Unet代码详解(二)数据预处理和后处理
一. 数据预处理
dataloader.py
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils.data.dataset import Dataset
from utils.utils import cvtColor, preprocess_input
class UnetDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, annotation_lines, input_shape, num_classes, train, dataset_path):
super(UnetDataset, self).__init__()
self.annotation_lines = annotation_lines
self.length = len(annotation_lines)
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.train = train
self.dataset_path = dataset_path
def __len__(self):
return self.length
def __getitem__(self, index):
annotation_line = self.annotation_lines[index]
name = annotation_line.split()[0]
#-------------------------------#
# 从文件中读取图像
#-------------------------------#
jpg = Image.open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "VOC2007/JPEGImages"), name + ".jpg"))
png = Image.open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "VOC2007/SegmentationClass"), name + ".png"))
#-------------------------------#
# 数据增强
#-------------------------------#
jpg, png = self.get_random_data(jpg, png, self.input_shape, random = self.train)
jpg = np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(jpg, np.float64)), [2,0,1])
png = np.array(png)
png[png >= self.num_classes] = self.num_classes
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 转化成one_hot的形式
# 在这里需要+1是因为voc数据集有些标签具有白边部分
# 我们需要将白边部分进行忽略,+1的目的是方便忽略。
#-------------------------------------------------------#
seg_labels = np.eye(self.num_classes + 1)[png.reshape([-1])]
seg_labels = seg_labels.reshape((int(self.input_shape[0]), int(self.input_shape[1]), self.num_classes + 1))
return jpg, png, seg_labels
def rand(self, a=0, b=1):
return np.random.rand() * (b - a) + a
def get_random_data(self, image, label, input_shape, jitter=.3, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, random=True):
image = cvtColor(image)
label = Image.fromarray(np.array(label))
h, w = input_shape
if not random:
iw, ih = image.size
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', [w, h], (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
label = label.resize((nw,nh), Image.NEAREST)
new_label = Image.new('L', [w, h], (0))
new_label.paste(label, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
return new_image, new_label
# resize image
rand_jit1 = self.rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
rand_jit2 = self.rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
new_ar = w/h * rand_jit1/rand_jit2
scale = self.rand(0.25, 2)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
label = label.resize((nw,nh), Image.NEAREST)
flip = self.rand()<.5
if flip:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
label = label.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
# place image
dx = int(self.rand(0, w-nw))
dy = int(self.rand(0, h-nh))
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_label = Image.new('L', (w,h), (0))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
new_label.paste(label, (dx, dy))
image = new_image
label = new_label
# distort image
hue = self.rand(-hue, hue)
sat = self.rand(1, sat) if self.rand()<.5 else 1/self.rand(1, sat)
val = self.rand(1, val) if self.rand()<.5 else 1/self.rand(1, val)
x = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(image,np.float32)/255, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
x[..., 0] += hue*360
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x[:,:, 0]>360, 0] = 360
x[:, :, 1:][x[:, :, 1:]>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
image_data = cv2.cvtColor(x, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)*255
return image_data,label
# DataLoader中collate_fn使用
def unet_dataset_collate(batch):
images = []
pngs = []
seg_labels = []
for img, png, labels in batch:
images.append(img)
pngs.append(png)
seg_labels.append(labels)
images = np.array(images)
pngs = np.array(pngs)
seg_labels = np.array(seg_labels)
return images, pngs, seg_labels
二. 后处理
unet.py
import colorsys
import copy
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from PIL import Image
from torch import nn
from nets.unet import Unet as unet
from utils.utils import cvtColor, preprocess_input, resize_image
class Unet(object):
_defaults = {
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
# model_path指向logs文件夹下的权值文件
# 训练好后logs文件夹下存在多个权值文件,选择验证集损失较低的即可。
# 验证集损失较低不代表miou较高,仅代表该权值在验证集上泛化性能较好。
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
"model_path" : 'model_data/unet_voc.pth',
#--------------------------------#
# 所需要区分的类的个数+1
#--------------------------------#
"num_classes" : 21,
#--------------------------------#
# 输入图片的大小
#--------------------------------#
"input_shape" : [512, 512],
#--------------------------------#
# blend参数用于控制是否
# 让识别结果和原图混合
#--------------------------------#
"blend" : True,
