我们为什么需要WF
本文是[我们为什么需要工作流]的姊妹篇,我使了类似的文风,
我们为什么需要WF
以前有人对我说,WF很难用,明明很简单的一个功能,用WF去做却那么繁琐,
有这种想法,那我觉得有两种可能,
一,你要实现的这个功能确实太简单
二,你把这个功能的实现过程想的太简单
先看一组列子
这是一组非常简单的例子,分别是四个主题,分别代表程序发展的四个阶段
-
什么是程序
-
什么是具有控制流语句程序的控制流语句
-
什么是交互程序
-
什么是可视化交互程序
程序
程序是一连串指令的集合,
下面是一个技术算法的程序,
记得在89年的时候,我上小学5年级,那时我在PC1500上第一次用Basic写出了具有这个功能的程序.
那时候,每要做一次计算都要把程序再敲一遍,在我眼里,PC1500这个大家活还不如一个计算器
这是我那个Basic功能的C#版
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int x = 1; //加数 int y = 2; //被加数 int z = x + y; // 相加 System.Console.WriteLine(z); //在屏幕打印结果 } } |
具有控制流语句程序的控制流语句
控制流语句,
不久,我学会了一个很有意思的指今,他可以根据我设定的条件执行不同的代码,这时,我觉得PC1500这个大家活还有点意思.
这是我那个Basic功能的C#版
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string input = "123"; double temp ; bool b=double.TryParse(input,out temp);
if (b) { System.Console.WriteLine("你输入的数字是:{0}",temp); } else { System.Console.WriteLine("你输入的不是数字"); } }
} |
交互程序
交互程序,有用户参与的,用户可以在程序的预设点控制程序的执行
初中三年,由于家人认为"玩"电脑是不务正业,会耽误学习,到了高中,胆大了,又开始"完"电脑了,这时用的是386,
我学会了一门新语言FoxBase,他很神奇,可以等我输入点什么以后再继续执行
这是我那个FoxBase功能的C#版
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { while (true) { System.Console.WriteLine("要查看系统日期请按[y],按其它键退出程序"); string input = System.Console.ReadLine(); if (input == "y") { System.Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now); } else { return; } } } } |
可视化程序
可视化程序
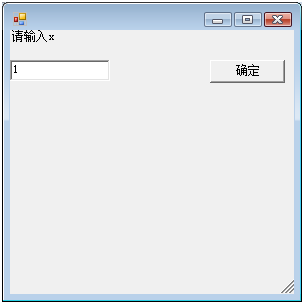
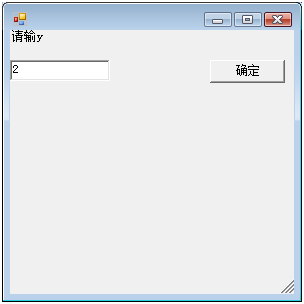
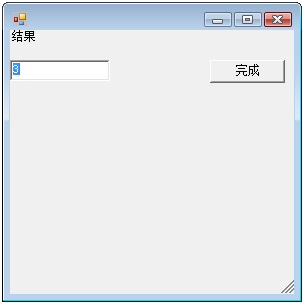
到了大学,虽然我学的是文科,但我对编程的热情依然没改,一次,我无意中接处到了VB,这是一个让我疯狂的语言,他竟然可以写出Windows中的窗口.
