基于yolov5和AIdLux的人流统计代码实现
本次项目主要⽤到⼈体检测+⼈体追踪+业务功能判断。
由于下载后的标注文件为odgt格式,所以需要将标注⽂件odgt格式转换成xml格式,需要注意的是Crowdhuman中,有三种标注内容,vbox、fbox、hbox,分别对应:可看到的⼈体,完整 ⼈体,⼈脸。 本次训练过程中主要使⽤完整⼈体进⾏训练,因此主要⽤到fbox的标签:
代码运行后可以得到VOC格式的xml⽂件。
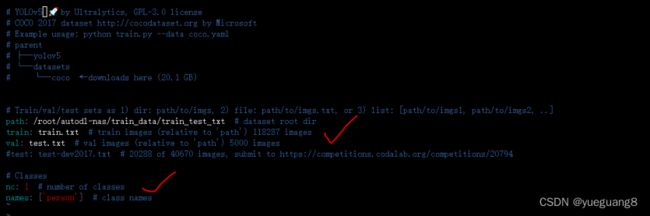
新建person.yaml :因为训练的是⼈体检测模型,所以在yolov5_code/data⽂件夹中,新增⼀个person.yaml。不过需要注意的是,训练集和验证集的路径都要修改⼀下,此外还有类别数,以及类别标签。
修改models/yolov5n.yaml :修改其中的类别数量,因为⼈体就⼀个类别,修改成1。
训练⼈体检测模型:因为训练的时候,需要⼀系列的库⽂件,根据提示安装正确的库后,既可以执行 python train.py进行训练。
PC端模型测试:训练过程中,⼀般会得到两个模型,⼀个best.pt,即epoch迭代的过程中,map精度对⽐⽐较好保存的 模型。⼀个是last.pt,即迭代过程中,最后⼀次epoch保存的模型。因为实际项⽬中主要使⽤视频进⾏推理,所以加载视频,使用best.pt进⾏推理测试。
Aidlux视频推理:将训 练好的tflite放到aidlux⽂件夹中。 其中包含了很多Aidlux专属的函数接⼝,⼤家可以在https://docs.aidlux.com/#/intro/ai/ai-aidlite,查 看下相关的函数说明。
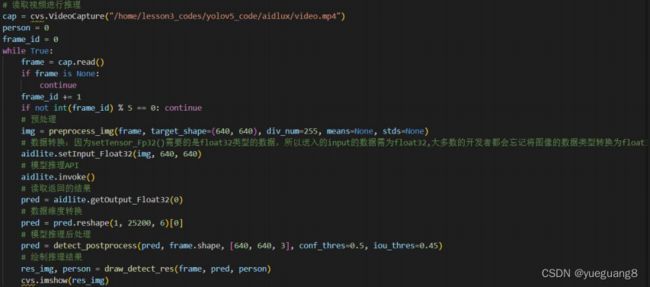
视频读取&模型推理:
代码复制到Aidlux中 ,通过SSH远程连接Aidlux软件,在vscode终端中运行代码即可
2.目标跟踪
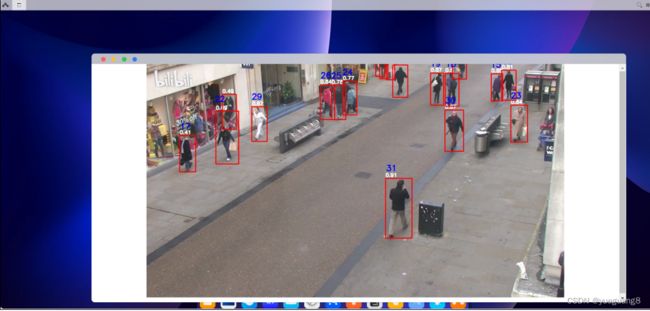
最终结果如下:
最后附代码:
# aidlux相关
from cvs import *
import aidlite_gpu
from utils import detect_postprocess, preprocess_img, draw_detect_res, scale_coords,process_points,is_in_poly,is_passing_line
import cv2
# bytetrack
from track.tracker.byte_tracker import BYTETracker
from track.utils.visualize import plot_tracking
import requests
import time
# 加载模型
model_path = '/home/lesson4_codes/aidlux/yolov5n_best-fp16.tflite'
in_shape = [1 * 640 * 640 * 3 * 4]
out_shape = [1 * 25200 * 6 * 4]
# 载入模型
aidlite = aidlite_gpu.aidlite()
# 载入yolov5检测模型
aidlite.ANNModel(model_path, in_shape, out_shape, 4, 0)
tracker = BYTETracker(frame_rate=30)
track_id_status = {}
cap = cvs.VideoCapture("/home/lesson4_codes/aidlux/video.mp4")
frame_id = 0
count = 0 #记录越界人数
count1 = 0 #记录越界人数
while True:
frame = cap.read()
if frame is None:
continue
frame_id += 1
if frame_id % 3 != 0:
continue
# print(frame.shape)
# 预处理
img = preprocess_img(frame, target_shape=(640, 640), div_num=255, means=None, stds=None)
# 数据转换:因为setTensor_Fp32()需要的是float32类型的数据,所以送入的input的数据需为float32,大多数的开发者都会忘记将图像的数据类型转换为float32
aidlite.setInput_Float32(img, 640, 640)
# 模型推理API
aidlite.invoke()
# 读取返回的结果
pred = aidlite.getOutput_Float32(0)
# 数据维度转换
pred = pred.reshape(1, 25200, 6)[0]
# 模型推理后处理
pred = detect_postprocess(pred, frame.shape, [640, 640, 3], conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.45)
