MTCNN详细解读
MTCNN详细解读
- 原理介绍
-
- 代码解读
-
- 实际效果
原理介绍
MTCNN,Multi-task convolutional neural network(多任务卷积神经网络),将人脸区域检测与人脸关键点检测放在了一起,它的主题框架类似于cascade。总体可分为P-Net、R-Net、和O-Net三层网络结构。
它是2016年中国科学院深圳研究院提出的用于人脸检测任务的多任务神经网络模型,该模型主要采用了三个级联的网络,采用候选框加分类器的思想,进行快速高效的人脸检测。这三个级联的网络分别是快速生成候选窗口的P-Net、进行高精度候选窗口过滤选择的R-Net和生成最终边界框与人脸关键点的O-Net。和很多处理图像问题的卷积神经网络模型,该模型也用到了图像金字塔、边框回归、非最大值抑制等技术。
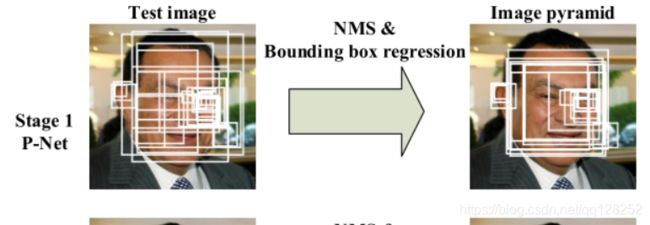
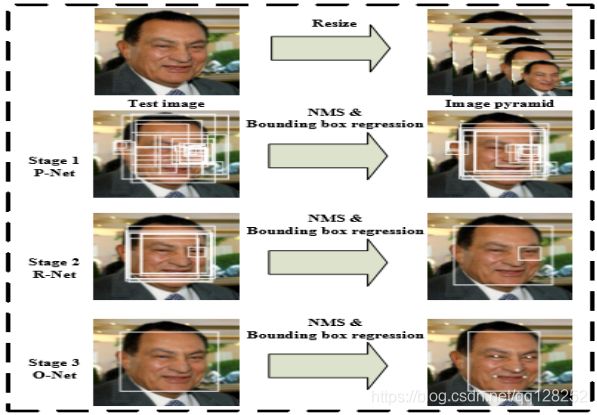
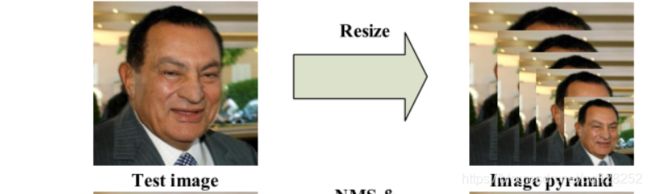
MTCNN实现的流程就是下面这张图:
1.构建图像金字塔。
2.P-Net,NMS。
3.R-Net,NMS。
4.O-Net,NMS。
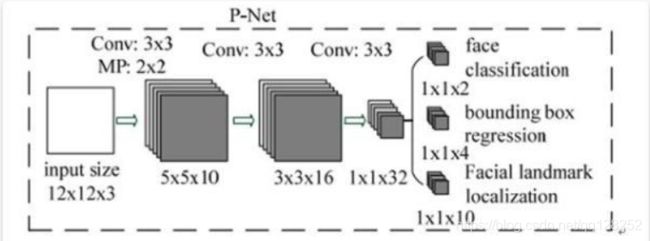
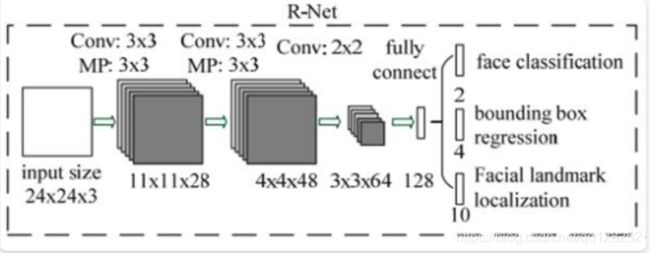
三者结构比较
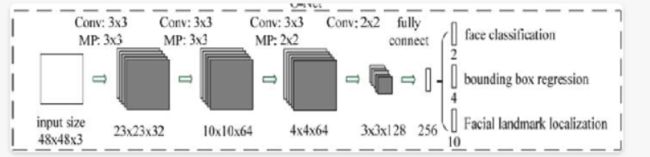
代码解读
1.构建图像金字塔
首先我们将图片进行不同程度的缩放,来构建图像金字塔,已检测不同大小的人脸。主要由缩放系数factor进行,factor取值为0.709。简单来说,就是将图片长宽乘以0.709,直到长宽小于12。
下面是代码:
我们输入一张图片,对图片的长宽进行调整,使其不低于500,这样不会太小
也不会太大。这里我们返回scale列表,里面是图片缩放比例。
#-----------------------------#
# 计算原始输入图像
# 每一次缩放的比例
#-----------------------------#
def calculateScales(img):
copy_img = img.copy()
pr_scale = 1.0
h,w,_ = copy_img.shape
if min(w,h)>500:
pr_scale = 500.0/min(h,w)
w = int(w*pr_scale)
h = int(h*pr_scale)
elif max(w,h)<500:
pr_scale = 500.0/max(h,w)
w = int(w*pr_scale)
h = int(h*pr_scale)
scales = []
factor = 0.709
factor_count = 0
minl = min(h,w)
while minl >= 12:
scales.append(pr_scale*pow(factor, factor_count))
minl *= factor
factor_count += 1
return scales
2.Pnet
全称为Proposal Network,其基本的构造是一个全卷积网络。对上一步构建完成的图像金字塔,通过一个全卷积网络进行初步特征提取与标定边框,并进行Bounding-Box Regression调整窗口与NMS进行大部分窗口的过滤。
下面是代码实现:
Pnet有两个输出,classifier用于判断这个网格点上的框的可信度,
bbox_regress表示框的位置。但是这里我们得到的位置不是真实位置,毕竟是缩放。
#-----------------------------#
# 粗略获取人脸框
# 输出bbox位置和是否有人脸
#-----------------------------#
def create_Pnet(weight_path):
input = Input(shape=[None, None, 3])
x = Conv2D(10, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv1')(input)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='PReLU1')(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=2)(x)
x = Conv2D(16, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv2')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='PReLU2')(x)
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv3')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='PReLU3')(x)