#-------------------------------#
# 是否使用Cuda
# 没有GPU可以设置成False
#-------------------------------#
"cuda" : True,
}
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化UNET
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 画框设置不同的颜色
#---------------------------------------------------#
if self.num_classes <= 21:
self.colors = [ (0, 0, 0), (128, 0, 0), (0, 128, 0), (128, 128, 0), (0, 0, 128), (128, 0, 128), (0, 128, 128),
(128, 128, 128), (64, 0, 0), (192, 0, 0), (64, 128, 0), (192, 128, 0), (64, 0, 128), (192, 0, 128),
(64, 128, 128), (192, 128, 128), (0, 64, 0), (128, 64, 0), (0, 192, 0), (128, 192, 0), (0, 64, 128),
(128, 64, 12)]
else:
hsv_tuples = [(x / self.num_classes, 1., 1.) for x in range(self.num_classes)]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)), self.colors))
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.generate()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得所有的分类
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
self.net = unet(num_classes = self.num_classes)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_path, map_location=device), strict=False)
self.net = self.net.eval()
print('{} model, and classes loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
if self.cuda:
self.net = nn.DataParallel(self.net)
self.net = self.net.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 对输入图像进行一个备份,后面用于绘图
#---------------------------------------------------#
old_img = copy.deepcopy(image)
orininal_h = np.array(image).shape[0]
orininal_w = np.array(image).shape[1]
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data, nw, nh = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1],self.input_shape[0]))
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, np.float32)), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 图片传入网络进行预测
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = self.net(images)[0]
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 取出每一个像素点的种类
#---------------------------------------------------#
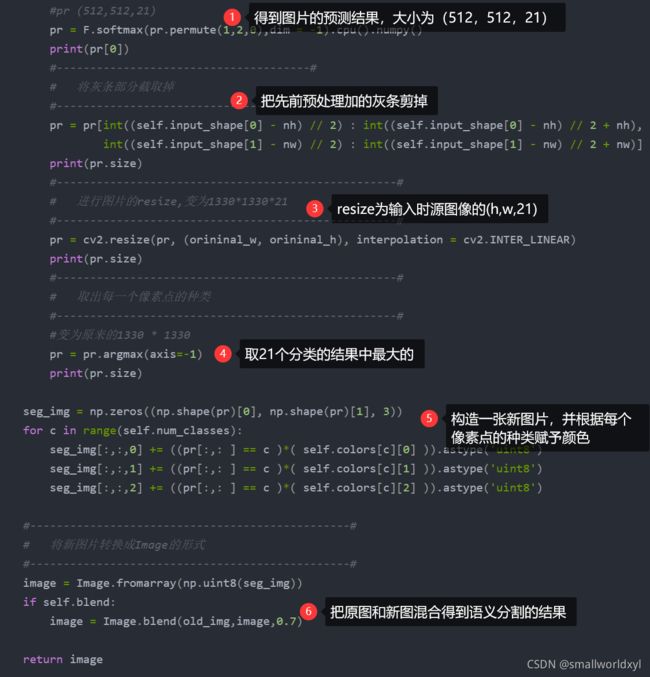
#pr (512,512,21)
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy()
print(pr[0])
#--------------------------------------#
# 将灰条部分截取掉
#--------------------------------------#
pr = pr[int((self.input_shape[0] - nh) // 2) : int((self.input_shape[0] - nh) // 2 + nh), \
int((self.input_shape[1] - nw) // 2) : int((self.input_shape[1] - nw) // 2 + nw)]
print(pr.size)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 进行图片的resize,变为1330*1330*21
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = cv2.resize(pr, (orininal_w, orininal_h), interpolation = cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
print(pr.size)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 取出每一个像素点的种类
#---------------------------------------------------#
#变为原来的1330 * 1330
pr = pr.argmax(axis=-1)
print(pr.size)
seg_img = np.zeros((np.shape(pr)[0], np.shape(pr)[1], 3))
for c in range(self.num_classes):
seg_img[:,:,0] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][0] )).astype('uint8')
seg_img[:,:,1] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][1] )).astype('uint8')
seg_img[:,:,2] += ((pr[:,: ] == c )*( self.colors[c][2] )).astype('uint8')
#------------------------------------------------#
# 将新图片转换成Image的形式
#------------------------------------------------#
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(seg_img))
if self.blend:
image = Image.blend(old_img,image,0.7)
return image
def get_miou_png(self, image):
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
orininal_h = np.array(image).shape[0]
orininal_w = np.array(image).shape[1]
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data, nw, nh = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1],self.input_shape[0]))
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, np.float32)), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 图片传入网络进行预测
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = self.net(images)[0]
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 取出每一个像素点的种类
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = F.softmax(pr.permute(1,2,0),dim = -1).cpu().numpy()
print(pr)
#--------------------------------------#
# 将灰条部分截取掉
#--------------------------------------#
pr = pr[int((self.input_shape[0] - nh) // 2) : int((self.input_shape[0] - nh) // 2 + nh), \
int((self.input_shape[1] - nw) // 2) : int((self.input_shape[1] - nw) // 2 + nw)]
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 进行图片的resize
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = cv2.resize(pr, (orininal_w, orininal_h), interpolation = cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 取出每一个像素点的种类
#---------------------------------------------------#
pr = pr.argmax(axis=-1)
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(pr))
return image