# 绘制推理结果
res_img = draw_detect_res(frame, pred)
# 目标追踪相关功能
det = []
# Process predictions
for box in pred[0]: # per image
box[2] += box[0]
box[3] += box[1]
det.append(box)
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
online_targets = tracker.update(det, [frame.shape[0], frame.shape[1]])
online_tlwhs = []
online_ids = []
online_scores = []
# 取出每个目标的追踪信息
for t in online_targets:
# 目标的检测框信息
tlwh = t.tlwh
# 目标的track_id信息
tid = t.track_id
online_tlwhs.append(tlwh)
online_ids.append(tid)
online_scores.append(t.score)
# 针对目标绘制追踪相关信息
res_img = plot_tracking(res_img, online_tlwhs, online_ids, 0,0)
### 越界识别功能实现 ###
# 1.绘制越界监测区域
#points = [[593,176],[904,243],[835,323],[507,259]]
#points = [[593,176],[904,243],[835,323],[507,259]]
points = [[123,276],[1280,276]]
color_light_green=(255, 0, 0) ##浅绿色 RGB
res_img = process_points(res_img,points,color_light_green)
# 2.计算得到人体下方中心点的位置(人体检测监测点调整)
pt = [tlwh[0]+1/2*tlwh[2],tlwh[1]+tlwh[3]]
pt1 = [tlwh[0]+1/2*tlwh[2],tlwh[1]]
# 3. 人体和违规区域的判断(人体状态追踪判断)
#track_info = is_in_poly(pt, points)
track_info = is_passing_line(pt, points)
if tid not in track_id_status.keys():
track_id_status.update( {tid:[track_info]})
else:
if track_info != track_id_status[tid][-1]:
track_id_status[tid].append(track_info)
# 4. 判断是否有track_id越界,有的话保存成图片
# 当某个track_id的状态,上一帧是-1,但是这一帧是1时,说明越界了 B->A
if track_id_status[tid][-1] == 1 and len(track_id_status[tid]) >1:
# 判断上一个状态是否是-1,是否的话说明越界,为了防止继续判别,随机的赋了一个3的值
if track_id_status[tid][-2] == -1:
track_id_status[tid].append(3)
# cv2.imwrite("overstep.jpg",res_img)
count += 1
print("count = %d" % count)
if track_id_status[tid][-1] == -1 and len(track_id_status[tid]) >1: #A->B
# 判断上一个状态是否是-1,是否的话说明越界,为了防止继续判别,随机的赋了一个3的值
if track_id_status[tid][-2] == 1:
track_id_status[tid].append(3)
# cv2.imwrite("overstep.jpg",res_img)
count1 += 1
print("count1 = %d" % count1)
cv2.putText(res_img, "B->A person:" +str(count), (100, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(res_img, "A->B person:" +str(count1), (100, 80), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(res_img, "A", (600, 250), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.putText(res_img, "B", (600, 320), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cvs.imshow(res_img)