bert源码解析-modeling.py
bert源码解析-modeling.py
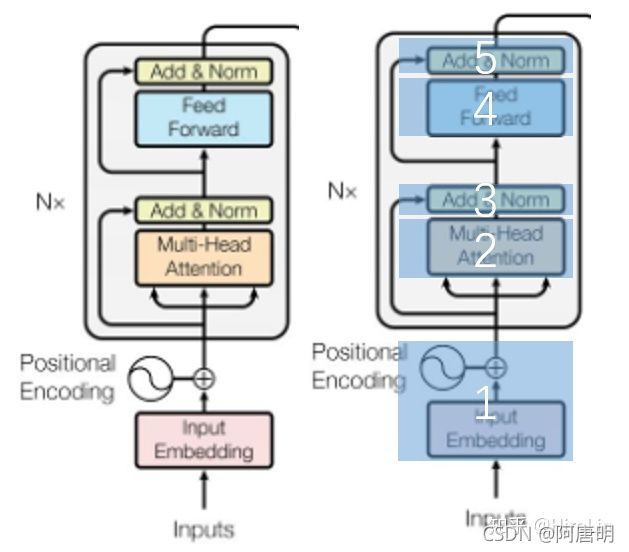
bert是transformer的encoder部分,以google-bert源代码为例。
由两个重要的class组成:
1.BertConfig 大多时候改动的参数并不多,知晓这些参数可以便于推算模型的大小,比如隐藏层大小768
class BertConfig(object):
def __init__(self,
vocab_size,
hidden_size=768,
num_hidden_layers=12,
num_attention_heads=12,
intermediate_size=3072,
hidden_act="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
max_position_embeddings=512,
type_vocab_size=16,
initializer_range=0.02):
"""
构造参数
:param vocab_size: 词汇量大小
:param hidden_size: 隐藏层输出大小
:param num_hidden_layers: 隐藏层单元层数
:param num_attention_heads: 注意力模块个数
:param intermediate_size: 中间层输出大小 用于前向传播时 由hidden_size->intermediate_size
:param hidden_act: 隐藏层激活函数
:param hidden_dropout_prob: 隐藏层dropout
:param attention_probs_dropout_prob: 注意力部分dropout
:param max_position_embeddings: 位置编码最大值默认是512
:param type_vocab_size: token_type_ids的词典大小,用于句子上下句是否是同一个用的标识,默认是大小是2 也就是用0或1表示
:param initializer_range: 初始化方法的范围
"""
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
2.BertModel 模型部分
模型部分主要分成三个部分说明,对应的可以看transformer单个block的结构。
从初始化方法__init__开始说明 初始化定义:
config 即上述BertConfig is_training 判断是否是训练,如果不是训练则不需要进行dropout,因为dropout是为了避免训练过程过拟合 input_ids 输入句子的数字化表示,例如源代码注释 tf.constant([[31, 51, 99], [15, 5, 0]]) input_mask 表示该位置是否有数字,长度和input_ids一致 token_type_ids 字的type use_one_hot_embeddings 输入初始化词是否使用独热编码 scope tf变量作用域的名称,默认是“bert”
初始化三个输入: input_shape 大小是的[batch_size, seq_length] input_mask 大小是的[batch_size, seq_length] token_type_ids 大小是的[batch_size, seq_length]
主要结构如下,一个个来介绍。
- 声明变量作用域(“bert”)
- 变量作用域(“embeddings”)
- 词嵌入
- 位置编码及mask编码
- 变量作用域(“encoder”)
- 变量作用域(“pooler”)
(1)embedding-词嵌入
①初始化词嵌入矩阵 矩阵大小及 [vocab_size, embedding_size] 词表大小*词向量维度
②输入input_ids拍平和嵌入矩阵相乘得到输入的嵌入矩阵,再reshape成[batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]输出。
详细注释如下:
def embedding_lookup(input_ids,
vocab_size,
embedding_size=128,
initializer_range=0.02,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=False):
"""
获取词嵌入
:param input_ids: 输入词的id
:param vocab_size: 词典大小
:param embedding_size: 词嵌入输出维度
:param initializer_range: 生成截断正态分布的初始化的标准差
:param word_embedding_name: 词嵌入再网络中的name
:param use_one_hot_embeddings: 判断是使用何种初始编码方式,one-hot或tf.gather
:return:
"""
#如果输入大小是[batch_size, seq_length]
#如果输入是二维的 reshape成三维[batch_size, seq_length, 1]
if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2:
input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1])
#这个矩阵大小就是[vocab_size, embedding_size] 那么每个词都可以通过one-hot获取到其对应的嵌入矩阵
embedding_table = tf.get_variable(
name=word_embedding_name,
shape=[vocab_size, embedding_size],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