这是我那个VB功能的C#版
//数据模型 public class myData { public int x; public int y; } |
//数据操作 public static class myMaths { public static int add(myData data) { int z = data.x + data.y; return z; } } |
//展现1 public class windows1 : System.Windows.Forms.Form { System.Windows.Forms.Label title_label = new System.Windows.Forms.Label() { Text="请输入x"}; System.Windows.Forms.TextBox x_textBox = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox() { Top = 30 }; System.Windows.Forms.Button ok_button = new System.Windows.Forms.Button() { Text = "确定",Top = 30, Left = 200}; public string x; public windows1() { this.Controls.Add(title_label); this.Controls.Add(x_textBox); this.Controls.Add(ok_button); ok_button.Click += new EventHandler(ok_button_Click); } void ok_button_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { x = x_textBox.Text; this.Hide(); } } |
//展现2 public class windows2 : System.Windows.Forms.Form { System.Windows.Forms.Label title_label = new System.Windows.Forms.Label() { Text = "请输入y" }; System.Windows.Forms.TextBox y_textBox = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox() { Top = 30 }; System.Windows.Forms.Button ok_button = new System.Windows.Forms.Button() { Text = "确定", Top = 30, Left = 200 }; public string y; public windows2() { this.Controls.Add(title_label); this.Controls.Add(y_textBox); this.Controls.Add(ok_button); ok_button.Click += new EventHandler(ok_button_Click); } void ok_button_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { y = y_textBox.Text; this.Hide(); } } |
//展现3 public class windows3 : System.Windows.Forms.Form { System.Windows.Forms.Label title_label = new System.Windows.Forms.Label() { Text = "结果" }; System.Windows.Forms.TextBox z_textBox = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox() { Top = 30 }; System.Windows.Forms.Button ok_button = new System.Windows.Forms.Button() { Text = "完成", Top = 30, Left = 200 };
public void showValue(string s) { this.z_textBox.Text = s; }
public windows3() { this.Controls.Add(title_label); this.Controls.Add(z_textBox); this.Controls.Add(ok_button); ok_button.Click += new EventHandler(ok_button_Click); } void ok_button_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.Hide(); } } |
public class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { myControl(); }
static void myControl() { //初始化数据对象 myData data = new myData();
//-输入x windows1 w1 = new windows1(); w1.ShowDialog();
//-输入y windows2 w2 = new windows2(); w2.ShowDialog();
//-计算 data.y = int.Parse(w2.y); data.x = int.Parse(w1.x); int value; value = myMaths.add(data);
//-显示结果 windows3 w3 = new windows3(); w3.showValue(z.ToString()); w3.ShowDialog(); } } |
第一步
第二步
第三步
|
面向流程开发基于配运行的程序
大学毕业后,干了一段时间律师,觉得无聊,于是决定改行做程序员
VB,VC,ASP,VB.NET,C#,一直没的再遇到一个让我激动的技术,
2005年时,我正在参考Shark用NET实现一个工作流平台,这时我接触了WF, 那时WF还没集成到NET中,是一个WinFX的组件,看到WF我就喜欢上这个家伙了.
后来我建议放弃Shark的思路,用WF做工作流平台.公司里所有人都反对,于是在WF与公司间,我选择了WF.
下面是一个用WF实现上面例子中的控制部分
[数据模型],[数据操作],[展现1],[展现2],[展现3],保持不变
先创建一组功能Avtivity
public partial class 初始化数据对象: Activity { public 初始化数据对象() { InitializeComponent(); }
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCode] private void InitializeComponent() { this.Name = "初始化数据对象"; } protected override ActivityExecutionStatus Execute(ActivityExecutionContext executionContext) { this.data = new myData(); return base.Execute(executionContext); }
public static DependencyProperty dataProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("data", typeof(myData ), typeof(初始化数据对象));
[DescriptionAttribute("data")] [CategoryAttribute("data Category")] [BrowsableAttribute(true)] [DesignerSerializationVisibilityAttribute(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public myData data { get { return ((myData )(base.GetValue(初始化数据对象.dataProperty))); } set { base.SetValue(初始化数据对象.dataProperty, value); } } } |
|
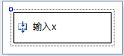
public partial class 输入x: Activity { public 输入x() { InitializeComponent(); }
