目标检测——Faster RCNN网络代码(二)之模型准备部分
文章目录
- model/utils/bbox_tools.py
-
- def bbox_iou:
- def bbox2loc:
- def loc2bbox:
- def generate_anchor_base:
- model/utils/creator_tool.py
-
- class ProposalTargetCreator(object):
- class AnchorTargetCreator(object):
代码参考链接: https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch
model/utils/bbox_tools.py
def bbox_iou:
def bbox_iou(bbox_a, bbox_b):
"""Calculate the Intersection of Unions (IoUs) between bounding boxes.
计算两个边界框之间的交集
IoU is calculated as a ratio of area of the intersection
and area of the union.
计算方法是求交集面积和并集面积的比率
This function accepts both :obj:`numpy.ndarray` and :obj:`cupy.ndarray` as
inputs. Please note that both :obj:`bbox_a` and :obj:`bbox_b` need to be
same type.
注意两个输入保持相同的数据类型
The output is same type as the type of the inputs.
输出类型和输入类型一致
Args:
bbox_a (array): An array whose shape is :math:`(N, 4)`.
:math:`N` is the number of bounding boxes.
The dtype should be :obj:`numpy.float32`.
bbox_b (array): An array similar to :obj:`bbox_a`,
whose shape is :math:`(K, 4)`.
The dtype should be :obj:`numpy.float32`.
Returns:
array:
An array whose shape is :math:`(N, K)`. \
An element at index :math:`(n, k)` contains IoUs between \
:math:`n` th bounding box in :obj:`bbox_a` and :math:`k` th bounding \
box in :obj:`bbox_b`.
"""
if bbox_a.shape[1] != 4 or bbox_b.shape[1] != 4:
raise IndexError
# 判断bbox的格式是否正确
# top left 左下两个坐标最大值,t1数组大小为
tl = xp.maximum(bbox_a[:, None, :2], bbox_b[:, :2])
# bottom right 右上两个坐标最小值
br = xp.minimum(bbox_a[:, None, 2:], bbox_b[:, 2:])
# 交集区域
area_i = xp.prod(br - tl, axis=2) * (tl < br).all(axis=2)
# xp.prod()指定某一个维度所有元素乘积
area_a = xp.prod(bbox_a[:, 2:] - bbox_a[:, :2], axis=1)
area_b = xp.prod(bbox_b[:, 2:] - bbox_b[:, :2], axis=1)
return area_i / (area_a[:, None] + area_b - area_i)
# 输出的数组形状为N*K,任意两个出入的bbox都需要计算,是由广播机制实现的
def bbox2loc:
def bbox2loc(src_bbox, dst_bbox):
"""Encodes the source and the destination bounding boxes to "loc".
Given bounding boxes, this function computes offsets and scales
to match the source bounding boxes to the target bounding boxes.
Mathematcially, given a bounding box whose center is
:math:`(y, x) = p_y, p_x` and
size :math:`p_h, p_w` and the target bounding box whose center is
:math:`g_y, g_x` and size :math:`g_h, g_w`, the offsets and scales
:math:`t_y, t_x, t_h, t_w` can be computed by the following formulas.
* :math:`t_y = \\frac{(g_y - p_y)} {p_h}`
* :math:`t_x = \\frac{(g_x - p_x)} {p_w}`
* :math:`t_h = \\log(\\frac{g_h} {p_h})`
* :math:`t_w = \\log(\\frac{g_w} {p_w})`
The output is same type as the type of the inputs.
The encoding formulas are used in works such as R-CNN [#]_.
.. [#] Ross Girshick, Jeff Donahue, Trevor Darrell, Jitendra Malik. \
Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic \
segmentation. CVPR 2014.
Args:
src_bbox (array): An image coordinate array whose shape is
:math:`(R, 4)`. :math:`R` is the number of bounding boxes.
These coordinates are
:math:`p_{ymin}, p_{xmin}, p_{ymax}, p_{xmax}`.
dst_bbox (array): An image coordinate array whose shape is
:math:`(R, 4)`.
These coordinates are
:math:`g_{ymin}, g_{xmin}, g_{ymax}, g_{xmax}`.
