MySQL高级知识(九)——order by优化
MySQL高级知识(九)——order by优化
- 准备
- 案例
- 总结
此博客的内容主要来源于尚硅谷的视频中,在此记录,以备以后自己查看。
准备
- 创建test表
drop table if exists test;
create table test(
id int primary key auto_increment,
c1 varchar(10),
c2 varchar(10),
c3 varchar(10),
c4 varchar(10),
c5 varchar(10)
) ENGINE=INNODB default CHARSET=utf8;
insert into test(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values('a1','a2','a3','a4','a5');
insert into test(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values('b1','b2','b3','b4','b5');
insert into test(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values('c1','c2','c3','c4','c5');
insert into test(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values('d1','d2','d3','d4','d5');
insert into test(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values('e1','e2','e3','e4','e5');
select * from test;
- 创建索引
create index idx_test_c1234 on test(c1,c2,c3,c4);
show index from test;
案例
- 案例1
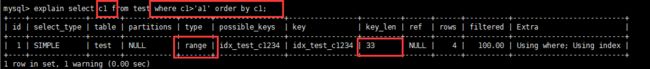
explain select * from test where c1>'a1' order by c1;
分析:
-
在c1,c2,c3,c4上创建了索引,直接在c1上使用范围,导致了索引失效,全表扫描:type=ALL,ref=Null。因为此时c1主要用于排序,并不是查询。
-
使用c1进行排序,出现了Using filesort。
-
解决方法:使用覆盖索引。
- 案例1.1
explain select c1 from test where c1>'a1' order by c1,c2;
分析:
- 排序时按照索引的顺序,所以不会出现Using filesort。
- 案例1.2
explain select c1 from test where c1>'a1' order by c2;
分析:
- 出现了Using filesort。原因:排序用的c2,与索引的创建顺序不一致,对比Case1.1可知,排序时少了c1(带头大哥),因此出现Using filesort。
- 案例1.3
explain select c1 from test where c1>'a1' order by c2,c1;
分析:
- 出现了Using filesort。因为排序索引列与索引创建的顺序相反,从而产生了重排,也就出现了Using filesort。
- 案例2
explain select c1 from test order by c2;
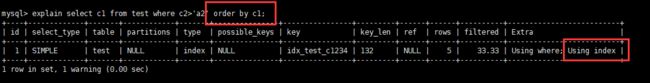
explain select c1 from test where c2>'a2' order by c2;
- 直接使用c2进行排序,出现Using filesort,因为不是从最左列索引开始排序的(没有带头大哥)。
- 案例2.1
explain select c1 from test where c2>'a2' order by c1;
- 排序使用了索引顺序(带头大哥在),因此不会出现Using filesort。
- 案例2.2
explain select c1 from test order by c1, c2;
explain select c1 from test order by c1 asc, c2 desc;
explain select c1 from test order by c1 desc, c2 desc;
-
order by默认升序
-
虽然排序的字段列与索引顺序一样,所有的排序字段的升降必须和带头大哥一样,否则会出现Using filesort。
总结
-
MySQL支持两种方式的排序filesort和index,Using index是指MySQL扫描索引本身完成排序。index效率高,filesort效率低。
-
order by满足两种情况会使用Using index。
-
order by语句使用索引最左前列准则
-
尽量在索引列上完成排序,遵循索引建立(索引创建的顺序)时的最佳左前缀法则。
-
使用where子句与order by子句条件组合满足最左前列
-
where子句中如果出现索引的范围查询(即explain中出现range)会导致order by 索引失效。
-
为排序使用索引:
- MySQL两种排序方式:
- 文件排序
- 扫描有序索引排序
- MySQL能为排序与查询使用相同的索引
KEY a_b_c(a,b,c)
- order by 能使用索引最左前缀
- order by a
- order by a,b
- order by a,b,c
- order by a desc,b desc, c desc
- 如果where使用索引的最左前缀定义常量,则order by能使用索引
- where a = const order by b,c
- where a = const and b = const order by c
- where a = const and b> const order by b,c
- 不能使用索引进行排序
- order by a asc, b desc, c desc #排序不一致
- where g = const order by b,c #丢失a索引
- where a = const order by c #丢失b索引
- where a = const order by a,d #d不是索引的一部分
- where a in (…) order by b,c #对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询
如果不在索引列上做排序,则filesort有两种算法:双路排序和单路排序
- 双路排序:
- 在MySQL4.1之前使用双路排序,就是两次磁盘扫描,得到最终数据。读取行指针和order by列,对他们进行排序,然后扫描已经排好序的列表,按照列表中的值重新从列表中读取对应的数据输出。即从磁盘中读取排序字段,在buffer进行排序,再从磁盘中取其他字段。
- 如果使用双路排序,取一批数据要对磁盘进行两次扫描,众所周知,I/O操作是很耗时的,因此在MySQL4.1以后,出现了改进的算法:单路排序
- 单路排序:
- 从磁盘中查询所需要的列,按照order by列在buffer中对他们进行排序,然后扫描排序后的列表进行输出。他的效率更高一点,避免了第二次读取数据,并且把随机I/O变成了顺序I/O,但是会使用更多的空间,因为它把每一行都保存在了内存中。
- 当读取数据超过sort_bufffer的容量时,就会导致多次读取数据,并创建临时表,最后多路合并,产生多次I/O,反而增加其I/O运算。
解决方式:
- 增加sort_buffer_size参数的设置——用于单路排序的内存大小
- 增大max_length_for_sort_data参数的设置——单单次排序字段大小
- 去掉select后面不需要的字段——select 后的多了,排序的时候也会带着一起,很占内存,所以去掉没有用的
- 提升order by速度的方式:
- 在使用order by时候,不要用select * ,只查询所需要的字段。
- 尝试提高sort_buffer_size。
- 尝试提高max_length_for_sort_data。
- group by与order by很类似,其实质是先排序后分组,遵照索引创建顺序的最佳左前缀法则。当无法使用索引列的时候,也要对sort_buffer_size和max_length_for_sort_data参数进行调整。注意where高于having,能写在where中的限定条件就不要去having限定了。