MindSpore实现图片分类
MindSpore图片分类
实验介绍
本实验主要介绍使用MindSpore在CIFAR-10数据集上训练ResNet50。本实验使用MindSpore model_zoo中提供的ResNet50模型定义,以及MindSpore官网教程在云上使用MindSpore里的训练脚本。
实验目的
- 了解如何使用MindSpore加载常用的CIFAR-10图片分类数据集。
- 了解MindSpore的model_zoo模块,以及如何使用model_zoo中的模型。
- 了解ResNet50这类大模型的基本结构和编程方法。
预备知识
- 熟练使用Python,了解Shell及Linux操作系统基本知识。
- 具备一定的深度学习理论知识,如卷积神经网络、损失函数、优化器,训练策略、Checkpoint等。
- 了解华为云的基本使用方法,包括OBS(对象存储)、ModelArts(AI开发平台)、训练作业等功能。华为云官网:https://www.huaweicloud.com
- 了解并熟悉MindSpore AI计算框架,MindSpore官网:https://www.mindspore.cn/
实验环境
- MindSpore 1.2.0;
- 华为云ModelArts(控制台左上角选择“华北-北京四”):ModelArts是华为云提供的面向开发者的一站式AI开发平台,集成了昇腾AI处理器资源池,用户可以在该平台下体验MindSpore。
实验准备
数据集准备
CIFAR-10是一个图片分类数据集,包含60000张32x32的彩色物体图片,训练集50000张,测试集10000张,共10类,每类6000张。
- 从CIFAR-10官网下载“CIFAR-10 binary version (suitable for C programs)”到本地并解压。
脚本准备
从MindSpore tutorial仓库里下载相关脚本。将脚本和数据集组织为如下形式:
experiment_3
├── dataset.py
├── resnet.py
├── resnet50_train.py
└── cifar10
├── batches.meta.txt
├── eval
│ └── test_batch.bin
└── train
├── data_batch_1.bin
├── data_batch_2.bin
├── data_batch_3.bin
├── data_batch_4.bin
└── data_batch_5.bin
创建OBS桶
本实验需要使用华为云OBS存储脚本和数据集,可以参考快速通过OBS控制台上传下载文件了解使用OBS创建桶、上传文件、下载文件的使用方法(下文给出了操作步骤)。
提示: 华为云新用户使用OBS时通常需要创建和配置“访问密钥”,可以在使用OBS时根据提示完成创建和配置。也可以参考获取访问密钥并完成ModelArts全局配置获取并配置访问密钥。
打开OBS控制台,点击右上角的“创建桶”按钮进入桶配置页面,创建OBS桶的参考配置如下:
- 区域:华北-北京四
- 数据冗余存储策略:单AZ存储
- 桶名称:如ms-course
- 存储类别:标准存储
- 桶策略:公共读
- 归档数据直读:关闭
- 企业项目、标签等配置:免
上传文件
点击新建的OBS桶名,再打开“对象”标签页,通过“上传对象”、“新建文件夹”等功能,将脚本和数据集上传到OBS桶中。上传文件后,查看页面底部的“任务管理”状态栏(正在运行、已完成、失败),确保文件均上传完成。若失败请:
- 参考上传对象大小限制/切换上传方式,
- 参考上传对象失败常见原因。
- 若无法解决请新建工单,产品类为“对象存储服务”,问题类型为“桶和对象相关”,会有技术人员协助解决。
实验步骤
推荐使用ModelArts训练作业进行实验,适合大规模并发使用。若使用ModelArts Notebook,请参考LeNet5及Checkpoint实验案例,了解Notebook的使用方法和注意事项。
代码梳理
- resnet50_train.py:主脚本,包含性能测试
PerformanceCallback、动态学习率get_lr、执行函数resnet50_train、主函数; - dataset.py:数据处理脚本。
- resnet.py: resnet模型定义脚本,包含ResidualBlock模块类
ResidualBlock、ResNet类、ResNet50类、ResNet101类等。
resnet50_train.py代码梳理
PerformanceCallback继承MindSpore Callback类,并统计每个训练step的时延:
class PerformanceCallback(Callback):
"""
Training performance callback.
Args:
batch_size (int): Batch number for one step.
"""
def __init__(self, batch_size):
super(PerformanceCallback, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.last_step = 0
self.epoch_begin_time = 0
def step_begin(self, run_context):
self.epoch_begin_time = time.time()
def step_end(self, run_context):
params = run_context.original_args()
cost_time = time.time() - self.epoch_begin_time
train_steps = params.cur_step_num -self.last_step
print(f'epoch {params.cur_epoch_num} cost time = {cost_time}, train step num: {train_steps}, '
f'one step time: {1000*cost_time/train_steps} ms, '
f'train samples per second of cluster: {device_num*train_steps*self.batch_size/cost_time:.1f}\n')
self.last_step = run_context.original_args().cur_step_num
get_lr生成学习率数组,其中每个元素对应每个step的学习率,这里学习率下降采用二次曲线的形式:
def get_lr(global_step,
total_epochs,
steps_per_epoch,
lr_init=0.01,
lr_max=0.1,
warmup_epochs=5):
"""
Generate learning rate array.