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCode] private void InitializeComponent() { this.Name = "输入x"; }
protected override ActivityExecutionStatus Execute(ActivityExecutionContext executionContext) { windows1 w1 = new windows1(); w1.ShowDialog(); this.data.x= int.Parse(w1.x); return base.Execute(executionContext); } public static DependencyProperty dataProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("data", typeof(myData), typeof(输入x));
[DescriptionAttribute("data")] [CategoryAttribute("data Category")] [BrowsableAttribute(true)] [DesignerSerializationVisibilityAttribute(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public myData data { get { return ((myData)(base.GetValue(输入x.dataProperty))); } set { base.SetValue(输入x.dataProperty, value); } } } |
|
public partial class 输入y: Activity { public 输入y() { InitializeComponent(); }
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCode] private void InitializeComponent() { this.Name = "输入y"; }
protected override ActivityExecutionStatus Execute(ActivityExecutionContext executionContext) { windows2 w2 = new windows2(); w2.ShowDialog(); this.data.y = int.Parse(w2.y); return base.Execute(executionContext); }
public static DependencyProperty dataProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("data", typeof(myData), typeof(输入y));
[DescriptionAttribute("data")] [CategoryAttribute("data Category")] [BrowsableAttribute(true)] [DesignerSerializationVisibilityAttribute(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public myData data { get { return ((myData)(base.GetValue(输入y.dataProperty))); } set { base.SetValue(输入y.dataProperty, value); } }
} |
|
public partial class 计算: Activity { public 计算() { InitializeComponent(); }
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCode] private void InitializeComponent() { this.Name = "计算"; }
protected override ActivityExecutionStatus Execute(ActivityExecutionContext executionContext) { value = myMaths.add(data); return base.Execute(executionContext); }
public static DependencyProperty valueProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("value", typeof(int), typeof(计算));
[DescriptionAttribute("value")] [CategoryAttribute("value Category")] [BrowsableAttribute(true)] [DesignerSerializationVisibilityAttribute(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public int value { get { return ((int)(base.GetValue(计算.valueProperty))); } set { base.SetValue(计算.valueProperty, value); } }
public static DependencyProperty dataProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("data", typeof(myData), typeof(计算));
[DescriptionAttribute("data")] [CategoryAttribute("data Category")] [BrowsableAttribute(true)] [DesignerSerializationVisibilityAttribute(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public myData data { get { return ((myData)(base.GetValue(计算.dataProperty))); } set { base.SetValue(计算.dataProperty, value); } }
} |
|
public partial class 显示结果:Activity { public 显示结果() { InitializeComponent(); }
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCode] private void InitializeComponent() { this.Name = "显示结果"; } protected override ActivityExecutionStatus Execute(ActivityExecutionContext executionContext) { windows3 w3 = new windows3(); w3.showValue(value.ToString()); w3.ShowDialog(); return base.Execute(executionContext); } public static DependencyProperty valueProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("value", typeof(int), typeof(显示结果));
[DescriptionAttribute("value")] [CategoryAttribute("value Category")] [BrowsableAttribute(true)] [DesignerSerializationVisibilityAttribute(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public int value { get { return ((int)(base.GetValue(显示结果.valueProperty))); } set { base.SetValue(显示结果.valueProperty, value); } }
} |
创建控制流程
在WorkflowRuntime中创建实例,并运行实例
