort(torch.rand(n_train) * 5)
def f(x):
return 2 * torch.sin(x) + x**0.8
y_train = f(x_train) + torch.normal(0.0, 0.5, (n_train,)) # 训练样本的输出
# 测试样本
x_test = torch.arange(0, 5, 0.1)
y_truth = f(x_test) # 测试样本的真实输出
n_test = len(x_test) # 测试样本数
n_test
2.2 定义绘制所有训练样本的函数
def plot_kernel_reg(y_hat):
d2l.plot(x_test, [y_truth, y_hat], 'x', 'y', legend=['Truth', 'Pred'],
xlim=[0, 5], ylim=[-1, 5])
d2l.plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'o', alpha=0.5);
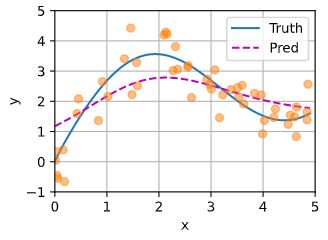
2.3 平均汇聚(Pooling)
y_hat = torch.repeat_interleave(y_train.mean(), n_test)
plot_kernel_reg(y_hat)
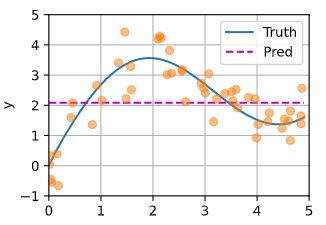
黄色的点表示训练的点,蓝线表示真实值,红色虚线表示最简单的平均线作为预测(不靠谱)。
2.3 非参数注意力汇聚(Pooling)
使用高斯核:
# X_repeat的形状:(n_test,n_train),
# 每一行都包含着相同的测试输入(例如:同样的查询)
X_repeat = x_test.repeat_interleave(n_train).reshape((-1, n_train))
# x_train包含着键。attention_weights的形状:(n_test,n_train),
# 每一行都包含着要在给定的每个查询的值(y_train)之间分配的注意力权重
attention_weights = nn.functional.softmax(-(X_repeat - x_train)**2 / 2, dim=1)
# y_hat的每个元素都是值的加权平均值,其中的权重是注意力权重
y_hat = torch.matmul(attention_weights, y_train)
plot_kernel_reg(y_hat)
2.4 注意力权重
这里测试数据的输入相当于查询(Query),而训练数据的输入相当于键(Key)。 因为两个输入都是经过排序的,因此由观察可知 “查询-键” 对(Q-K)越接近, 注意力汇聚的注意力权重就越高。
d2l.show_heatmaps(attention_weights.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),
xlabel='Sorted training inputs',
ylabel='Sorted testing inputs')
2.5 带参数注意力池化(Pooling)
假定两个张量的形状分别是 ( n , a , b ) (n, a, b) (n,a,b) 和 ( n , b , c ) (n, b, c) (n,b,c),它们的批量矩阵乘法输出的形状为 ( n , a , c ) (n, a, c) (n,a,c):
X = torch.ones((2, 1, 4))
Y = torch.ones((2, 4, 6))
# bmm 表示批量矩阵乘法函数
torch.bmm(X, Y).shape
![]()
2.5.1 定义模型
class NWKernelRegression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.w = nn.Parameter(torch.rand((1,), requires_grad=True))
def forward(self, queries, keys, values):
# queries和attention_weights的形状为(查询个数,“键-值”对个数)
queries = queries.repeat_interleave(keys.shape[1]).reshape((-1, keys.shape[1]))
self.attention_weights = nn.functional.softmax(
-((queries - keys) * self.w)**2 / 2, dim=1)
# values的形状为(查询个数,“键-值”对个数)
return torch.bmm(self.attention_weights.unsqueeze(1),
values.unsqueeze(-1)).reshape(-1)
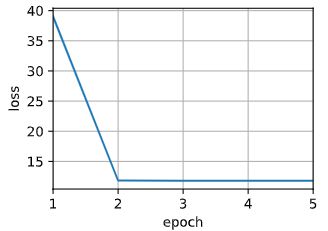
2.5.2 训练
# X_tile的形状:(n_train,n_train),每一行都包含着相同的训练输入
X_tile = x_train.repeat((n_train, 1))
# Y_tile的形状:(n_train,n_train),每一行都包含着相同的训练输出
Y_tile = y_train.repeat((n_train, 1))
# keys的形状:('n_train','n_train'-1)
keys = X_tile[(1 - torch.eye(n_train)).type(torch.bool)].reshape((n_train, -1))
# values的形状:('n_train','n_train'-1)
values = Y_tile[(1 - torch.eye(n_train)).type(torch.bool)].reshape((n_train, -1))
net = NWKernelRegression()
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.5)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', xlim=[1, 5])
for epoch in range(5):
trainer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(x_train, keys, values), y_train)
l.sum().backward()
trainer.step()
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(l.sum()):.6f}')
animator.add(epoch + 1, float(l.sum()))
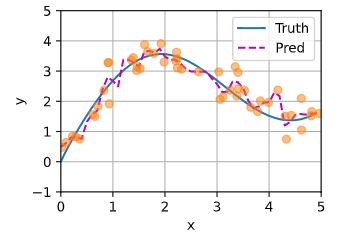
预测结果绘制的线不如之前非参数模型的平滑:
# keys的形状:(n_test,n_train),每一行包含着相同的训练输入(例如,相同的键)
keys = x_train.repeat((n_test, 1))
# value的形状:(n_test,n_train)
values = y_train.repeat((n_test, 1))
y_hat = net(x_test, keys, values).unsqueeze(1).detach()
plot_kernel_reg(y_hat)
与非参数的注意力汇聚模型相比, 带参数的模型加入可学习的参数后, 曲线在注意力权重较大的区域变得更不平滑:
d2l.show_heatmaps(net.attention_weights.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),
xlabel='Sorted training inputs',
ylabel='Sorted testing inputs')