【yolov3损失函数】
文章目录
- compute_loss()函数
- loss_layer()函数
- 计算giou
YOLOv3源码解析1-代码整体结构
解析的代码地址:
github:tensorflow-yolov3
本文解析计算各部分损失compute_loss()部分:
yolov3的损失函数稍微有点复杂,花了点时间看了好多篇有关yolov3的损失函数,总算有了一点点眉目,下篇文章写一下有关yolov3损失函数的理论部分。这篇源码的解析主要提现在结构图和源码的注释中,相关部分没有写专门的文字说明。

开始在train.py的第55行调用compute_loss()计算模型训练的损失,然后再yolov3.py中进入到compute_loss()函数
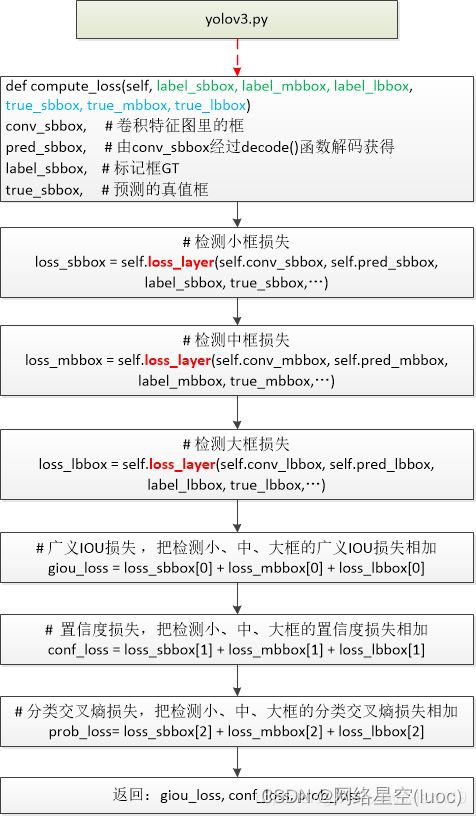
compute_loss()函数
其实这部分代码并没有进行核心的计算,主要是传入相关参数,然后调用loss_layer()函数进行相关计算。
源码:
# 计算损失
'''
conv_sbbox, # 卷积特征图里的原始值
pred_sbbox, # 由conv_sbbox经过decode()函数解码获得
label_sbbox, # [52,52,3,85] 标记框GT的坐标值,置信度,概率等多个值
true_sbbox, # 只含标记框GT的坐标值 (3,150,4) true_box在实际训练时传入的是下面的值
self.true_sbboxes: train_data[4]==sbboxes == bboxes_xywh[..,0] # 获取小中大标记框的坐标值
self.true_mbboxes: train_data[5]==mbboxes == bboxes_xywh[..,1] # 获取小中大标记框的坐标值
self.true_lbboxes: train_data[6]==lbboxes == bboxes_xywh[..,2] # 获取小中大标记框的坐标值
'''
def compute_loss(self, label_sbbox, label_mbbox, label_lbbox, true_sbbox, true_mbbox, true_lbbox):
# 检测小框损失 52*52
with tf.name_scope('smaller_box_loss'):
loss_sbbox = self.loss_layer(self.conv_sbbox, self.pred_sbbox, label_sbbox, true_sbbox,
anchors = self.anchors[0], stride = self.strides[0])
# 检测中框损失 26*26
with tf.name_scope('medium_box_loss'):
loss_mbbox = self.loss_layer(self.conv_mbbox, self.pred_mbbox, label_mbbox, true_mbbox,
anchors = self.anchors[1], stride = self.strides[1])
# 检测大框损失 13*13
with tf.name_scope('bigger_box_loss'):
loss_lbbox = self.loss_layer(self.conv_lbbox, self.pred_lbbox, label_lbbox, true_lbbox,
anchors = self.anchors[2], stride = self.strides[2])
# 广义IOU损失 ,把检测小、中、大框的广义IOU损失相加
with tf.name_scope('giou_loss'):
giou_loss = loss_sbbox[0] + loss_mbbox[0] + loss_lbbox[0]
# 置信度损失,把检测小、中、大框的置信度损失相加
with tf.name_scope('conf_loss'):
conf_loss = loss_sbbox[1] + loss_mbbox[1] + loss_lbbox[1]
# 分类交叉熵损失,把检测小、中、大框的分类交叉熵损失相加
with tf.name_scope('prob_loss'):
prob_loss = loss_sbbox[2] + loss_mbbox[2] + loss_lbbox[2]
return giou_loss, conf_loss, prob_loss
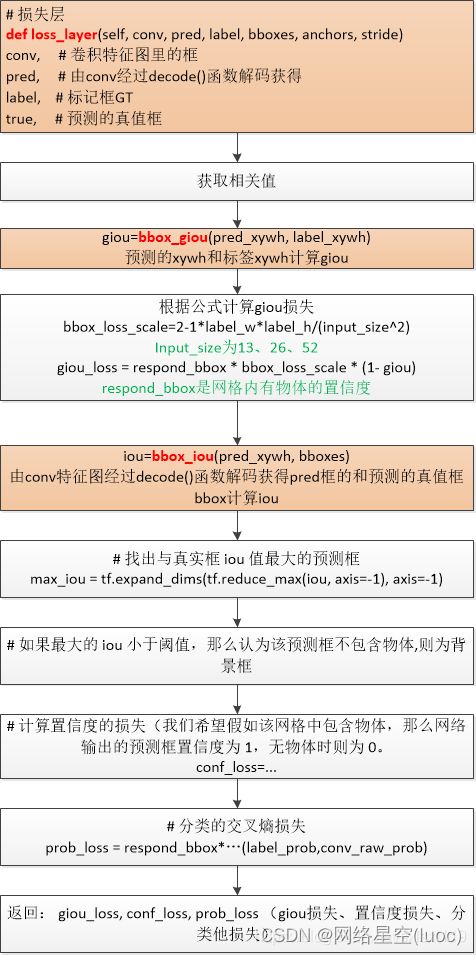