Returns:
array:
Bounding box offsets and scales from :obj:`src_bbox` \
to :obj:`dst_bbox`. \
This has shape :math:`(R, 4)`.
The second axis contains four values :math:`t_y, t_x, t_h, t_w`.
"""
height = src_bbox[:, 2] - src_bbox[:, 0] # 预测框的高和宽
width = src_bbox[:, 3] - src_bbox[:, 1]
ctr_y = src_bbox[:, 0] + 0.5 * height # 求出预测框的中心坐标
ctr_x = src_bbox[:, 1] + 0.5 * width
base_height = dst_bbox[:, 2] - dst_bbox[:, 0] # 目标框的高和宽
base_width = dst_bbox[:, 3] - dst_bbox[:, 1]
base_ctr_y = dst_bbox[:, 0] + 0.5 * base_height # 求出目标框的中心坐标
base_ctr_x = dst_bbox[:, 1] + 0.5 * base_width
# 保证下面四个公式当中不出现数学上的不符
# finfo函数是根据括号中的类型来获得信息,获得符合这个类型的数型
# eps是取非负的最小值
eps = xp.finfo(height.dtype).eps
height = xp.maximum(height, eps)
width = xp.maximum(width, eps)
dy = (base_ctr_y - ctr_y) / height # 偏移量
dx = (base_ctr_x - ctr_x) / width
dh = xp.log(base_height / height) # 比例
dw = xp.log(base_width / width)
loc = xp.vstack((dy, dx, dh, dw)).transpose()
# xp.vstack将数按行放到一起,在经过transpose转置
return loc
def loc2bbox:
def loc2bbox(src_bbox, loc):
"""Decode bounding boxes from bounding box offsets and scales.
Given bounding box offsets and scales computed by
:meth:`bbox2loc`, this function decodes the representation to
coordinates in 2D image coordinates.
Given scales and offsets :math:`t_y, t_x, t_h, t_w` and a bounding
box whose center is :math:`(y, x) = p_y, p_x` and size :math:`p_h, p_w`,
the decoded bounding box's center :math:`\\hat{g}_y`, :math:`\\hat{g}_x`
and size :math:`\\hat{g}_h`, :math:`\\hat{g}_w` are calculated
by the following formulas.
* :math:`\\hat{g}_y = p_h t_y + p_y`
* :math:`\\hat{g}_x = p_w t_x + p_x`
* :math:`\\hat{g}_h = p_h \\exp(t_h)`
* :math:`\\hat{g}_w = p_w \\exp(t_w)`
The decoding formulas are used in works such as R-CNN [#]_.
The output is same type as the type of the inputs.
.. [#] Ross Girshick, Jeff Donahue, Trevor Darrell, Jitendra Malik. \
Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic \
segmentation. CVPR 2014.
Args:
src_bbox (array): A coordinates of bounding boxes.
Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`. These coordinates are
:math:`p_{ymin}, p_{xmin}, p_{ymax}, p_{xmax}`.
loc (array): An array with offsets and scales.
The shapes of :obj:`src_bbox` and :obj:`loc` should be same.
This contains values :math:`t_y, t_x, t_h, t_w`.
Returns:
array:
Decoded bounding box coordinates. Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`. \
The second axis contains four values \
:math:`\\hat{g}_{ymin}, \\hat{g}_{xmin},
\\hat{g}_{ymax}, \\hat{g}_{xmax}`.
"""
if src_bbox.shape[0] == 0:
return xp.zeros((0, 4), dtype=loc.dtype)
src_bbox = src_bbox.astype(src_bbox.dtype, copy=False)
src_height = src_bbox[:, 2] - src_bbox[:, 0]
src_width = src_bbox[:, 3] - src_bbox[:, 1]
src_ctr_y = src_bbox[:, 0] + 0.5 * src_height
src_ctr_x = src_bbox[:, 1] + 0.5 * src_width
dy = loc[:, 0::4] # python [start:stop:step]
dx = loc[:, 1::4]
dh = loc[:, 2::4]
dw = loc[:, 3::4]
ctr_y = dy * src_height[:, xp.newaxis] + src_ctr_y[:, xp.newaxis]
ctr_x = dx * src_width[:, xp.newaxis] + src_ctr_x[:, xp.newaxis]
h = xp.exp(dh) * src_height[:, xp.newaxis]
w = xp.exp(dw) * src_width[:, xp.newaxis]
dst_bbox = xp.zeros(loc.shape, dtype=loc.dtype)
dst_bbox[:, 0::4] = ctr_y - 0.5 * h
dst_bbox[:, 1::4] = ctr_x - 0.5 * w
dst_bbox[:, 2::4] = ctr_y + 0.5 * h
dst_bbox[:, 3::4] = ctr_x + 0.5 * w
return dst_bbox
def generate_anchor_base:
def generate_anchor_base(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
anchor_scales=[8, 16, 32]):
"""Generate anchor base windows by enumerating aspect ratio and scales.