#输入id reshape 成一维 例如[[1,2],[3,4]]=>[1,2,3,4]
flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1])
#获取输出矩阵 两种方式
#1.用one-hot与embedding_table相乘得到嵌入矩阵
#2.tf.gather直接切片提取
#得到output是(batch_size * seq_length) * embedding_size
if use_one_hot_embeddings:
one_hot_input_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_input_ids, depth=vocab_size)
output = tf.matmul(one_hot_input_ids, embedding_table)
else:
output = tf.gather(embedding_table, flat_input_ids)
#获取input_ids的 [batch_size, seq_length]
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids)
#reshape的尺寸input_shape[0:-1]是[batch_size, seq_length] + 1*embedding_size
#所以输出是[batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]
output = tf.reshape(output,
input_shape[0:-1] + [input_shape[-1] * embedding_size])
return (output, embedding_table)
(2)embedding-位置编码及mask编码
①token type 用于标识当前字的类型,比如上下句标识。“小明爱学习,小林爱学习”标识上下句[0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1] bert-chinese模型默认大小为2
token_type_ids 输入大小是 [batch_size, seq_length],对应的嵌入矩阵是[token_type_vocab_size, embedding_size]
输入拍平之后和嵌入矩阵相乘在reshape得到[batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]直接和词嵌入相加
②use_position_embeddings 位置编码,因为注意力机制部分没有位置信息,所以输入时候单独添加,注意!!bert的位置是通过参数学习的,不是使用sin cos组合得到。
初始化嵌入矩阵 大小为[max_position_embeddings, embedding]
根据seq_length直接截取前seq_length即可,但是此时矩阵大小是[seq_length,embedding ]
因为每个batch使用相同的位置向量,为了能直接相加,进行广播到batch size 得到[batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]
和上述output相加
③接入layer_norm_and_dropout 输出
详细注释如下:
def embedding_postprocessor(input_tensor,
use_token_type=False,
token_type_ids=None,
token_type_vocab_size=16,
token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings",
use_position_embeddings=True,
position_embedding_name="position_embeddings",
initializer_range=0.02,
max_position_embeddings=512,
dropout_prob=0.1):
"""
:param input_tensor: 输入id对应的词嵌入矩阵
:param use_token_type: 是否使用type
:param token_type_ids: type对应的ids数组
:param token_type_vocab_size: 表示token type的大小,比如在中文bert模型使用0或1标识上下句关系,则大小为2.
:param token_type_embedding_name: token type的嵌入层name
:param use_position_embeddings: 是否使用位置编码
:param position_embedding_name: 位置编码层name
:param initializer_range: 生成截断正态分布的初始化的标准差
:param max_position_embeddings: 最大位置编码长度
:param dropout_prob: dropout的大小,用于输出时的layer_norm_and_dropout
:return:
"""
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
width = input_shape[2]
output = input_tensor
#token_type_vocab_size在 bert-chinese中默认值是2 SegmentPosition信息分离上句和下句
if use_token_type:
if token_type_ids is None:
raise ValueError("`token_type_ids` must be specified if"
"`use_token_type` is True.")
