【Java】每日小结(内含常见面试知识)
![]()
![]()
![]()
前言:
“前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默
经过小新缜密的思考与亲身体验,忍不住分享一下给大家。有人工智能兴趣的朋友们,推荐大家一起学习 点击直接访问
里面有丰富的人工智能学习资料,真正做到从入门到入土,还不快来一起学习
个人名片:
作者简介:一名大一在校生
❄️个人主页:小新爱学习.
个人WeChat:hmmwx53
️系列专栏:零基础学java ----- 重识c语言
每日一句:等风来,不如追风去~
文章目录
- 今日学习总结
-
- 一、Java StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类
- 二、日期工具类Date
-
-
- 获取当前日期时间
- SimpleDateFormat 格式化日期
-
- 三、包装类:
-
-
- 包装类Integer
- 自动拆箱,装箱
-
- 四、==与equals的区别✨✨✨
- 五、精度缺失处理方法:
今日学习总结
一、Java StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类
当对字符串进行修改的时候,需要使用 StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类。
和 String 类不同的是,StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类的对象能够被多次的修改,并且不产生新的未使用对象。
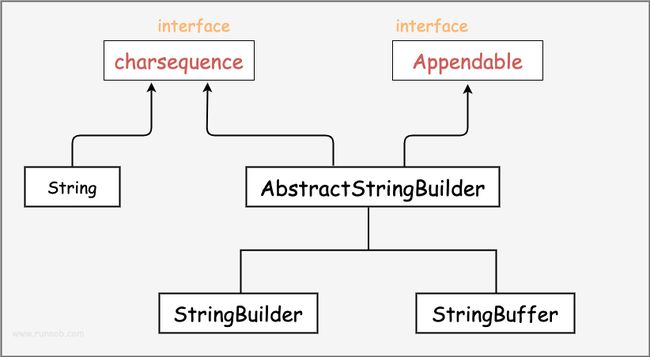
在使用 StringBuffer 类时,每次都会对 StringBuffer 对象本身进行操作,而不是生成新的对象,所以如果需要对字符串进行修改推荐使用 StringBuffer。
- 特点: 封装了char[]数组,是可变的字符序列,提供了一直可以对字符串进行修改的方法
- StringBuilder非线程安全,同步处理,始于jdk1.5
- StringBuffer:线程安全,并发处理,性能稍慢,始于jdk1.0
- 执行效率:StringBuilder>StringBuffer>String
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public StringBuffer append(String s) | 将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。 |
| public StringBuffer reverse() | 将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。 |
| public delete(int start, int end) | 移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
| public insert(int offset, int i) | 将 int 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。 |
| replace(int start, int end, String str) | 使用给定 String 中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
代码示例:
package cn.tedu.day17;
public class Test_String2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "好好学习java";
/**
* public StringBuilder(String var1) {
* super(var1.length() + 16);
* this.append(var1);
* 内部字符数组默认初识容量为16,if>16扩容
*/
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(str);//将str内容复制到StringBuilder里面,
//追加
sb.append("为了月薪过万");//好好学习java为了月薪过万
//replace()替换部分内容
sb.replace(10,sb.length(),"改变世界");//好好学习java为了改变世界
//delete()删除部分内容
sb.delete(8,14);//好好学习java 删除下标7-13,含头不含尾
//insert()插入操作
sb.replace(0,1,"我要");//我要好学习java
//reverse()
// 将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。
sb.reverse();//avaj习学好要我
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
二、日期工具类Date
概述:类 Date 表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒。,java.util 包提供了 Date 类来封装当前的日期和时间。
常用方法摘要:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| long getTime() | 返回自 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 GMT 以来此 Date 对象表示的毫秒数。 |
| int getMonth() | 获取当前月份(+1) |
| toLocaleString() | 获取当前时间 yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss |
| int getDay() | 获取当前天 |
| int getHours() | 获取当前小时 |
| int getMinutes() | 获取当前分钟 |
| int getSeconds() | 获取当前秒数 |
| String toString( ) | 把此 Date 对象转换为以下形式的 String: dow mon dd hh:mm:ss zzz yyyy 其中: dow 是一周中的某一天 (Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat)。 |
获取当前日期时间
import java.util.Date;
public class DateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化 Date 对象
Date date = new Date();
// 使用 toString() 函数显示日期时间
System.out.println(date.toString());
}
}
SimpleDateFormat 格式化日期
SimpleDateFormat ft = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
把String类型的日期转化为Date类型,
SimpleDateFormat 类有一些附加的方法,特别是parse(),它试图按照给定的SimpleDateFormat 对象的格式化存储来解析字符串。
Demo: 输入生日求活了多少天
public static void method2() throws ParseException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你的生日");
String birthday = scanner.nextLine();
//long start = d.getTime()+32*365*24*60*60*1000;//毫秒
//吧String类型的日期转化为Date类型