Generate anchors that are scaled and modified to the given aspect ratios.
Area of a scaled anchor is preserved when modifying to the given aspect
ratio.
:obj:`R = len(ratios) * len(anchor_scales)` anchors are generated by this
function.
The :obj:`i * len(anchor_scales) + j` th anchor corresponds to an anchor
generated by :obj:`ratios[i]` and :obj:`anchor_scales[j]`.
For example, if the scale is :math:`8` and the ratio is :math:`0.25`,
the width and the height of the base window will be stretched by :math:`8`.
For modifying the anchor to the given aspect ratio,
the height is halved and the width is doubled.
Args:
base_size (number): The width and the height of the reference window.
ratios (list of floats): This is ratios of width to height of
the anchors.
anchor_scales (list of numbers): This is areas of anchors.
Those areas will be the product of the square of an element in
:obj:`anchor_scales` and the original area of the reference
window.
Returns:
~numpy.ndarray:
An array of shape :math:`(R, 4)`.
Each element is a set of coordinates of a bounding box.
The second axis corresponds to
:math:`(y_{min}, x_{min}, y_{max}, x_{max})` of a bounding box.
"""
py = base_size / 2.
px = base_size / 2.
anchor_base = np.zeros((len(ratios) * len(anchor_scales), 4),
dtype=np.float32)
for i in six.moves.range(len(ratios)):
for j in six.moves.range(len(anchor_scales)):
h = base_size * anchor_scales[j] * np.sqrt(ratios[i])
w = base_size * anchor_scales[j] * np.sqrt(1. / ratios[i])
# ratios=[0.5,1,2]是长宽比,anchor_scales=[8, 16, 32]是缩放比
index = i * len(anchor_scales) + j
anchor_base[index, 0] = py - h / 2.
anchor_base[index, 1] = px - w / 2.
anchor_base[index, 2] = py + h / 2.
anchor_base[index, 3] = px + w / 2.
return anchor_base
#计算出anchor_base画的9个框的左下角和右上角的4个anchor坐标值
model/utils/creator_tool.py
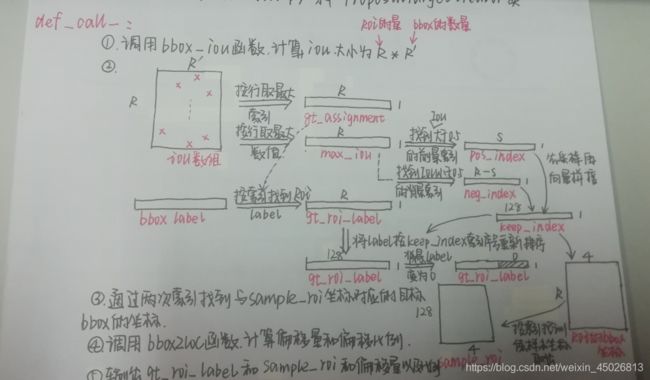
class ProposalTargetCreator(object):
class ProposalTargetCreator(object):
"""Assign ground truth bounding boxes to given RoIs.
将ground truth的bbox分配给RoIs
The :meth:`__call__` of this class generates training targets
for each object proposal.
This is used to train Faster RCNN [#]_.
.. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \
Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \
Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015.
