数独 C++版
上两篇用C#写了数独构造与求解的程序,不过我还是喜欢用C++实现,所以又将程序用C++实现了一下,至于方法什么的就不再重复了,见上两篇博文
一下是程序的一些关键代码
将每一小格抽象为一个对象:
Cell.h
#ifndef GUARD_Cell_h #define GUARD_Cell_h #include "Coord.h" #include <list> class Cell { public: Cell(int x=0,int y=0); bool IsProcessed() const; int X() const; int Y() const; void SetX(int x); void SetY(int y); void AddNextValidNumber(int number); void PickNextValidNumber(); void Clear(); bool IsvalidListEmpty() const; int number; private: Coord coord; bool isProcessed; std::list<int> validList; }; #endif
实现过程Cell.cpp
#include "Cell.h" Cell::Cell(int x,int y) :isProcessed(false),number(0) { coord.X=x; coord.Y=y; } bool Cell::IsProcessed() const { return isProcessed; } int Cell::X() const { return coord.X; } int Cell::Y() const { return coord.Y; } void Cell::SetX(int x) { coord.X=x; } void Cell::SetY(int y) { coord.Y=y; } bool Cell::IsvalidListEmpty() const { return validList.empty(); } void Cell::AddNextValidNumber(int number) { validList.push_back(number); } void Cell::PickNextValidNumber() { //取得下一个数字 int nextValidNumber=validList.front(); //在链表中移去该数字 validList.pop_front(); number=nextValidNumber; isProcessed=true; //这里不要忘了 } void Cell::Clear() { validList.clear(); number=0; isProcessed=false; }
将9*9的表格抽象为一个对象
实现Table.cpp
#include "Table.h" #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; //const int Table::TableSize; Table::Table() { table=new Cell[TableSize][TableSize]; Table::InitTable(); } void Table::GenerateValidMatrix() { Coord currentCoord; Cell* currentCell=NULL; while(true) { currentCell=&table[currentCoord.X][currentCoord.Y]; if(!currentCell->IsProcessed()) { GetNextValidNumberList(currentCell); } if(!currentCell->IsvalidListEmpty()) { currentCell->PickNextValidNumber(); if(currentCoord.X==TableSize-1 && currentCoord.Y==TableSize-1) break; else NextCoord(currentCoord); } else { if(currentCoord.X==0 && currentCoord.Y==0) break; else { currentCell->Clear(); PrevCoord(currentCoord); } } } } void Table::GetNextValidNumberList(Cell* currentCell) { for(int i=1;i<=TableSize;i++) { if(ValidInLine(i,currentCell->X(),currentCell->Y())&& ValidInColumn(i,currentCell->X(),currentCell->Y())&& ValidInSmallTable(i,currentCell->X(),currentCell->Y()) ) { currentCell->AddNextValidNumber(i); } } } bool Table::ValidInLine(int number,int x,int y) { for(int i=0;i<y;i++) { if(!table[x][i].IsProcessed()) continue; if(table[x][i].number==number) return false; } return true; } bool Table::ValidInColumn(int number,int x,int y) { for(int i=0;i<x;i++) { if(!table[i][y].IsProcessed()) continue; if(table[i][y].number==number) return false; } return true; } bool Table::ValidInSmallTable(int number,int x,int y) { int startRow = (x / 3) * 3, endRow = (x / 3) * 3 + 3; int startColumn = (y / 3) * 3, endColumn = (y / 3) * 3 + 3; for (int i = startRow; i < endRow; i++) { //如果到达了小格所在行 //if (i == x) // endColumn = y; for (int j = startColumn; j < endColumn; j++) { if (!table[i][j].IsProcessed()) continue; if (table[i][j].number == number) return false; } } return true; } void Table::InitTable() { for(int i=0;i<TableSize;i++) for(int j=0;j<TableSize;j++) { table[i][j].SetX(i); table[i][j].SetY(j); } } void Table::PrintTable() const { for(int i=0;i<TableSize;i++) { for(int j=0;j<TableSize;j++) cout<<table[i][j].number<<" "; cout<<endl; } } void Table::NextCoord(Coord& currentCoord) { if (currentCoord.Y == TableSize - 1) { currentCoord.Y = 0; currentCoord.X = currentCoord.X + 1; } else { currentCoord.Y = currentCoord.Y + 1; currentCoord.X = currentCoord.X; } } void Table::PrevCoord(Coord& currentCoord) { if (currentCoord.Y == 0) { currentCoord.Y = TableSize - 1; currentCoord.X = currentCoord.X - 1; } else { currentCoord.X = currentCoord.X; currentCoord.Y = currentCoord.Y - 1; } } Table::~Table() { delete[] table; }
OK,下面是简单的测试
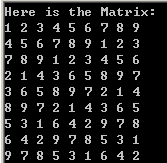
#include <iostream> #include "Table.h" using namespace std; int main() { Table table; table.GenerateValidMatrix(); cout<<"Here is the Matrix: "<<endl; table.PrintTable(); system("PAUSE"); return 0; }