强化学习实战(一)—— 使用BaslineDQN学习飞船降落
文章目录
- 实验过程1
-
- 1. 引入库并创建环境
- 2. 创建模型
- 3. 模型学习
- 4. 模型评估
- 5. 附录
- 实验过程2
-
- 1. 修改模型参数
本文将介绍如何使用Stable Basline3中的DQN算法学习飞船降落问题。
实验过程1
1. 引入库并创建环境
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import DQN
from stable_baselines3.common.evaluation import evaluate_policy
# Create environment
env = gym.make("LunarLander-v2")
(1)了解环境信息
成功创建环境后,我们可以通过env.action_space和env.observation_space查看环境的动作和状态空间。也可以通过env.action_space.sample()和env.observation_space.sample()随机采样,了解具体的动作和状态表示情况。
print(env.action_space)
print(env.action_space.sample())
print(env.observation_space)
print(env.observation_space.sample())
Discrete(4)
3
Box([-inf -inf -inf -inf -inf -inf -inf -inf], [inf inf inf inf inf inf inf inf], (8,), float32)
[-0.39453888 0.88357323 -2.6758633 0.26985604 -0.31590447 -0.5141233
1.2682225 0.7396759 ]
接着我们可以通过查询gym官方文档了解动作和状态空间更细节的信息。

2. 创建模型
# Instantiate the agent
model = DQN("MlpPolicy",
env,
tensorboard_log = './logs',
verbose=1)
Parameters
下面将对一些特殊的常用的参数进行说明:
-
policy – The policy model to use
①MlpPolicy:DQNPolicy
②CnnPolicy:Policy class for DQN when using images as input.
③MultiInputPolicy:Policy class for DQN when using dict observations as input. -
tensorboard_log – the log location for tensorboard (if None, no logging)
-
verbose – Verbosity level: 0 for no output, 1 for info messages (such as device or wrappers used), 2 for debug messages
-
policy_kwargs (Optional[Dict[str, Any]]) – additional arguments to be passed to the policy on creation
-
seed – Seed for the pseudo random generators
-
device – Device (cpu, cuda, …) on which the code should be run. Setting it to auto, the code will be run on the GPU if possible.
3. 模型学习
# Train the agent and display a progress bar
model.learn(total_timesteps=int(5e5),
tb_log_name = 'DQN2',
progress_bar= True,)
# Save the agent
model.save("dqn_lunar")
del model # delete trained model to demonstrate loading
Parameters
下面将对一些特殊的常用的参数进行说明:
- total_timesteps – The total number of samples (env steps) to train on
- log_interval (int) – The number of timesteps before logging.
- tb_log_name (str) – the name of the run for TensorBoard logging
- progress_bar (bool) – Display a progress bar using tqdm and rich.
4. 模型评估
# Load the trained agent
# model = DQN.load("dqn_lunar", env=env, print_system_info=True)
model = DQN.load("dqn_lunar", env=env)
# Evaluate the agent
# NOTE: If you use wrappers with your environment that modify rewards,
# this will be reflected here. To evaluate with original rewards,
# wrap environment in a "Monitor" wrapper before other wrappers.
mean_reward, std_reward = evaluate_policy(model,
model.get_env(),
render = True,
n_eval_episodes=10)
方式二
model = DQN.load("dqn_lunar", env=env)
# Evaluate the agent
episodes = 10
for ep in range(episodes):
obs = env.reset()
done = False
rewards = 0
while not done:
# action = env.action_space.sample()
action, _states = model.predict(obs, deterministic=True)
obs,reward,done,info = env.step(action)
env.render()
rewards += reward
print(rewards)
5. 附录
Code
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import DQN
from stable_baselines3.common.evaluation import evaluate_policy
# Create environment
env = gym.make("LunarLander-v2")
print(env.action_space)
print(env.action_space.sample())
# do nothing, fire left orientation engine, fire main engine, fire right orientation engine.
print(env.observation_space)
print(env.observation_space.sample())