Args:
n_sample (int): The number of sampled regions.
pos_ratio (float): Fraction of regions that is labeled as a
foreground.被标记为前景的占比
pos_iou_thresh (float): IoU threshold for a RoI to be considered as a
foreground. 在ROI中被认为是前景的阈值
neg_iou_thresh_hi (float): RoI is considered to be the background
if IoU is in
[:obj:`neg_iou_thresh_hi`, :obj:`neg_iou_thresh_hi`).
neg_iou_thresh_lo (float): See above.
"""
def __init__(self,
n_sample=128,
pos_ratio=0.25, pos_iou_thresh=0.5,
neg_iou_thresh_hi=0.5, neg_iou_thresh_lo=0.0
):
self.n_sample = n_sample
self.pos_ratio = pos_ratio
self.pos_iou_thresh = pos_iou_thresh
self.neg_iou_thresh_hi = neg_iou_thresh_hi
self.neg_iou_thresh_lo = neg_iou_thresh_lo # NOTE:default 0.1 in py-faster-rcnn
def __call__(self, roi, bbox, label,
loc_normalize_mean=(0., 0., 0., 0.),
loc_normalize_std=(0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2)):
"""Assigns ground truth to sampled proposals.
This function samples total of :obj:`self.n_sample` RoIs
from the combination of :obj:`roi` and :obj:`bbox`.
The RoIs are assigned with the ground truth class labels as well as
bounding box offsets and scales to match the ground truth bounding
boxes. As many as :obj:`pos_ratio * self.n_sample` RoIs are
sampled as foregrounds.
Offsets and scales of bounding boxes are calculated using
:func:`model.utils.bbox_tools.bbox2loc`.
Also, types of input arrays and output arrays are same.
Here are notations.
* :math:`S` is the total number of sampled RoIs, which equals \
:obj:`self.n_sample`.
* :math:`L` is number of object classes possibly including the \
background.
Args:
roi (array): Region of Interests (RoIs) from which we sample.
Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`
bbox (array): The coordinates of ground truth bounding boxes.
Its shape is :math:`(R', 4)`.
label (array): Ground truth bounding box labels. Its shape
is :math:`(R',)`. Its range is :math:`[0, L - 1]`, where
:math:`L` is the number of foreground classes.
loc_normalize_mean (tuple of four floats): Mean values to normalize
coordinates of bouding boxes.
loc_normalize_std (tupler of four floats): Standard deviation of
the coordinates of bounding boxes.
Returns:
(array, array, array):
* **sample_roi**: Regions of interests that are sampled. \
Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`.
* **gt_roi_loc**: Offsets and scales to match \
the sampled RoIs to the ground truth bounding boxes. \
Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`.
* **gt_roi_label**: Labels assigned to sampled RoIs. Its shape is \
:math:`(S,)`. Its range is :math:`[0, L]`. The label with \
value 0 is the background.
"""
n_bbox, _ = bbox.shape
roi = np.concatenate((roi, bbox), axis=0)
# 按轴axis连接array组成一个新的array,axis=0增加行行拼接
pos_roi_per_image = np.round(self.n_sample * self.pos_ratio)
# 返回四舍五入后的值,可指定精度,默认精度为取整
iou = bbox_iou(roi, bbox) # 计算roi和bbox(groundtruth)的IOU
gt_assignment = iou.argmax(axis=1)
# iou大小为R*R',输出iou值里面每一行最大值的索引,输出大小应该是1*R
max_iou = iou.max(axis=1) # 输出每一行最大值的数值,输出大小应该是1*R
# Offset range of classes from [0, n_fg_class - 1] to [1, n_fg_class].
# The label with value 0 is the background.
gt_roi_label = label[gt_assignment] + 1 # 存储roi的label
# Select foreground RoIs as those with >= pos_iou_thresh IoU.
pos_index = np.where(max_iou >= self.pos_iou_thresh)[0]
# pos_iou_thresh=0.5 , max_iou当中大于阈值的被认为是前景
# np.where找到n维数组中满足特定条件的数值索引
pos_roi_per_this_image = int(min(pos_roi_per_image, pos_index.size))
if pos_index.size > 0:
pos_index = np.random.choice(
pos_index, size=pos_roi_per_this_image, replace=False)
