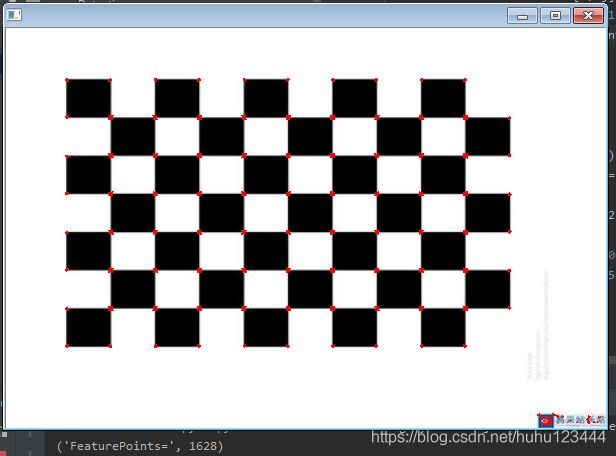
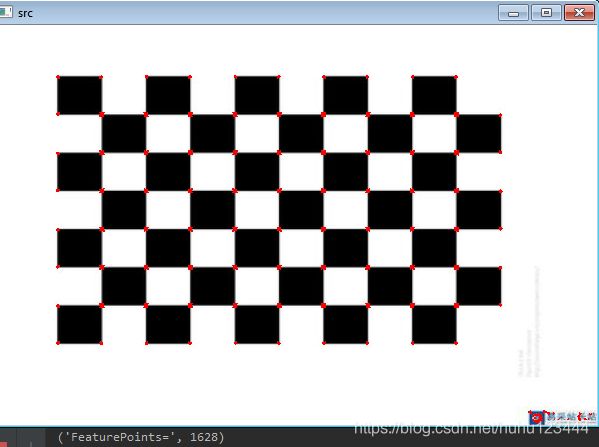
Harris 角点检测原理及实现
1. 图像中角点定义
沿各个方向,图像灰度均发生变化;
2.Harris原理
Harris中也是根据角点定义经角点定义,Harris中使用该像素点周围像素块和其周围的其它像素块的相关性刻画角点,相关性用平方差之和进行计算(SSD),SSD越大,相关性差,中心像素点越有可能成为角点。其数学表达形式为:
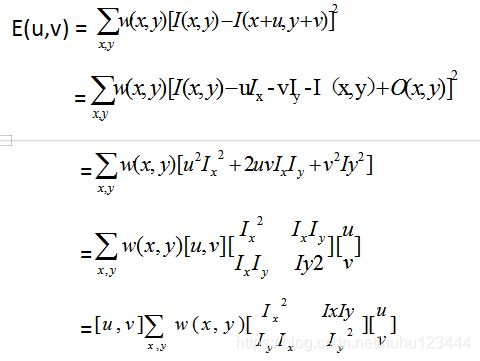

Where Q 是矩阵M的特征向量组成的正交矩阵,向量左乘正交矩阵相当于旋转了一定角度,但是大小保持不变。
在x轴和y轴梯度均增大的点就是梯度点,为了方便,设置相应函数,相应函数的设计原理如下图所示:
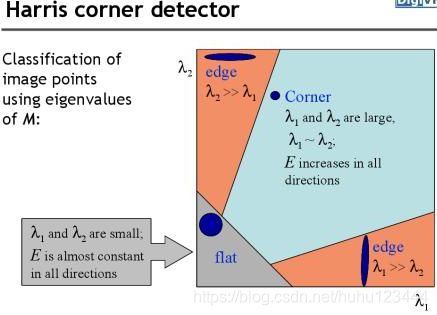
图(1) Harris角点检测原理图
响应函数为:
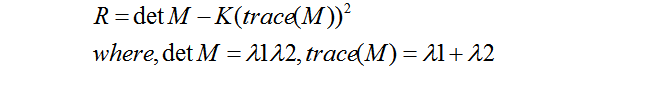
Where K是一个经验值,通常取0.04~0.06。
3.Harris代码实现
'''
@Author:noodles
@date:2020-7-17 20:31:46
'''
import cv2
import numpy as np
threshold = 0.01
def responseFunc(M):
k = 0.04
det = np.linalg.det(M)
trace = np.trace(M)
R = det - k * trace **2
return R
def getHarrisFeaturePoints(src,NMS=False):
global threshold
h, w = src.shape[:2]
# Step1: convert rgb image grayScale
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(src, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cornerPoint = np.zeros_like(gray_image,dtype=np.float32)
# Step2: compute gradient of x,y axis respectively
grad = np.zeros((h, w, 2), dtype=np.float32)
grad[:,:,0] = cv2.Sobel(gray_image,cv2.CV_16S,1,0)
grad[:,:,1] = cv2.Sobel(gray_image,cv2.CV_16S,0,1)
Ixx = grad[:,:,0] ** 2
Iyy = grad[:,:,1] ** 2
Ixy = grad[:,:,0] * grad[:,:,1]
# gaussian_kernal =cv2.getGaussianKernel(3,2)
Ixx = cv2.GaussianBlur(Ixx, (3, 3), sigmaX=2)
Iyy = cv2.GaussianBlur(Iyy, (3, 3), sigmaX=2)
Ixy = cv2.GaussianBlur(Ixy, (3, 3), sigmaX=2)