classifier = Conv2D(2, (1, 1), activation='softmax', name='conv4-1')(x)
# 无激活函数,线性。
bbox_regress = Conv2D(4, (1, 1), name='conv4-2')(x)
model = Model([input], [classifier, bbox_regress])
model.load_weights(weight_path, by_name=True)
return model
下面是将bbox_regress映射到真实图像上,进行一次解码过程。
解码过程利用detect_face_12net函数实现,其实现步骤如下(需要配合代码理解):
1、判断哪些网格点的置信度较高,即该网格点内存在人脸。
2、记录该网格点的x,y轴。
3、利用函数计算bb1和bb2,分别代表图中框的左上角基点和右下角基点,二者之间差了11个像素,堆叠得到boundingbox 。(因为最小是12x12,所以用11)
4、利用bbox_regress计算解码结果,解码公式为boundingbox = boundingbox + offset12.0scale。(映射到原图)
#-------------------------------------#
# 对pnet处理后的结果进行处理
#-------------------------------------#
def detect_face_12net(cls_prob,roi,out_side,scale,width,height,threshold):
# 0,1表示维度的翻转
cls_prob = np.swapaxes(cls_prob, 0, 1)
roi = np.swapaxes(roi, 0, 2)
stride = 0
# stride略等于2,图片压缩比例(经过p-net导致的),(x,y)是有人脸概率大于threshold的点
if out_side != 1:
stride = float(2*out_side-1)/(out_side-1)
(x,y) = np.where(cls_prob>=threshold)
boundingbox = np.array([x,y]).T
# 找到对应原图的位置,p-net比例+图像金字塔比例
bb1 = np.fix((stride * (boundingbox) + 0 ) * scale)
bb2 = np.fix((stride * (boundingbox) + 11) * scale)
# plt.scatter(bb1[:,0],bb1[:,1],linewidths=1)
# plt.scatter(bb2[:,0],bb2[:,1],linewidths=1,c='r')
# plt.show()
boundingbox = np.concatenate((bb1,bb2),axis = 1)
dx1 = roi[0][x,y]
dx2 = roi[1][x,y]
dx3 = roi[2][x,y]
dx4 = roi[3][x,y]
score = np.array([cls_prob[x,y]]).T
offset = np.array([dx1,dx2,dx3,dx4]).T
# offset为偏置,得到在原图的框
boundingbox = boundingbox + offset*12.0*scale
rectangles = np.concatenate((boundingbox,score),axis=1)
# 把框变成正方形
rectangles = rect2square(rectangles)
pick = []
# 坐标不为0,且不超过长宽。
for i in range(len(rectangles)):
x1 = int(max(0 ,rectangles[i][0]))
y1 = int(max(0 ,rectangles[i][1]))
x2 = int(min(width ,rectangles[i][2]))
y2 = int(min(height,rectangles[i][3]))
sc = rectangles[i][4]
if x2>x1 and y2>y1:
pick.append([x1,y1,x2,y2,sc])
return NMS(pick,0.3)
#-----------------------------#
# 将长方形调整为正方形
#-----------------------------#
def rect2square(rectangles):
w = rectangles[:,2] - rectangles[:,0]
h = rectangles[:,3] - rectangles[:,1]
l = np.maximum(w,h).T
rectangles[:,0] = rectangles[:,0] + w*0.5 - l*0.5
rectangles[:,1] = rectangles[:,1] + h*0.5 - l*0.5
rectangles[:,2:4] = rectangles[:,0:2] + np.repeat([l], 2, axis = 0).T
return rectangles
3.RNet.