# np.random.choice从给定的1维数组中随机采样的函数
# Select background RoIs as those within
# [neg_iou_thresh_lo, neg_iou_thresh_hi).
neg_index = np.where((max_iou < self.neg_iou_thresh_hi) &
(max_iou >= self.neg_iou_thresh_lo))[0]
neg_roi_per_this_image = self.n_sample - pos_roi_per_this_image
neg_roi_per_this_image = int(min(neg_roi_per_this_image,
neg_index.size))
if neg_index.size > 0:
neg_index = np.random.choice(
neg_index, size=neg_roi_per_this_image, replace=False)
# The indices that we're selecting (both positive and negative).
keep_index = np.append(pos_index, neg_index) # 向量拼接
gt_roi_label = gt_roi_label[keep_index] # 获取keep_index的label
gt_roi_label[pos_roi_per_this_image:] = 0 # negative labels --> 0
sample_roi = roi[keep_index] # 把对应训练样本坐标取出来
# Compute offsets and scales to match sampled RoIs to the GTs.
gt_roi_loc = bbox2loc(sample_roi, bbox[gt_assignment[keep_index]])
gt_roi_loc = ((gt_roi_loc - np.array(loc_normalize_mean, np.float32)
) / np.array(loc_normalize_std, np.float32))
return sample_roi, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label
# 输出训练样本的label,坐标和偏移量及偏移比例
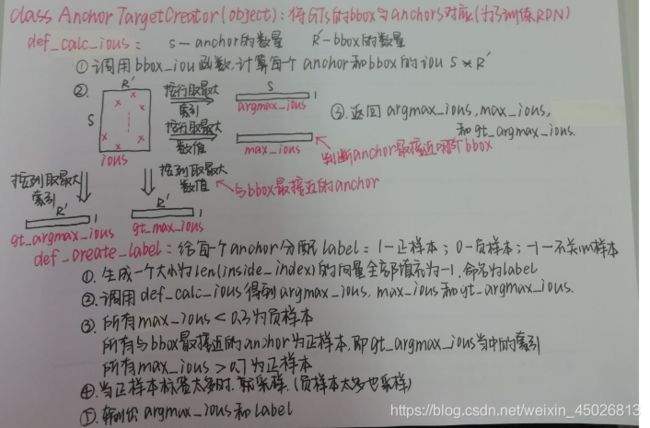
class AnchorTargetCreator(object):
class AnchorTargetCreator(object):
"""Assign the ground truth bounding boxes to anchors.
Assigns the ground truth bounding boxes to anchors for training Region
Proposal Networks introduced in Faster R-CNN [#]_.
Offsets and scales to match anchors to the ground truth are
calculated using the encoding scheme of
:func:`model.utils.bbox_tools.bbox2loc`.
.. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \
Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \
Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015.
Args:
n_sample (int): The number of regions to produce.
pos_iou_thresh (float): Anchors with IoU above this
threshold will be assigned as positive.
neg_iou_thresh (float): Anchors with IoU below this
threshold will be assigned as negative.
pos_ratio (float): Ratio of positive regions in the
sampled regions.
"""
def __init__(self,
n_sample=256,
pos_iou_thresh=0.7, neg_iou_thresh=0.3,
pos_ratio=0.5):
self.n_sample = n_sample
self.pos_iou_thresh = pos_iou_thresh
self.neg_iou_thresh = neg_iou_thresh
self.pos_ratio = pos_ratio
def __call__(self, bbox, anchor, img_size):
"""Assign ground truth supervision to sampled subset of anchors.
Types of input arrays and output arrays are same.
Here are notations.
* :math:`S` is the number of anchors.
* :math:`R` is the number of bounding boxes.
Args:
bbox (array): Coordinates of bounding boxes. Its shape is
:math:`(R, 4)`.
anchor (array): Coordinates of anchors. Its shape is
:math:`(S, 4)`.
img_size (tuple of ints): A tuple :obj:`H, W`, which
is a tuple of height and width of an image.
Returns:
(array, array):
#NOTE: it's scale not only offset
* **loc**: Offsets and scales to match the anchors to \
the ground truth bounding boxes. Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`.
* **label**: Labels of anchors with values \
:obj:`(1=positive, 0=negative, -1=ignore)`. Its shape \
is :math:`(S,)`.