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date birthday1 = sdf.parse(birthday);
//获取毫秒值
long time = birthday1.getTime();//获取出生时的毫秒数
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//1970到现在的毫秒数
System.out.println((currentTime - time)/24/60/60/ 1000);//单位:天
}
三、包装类:
包装类:java中定义了8个包装类,目的是为了解决基本数据类型不能直接参与面向对象的开发问题
Integer、Character、Byte、Short、Long、Float、Double、Boolean
Character和Boolean继承自Object,其余六个都是继承自java.lang.Number
Number:是数字包装类的抽象父类
包装类Integer
int 的包装类 Integer
Integer i0;//Integer以对象的形式存在,默认值null
Integer i1 = new Integer(1);//Integer
底层逻辑:
public Integer(int var1) {
this.value = var1;
}
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static Integer valueOf(int i) | 返回一个表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例。 |
| static int parseInt(String s) | 将字符串参数作为有符号的十进制整数进行解析。 |
自动拆箱,装箱
- 装箱:把基本数据类型转换为对应包装类类型
- 拆箱:把包装类型转换为对应的基本数据类型
自动装箱底层发生的代码:Integer.valueOf(127); int -->Integer
public static void main(String[] args) {
// - 装箱:把基本数据类型转换为对应包装类类型
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer ii =100;//自动装箱Integer.valueOf(100);
//- 拆箱:把包装类型转换为对应的基本数据类型
/* ii = ii.intValue()+200;
System.out.println(ii);*/
ii+=200;//内部隐含ii.intValue()
System.out.println(ii);
Integer iii = null;
if(iii!=null){
iii+=300;//NullPointerException//内部隐含ii.intValue(),所以null掉对象,会触发空指针异常
}
}
- Integer iii = 5;//iii 是引用数据类型,5是基本数据类型,引用了包装类的地址
- int a = iii;//编译器自动完成拆箱:从包装类型的值,自动变成基本数据类型的值
四、==与equals的区别✨✨✨
1.当使用== 比较时,如果相比较的两个两个变量是引用数据类型,那么比较的是两者的物理地址(内存地址),
如果相比较的两个变量是基本数据类型,那么比较的是具体数值是否相等;
2.当使用equals比较时,比较的结果实际上取决于equals方法的具体实现
3. 任何类都是继承自Object类,因此所有类都具有Object类的特性,比如String,Integer等
它们在自己的类中重写了equals方法,此时它们比较的就是内容是否相同,而在Object了类的默认实现中,
equals方法的底层是通过== 实现的
五、精度缺失处理方法:
BigDecimal:常用来解决精确的浮点数运算
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend) | 返回一个 BigDecimal,其值为 (this + augend),其标度为 max(this.scale(), augend.scale())。 |
| BigDecimal negate() | 返回 BigDecimal,其值为 (-this),其标度为 this.scale()。 |
| BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand) | 返回一个 BigDecimal,其值为 (this × multiplicand),其标度为 (this.scale() + multiplicand.scale())。 |
| BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, RoundingMode roundingMode) | 返回一个 BigDecimal,其值为 (this / divisor),其标度为 this.scale()。 |
在除法中:
- divisor - 此 BigDecimal 要除以的值。
- scale - 要返回的 BigDecimal 商的标度。
- roundingMode - 要应用的舍入模式。
代码示例:
package cn.tedu.day17;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 本类用来测试浮点数运算时不精确的解决方案
*/
public class Test_BigDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//method1();
method2();
}
public static void method1(){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要计算的两个小数");
double a = sc.nextDouble();
double b = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println(a+b);
System.out.println(a-b);
System.out.println(a*b);
System.out.println(a/b);
}
public static void method2(){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要计算的两个小数");
double a = sc.nextDouble();
double b = sc.nextDouble();
/**
* 创建工具类对象
* 最好不要使用double类型作为构造函数参数,不然会产生精度丢失
* 最好使用重载,参数类型是String类型的构造函数,double 转换成String ,直接拼接一个空字符串
* BigDecimal(double val)不建议
* BigDecimal(String val)建议,将String类型的字符串转化为BigDecimal
*/
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(a+"");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal(b+"");
BigDecimal bd3;
bd3 = bd1.add(bd2);//加法运算
System.out.println(bd3);
bd3 = bd1.subtract(bd2);//减法
System.out.println(bd3);
bd3 = bd1.multiply(bd2);//乘法运算
System.out.println(bd3);
bd3 = bd1.divide(bd2,3, RoundingMode.UP);//除法
//第一个参数是要除以那个数,第二个是要保留的几位,第三个是舍入方式
System.out.println(bd3);
//divisor - 此 BigDecimal 要除以的值。
//scale - 要返回的 BigDecimal 商的标度。
//roundingMode - 要应用的舍入模式。
}
}