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { using(WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime()) { AutoResetEvent waitHandle = new AutoResetEvent(false); workflowRuntime.WorkflowCompleted += delegate(object sender, WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e) {waitHandle.Set();}; workflowRuntime.WorkflowTerminated += delegate(object sender, WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Exception.Message); waitHandle.Set(); };
WorkflowInstance instance = workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(typeof(example5.myWorkflow)); instance.Start();
waitHandle.WaitOne(); } } } |
|
为什么需要使用WF
下面,说一下为什么需要使用WF
说实话,我不是没见过世面,工作流的理轮,设计模式的理论我也学过一些
为什么需要使用WF,要实现流程控制我们也可用一些经典的设计模式去实现,比如下面的例子
职责链方式实现流程控制
引擎设计
//引擎 public class wfEngine { //实例池 protected System.Collections.SortedList InstancePool; public wfEngine() { InstancePool = new System.Collections.SortedList(); }
//添加实例到引擎 public string AddInstance(wfTemplet Instance) { InstancePool.Add(Instance.InstanceID, Instance.CurrentNode); return Instance.InstanceID; }
//工作流下移一结点 public bool ExecuteNextNode(string InstanceID) { if (InstancePool.Contains(InstanceID)) { if (((wfNode)InstancePool[InstanceID]).NextNode != null) { InstancePool[InstanceID] = ((wfNode)InstancePool[InstanceID]).execute(); return true; } else { ((wfNode)InstancePool[InstanceID]).execute(); InstancePool.Remove(InstanceID); return false; } } return false; }
// 一次执行完实例的所有结点 public void AutoExecute(string InstanceID) { while (ExecuteNextNode(InstanceID)) { AutoExecute(InstanceID); } }
//得到实例状态 public string getInstanceState(string InstanceID) { if (InstancePool.Contains(InstanceID)) { return ((wfNode)InstancePool[InstanceID]).NodeId; } return null; }
//得到引擎内的所有实例 public System.Collections.SortedList getInstances() { return this.InstancePool; } } |
工作流模板
//工作流模板 public class wfTemplet { public string InstanceID;//实例ID public wfTemplet(string InstanceID) { this.InstanceID = InstanceID; } public wfNode CurrentNode; } |
结点模板
//结点模板 public abstract class wfNode { public string InstanceId;//实例ID public string NodeId;//结点ID
public wfNode(string InstanceID, string NodeId) { this.InstanceId = InstanceID; this.NodeId = NodeId; }
//下一结点 public wfNode NextNode;
//执行区 public abstract wfNode execute(); } |
代码结点模板
//条件表达式类 public class conditionExpression { public object leftExpression;//左表达式 public object rightExpression;//右表达式
//比效方法 //可以跟据需要自定义左、右表达式,并重载比效运算符 public bool contrast() { if (leftExpression.Equals(rightExpression)) { return true; } else { return false; } } }
//条件结点模板类 public class conditionNode : wfNode { //构造函数 public conditionNode(string InstanceID, string NodeId) : base(InstanceID, NodeId) { }
public conditionExpression expression;//表达式对象 public wfNode ElseNode;//否则结点
//执行区 public override wfNode execute() { if (expression.contrast()) { return this.NextNode; } else { return this.ElseNode; } } } |
条件结点模板
//条件表达式类 public class conditionExpression { public object leftExpression;//左表达式 public object rightExpression;//右表达式
//比效方法 //可以跟据需要自定义左、右表达式,并重载比效运算符 public bool contrast() { if (leftExpression.Equals(rightExpression)) { return true; } else { return false; } } }
//条件结点模板类 public class conditionNode : wfNode { //构造函数 public conditionNode(string InstanceID, string NodeId) : base(InstanceID, NodeId) { }
public conditionExpression expression;//表达式对象 public wfNode ElseNode;//否则结点
//执行区 public override wfNode execute() { if (expression.contrast()) { return this.NextNode; } else { return this.ElseNode; } } } |
业务程流
public class 我的业务程流 : wfTemplet {
public codeNode 结点A; //结点A:代码结点 public conditionNode 结点B; //结点B:条件结点 public codeNode 结点C; //结点C:代码结点 public codeNode 结点D; //结点D:代码结点 public codeNode 结点E; //结点E:代码结点 public 我的业务程流(string InstanceID) : base(InstanceID) { /* * 结点A * | * | * 结点B * (true)/ \(false) * / \ * 结点C 结点D * \ / * \ / * 结点E */
//结点A:代码结点 结点A = new codeNode(this.InstanceID, "结点A"); 结点A.Code += new codeMethod(结点A_Code); 结点A.CodeParameter = "wxwinter的一个测试";
//结点B:条件结点 结点B = new conditionNode(this.InstanceID, "结点B");