loss_layer()函数
源码:
# 损失层
'''
conv, # 卷积特征图里的原始值
pred, # 由conv经过decode()函数解码获得
label, # 标记框GT的坐标值,置信度,概率等多个值 [52,52,3,85]
bboxes, # 只含标记框GT的坐标值 (3,150,4)
anchors # 基准anchor的宽高
stride # 特征图相对于原图的缩放率
'''
def loss_layer(self, conv, pred, label, bboxes, anchors, stride):
conv_shape = tf.shape(conv) # 原图卷积得到的值
batch_size = conv_shape[0] # 一次多少张图
output_size = conv_shape[1] # 特征图大小 13*13, 26*26, 52*52
input_size = stride * output_size # 13*32 26*16 52*8
# conv is reshaped here to 5 dimensions
conv = tf.reshape(conv, (batch_size, output_size, output_size,
self.anchor_per_scale, 5 + self.num_class))
# this is the logit before going into sigmoid functions
conv_raw_conf = conv[:, :, :, :, 4:5] # 原始的置信度,起始值就是特征图像的值
conv_raw_prob = conv[:, :, :, :, 5:] # 原始的预测概率,起始值就是特征图像的值
pred_xywh = pred[:, :, :, :, 0:4] # 预测框xywh
pred_conf = pred[:, :, :, :, 4:5] # 预测置信度
# true coordinates (x, y, w, h) 标记坐标GT
label_xywh = label[:, :, :, :, 0:4] # 标记框坐标
# what is this?
respond_bbox = label[:, :, :, :, 4:5] # 置信度,判断网格内有无物体
# true probabilities
label_prob = label[:, :, :, :, 5:] # 真值概率
# GIOU损失
# label_xywh and pred_xywh are used to compute giou
# 标记框的xywh和预测框的xywh用来计算giou
giou = tf.expand_dims(self.bbox_giou(pred_xywh, label_xywh), axis=-1) #在第axis位置增加一个维度,-1表示最后一维
input_size = tf.cast(input_size, tf.float32) # 数据类型转换
bbox_loss_scale = 2.0 - 1.0 * label_xywh[:, :, :, :, 2:3] * label_xywh[:, :, :, :, 3:4] / (input_size ** 2)
giou_loss = respond_bbox * bbox_loss_scale * (1- giou)
# 置信度损失
# bboxes (true_bboxes) and pred_xywh are used to compute iou
# 计算true_bboxes和pred_xywh的交并比
iou = self.bbox_iou(pred_xywh[:, :, :, :, np.newaxis, :], bboxes[:, np.newaxis, np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :, :])
# 找出与真实框 iou 值最大的预测框
max_iou = tf.expand_dims(tf.reduce_max(iou, axis=-1), axis=-1)
# 如果最大的 iou 小于阈值,那么认为该预测框不包含物体,则为背景框
respond_bgd = (1.0 - respond_bbox) * tf.cast( max_iou < self.iou_loss_thresh, tf.float32 )
conf_focal = self.focal(respond_bbox, pred_conf) # ???
