MapReduce案例-1
天气案例:
需求:
找出每个月温度最高的两天
数据集:
1949-10-01 14:21:02 34c
1949-10-01 19:21:02 38c
1949-10-02 14:01:02 36c
1950-01-01 11:21:02 32c
1950-10-01 12:21:02 37c
1951-12-01 12:21:02 23c
1950-10-02 12:21:02 41c
1950-10-03 12:21:02 27c
1951-07-01 12:21:02 45c
1951-07-02 12:21:02 46c
案例分析:
在MR中,原语是“相同”key的键值对为一组,调用一次reduce方法,方法内迭代这组数据计算。
找出每个月气温最高的两天
分组:
年-组
reduce:年 手动找出每个月的气温数据(创建12个list集合/数组)
日-组
月-组
reduce:一个月的所有气温
如何按月分组?
1951-07-03 12:21:03 47c
分组比较器,按key分组
自定义分组比较器:
class MyGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
a和b表示两个key进行比较,key要包含月份和年份
return 0 1 -1;
}
}
nextKeyIsSame boolean排序:
要求在reduce端的一组数据中按温度倒序排序
同年同月的一组
reduce排序,还是map排序?
map端排序,按照温度倒序排序
实现了环形缓冲区
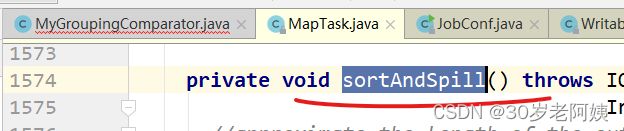
有一个排序溢写的方法:sortAndSpill
该方法如何进行排序的?
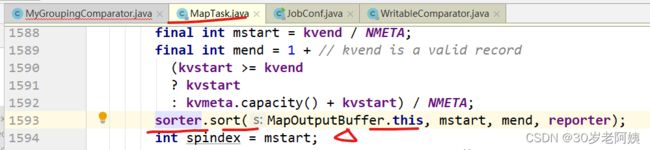
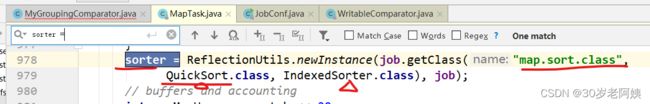
注意:sorter.sort,此处默认使用快排进行排序
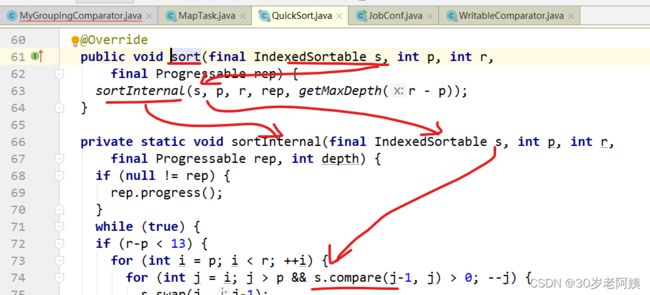