"""
img_H, img_W = img_size
n_anchor = len(anchor) # anchor的数量
inside_index = _get_inside_index(anchor, img_H, img_W)
# _get_inside_index函数返回完全位于图像内部的anchor索引
anchor = anchor[inside_index] # 按照索引把位于图像内部的anchor坐标取出来
argmax_ious, label = self._create_label(
inside_index, anchor, bbox)
# compute bounding box regression targets
loc = bbox2loc(anchor, bbox[argmax_ious])
# map up to original set of anchors
label = _unmap(label, n_anchor, inside_index, fill=-1)
loc = _unmap(loc, n_anchor, inside_index, fill=0)
return loc, label
def _create_label(self, inside_index, anchor, bbox):
# label: 1 is positive, 0 is negative, -1 is dont care
label = np.empty((len(inside_index),), dtype=np.int32)
label.fill(-1)
argmax_ious, max_ious, gt_argmax_ious = \
self._calc_ious(anchor, bbox, inside_index)
# assign negative labels first so that positive labels can clobber them
# 在负标签阈值之下的为negative labels
label[max_ious < self.neg_iou_thresh] = 0
# positive label: for each gt, anchor with highest iou
label[gt_argmax_ious] = 1
# positive label: above threshold IOU
label[max_ious >= self.pos_iou_thresh] = 1
# 所有max_ious大于0.7的和gt_argmax_ious当中的索引值均为正样本
# subsample positive labels if we have too many
n_pos = int(self.pos_ratio * self.n_sample)
# pos_ratio = 0.5;n_sample = 256;取整。
pos_index = np.where(label == 1)[0] # 对positive labels定位
if len(pos_index) > n_pos:
disable_index = np.random.choice(
pos_index, size=(len(pos_index) - n_pos), replace=False)
label[disable_index] = -1 # 把多的样本定义为不关心
# subsample negative labels if we have too many
n_neg = self.n_sample - np.sum(label == 1)
neg_index = np.where(label == 0)[0] # 对negative labels定位
if len(neg_index) > n_neg:
disable_index = np.random.choice(
neg_index, size=(len(neg_index) - n_neg), replace=False)
label[disable_index] = -1 # 把多的样本定义为不关心
return argmax_ious, label
def _calc_ious(self, anchor, bbox, inside_index):
# ious between the anchors and the gt boxes
# 计算anchors(已经筛选过全部在图像里面的)和GTs bboxs的IOU
ious = bbox_iou(anchor, bbox)
argmax_ious = ious.argmax(axis=1)
# 输出iou值里面每一行最大值的索引,大小和anchor数量一样
max_ious = ious[np.arange(len(inside_index)), argmax_ious]
# np.arange一个参数时,参数值为终点,起点取默认值0,步长取默认值1
gt_argmax_ious = ious.argmax(axis=0)
# 输出iou值里面每一列最大值的索引,大小和GTs bboxs数量一样
gt_max_ious = ious[gt_argmax_ious, np.arange(ious.shape[1])]
# 取出每一列最大值
gt_argmax_ious = np.where(ious == gt_max_ious)[0]
return argmax_ious, max_ious, gt_argmax_ious
class ProposalCreator:
# unNOTE: I'll make it undifferential
# unTODO: make sure it's ok
# It's ok
"""Proposal regions are generated by calling this object.
The :meth:`__call__` of this object outputs object detection proposals by
applying estimated bounding box offsets
to a set of anchors.
This class takes parameters to control number of bounding boxes to
pass to NMS and keep after NMS.
If the paramters are negative, it uses all the bounding boxes supplied
or keep all the bounding boxes returned by NMS.
This class is used for Region Proposal Networks introduced in
Faster R-CNN [#]_.
.. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \
Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \
Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015.
Args:
nms_thresh (float): Threshold value used when calling NMS.
n_train_pre_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes
to keep before passing to NMS in train mode.
n_train_post_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes
to keep after passing to NMS in train mode.
n_test_pre_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes
to keep before passing to NMS in test mode.
n_test_post_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes
to keep after passing to NMS in test mode.
force_cpu_nms (bool): If this is :obj:`True`,
always use NMS in CPU mode. If :obj:`False`,
the NMS mode is selected based on the type of inputs.
min_size (int): A paramter to determine the threshold on
discarding bounding boxes based on their sizes.