token_type_table = tf.get_variable(
name=token_type_embedding_name,
shape=[token_type_vocab_size, width],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
#token_type_ids 大小是 [batch_size, seq_length]
#flat_token_type_ids 矩阵拍平,此处类似上面embedding做法,得到SegmentPosition嵌入矩阵
flat_token_type_ids = tf.reshape(token_type_ids, [-1])
one_hot_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_token_type_ids, depth=token_type_vocab_size)
token_type_embeddings = tf.matmul(one_hot_ids, token_type_table)
token_type_embeddings = tf.reshape(token_type_embeddings,
[batch_size, seq_length, width])
#将Segment position信息叠加到词向量
output += token_type_embeddings
#Position embedding信息 位置编码
if use_position_embeddings:
assert_op = tf.assert_less_equal(seq_length, max_position_embeddings)
with tf.control_dependencies([assert_op]):
#full_position_embeddings 尺寸大小是中文base bert模型是512 * 768,因为位置编码最大值是512,每个嵌入大小是768
full_position_embeddings = tf.get_variable(
name=position_embedding_name,
shape=[max_position_embeddings, width],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
#获取词嵌入矩阵,这里因为是单纯的顺序所以不需要乘法,直接slice获取前seq_length长度的向量即可
position_embeddings = tf.slice(full_position_embeddings, [0, 0],
[seq_length, -1])
num_dims = len(output.shape.as_list())
# 因为token type和词嵌入都是大小 batch_size,seq_length,embedding 可以直接相加
# 但是position_embeddings是seq_length,embedding,因为每个batch使用相同的位置向量,为了能直接相加,进行广播到batch size
position_broadcast_shape = []
for _ in range(num_dims - 2):
position_broadcast_shape.append(1)
position_broadcast_shape.extend([seq_length, width])
position_embeddings = tf.reshape(position_embeddings,
position_broadcast_shape)
output += position_embeddings
#进行layer norm和dropout
output = layer_norm_and_dropout(output, dropout_prob)
return output
(3)encoder主体部分
attention_mask 需要通过mask矩阵得到哪些位置有词,例如seq_length=10,但是输入时"小明爱学习"那么mask[1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0]
# 用于计算 attention分数,需要通过mask矩阵得到哪些位置有词,例如seq_length=10,但是输入时"小明爱学习"那么mask[1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0]
attention_mask = create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(
input_ids, input_mask)
创建attention_model 例如这里num_hidden_layers=12个
- 循环12次:
- attention_layer attention_layer方法见下面
- 增加一个全连接层,构建残差网络将输入加到attention输出,再进行layer_norm
- 前向传播 例如Chinese-bert参数 786-》768*4-》768再进行残差网络,再layer_norm
- 确认是否返回全部层数据,或者只返回最后一层
详细注释如下:
def transformer_model(input_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
hidden_size=768,
num_hidden_layers=12,
num_attention_heads=12,
intermediate_size=3072,
intermediate_act_fn=gelu,
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_all_layers=False):
"""
:param input_tensor: 输入融合之后向量输入
:param attention_mask:mask矩阵用于表示当前词是否有值
:param hidden_size: 隐藏层输出大小
:param num_hidden_layers: 主体部分层数
:param num_attention_heads: 多头注意力机制个数
:param intermediate_size: 中间层输出大小(attention之后的全连接层)
:param intermediate_act_fn: 中间层激活函数
:param hidden_dropout_prob: 隐藏层dropout
:param attention_probs_dropout_prob: 注意力部分dropout
:param initializer_range:
:param do_return_all_layers: 是否需要返回所有层
:return:
"""
#因为多头是直接从hidden_size均分,所以一定是整除的
if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention "
"heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads))
attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads)
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
input_width = input_shape[2]
# The Transformer performs sum residuals on all layers so the input needs
# to be the same as the hidden size.
if input_width != hidden_size:
raise ValueError("The width of the input tensor (%d) != hidden size (%d)" %
(input_width, hidden_size))
#我们将表示保留为2D张量,以避免将其从3D张量来回整形为2D张量。
# 重构在GPU/CPU上通常是免费的,但在TPU上可能不是免费的,因此我们希望最小化它们以帮助优化器。
#看起来是便于在tpu处理
prev_output = reshape_to_matrix(input_tensor)
all_layer_outputs = []
for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers):
with tf.variable_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx):
#prev_output保存最新一层得输出
layer_input = prev_output
with tf.variable_scope("attention"):
attention_heads = []
with tf.variable_scope("self"):
attention_head = attention_layer(
from_tensor=layer_input,
to_tensor=layer_input,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
size_per_head=attention_head_size,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=initializer_range,
do_return_2d_tensor=True,
batch_size=batch_size,
from_seq_length=seq_length,
to_seq_length=seq_length)
attention_heads.append(attention_head)
attention_output = None
if len(attention_heads) == 1:
attention_output = attention_heads[0]
else:
# In the case where we have other sequences, we just concatenate
# them to the self-attention head before the projection.
attention_output = tf.concat(attention_heads, axis=-1)
# 增加一个全连接层,构建残差网络将输入加到attention输出,再进行layer_norm
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
attention_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input)
# 前向传播 例如Chinese-bert参数 786-》768*4-》768再进行残差网络,再layer_norm
with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"):
intermediate_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
intermediate_size,
activation=intermediate_act_fn,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
layer_output = tf.layers.dense(
intermediate_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
layer_output = dropout(layer_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
layer_output = layer_norm(layer_output + attention_output)
prev_output = layer_output
all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output)
#确认是否返回全部层数据,或者只返回最后一层
if do_return_all_layers:
final_outputs = []
for layer_output in all_layer_outputs:
final_output = reshape_from_matrix(layer_output, input_shape)
final_outputs.append(final_output)
return final_outputs
else:
final_output = reshape_from_matrix(prev_output, input_shape)
return final_output
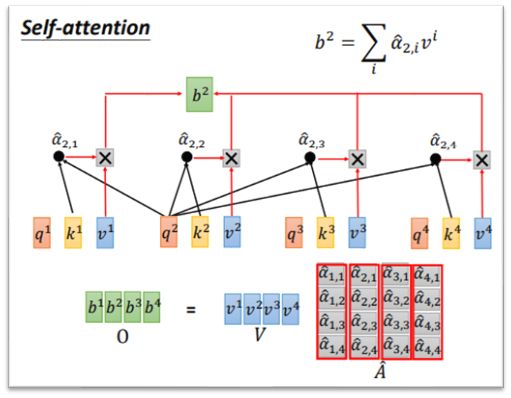
attention_layer方法
1.计算q,k,v,计算方式输入其实都是根据词嵌入融合的结果得来。
2.将query 和 key进行点乘得到scores,然后除以根号d tf.multiply是两个矩阵中对应元素各自相乘,将每个值乘以根号d。
3.attention_mask为什么?这里给mask部分一个很大负数,为什么呢,因为再进行softmax时候,如果改值是0,那么e得0次幂是1,势必会影响,如果是一个很大的负数,那么e的负数次幂=0,则相关性求softmax接近0。
4.归一化 输入到一个softmax 得到相关程度矩阵。
5.获取value值,将相关性矩阵attention_scores [B, N, F, T]和value [B, N, T, H]相乘。
def attention_layer(from_tensor,
to_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
num_attention_heads=1,
size_per_head=512,
query_act=None,
key_act=None,
value_act=None,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_2d_tensor=False,
batch_size=None,
from_seq_length=None,
to_seq_length=None):
"""
:param from_tensor: 第一步词向量融合输入
:param to_tensor: 第一步词向量融合输入
:param attention_mask: mask矩阵用于表示当前词是否有值
:param num_attention_heads: 多头个数例如12
:param size_per_head: 每个头的大小 例如768//12=64
:param key_act:
:param value_act:
:param attention_probs_dropout_prob:
:param initializer_range:
:param do_return_2d_tensor:
:param batch_size:
:param from_seq_length:
:param to_seq_length:
:return:
"""
def transpose_for_scores(input_tensor, batch_size, num_attention_heads,
seq_length, width):
output_tensor = tf.reshape(
input_tensor, [batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads, width])
output_tensor = tf.transpose(output_tensor, [0, 2, 1, 3])
return output_tensor
from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
to_shape = get_shape_list(to_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
if len(from_shape) != len(to_shape):
raise ValueError(
"The rank of `from_tensor` must match the rank of `to_tensor`.")
if len(from_shape) == 3:
batch_size = from_shape[0]
from_seq_length = from_shape[1]
to_seq_length = to_shape[1]
elif len(from_shape) == 2:
if (batch_size is None or from_seq_length is None or to_seq_length is None):
raise ValueError(
"When passing in rank 2 tensors to attention_layer, the values "
"for `batch_size`, `from_seq_length`, and `to_seq_length` "
"must all be specified.")