默认情况下,sorter就是快排:QuickSort。
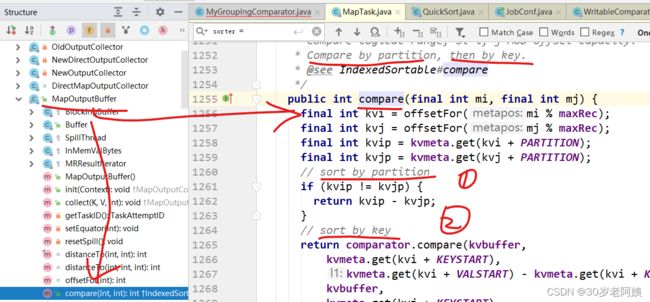
s也就是MapOutputBuffer.this。该对象有一个compare方法,因为上图中有一个s.compare方法
看一下MapOutputBuffer如何实现的compare方法:
该compare方法首先按照分区号排序,相同分区号的按照key的字典序排序。
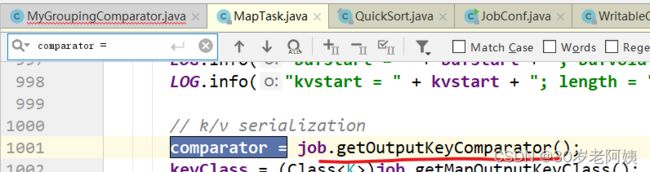
而按照key进行排序的时候,使用的是comparator的compare方法
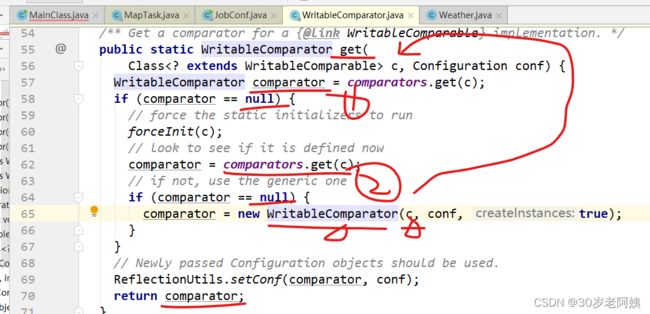
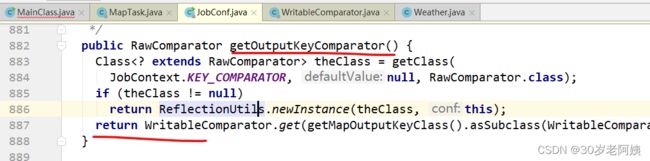
comparator是谁?
上图中的方法返回值就是该比较器
上述方法返回的是什么比较器?
ctrl+alt+b
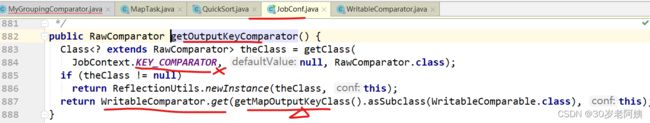
getOutputKeyComparator方法要么返回我们自定义的,要么返回WritableComparator的get方法返回的比较器。
自己没有设置过,所以肯定是WwritableComparator的get返回值。
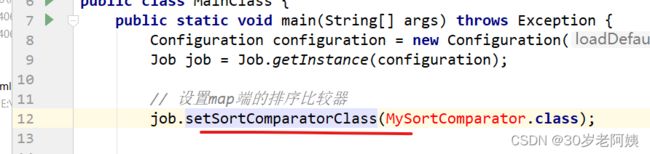
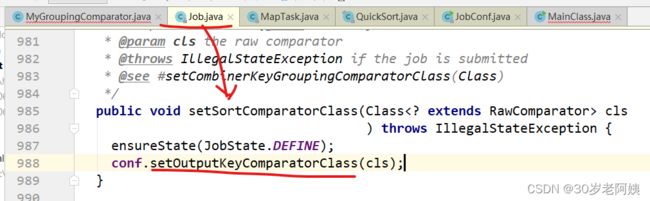
如果自己设置,job.setSortComparatorClass(MySortComparator.class)
如何实现的set?
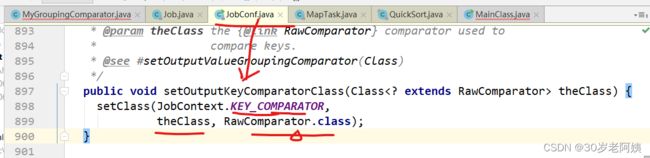
设置的时候用的是setOutputKeyComparatorClass,使用的时候用getOutputKeyComparator方法
上图中,假如用户自定义的key,则要求该key提供排序比较器。
该比较器如何提供?