"""
def __init__(self,
parent_model,
nms_thresh=0.7,
n_train_pre_nms=12000,
n_train_post_nms=2000,
n_test_pre_nms=6000,
n_test_post_nms=300,
min_size=16
):
self.parent_model = parent_model
self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh
self.n_train_pre_nms = n_train_pre_nms
self.n_train_post_nms = n_train_post_nms
self.n_test_pre_nms = n_test_pre_nms
self.n_test_post_nms = n_test_post_nms
self.min_size = min_size
def __call__(self, loc, score,
anchor, img_size, scale=1.):
"""input should be ndarray
Propose RoIs.
Inputs :obj:`loc, score, anchor` refer to the same anchor when indexed
by the same index.
On notations, :math:`R` is the total number of anchors. This is equal
to product of the height and the width of an image and the number of
anchor bases per pixel.
Type of the output is same as the inputs.
Args:
loc (array): Predicted offsets and scaling to anchors.
anchors预测的偏移量和偏移比例
Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`.
score (array): Predicted foreground probability for anchors.
anchors预测的得分
Its shape is :math:`(R,)`.
anchor (array): Coordinates of anchors坐标. Its shape is
:math:`(R, 4)`.
img_size (tuple of ints): A tuple :obj:`height, width`,
which contains image size after scaling.图像缩放之后的统一规格
scale (float): The scaling factor used to scale an image after
reading it from a file.图像缩放时的比例
Returns:
array:
An array of coordinates of proposal boxes.
Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`. :math:`S` is less than
:obj:`self.n_test_post_nms` in test time and less than
:obj:`self.n_train_post_nms` in train time. :math:`S` depends on
the size of the predicted bounding boxes and the number of
bounding boxes discarded by NMS.
"""
# NOTE: when test, remember
# faster_rcnn.eval()
# to set self.traing = False
if self.parent_model.training: # 判断是测试还是训练
n_pre_nms = self.n_train_pre_nms
n_post_nms = self.n_train_post_nms
else:
n_pre_nms = self.n_test_pre_nms
n_post_nms = self.n_test_post_nms
# Convert anchors into proposal via bbox transformations.
# roi = loc2bbox(anchor, loc)
roi = loc2bbox(anchor, loc)
# Clip predicted boxes to image.
roi[:, slice(0, 4, 2)] = np.clip(
roi[:, slice(0, 4, 2)], 0, img_size[0])
roi[:, slice(1, 4, 2)] = np.clip(
roi[:, slice(1, 4, 2)], 0, img_size[1])
# numpy.clip(a, a_min, a_max, out=None)[source]
# 将a中的元素限制在最大值和最小值之间
# Remove predicted boxes with either height or width < threshold.
# 删除宽度和高度小于阈值的检测框
min_size = self.min_size * scale
hs = roi[:, 2] - roi[:, 0] # 高度
ws = roi[:, 3] - roi[:, 1] # 宽度
keep = np.where((hs >= min_size) & (ws >= min_size))[0]
roi = roi[keep, :]
score = score[keep]
# Sort all (proposal, score) pairs by score from highest to lowest.
# 将所有检测框按照得分从高到低排序
# Take top pre_nms_topN (e.g. 6000).
order = score.ravel().argsort()[::-1]
# ravel()降维,排列成一行
# 将x中的元素从小到大排列,提取其对应的index(索引),赋值给order这个变量
# [::-1]所有元素反过来排列
if n_pre_nms > 0:
order = order[:n_pre_nms]
roi = roi[order, :]
# 取得分靠前的检测框
# Apply nms (e.g. threshold = 0.7).
# Take after_nms_topN (e.g. 300).
# unNOTE: somthing is wrong here!
# TODO: remove cuda.to_gpu
keep = non_maximum_suppression(
cp.ascontiguousarray(cp.asarray(roi)),
thresh=self.nms_thresh)
# non_maximum_suppression非极大值抑制函数
if n_post_nms > 0:
keep = keep[:n_post_nms]
roi = roi[keep]
return roi