Spark Core源代码分析: Spark任务运行模型
DAGScheduler
面向stage的调度层,为job生成以stage组成的DAG,提交TaskSet给TaskScheduler运行。
每个Stage内,都是独立的tasks,他们共同运行同一个compute function,享有同样的shuffledependencies。DAG在切分stage的时候是按照出现shuffle为界限的。
private[spark]
class DAGScheduler(
taskScheduler: TaskScheduler,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus,
mapOutputTracker: MapOutputTrackerMaster,
blockManagerMaster: BlockManagerMaster,
env: SparkEnv)
extends Logging {
// Actor模式收取发来的DAGSchedulerEvent,并进行processEvent private var eventProcessActor: ActorRef = _ private[scheduler] val nextJobId = new AtomicInteger(0) private[scheduler] def numTotalJobs: Int = nextJobId.get() private val nextStageId = new AtomicInteger(0) // 一系列信息维护,非常清晰 private[scheduler] val jobIdToStageIds = new HashMap[Int, HashSet[Int]] private[scheduler] val stageIdToJobIds = new HashMap[Int, HashSet[Int]] private[scheduler] val stageIdToStage = new HashMap[Int, Stage] private[scheduler] val shuffleToMapStage = new HashMap[Int, Stage] private[scheduler] val jobIdToActiveJob = new HashMap[Int, ActiveJob] private[scheduler] val resultStageToJob = new HashMap[Stage, ActiveJob] private[scheduler] val stageToInfos = new HashMap[Stage, StageInfo] // 不同状态stages的维护,非常清晰 // Stages we need to run whose parents aren't done private[scheduler] val waitingStages = new HashSet[Stage] // Stages we are running right now private[scheduler] val runningStages = new HashSet[Stage] // Stages that must be resubmitted due to fetch failures private[scheduler] val failedStages = new HashSet[Stage] // Missing tasks from each stage private[scheduler] val pendingTasks = new HashMap[Stage, HashSet[Task[_]]] private[scheduler] val activeJobs = new HashSet[ActiveJob] // Contains the locations that each RDD's partitions are cached on private val cacheLocs = new HashMap[Int, Array[Seq[TaskLocation]]]
在start()方法中会初始化Actor,然后接收DAGSchedulerEvent处理。Scheduler会在SparkContext里start起来。
Event处理
源代码的阅读入口:能够依据processEvent(event:DAGSchedulerEvent)方法展开。
处理的事件包含这么一些:
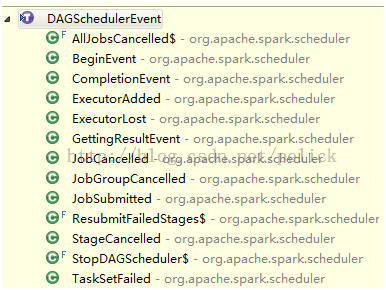
Submit Job
JobSubmitted事件:
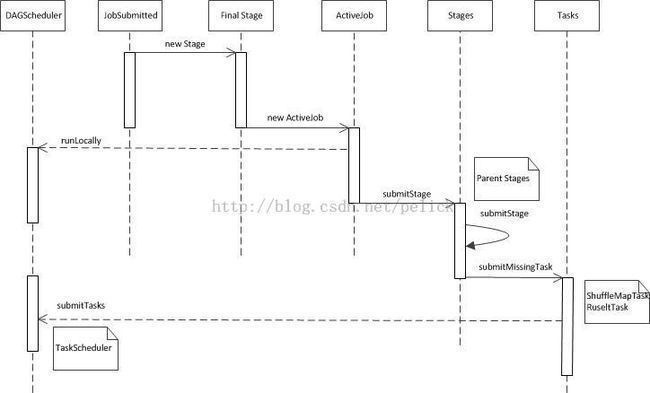
提交任务的事件传入參数例如以下
case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, allowLocal, callSite, listener, properties)
处理过程能够拆成三步看,每一步里面涉及的详细逻辑在以下补充展开
finalStage = newStage(rdd, partitions.size, None, jobId, Some(callSite))
本次newStage()操作能够相应新的result stage或者shuffle stage。返回Stage类(里面记录一些信息)。Stage类会传入Option[ShuffleDependency[_,_]]參数,内部有一个isShuffleMap变量,以标识该Stage是shuffle or result。
val job = new ActiveJob(jobId, finalStage, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)
ActiveJob类也是记录一些信息的类,能够当作是一个VO类
if (allowLocal && finalStage.parents.size == 0 && partitions.length == 1) {
// Compute very short actions like first() or take()
// with no parent stages locally.