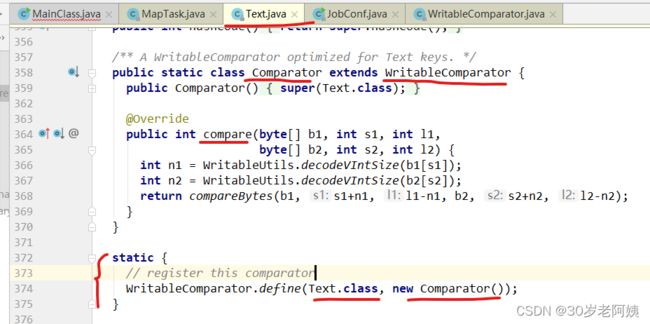
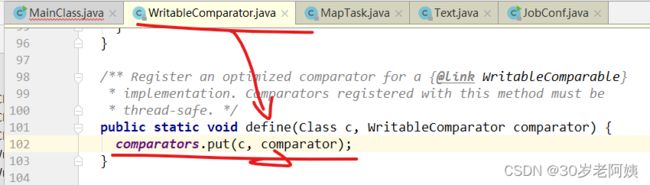
WritableComparator类的get方法用到了HashMap:comparators,该map的key是MR map输出key的类型:Text.class,value是MR的map输出key类型的比较器对象。comparators中的元素是如何放进去的?何时放进去的?
比如说Text.class
Text类的静态块负责将Text.class作为key,将Text自己提供的比较器对象作为value调用了一次WritableComparator的define方法。
define做了什么?
如果自己提供一个key,如何实现?
package com.bjsxt.mr.weather;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Weather implements WritableComparable {
private Integer year;
private Integer month;
private Integer day;
private Integer temperature;
public Integer getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Integer year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Integer getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Integer month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Integer getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Integer day) {
this.day = day;
}
public Integer getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(Integer temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Weather o) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
}
static class Comparator extends WritableComparator {
public Comparator() {
super(Weather.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
Weather wa = (Weather) a;
Weather wb = (Weather) b;
int result = wa.getYear().compareTo(wb.getYear());
if (result == 0) {
result = wa.getMonth().compareTo(wb.getMonth());
if (result == 0) {
// 同年同月的数据,按照温度倒序
// result = wa.getTemperature().compareTo(wb.getTemperature());
result = wb.getTemperature().compareTo(wa.getTemperature());
}
}
return result;
}
}
static {
WritableComparator.define(Weather.class, new Comparator());
}
}
如果第一次没有获取到当前MR的MapOutputKey的比较器,则重新强制执行初始化静态块内容,如果还获取不到,则直接返回WritableComparator对象。
返回的WritableComparator对象本身给getOutputKeyComparator方法返回了。
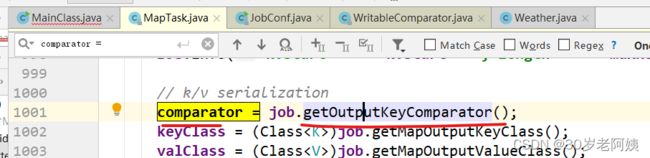
comparator就是返回的这个WritableComparator对象。
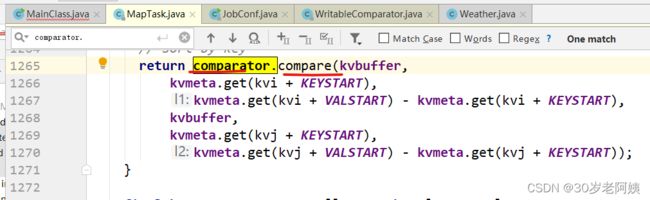
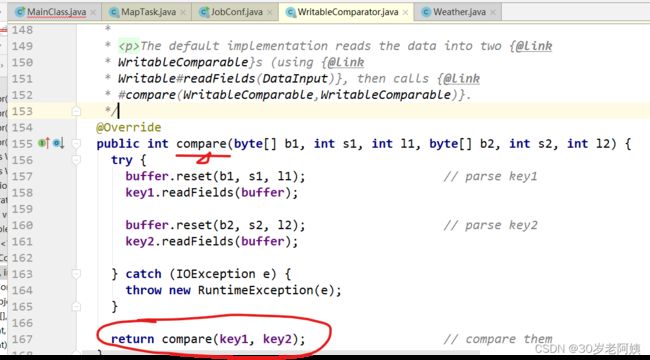
此处的compare方法调用的是哪个?就是WritableComparator的compare方法
该方法最终要调用compare(key1,key2)方法,也就是:
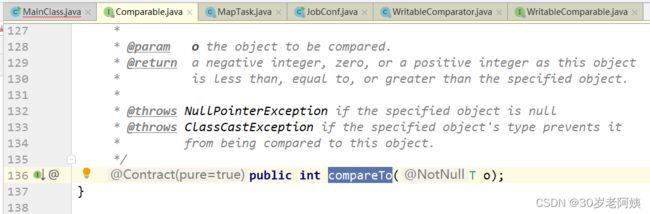
该方法又调用了WritableComparable的compareTo方法,也就是:
该方法做什么用?应该返回什么值?