# print(Ixx, Iyy,Ixy)
# Step3: compute structure matrix
for i in range(gray_image.shape[0]):
for j in range(gray_image.shape[1]):
struture_matrix = [[Ixx[i][j], Ixy[i][j]], [Ixy[i][j], Iyy[i][j]]]
# Step4: response calculation,determine weather it is corner or not
R = responseFunc(struture_matrix)
cornerPoint[i][j] = R
# Step5: non-max suppression,reduce the quantity of corner
corners = np.zeros_like(gray_image,dtype=np.float32)
counter = 0
maxValue = np.max(cornerPoint)
for i in range(cornerPoint.shape[0]):
for j in range(cornerPoint.shape[1]):
if NMS:
if cornerPoint[i][j] > threshold * maxValue and cornerPoint[i][j] == np.max(cornerPoint[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 1, h - 1), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 1, w - 1)] ):
counter+=1
corners[i][j] = 255
else:
if cornerPoint[i][j] > threshold * maxValue:
counter+=1
corners[i][j] = 255
print('FeaturePoints=', counter)
return corners
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_path = 'grid.jpg'
src = cv2.imread(image_path)
img = cv2.resize(src, dsize=(600, 400))
NMS = False
dst = getHarrisFeaturePoints(img,NMS)
#print(dst)
img[dst == 255] = [0, 0, 255]
cv2.imshow('src',img)
cv2.waitKey()
实验结果:
图(3) 编码实现测试结果
可以看到对于同一张图,调用opencv和和自己编码实现检测的角点的位置和数量一致,验证了自己代码的正确性。
4.疑难和理解
Q1:为什么研究M矩阵?
A1:根据化简式子1,发现M影响E(x,y)变化快慢。
Q2:为什么要求M的特征值?
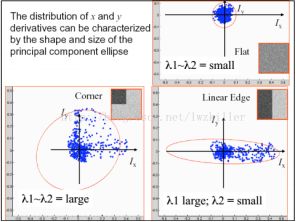
图(4) 矩阵特征值和Ix,Iy分布关系图
理解思路1:绘制了特征值和窗口内Ix,Iy的函数,如上图(4),发现了对应结论。
理解思路2:发现M矩阵和PCA中的矩阵很相似,原始数据可以理解为窗口中的Ix,Iy二维数据,M的特征值对应Ix,Iy的主成分,两个主成分都比较大,则认为在像素点周围存在至少两个像素变化的方向。
Q3:响应函数设计的原理?