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerJobStart(
job.jobId, Array[Int](), properties))
runLocally(job)
} else {
jobIdToActiveJob(jobId) = job
activeJobs += job
resultStageToJob(finalStage) = job
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerJobStart(
job.jobId, jobIdToStageIds(jobId).toArray, properties))
submitStage(finalStage)
}
首先推断stage没有父亲依赖,且partition为1的话,就运行本地任务。否则,submitStage。
submitStage的逻辑为,首先寻找本次stage的parents。假设没有missing的parent stage,那么就submitMissingTask,即提交本次stage的tasks了。假设有,会对parent stage进行递归submitStage,并且getMissingParentStages得到的结果集是按id降序排的,也就是说递归submitStage的时候会按parent stage的id顺序进行。
submitMissingTask处理的是stage的parent已经available的stage。主要逻辑例如以下:
第一步:通过stage.isShuffleMap来决定生成ShuffleMapTask还是ResultTask,生成的ShuffleMapTask数目和partition数目相等。
第二步:把生成的tasks组建成一个TaskSet,提交给TaskScheduler的submitTasks方法。
TaskScheduler
DAGScheduler以stage为单位,提tasks给TaskScheduer,实现类为TaskSchedulerImpl。
TaskSchedulerImpl几个内部部件:
SchedulerBackend
SchedulableBuilder
DAGScheduler
TaskSetManager
TaskResultGetter
Tasks信息(taskIdToTaskSetId,taskIdToExecutorId,activeExecutorIds)
别的信息(SchedulerMode)
TaskScheduler做接收task、接收分到的资源和executor、维护信息、与backend打交道、把任务分配好等事情。
start(),stop()的时候,backend的start(),stop()
submitTasks(TaskSet)逻辑:
为这批Task生成新的TaskSetManager,把TaskSetManager加到SchedulerBuilder里,然后向backend进行一次reviveOffer()操作。
SchedulerBuilder
SchedulableBuilder有FIFO和Fair两种实现, addTaskSetManager会把TaskSetManager加到pool里。FIFO的话仅仅有一个pool。Fair有多个pool,Pool也分FIFO和Fair两种模式。
SchedulableBuilder的rootPool里面能够新增pool或者TaskSetManager,两者都是Scheduable的继承类,所以SchedulableBuilder用于维护rootPool这棵Scheduable 树结构。Pool是树上的非叶子节点,而TaskSetManager就是叶子节点。
在TaskScheduler初始化的时候会buildDafaultPool。
TaskSetManager
TaskSetManager负责这批Tasks的启动,失败重试,感知本地化等事情。每次reourseOffer方法会寻找合适(符合条件execId, host, locality)的Task并启动它。
reourseOffer方法,
def resourceOffer(
execId: String,
host: String,
maxLocality: TaskLocality.TaskLocality)
寻找符合execId, host和locality的task,找到的话就启动这个Task。启动的时候,把task加到runningTask的HashSet里,然后调DAGScheduler的taskStarted方法,taskStarted方法向eventProcessorActor发出BeginEvent的DAGSchedulerEvent。
TaskResultGetter
维护一个线程池,用来反序列化和从远端获取task结果。
def enqueueSuccessfulTask(taskSetManager: TaskSetManager, tid: Long, serializedData: ByteBuffer)
把序列化的数据反序列化解析出来之后,有两种情况:直接可读的result和间接task result。
前者是DirectTaskResult[T]类:
class DirectTaskResult[T](var valueBytes: ByteBuffer, var accumUpdates: Map[Long, Any], var metrics: TaskMetrics)
后者是IndirectTaskResult[T]类:
case class IndirectTaskResult[T](blockId: BlockId) extends TaskResult[T] with Serializable
在反解析出IndirectTaskResult后,能够得到BlockId这个类,他的实现有这么些:

在TaskResultGetter里,会通过blockManager的getRemoteBytes(BlockId)方法来获得序列化的task result,对这个task result进行反解析后得到DirectTaskResult类,从而获得反序列化后的真正结果数据。
这是大致的一个过程,详细另一些细节在之中,比方会向scheduler发送不同的event、blockManager会调用BlockManagerMaster把该Block remove掉。
BlockId类有这么些关键变量:
private[spark] sealed abstract class BlockId {
/** A globally unique identifier for this Block. Can be used for ser/de. */
def name: String
// convenience methods
def asRDDId = if (isRDD) Some(asInstanceOf[RDDBlockId]) else None
def isRDD = isInstanceOf[RDDBlockId]
def isShuffle = isInstanceOf[ShuffleBlockId]
def isBroadcast = isInstanceOf[BroadcastBlockId]
以下看BlockManager怎样通过BlockId获得数据:
调用的是BlockManager的内部方法
private def doGetRemote(blockId: BlockId, asValues: Boolean): Option[Any] = {
require(blockId != null, "BlockId is null")
// 通过BlockManagerMaster获得这个blockId的locations
val locations = Random.shuffle(master.getLocations(blockId))
for (loc <- locations) {
logDebug("Getting remote block " + blockId + " from " + loc)
// 使用BlockManagerWorker来获得block的数据
val data = BlockManagerWorker.syncGetBlock(
GetBlock(blockId), ConnectionManagerId(loc.host, loc.port))
if (data != null) {
if (asValues) {
// 取到就返回
return Some(dataDeserialize(blockId, data))
} else {
return Some(data)
}
}
logDebug("The value of block " + blockId + " is null")
}
logDebug("Block " + blockId + " not found")
None
}
思路是通过BlockManagerMaster来获得block的位置信息,得到的集合打乱后,遍历位置信息,通过BlockManagerWorker去获得数据,仅仅要得到了,就反序列化之后返回。
在TaskResultGetter处理的时候,成功和失败分别向Scheduler调用handleSuccessfulTask和handleFailedTask方法。
handleSuccessfulTask在DAGScheduler里,会发出CompletionEvent事件,这一步结尾工作会有非常多细节处理,这里先不阅读了。
handleFailedTask的话,仅仅要TaskSetManager不是zombie,task没有被kill,那么会继续调用backend.reviveOffers()来re-run。
全文完 :)


