Pytorch基本操作(8)——搭建实战、Sequential、损失函数以及优化器
1 前言
在学习李沐在B站发布的《动手学深度学习》PyTorch版本教学视频中发现在操作使用PyTorch方面有许多地方看不懂,往往只是“动手”了,没有动脑。所以打算趁着寒假的时间好好恶补、整理一下PyTorch的操作,以便跟上课程。
学习资源:
- B站up主:我是土堆的视频:PyTorch深度学习快速入门教程(绝对通俗易懂!)【小土堆】
- PyTorch中文手册:(pytorch handbook)
- Datawhale开源内容:深入浅出PyTorch(thorough-pytorch)
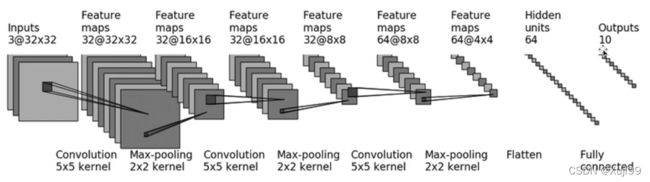
2 CIFAR 10 模型结构
2.1 通过Sequential搭建网络
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Flatten, Linear, Sequential
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
- 试着用
Sequential()函数来简化代码,记得每层之间用括号分割
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui, self).__init__()
# self.conv1 = Conv2d(3, 32, 5, padding = 2)
# self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(2)
# self.conv2 = Conv2d(32, 32, 5, padding = 2)
# self.maxpool2 = MaxPool2d(2)
# self.conv3 = Conv2d(32, 64, 5, padding = 2)
# self.maxpool3 = MaxPool2d(2)
# self.flatten = Flatten()
# self.linear1 = Linear(1024, 64) # flatten的输出不知道维数的话,可以模拟一个数据跑到这一层看看输出的shape
# self.linear2 = Linear(64, 10)
self.model1 = Sequential(
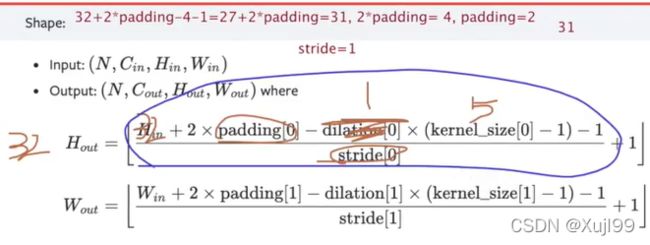
Conv2d(3, 32, 5, padding = 2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 32, 5, padding = 2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 64, 5, padding = 2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024, 64),
Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
# x = self.conv1(x)
# x = self.maxpool1(x)
# x = self.conv2(x)
# x = self.maxpool2(x)
# x = self.conv3(x)
# x = self.maxpool3(x)
# x = self.flatten(x)
# x = self.linear1(x)
# x = self.linear2(x)
x = self.model1(x)
return x
tudui = Tudui()
tudui
Tudui(
(model1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(2): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(3): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(4): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(7): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=64, bias=True)
(8): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
'''模拟一个试试网络能不能走通,输入输出能不能对上'''
input = torch.ones([64, 3, 32, 32]) # 模拟一个64批量,3通道,32*32的图片
output = tudui(input)
output.shape
torch.Size([64, 10])
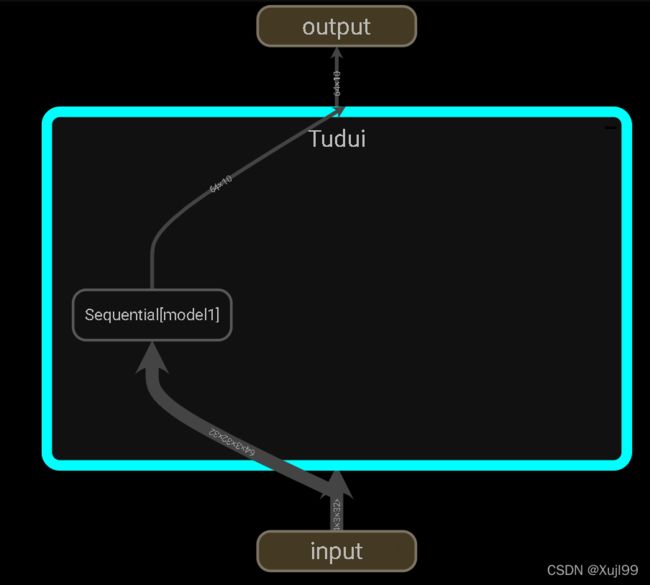