//结点B的条件表达式 conditionExpression 条件表达式 = new conditionExpression();
结点B.expression = 条件表达式; //绑定条件表达式到结点B
//结点C:代码结点 结点C = new codeNode(this.InstanceID, "结点C"); 结点C.Code += new codeMethod(结点C_Code); 结点C.CodeParameter = "结点C,条件的真结点";
//结点D:代码结点 结点D = new codeNode(this.InstanceID, "结点D"); 结点D.Code += new codeMethod(结点D_Code); 结点D.CodeParameter = "结点D,条件的假结点";
//结点E:代码结点 结点E = new codeNode(this.InstanceID, "结点E"); 结点E.Code += new codeMethod(结点E_Code); 结点E.CodeParameter = "完成";
//指定入口结点 this.CurrentNode = 结点A;
//设置结点关系 结点A.NextNode = 结点B; 结点B.NextNode = 结点C; 结点B.ElseNode = 结点D; 结点C.NextNode = 结点E; 结点D.NextNode = 结点E; }
//结点A:代码 private void 结点A_Code(wfNode sender, object data) { Console.WriteLine("实例ID:" + sender.InstanceId + ":" + sender.NodeId + ":" + data.ToString()); }
//结点C:代码 private void 结点C_Code(wfNode sender, object data) { Console.WriteLine("实例ID:" + sender.InstanceId + ":" + sender.NodeId + ":" + data.ToString()); }
//结点B:代码 private void 结点D_Code(wfNode sender, object data) { Console.WriteLine("实例ID:" + sender.InstanceId + ":" + sender.NodeId + ":" + data.ToString()); }
//结点E:代码 private void 结点E_Code(wfNode sender, object data) { Console.WriteLine("实例ID:" + sender.InstanceId + ":" + sender.NodeId + ":" + data.ToString()); } } |
使用
class Program { static void Main() { wfEngine 引擎 = new wfEngine();
//实例03 我的业务程流 obj1 = new 我的业务程流("03"); obj1.结点B.expression.leftExpression = 100; obj1.结点B.expression.rightExpression = 100;
//实例04 我的业务程流 obj2 = new 我的业务程流("04"); obj2.结点B.expression.leftExpression = 99; obj2.结点B.expression.rightExpression = 100;
//将实例添加到引擎 引擎.AddInstance(obj1); 引擎.AddInstance(obj2);
while (true) { System.Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------"); System.Console.WriteLine("引擎中的实例:"); foreach (object obj in 引擎.getInstances().Keys) { string insID = obj.ToString(); string insStd = 引擎.getInstanceState(insID); System.Console.WriteLine(insID + ":" + insStd); } System.Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------"); System.Console.WriteLine("请输入要下一步的实例号:[exit为退出]");
string s = System.Console.ReadLine(); if (s == "exit") { break; } 引擎.ExecuteNextNode(s);
} }
} |
数据的持久化
光实现流程控制是不够的,我们还需要流程的持久化功能,这也不难,用如下方式就可以了
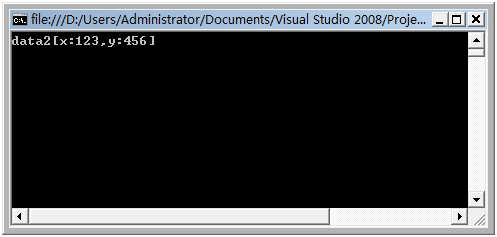
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { myData data1 = new myData(); data1.x = 123; data1.y = 456; data1.saveToFile(@"c:\data.xml");
myData data2 = new myData(); data2.loadFromFile(@"c:\data.xml"); System.Console.WriteLine("data2[x:{0},y:{1}]",data2.x,data2.y );
System.Console.Read(); } }
//数据 [System.Serializable] public class myData { public int x { get; set; }
public int y { get; set; }
public void saveToFile(string path) { System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer xs; xs = new System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer(typeof(myData)); System.IO.FileStream file = new System.IO.FileStream(path, System.IO.FileMode.Create); xs.Serialize(file, this); file.Flush(); file.Close(); }
public void loadFromFile(string path) { System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer xs; xs = new System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer(typeof(myData)); System.IO.FileStream file = new System.IO.FileStream(path, System.IO.FileMode.Open); myData data = (myData)xs.Deserialize(file); this.x = data.x; this.y = data.y; file.Close(); } } |
如果自已做,还要做些什么
为了修改方便,我们应该提供一个可以基于配置文件运行流程的接口,这个也可实现,当时我就已经做出来了
为了设计方便,我们应该提供一个可视化设计流程的UI,这个也可实现,当时我就已经做出来了
如果不是单机运行,我们还应该提供一个网络访问的接口,这个也可实现,当时我就已经做出来了
还有,流程可能要对数据库操作,我们应该提供一套事务处理案,
在这里,我遇到了问题,当时我的唯一选择是COM+,在用VB开发时,我就用COM+ ,
其实COM+并不好用,我一直想有一个DCOM 与 COM+ 结合的东西,而我当时的选择是COM+ 与 Remoting ,我不喜欢这个组合,
当时我想回到以前用VB开发DCOM的方式做,而组件事务部分就不要用,用传统的数据库事务.
这时,WF出现了,WF提供了上面我所说有全部功能,另外WF + WCF 的组合是我非常欢的(早期我的例子都是WF+ Remoting的,2007年后的例子都是WF+ WCF的)
而另一个成员WPF也不错,让我找到了xml + xslt 的感觉,对了,还有点 DHTML behaviors 的感觉,(跑题了,不说了)
总结
我们为什么需要WF,因为不选WF,有很多功能都要自己去实现,很麻烦
除非
一,你要实现的这个功能确实太简单
二,你把这个功能的实现过程想的太简单