A3:为了避免计算特征值。

图(5)原文中响应函数设计原理
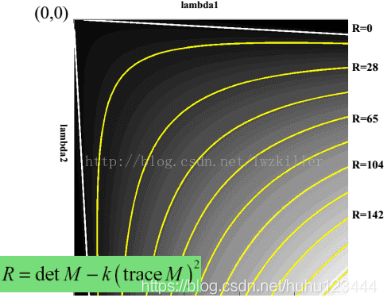
图(6)Harris响应函数的曲线图
结合Harris函数的本身特点和二维矩阵与特征值与矩阵元素的关系设计。
矩阵值和矩阵元素存在如下关系:
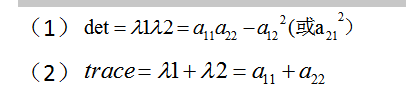
Q4:为什么具有旋转不变性?
A4:图像旋转只会改变特征椭圆的方向,并不会改变椭圆的长短轴的长度,因此R并不会改变。
Q5:Harris角点检测算子对亮度和对比度的变化不灵敏
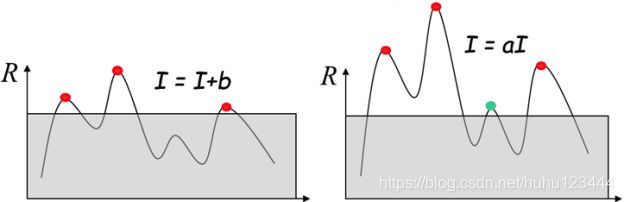
该算法通过图像差分计算角点,两种对比度变化如上图所示,可见光照图像差分影响并不大,也不会改变角点在图像中的位置,但是因为阈值设置的原因,会形象特征点的数量。
Note:
交单检测主要分为基于灰度图像的角点检测、基于二值图像的角点检测、基于轮廓曲线的角点检测。而Harris角点检测属于基于灰度图像的角点检测。
下面这张图像使用基于灰度检测的角点图像效果就会很差:
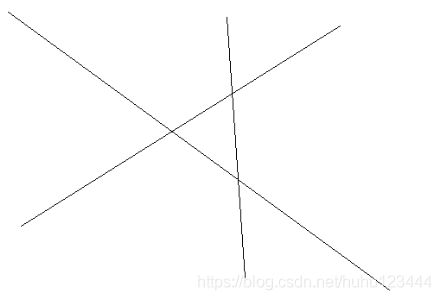
原图
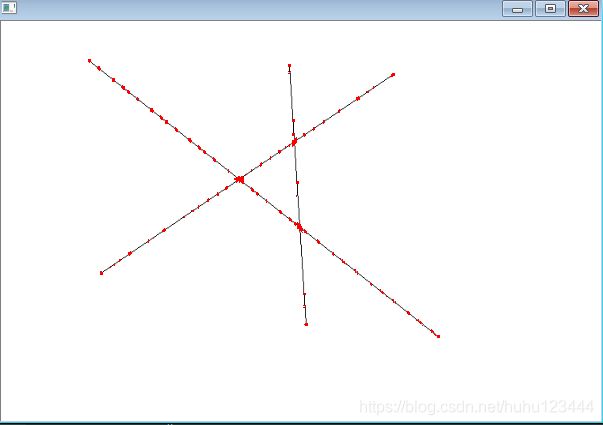
使用Harris角点检测出来的结果
通过对比发现,角点检测过程,首先需要确定角点的种类,然后选用不同的角点检测算法,这样才能有效准确的检测处图像角点。
5.reference
参考文献:
[1]: https://www.cnblogs.com/zyly/p/9508131.html
[2]: https://www.cnblogs.com/ronny/p/4009425.html
[3]: https://blog.csdn.net/f290131665/article/details/80064479
[4]: A Combined Corner and Edge Detector[J],1988.Jianbo Shi and Carlo Tomasi