# 计算置信度的损失(我们希望假如该网格中包含物体,那么网络输出的预测框置信度为 1,无物体时则为 0。
conf_loss = conf_focal * (
respond_bbox * tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=respond_bbox, logits=conv_raw_conf)
+
respond_bgd * tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=respond_bbox, logits=conv_raw_conf)
)
# cross-entropy for classifications
# 分类的交叉熵损失
prob_loss = respond_bbox * tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=label_prob, logits=conv_raw_prob)
giou_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(giou_loss, axis=[1,2,3,4]))
conf_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(conf_loss, axis=[1,2,3,4]))
prob_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(prob_loss, axis=[1,2,3,4]))
return giou_loss, conf_loss, prob_loss
其中调用的3个小函数:
Focal loss让one stage detecor也变的牛逼起来,解决了class imbalance的问题。 是同时解决了正负样本不平衡以及区分简单与复杂样本的问题。
def focal(self, target, actual, alpha=1, gamma=2):
focal_loss = alpha * tf.pow(tf.abs(target - actual), gamma)
return focal_loss
计算giou
# 计算giou
def bbox_giou(self, boxes1, boxes2):
boxes1 = tf.concat([boxes1[..., :2] - boxes1[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes1[..., :2] + boxes1[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes2 = tf.concat([boxes2[..., :2] - boxes2[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes2[..., :2] + boxes2[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes1 = tf.concat([tf.minimum(boxes1[..., :2], boxes1[..., 2:]),
tf.maximum(boxes1[..., :2], boxes1[..., 2:])], axis=-1)
boxes2 = tf.concat([tf.minimum(boxes2[..., :2], boxes2[..., 2:]),
tf.maximum(boxes2[..., :2], boxes2[..., 2:])], axis=-1)
boxes1_area = (boxes1[..., 2] - boxes1[..., 0]) * (boxes1[..., 3] - boxes1[..., 1])
boxes2_area = (boxes2[..., 2] - boxes2[..., 0]) * (boxes2[..., 3] - boxes2[..., 1])
left_up = tf.maximum(boxes1[..., :2], boxes2[..., :2]) # 左上
right_down = tf.minimum(boxes1[..., 2:], boxes2[..., 2:]) # 右下
inter_section = tf.maximum(right_down - left_up, 0.0)
inter_area = inter_section[..., 0] * inter_section[..., 1]
union_area = boxes1_area + boxes2_area - inter_area
# 计算两个边界框之间的 iou 值
iou = inter_area / union_area
# 计算最小闭合凸面 C 左上角和右下角的坐标
enclose_left_up = tf.minimum(boxes1[..., :2], boxes2[..., :2])
enclose_right_down = tf.maximum(boxes1[..., 2:], boxes2[..., 2:])
enclose = tf.maximum(enclose_right_down - enclose_left_up, 0.0)
# 计算最小闭合凸面 C 的面积
enclose_area = enclose[..., 0] * enclose[..., 1]
# 根据 GIoU 公式计算 GIoU 值
giou = iou - 1.0 * (enclose_area - union_area) / enclose_area
return giou
两个框的交并比
# 两个框的交并比
def bbox_iou(self, boxes1, boxes2):
boxes1_area = boxes1[..., 2] * boxes1[..., 3]
boxes2_area = boxes2[..., 2] * boxes2[..., 3]
boxes1 = tf.concat([boxes1[..., :2] - boxes1[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes1[..., :2] + boxes1[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes2 = tf.concat([boxes2[..., :2] - boxes2[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes2[..., :2] + boxes2[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
left_up = tf.maximum(boxes1[..., :2], boxes2[..., :2])
right_down = tf.minimum(boxes1[..., 2:], boxes2[..., 2:])
inter_section = tf.maximum(right_down - left_up, 0.0)
inter_area = inter_section[..., 0] * inter_section[..., 1]
union_area = boxes1_area + boxes2_area - inter_area
iou = 1.0 * inter_area / union_area
return iou