第二种方式:
package com.bjsxt.mr.weather;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Weather2 implements WritableComparable {
private Integer year;
private Integer month;
private Integer day;
private Integer temperature;
public Integer getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Integer year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Integer getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Integer month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Integer getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Integer day) {
this.day = day;
}
public Integer getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(Integer temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Weather2 that) {
int result = this.getYear().compareTo(that.getYear());
if (result == 0) {
result = this.getMonth().compareTo(that.getMonth());
if (result == 0) {
// 温度倒序
result = that.getTemperature().compareTo(this.getTemperature());
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
// 序列化输出
out.writeInt(year);
out.writeInt(month);
out.writeInt(day);
out.writeInt(temperature);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
//反序列化
setYear(in.readInt());
setMonth(in.readInt());
setDay(in.readInt());
setTemperature(in.readInt());
}
}
map端排序比较器:SortComparator
class MySortComparator extends WritableComparator {
int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
按照温度倒序排序,但是只有同年同月的数据按照温度倒排才有意义。
按key排序,key需要包含年,月,温度
return 0 1 -1;
}
}
key的设计
map端输出key,包含年/月/温度
如何设计key?
是否可以自定义key?
class MyKey implements WritableComparable {
private Integer year;
private Integer month;
private Integer day;
private Integer wenDu;
// 会被排序比较器覆盖
int compareTo(MyKey other) {
this.wendu.compareTo(other.wendu)
this.year.compareTo(other.year)
this.month.compareTo(other.month) this.day.compareTo(other.day)
return 0 1 -1
}
}
MyMapper extends Mapper {
map{
MyKey mk = new MyKey();
mk.setday
mk.setyear
mk.setmonth
mk.setwendu
context.write(MyKey.obj, value);
}
}
分区器
如何分区?
- 分区保证同组数据在一起
- reduce端负载均衡,数据倾斜
自定义分区器
class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner {
int getPartition(key, value, reduceNum) {
return 1 2 3 4 0;
}
}
提示一
1,MR
*保证原语
怎样划分数据,怎样定义一组
2,k:v映射的设计
考虑reduce的计算复杂度
3,能不能多个reduce
倾斜:抽样
集群资源情况
4,自定义数据类型
提示二
记录特点
每年
每个月
最高
2天
1天多条记录?
进一步思考
年月分组
温度升序
key中要包含时间和温度!
MR原语:相同的key分到一组
通过GroupCompartor设置分组规则
步骤
自定义数据类型Weather
包含时间
包含温度
自定义排序比较规则
自定义分组比较
年月相同被视为相同的key
那么reduce迭代时,相同年月的记录有可能是同一天的,reduce中需要判断是否同一天
注意OOM
数据量很大
全量数据可以切分成最少按一个月份的数据量进行判断
这种业务场景可以设置多个reduce
通过实现partition