【数据结构】——优先级队列(堆)
一、概念
在一些情况下,操作的数据可能带有优先级,一般出队列时,可能需要优先级高的元素出队;在这种的情况下,就可以使用优先级队列:返回最高优先级对象和添加新的对象。
堆的性质:
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或小于其父亲节点的值
- 堆总是一颗完全二叉树
二、优先级队列的实现
顺序存储实现堆:
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem = new int[10];
this.usedSize = 0;
}
public void initArray(int[] array){
elem = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
usedSize = elem.length;
}建大根堆:
/**
* 建堆[大根堆]
*/
public void createHeap(){
for (int parent = (usedSize-1-1)/2; parent >= 0; parent--) {
shiftDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
/**
* 实现向下调整
* @param parent 每颗子树的根结点的下标
* @param len
*/
private void shiftDown(int parent,int len){
int child = 2*parent+1;
//最起码有左孩子
while(child < len){
//判断左右孩子谁最大,前提 必须有右孩子
if (child+1 < len&& elem[child] < elem[child+1]){
child++;//此时保留了最大值下标
}
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]){
swap(elem,child,parent);
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] array,int i,int j){
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
入队:
public void offer(int x){
if (isFull()){
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem, elem.length*2);
}
this.elem[usedSize] = x;
usedSize++;
shiftUp(usedSize-1);
}
private void shiftUp(int child) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0) {
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]) {
swap(elem, child, parent);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
private boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}删除:
//优先级队列的删除 只能删除堆顶的元素
public int poll(){
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int old = elem[0];
swap(elem,0,usedSize-1);
usedSize--;
shiftDown(0,usedSize);
return old;
}
private boolean isEmpty(){
return usedSize == 0;
}三、常用接口的介绍
Java集合框架中提供了PriorityQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue两种类型的优先级队列,PriorityQueue是线程不安全的,PriorityBlockingQueue是线程安全的,本文主要介绍PriorityQueue。
使用PriorityQueue的使用注意:
- 使用时必须要导入PriorityQueue所在的包:

- PriorityQueue中放置的元素必须要能够比较大小,不能插入无法比较大小的对象,否则会出ClassCastException异常
- 不能插入null对象,否则会抛出NullPointerException
- 没有容量限制,可以插入任意多个元素,其内部可以自动扩容
- 插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为
- PriorityQueue底层使用了堆数据结构
- PriorityQueue默认情况下是小堆---即每次获取到的元素都是最小的元素
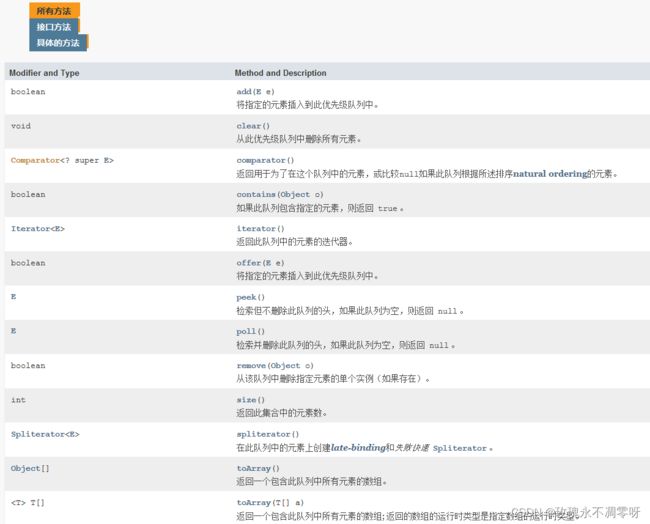
接口的介绍:
- 优先级队列的应用:面试题 17.14. 最小K个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路一:
- 把数据全部放到一个小根堆当中,堆顶元素就是最小值
- 出队k次,就能找到k个最小的值,每出队一次就会重新调整为小根堆,时间复杂度为O(n^2).
public class Test {
public static void topK1(int[] array,int k){
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
priorityQueue.offer(array[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int val = priorityQueue.poll();
System.out.print(val+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,45,32,17,2,18,5,10};
topK1(array,3);
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
TestHeap testHeap = new TestHeap();
int[] array = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};
testHeap.initArray(array);
testHeap.createHeap();
testHeap.offer(100);
System.out.println();
}
}
思路二:
- 建立一个只有k个元素的大根堆,入队数组的前k个元素,此时堆顶元素就是最大的元素,
- 然后再遍历数组剩下的元素,如果小于堆顶元素,就交换,,再调整为大根堆
- 遍历完数组之后,大根堆里就是前k个最小的元素
class Solution {
public int[] smallestK(int[] array, int k) {
int[] ret = new int[k];
if(k == 0){
return ret;
}
PriorityQueue maxPq = new PriorityQueue<>(k,new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (maxPq.size() < k){
maxPq.offer(array[i]);
}else {
int top = maxPq.peek();
if (array[i] < top){
maxPq.poll();
maxPq.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int val = maxPq.poll();
ret[i] = val;
}
return ret;
}
} 大根堆实现从小到大排序:
/**
* 实现向下调整
* @param parent 每颗子树的根结点的下标
* @param len
*/
private void shiftDown(int parent,int len){
int child = 2*parent+1;
//最起码有左孩子
while(child < len){
//判断左右孩子谁最大,前提 必须有右孩子
if (child+1 < len && elem[child] < elem[child+1]){
child++;//此时保留了最大值下标
}
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]){
swap(elem,child,parent);
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] array,int i,int j){
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
public void heapSort(){
int end = usedSize-1;
while (end > 0){
swap(elem,0,end);
shiftDown(0,end);
end--;
}
}