# the coordinates of the lander in x & y, its linear velocities in x & y, its angle, its angular velocity,
# and two booleans that represent whether each leg is in contact with the ground or not.
# Instantiate the agent
model = DQN("MlpPolicy",
env,
tensorboard_log = './logs',
verbose=1)
# Train the agent and display a progress bar
model.learn(total_timesteps=int(5e5),
tb_log_name = 'DQN2',
progress_bar= True,)
# Save the agent
model.save("dqn_lunar")
del model # delete trained model to demonstrate loading
# Load the trained agent
# NOTE: if you have loading issue, you can pass `print_system_info=True`
# to compare the system on which the model was trained vs the current one
# model = DQN.load("dqn_lunar", env=env, print_system_info=True)
model = DQN.load("dqn_lunar", env=env)
# Evaluate the agent
episodes = 10
for ep in range(episodes):
obs = env.reset()
done = False
rewards = 0
while not done:
# action = env.action_space.sample()
action, _states = model.predict(obs, deterministic=True)
obs,reward,done,info = env.step(action)
# env.render()
rewards += reward
print(rewards)
Result
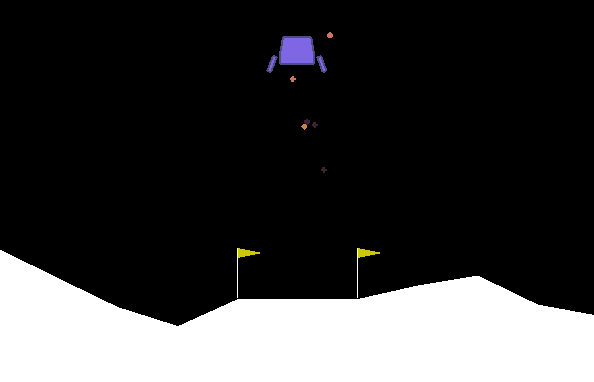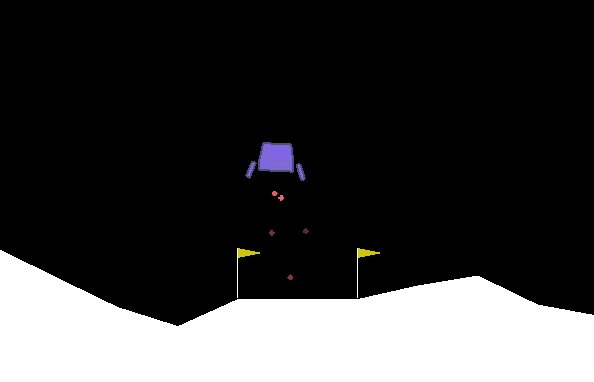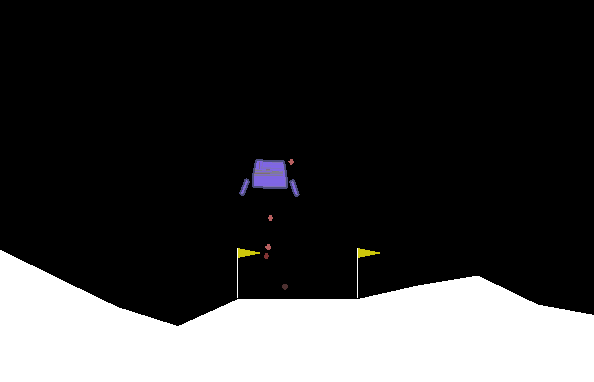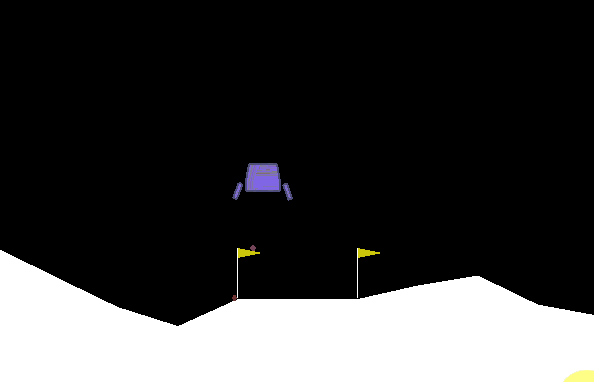
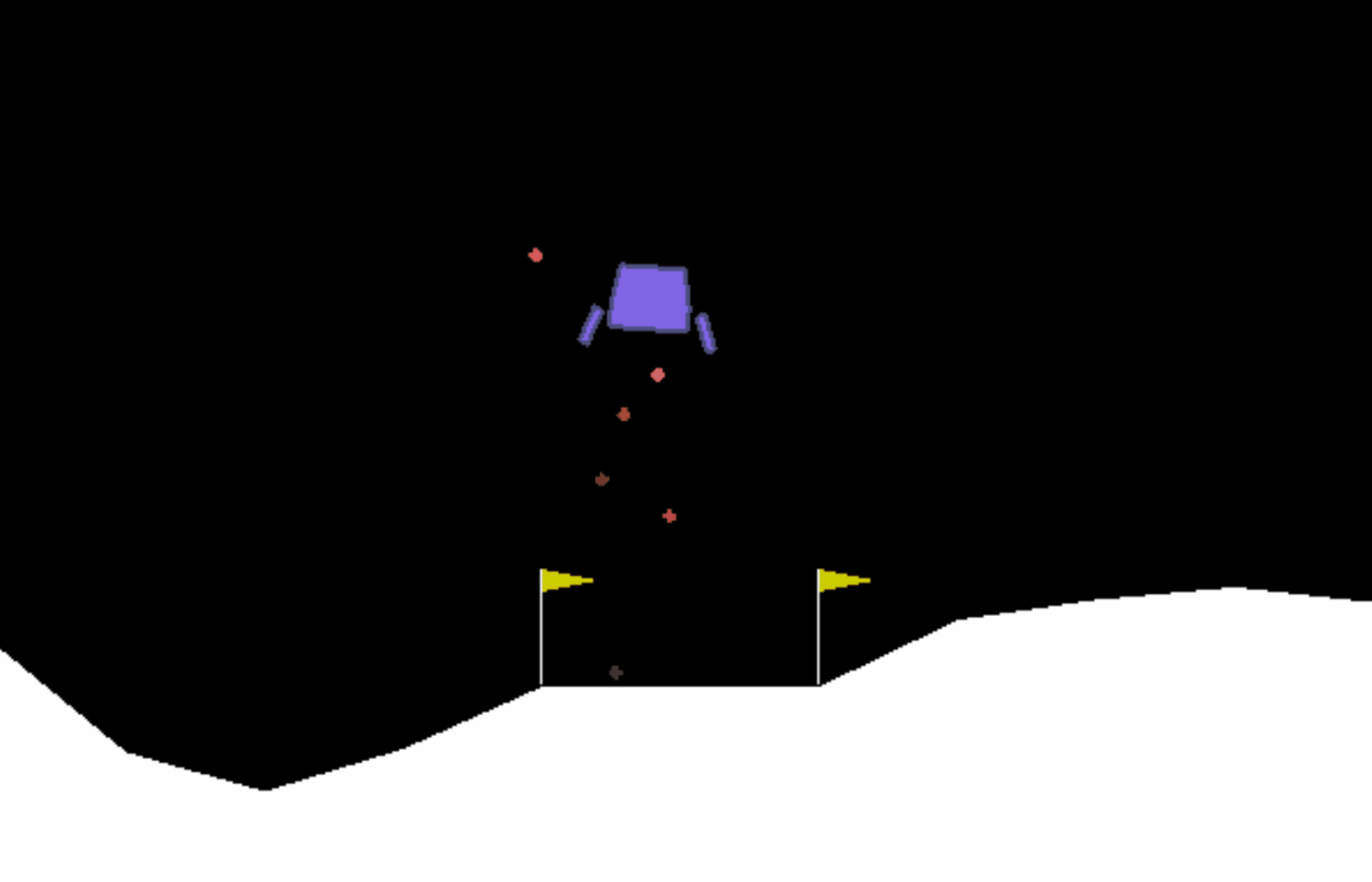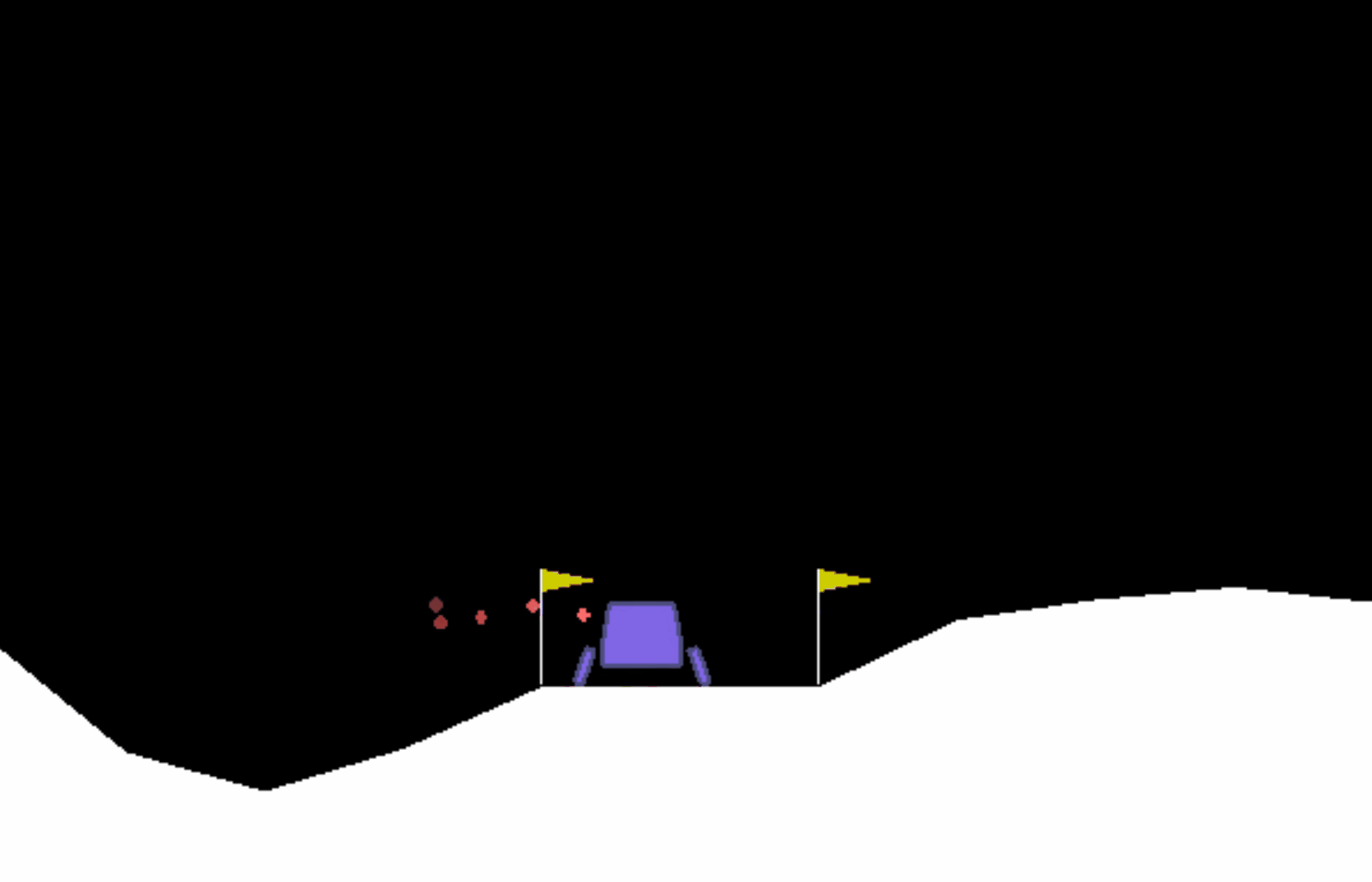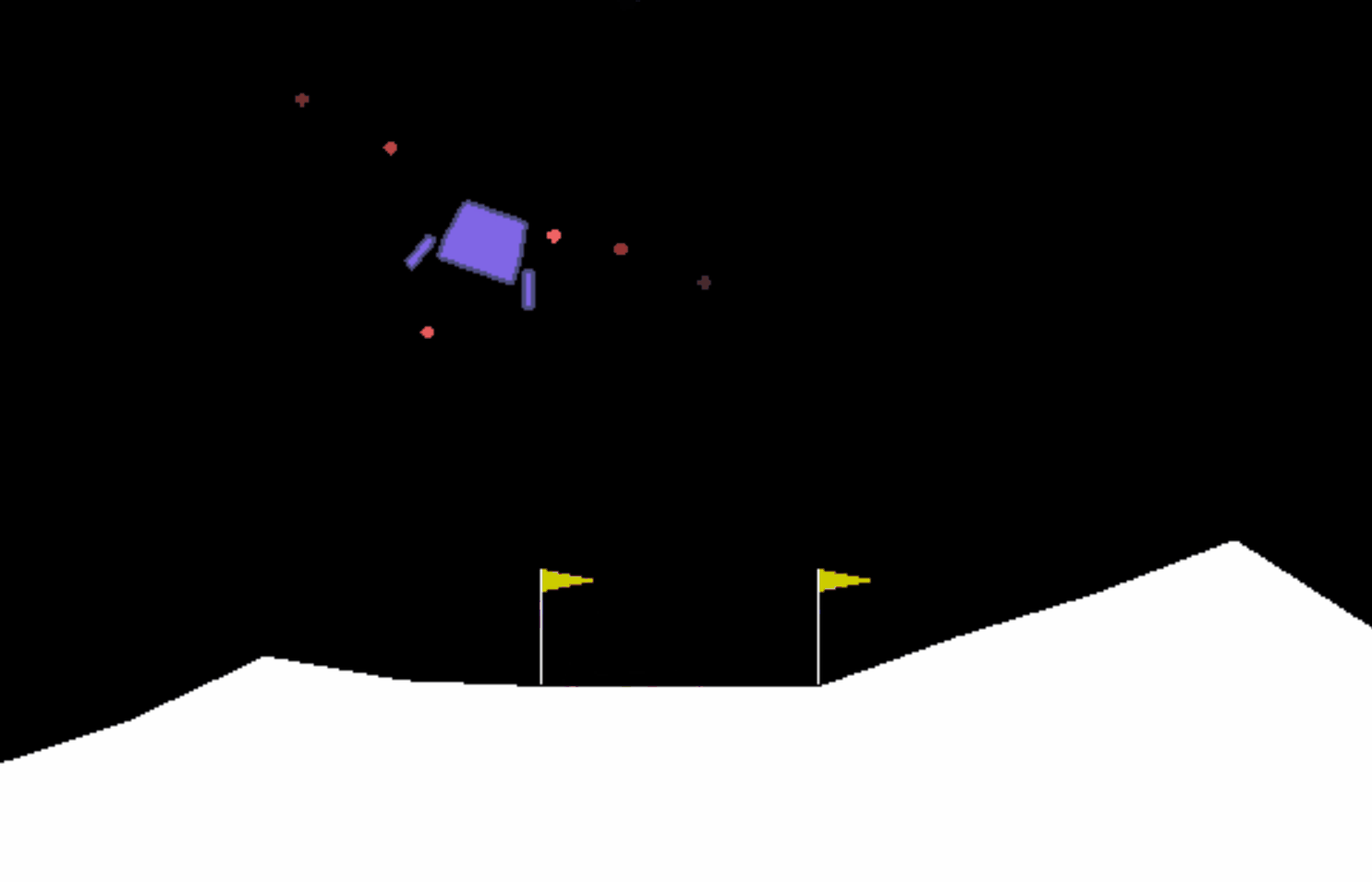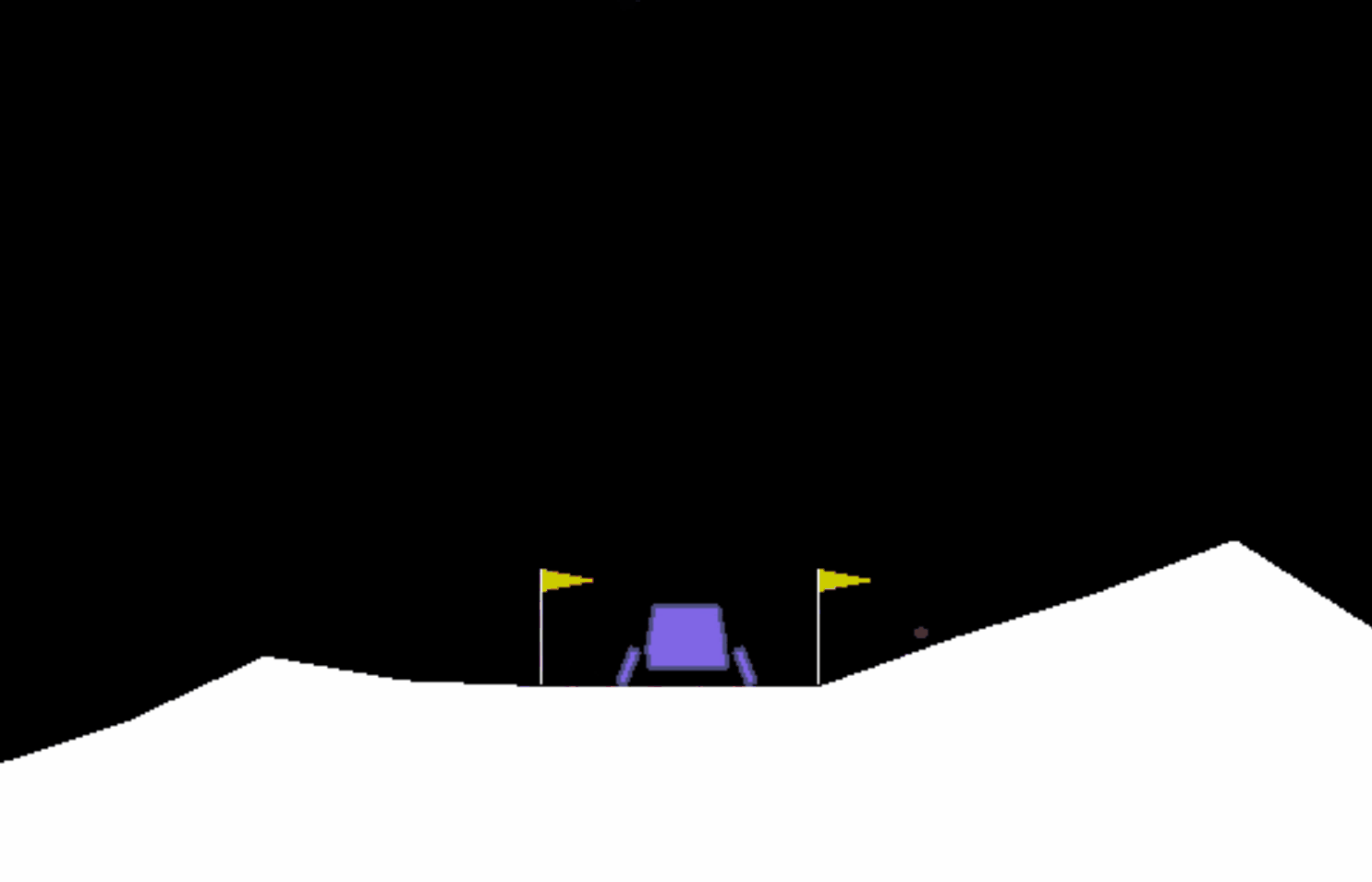
很明显飞船表现得并不好,当它下降到一定位置后便开始悬浮,不符合要求。我们需要修改训练参数。