全称为Refine Network,其基本的构造是一个卷积神经网络,相对于第一层的P-Net来说,增加了一个全连接层,因此对于输入数据的筛选会更加严格。在图片经过P-Net后,会留下许多预测窗口,我们将所有的预测窗口送入R-Net,这个网络会滤除大量效果比较差的候选框,最后对选定的候选框进行Bounding-Box Regression和NMS进一步优化预测结果。R-Net使用在最后一个卷积层之后使用了一个128的全连接层,保留了更多的图像特征,准确度性能也优于P-Net。
代码如下:
#-----------------------------#
# mtcnn的第二段
# 精修框
#-----------------------------#
def create_Rnet(weight_path):
input = Input(shape=[24, 24, 3])
# 24,24,3 -> 11,11,28
x = Conv2D(28, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv1')(input)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1, 2], name='prelu1')(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=3,strides=2, padding='same')(x)
# 11,11,28 -> 4,4,48
x = Conv2D(48, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv2')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1, 2], name='prelu2')(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2)(x)
# 4,4,48 -> 3,3,64
x = Conv2D(64, (2, 2), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv3')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1, 2], name='prelu3')(x)
# 3,3,64 -> 64,3,3
x = Permute((3, 2, 1))(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
# 576 -> 128
x = Dense(128, name='conv4')(x)
x = PReLU( name='prelu4')(x)
# 128 -> 2 128 -> 4
classifier = Dense(2, activation='softmax', name='conv5-1')(x)
bbox_regress = Dense(4, name='conv5-2')(x)
model = Model([input], [classifier, bbox_regress])
model.load_weights(weight_path, by_name=True)
return model
同样,我们需要调整框位置和映射。
#-------------------------------------#
# 对pnet处理后的结果进行处理
#-------------------------------------#
def filter_face_24net(cls_prob,roi,rectangles,width,height,threshold):
prob = cls_prob[:,1]
pick = np.where(prob>=threshold)
rectangles = np.array(rectangles)
x1 = rectangles[pick,0]
y1 = rectangles[pick,1]
x2 = rectangles[pick,2]
y2 = rectangles[pick,3]
sc = np.array([prob[pick]]).T
dx1 = roi[pick,0]
dx2 = roi[pick,1]
dx3 = roi[pick,2]
dx4 = roi[pick,3]
w = x2-x1
h = y2-y1
x1 = np.array([(x1+dx1*w)[0]]).T
y1 = np.array([(y1+dx2*h)[0]]).T
x2 = np.array([(x2+dx3*w)[0]]).T
y2 = np.array([(y2+dx4*h)[0]]).T
rectangles = np.concatenate((x1,y1,x2,y2,sc),axis=1)
rectangles = rect2square(rectangles)
pick = []
for i in range(len(rectangles)):
x1 = int(max(0 ,rectangles[i][0]))
y1 = int(max(0 ,rectangles[i][1]))
x2 = int(min(width ,rectangles[i][2]))
y2 = int(min(height,rectangles[i][3]))
sc = rectangles[i][4]
if x2>x1 and y2>y1:
pick.append([x1,y1,x2,y2,sc])
return NMS(pick,0.3)
4、Onet
全称为Output Network,基本结构是一个较为复杂的卷积神经网络,相对于R-Net来说多了一个卷积层。O-Net的效果与R-Net的区别在于这一层结构会通过更多的监督来识别面部的区域,而且会对人的面部特征点进行回归,最终输出五个人脸面部特征点。
#-----------------------------#
# mtcnn的第三段
# 精修框并获得五个点
#-----------------------------#
def create_Onet(weight_path):
input = Input(shape = [48,48,3])
# 48,48,3 -> 23,23,32
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv1')(input)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='prelu1')(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, padding='same')(x)
# 23,23,32 -> 10,10,64
x = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv2')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='prelu2')(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2)(x)