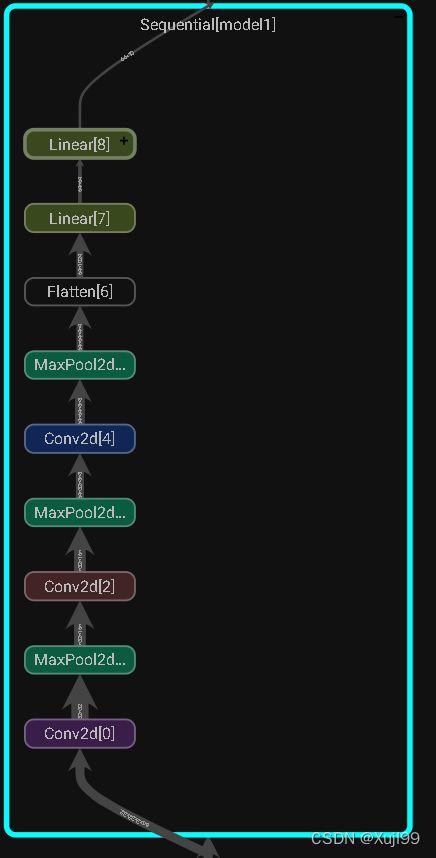
2.2 可视化writer.add_graph()
writer = SummaryWriter("logs_seq")
writer.add_graph(tudui, input)
writer.close()
3 损失函数
3.1 L1Loss,MSELoss
import torch
from torch.nn import L1Loss
from torch import nn
inputs = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype = torch.float32)
targets = torch.tensor([1, 2, 5], dtype = torch.float32)
inputs = torch.reshape(inputs, (1, 1, 1, 3))
targets = torch.reshape(targets, (1, 1, 1, 3))
loss = L1Loss(reduction = 'sum') # 损失相加,默认是算平均
result = loss(inputs, targets)
result
tensor(2.)
loss_mse = nn.MSELoss()
result_mse = loss_mse(inputs, targets)
result_mse
tensor(1.3333)
3.2 交叉熵损失CrossEntropyLoss
- 注意input的形状
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.3])
y = torch.tensor([1])
x = torch.reshape(x, (1, 3))
loss_cross = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
result_cross = loss_cross(x, y)
result_cross
tensor(1.1019)
4 优化器
官方文档
import torchvision
from torch.nn import Sequential, Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Flatten, Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("dataset", train = False, transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download = True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size = 1)
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui, self).__init__()
self.model1 = Sequential(
Conv2d(3, 32, 5, padding = 2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 32, 5, padding = 2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 64, 5, padding = 2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024, 64),
Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model1(x)
return x
Files already downloaded and verified
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
tudui = Tudui()
optim = torch.optim.SGD(tudui.parameters(), lr = 0.01)
for epoch in range(20):
running_loss = 0.0
for data in dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
outputs = tudui(imgs)
result_loss = loss(outputs, targets)
optim.zero_grad()
result_loss.backward()
optim.step()
running_loss = running_loss + result_loss
print(running_loss)
tensor(18720.8652, grad_fn=)
tensor(16169.7070, grad_fn=)
tensor(15471.6523, grad_fn=)