手撕代码:ResNet实战
关于resnet原理的教程有很多,这里推荐一个~
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1T7411T7wa?from=search&%3Bseid=1879396105190151950
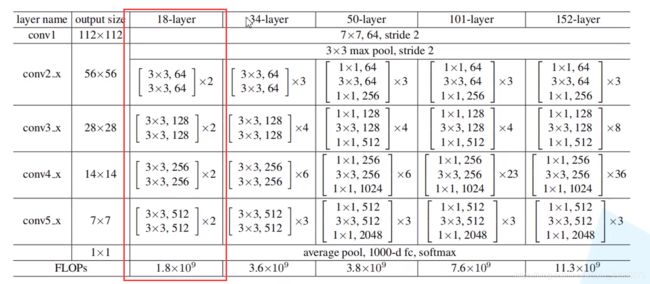
然后本次学习手写的代码是resnet18,数据集为CIFAR100,网络结构即为下图红框中的结构
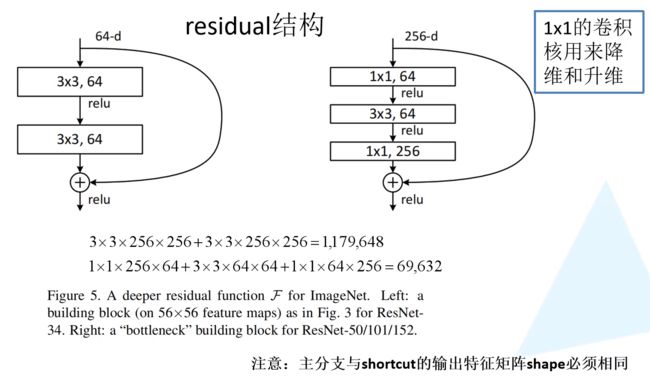
图片截自开头提到的教程
代码
网络结构部分:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers, Sequential
# 构造含有一个短接层的residual结构
class BasicBlock(layers.Layer): # 继承layers.Layer
def __init__(self, filter_num, stride=1): # filer_num即channel
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() # 对继承自父类的属性进行初始化。而且是用父类的初始化方法来初始化继承的属性。
# 子类新定义属性初始化
self.conv1 = layers.Conv2D(filter_num, (3, 3), strides=stride, padding='same')
self.bn1 = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.relu = layers.Activation('relu')
self.conv2 = layers.Conv2D(filter_num, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='same')
self.bn2 = layers.BatchNormalization()
if stride != 1:
self.downsample = Sequential()
self.downsample.add(layers.Conv2D(filter_num, (1, 1), strides=stride))
else:
self.downsample = lambda x:x # 若stride=1,不需要下采样
# 前向传播
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# [b, h, w, c]
out = self.conv1(inputs)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
# residual结构
identity = self.downsample(inputs)
# 短接层与卷积层的相加
output = layers.add([out, identity])
output = tf.nn.relu(output)
return output
# 将多个BasicBlock连接形成Res Block
class ResNet(keras.Model):
# 第一个参数为层数组合,Eg:[2, 2, 2, 2];第二个参数为分类数量(全连接层)
def __init__(self, layer_dims, num_classes=100):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
# 预处理层
self.stem = Sequential([layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), strides=(1, 1)),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.Activation('relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')
])
# resnet主干部分
self.layer1 = self.build_resblock(64, layer_dims[0]) # Eg:【2,2,2,2】,第一个resblock就含有两个basblock
self.layer2 = self.build_resblock(128, layer_dims[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self.build_resblock(256, layer_dims[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self.build_resblock(512, layer_dims[3], stride=2)
# 全连接层 output: [b, 512, h, w],
self.avgpool = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D() # 自适应确定输出,以输入全连接层
self.fc = layers.Dense(num_classes)
# 前向运算
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
x = self.stem(inputs)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
# [b, c]
x = self.avgpool(x)
# [b, 100]
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def build_resblock(self, filter_num, blocks, stride=1):
res_blocks = Sequential()
# may down sample
res_blocks.add(BasicBlock(filter_num, stride))
# 后续的BasicBlock没有下采样,保持shape不变
for _ in range(1, blocks):
res_blocks.add(BasicBlock(filter_num, stride=1))
return res_blocks
# 四个Res Block,其中每个包含两个Basicblock
def resnet18():
return ResNet([2, 2, 2, 2])
def resnet34():
return ResNet([3, 4, 6, 3])训练部分
可和VGG的训练部分对比,学习代码逻辑结构
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, optimizers, datasets, Sequential
import os
from resnet import resnet18 # 导入resnet18网络
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
tf.random.set_seed(2345)
def preprocess(x, y):
# [-1~1]
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255. - 0.5 # 调整这里可以改善梯度弥散现象
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x,y
(x,y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.cifar100.load_data()
y = tf.squeeze(y, axis=1)
y_test = tf.squeeze(y_test, axis=1)
print(x.shape, y.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y))
train_db = train_db.shuffle(1000).map(preprocess).batch(512)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test,y_test))
test_db = test_db.map(preprocess).batch(512)
sample = next(iter(train_db))
print('sample:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape,
tf.reduce_min(sample[0]), tf.reduce_max(sample[0]))
def main():
# [b, 32, 32, 3] => [b, 1, 1, 512]
model = resnet18()
model.build(input_shape=(None, 32, 32, 3))
model.summary()
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-3)
for epoch in range(500):
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(train_db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 32, 32, 3] => [b, 100]
logits = model(x)
# [b] => [b, 100]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=100)
# compute loss
loss = tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, logits, from_logits=True)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
if step %50 == 0:
print(epoch, step, 'loss:', float(loss))
total_num = 0
total_correct = 0
for x,y in test_db:
logits = model(x)
prob = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1)
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y), dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]
total_correct += int(correct)
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'acc:', acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()