实验过程2
1. 修改模型参数

(1)加大学习率learning_rate,加快收敛。
(2)修改网络结构
可以通过policy_kwargs传递网络参数,通过查看MLPPolicy参数可知net_arch可以修改网络结构。
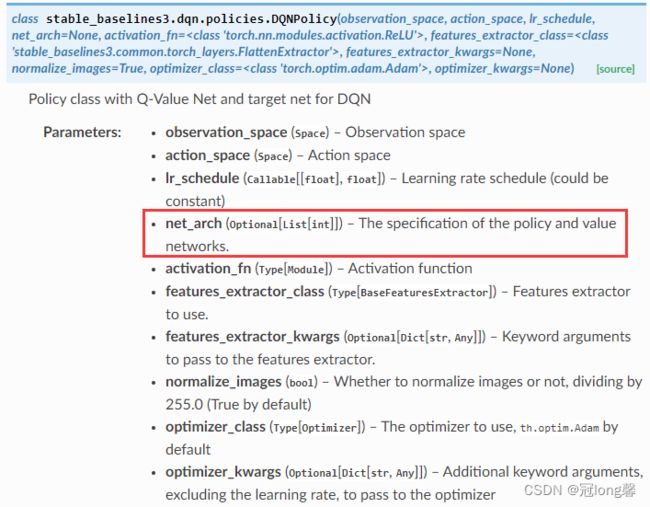
查看源码我们知道初始网络结构为[64, 64],因此我们修改结构为[256, 256]。
# Instantiate the agent
model = DQN("MlpPolicy",
env,
tensorboard_log = './logs',
learning_rate = 5e-4,
policy_kwargs = {'net_arch': [256,256]},
verbose=1)