# 8,8,64 -> 4,4,64
x = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv3')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='prelu3')(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=2)(x)
# 4,4,64 -> 3,3,128
x = Conv2D(128, (2, 2), strides=1, padding='valid', name='conv4')(x)
x = PReLU(shared_axes=[1,2],name='prelu4')(x)
# 3,3,128 -> 128,12,12
x = Permute((3,2,1))(x)
# 1152 -> 256
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(256, name='conv5') (x)
x = PReLU(name='prelu5')(x)
# 鉴别
# 256 -> 2 256 -> 4 256 -> 10
classifier = Dense(2, activation='softmax',name='conv6-1')(x)
bbox_regress = Dense(4,name='conv6-2')(x)
landmark_regress = Dense(10,name='conv6-3')(x)
model = Model([input], [classifier, bbox_regress, landmark_regress])
model.load_weights(weight_path, by_name=True)
return model
同样,我们需要对结果进行处理:
#-------------------------------------#
# 对onet处理后的结果进行处理
#-------------------------------------#
def filter_face_48net(cls_prob,roi,pts,rectangles,width,height,threshold):
prob = cls_prob[:,1]
pick = np.where(prob>=threshold)
rectangles = np.array(rectangles)
x1 = rectangles[pick,0]
y1 = rectangles[pick,1]
x2 = rectangles[pick,2]
y2 = rectangles[pick,3]
sc = np.array([prob[pick]]).T
dx1 = roi[pick,0]
dx2 = roi[pick,1]
dx3 = roi[pick,2]
dx4 = roi[pick,3]
w = x2-x1
h = y2-y1
pts0= np.array([(w*pts[pick,0]+x1)[0]]).T
pts1= np.array([(h*pts[pick,5]+y1)[0]]).T
pts2= np.array([(w*pts[pick,1]+x1)[0]]).T
pts3= np.array([(h*pts[pick,6]+y1)[0]]).T
pts4= np.array([(w*pts[pick,2]+x1)[0]]).T
pts5= np.array([(h*pts[pick,7]+y1)[0]]).T
pts6= np.array([(w*pts[pick,3]+x1)[0]]).T
pts7= np.array([(h*pts[pick,8]+y1)[0]]).T
pts8= np.array([(w*pts[pick,4]+x1)[0]]).T
pts9= np.array([(h*pts[pick,9]+y1)[0]]).T
x1 = np.array([(x1+dx1*w)[0]]).T
y1 = np.array([(y1+dx2*h)[0]]).T
x2 = np.array([(x2+dx3*w)[0]]).T
y2 = np.array([(y2+dx4*h)[0]]).T
rectangles=np.concatenate((x1,y1,x2,y2,sc,pts0,pts1,pts2,pts3,pts4,pts5,pts6,pts7,pts8,pts9),axis=1)
pick = []
for i in range(len(rectangles)):
x1 = int(max(0 ,rectangles[i][0]))
y1 = int(max(0 ,rectangles[i][1]))
x2 = int(min(width ,rectangles[i][2]))
y2 = int(min(height,rectangles[i][3]))
if x2>x1 and y2>y1:
pick.append([x1,y1,x2,y2,rectangles[i][4],
rectangles[i][5],rectangles[i][6],rectangles[i][7],rectangles[i][8],rectangles[i][9],rectangles[i][10],rectangles[i][11],rectangles[i][12],rectangles[i][13],rectangles[i][14]])
return NMS(pick,0.3)
最后,也就是我们的非极大抑制NMS
def NMS(rectangles,threshold):
if len(rectangles)==0:
return rectangles
boxes = np.array(rectangles)
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,2]
y2 = boxes[:,3]
s = boxes[:,4]
area = np.multiply(x2-x1+1, y2-y1+1)
I = np.array(s.argsort())
pick = []
while len(I)>0:
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[I[-1]], x1[I[0:-1]]) #I[-1] have hightest prob score, I[0:-1]->others
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[I[-1]], y1[I[0:-1]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[I[-1]], x2[I[0:-1]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[I[-1]], y2[I[0:-1]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
o = inter / (area[I[-1]] + area[I[0:-1]] - inter)
pick.append(I[-1])
I = I[np.where(o<=threshold)[0]]
result_rectangle = boxes[pick].tolist()
return result_rectangle