# Scalar dimensions referenced here:
# B = batch size (number of sequences)
# F = `from_tensor` sequence length
# T = `to_tensor` sequence length
# N = `num_attention_heads`
# H = `size_per_head`
from_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(from_tensor)
to_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(to_tensor)
#计算q,k,v,计算方式输入其实都是根据词嵌入融合的结果得来的
#输入是batch_size*sequence_length 输出大小是num_attention_heads*size_per_head 其实就是hidden_size 768
#相同的方式得到q, k, v
# `query_layer` = [B*F, N*H]
query_layer = tf.layers.dense(
from_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=query_act,
name="query",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `key_layer` = [B*T, N*H]
key_layer = tf.layers.dense(
to_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=key_act,
name="key",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `value_layer` = [B*T, N*H]
value_layer = tf.layers.dense(
to_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=value_act,
name="value",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
#这里对原始结构进行位置更换,原始:[batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads, width]
#变换方式是[0, 2, 1, 3]
#变换之后的是 [batch_size, num_attention_heads, seq_length, size_per_head]
#key 相同的处理方式
# `query_layer` = [B, N, F, H]
query_layer = transpose_for_scores(query_layer, batch_size,
num_attention_heads, from_seq_length,
size_per_head)
# `key_layer` = [B, N, T, H]
key_layer = transpose_for_scores(key_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads,
to_seq_length, size_per_head)
#将query 和 key进行点乘得到scores
#然后除以根号d tf.multiply是两个矩阵中对应元素各自相乘,将每个值乘以根号d
#矩阵大小是[batch_size, num_attention_heads, seq_length, seq_length]
# `attention_scores` = [B, N, F, T]
attention_scores = tf.matmul(query_layer, key_layer, transpose_b=True)
attention_scores = tf.multiply(attention_scores,
1.0 / math.sqrt(float(size_per_head)))
#这里给mask部分一个很大负数,为什么呢,因为再进行softmax时候,如果改值是0,那么e得0次幂是1,势必会影响,如果是一个很大的负数,
#那么e的负数次幂=0,则相关性求softmax接近0
if attention_mask is not None:
# `attention_mask` = [B, 1, F, T]
attention_mask = tf.expand_dims(attention_mask, axis=[1])
# Since attention_mask is 1.0 for positions we want to attend and 0.0 for
# masked positions, this operation will create a tensor which is 0.0 for
# positions we want to attend and -10000.0 for masked positions.
adder = (1.0 - tf.cast(attention_mask, tf.float32)) * -10000.0
# Since we are adding it to the raw scores before the softmax, this is
# effectively the same as removing these entirely.
attention_scores += adder
# 归一化 输入到一个softmax 得到相关程度矩阵
# `attention_probs` = [B, N, F, T]
attention_probs = tf.nn.softmax(attention_scores)
# 是否需要对所有的字符都进行处理,dropout丢失一些
attention_probs = dropout(attention_probs, attention_probs_dropout_prob)
#获取value值
# `value_layer` = [B, T, N, H]
value_layer = tf.reshape(
value_layer,
[batch_size, to_seq_length, num_attention_heads, size_per_head])
# `value_layer` = [B, N, T, H]
value_layer = tf.transpose(value_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3])
#将相关性矩阵[B, N, F, T]和value[B, N, T, H]相乘
# `context_layer` = [B, N, F, H]
context_layer = tf.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
# `context_layer` = [B, F, N, H]
context_layer = tf.transpose(context_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3])
#这里[B, F, N*H] 即[batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads*hidden_size]
if do_return_2d_tensor:
# `context_layer` = [B*F, N*H]
context_layer = tf.reshape(
context_layer,
[batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head])
else:
# `context_layer` = [B, F, N*H]
context_layer = tf.reshape(
context_layer,
[batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head])
return context_layer
(3)pooler
只提取第一个token对应的向量,因为每一个token其实已经学习到其他所有的信息。
with tf.variable_scope("pooler"):
# 只提取第一个token对应的向量,因为每一个token其实已经学习到其他所有的信息。
# 再链接一个全连接层输出大小 [batch_size, hidden_size]
first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1)
self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense(
first_token_tensor,
config.hidden_size,
activation=tf.tanh,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range))