Args:
global_step (int): Initial step of training.
total_epochs (int): Total epoch of training.
steps_per_epoch (float): Steps of one epoch.
lr_init (float): Initial learning rate. Default: 0.01.
lr_max (float): Maximum learning rate. Default: 0.1.
warmup_epochs (int): The number of warming up epochs. Default: 5.
Returns:
np.array, learning rate array.
"""
lr_each_step = []
total_steps = steps_per_epoch * total_epochs
warmup_steps = steps_per_epoch * warmup_epochs
if warmup_steps != 0:
inc_each_step = (float(lr_max) - float(lr_init)) / float(warmup_steps)
else:
inc_each_step = 0
for i in range(int(total_steps)):
if i < warmup_steps:
lr = float(lr_init) + inc_each_step * float(i)
else:
base = ( 1.0 - (float(i) - float(warmup_steps)) / (float(total_steps) - float(warmup_steps)) )
lr = float(lr_max) * base * base
if lr < 0.0:
lr = 0.0
lr_each_step.append(lr)
current_step = global_step
lr_each_step = np.array(lr_each_step).astype(np.float32)
learning_rate = lr_each_step[current_step:]
return learning_rate
dataset.py代码梳理
MindSpore支持直接读取CIFAR-10数据集:
if device_num == 1 or not do_train:
ds = de.Cifar10Dataset(dataset_path, num_parallel_workers=8, shuffle=do_shuffle)
else:
ds = de.Cifar10Dataset(dataset_path, num_parallel_workers=8, shuffle=do_shuffle,num_shards=device_num, shard_id=device_id)
使用数据增强,如随机裁剪、随机水平反转:
# define map operations
random_crop_op = C.RandomCrop((32, 32), (4, 4, 4, 4))
random_horizontal_flip_op = C.RandomHorizontalFlip(device_id / (device_id + 1))
resize_op = C.Resize((resize_height, resize_width))
rescale_op = C.Rescale(rescale, shift)
normalize_op = C.Normalize([0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010])
change_swap_op = C.HWC2CHW()
trans = []
if do_train:
trans += [random_crop_op, random_horizontal_flip_op]
trans += [resize_op, rescale_op, normalize_op, change_swap_op]
type_cast_op = C2.TypeCast(mstype.int32)
ds = ds.map(input_columns="label", num_parallel_workers=8, operations=type_cast_op)
ds = ds.map(input_columns="image", num_parallel_workers=8, operations=trans)
resnet.py代码梳理
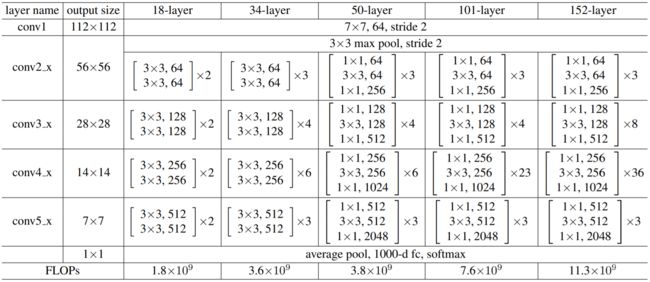
ResNet的不同版本均由5个阶段(stage)组成,其中ResNet50结构为Convx1 -> ResidualBlockx3 -> ResidualBlockx4 -> ResidualBlockx6 -> ResidualBlockx5 -> Pooling+FC。
[1] 图片来源于https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf
ResidualBlock为残差模块,相比传统卷积多了一个short-cut支路,用于将浅层的信息直接传递到深层,使得网络可以很深,而不会出现训练时梯度消失/爆炸的问题。ResNet50采用了下图右侧Bottleneck形式的残差模块:
[2] 图片来源于https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf
ResNet的ResidualBlock(残差模块)定义如下,是组成ResNet网络的基础模块。
class ResidualBlock(nn.Cell):
"""
ResNet V1 residual block definition.
Args:
in_channel (int): Input channel.
out_channel (int): Output channel.
stride (int): Stride size for the first convolutional layer. Default: 1.
Returns:
Tensor, output tensor.
Examples:
>>> ResidualBlock(3, 256, stride=2)
"""
expansion = 4
def __init__(self,
in_channel,
out_channel,
stride=1):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
channel = out_channel // self.expansion
self.conv1 = _conv1x1(in_channel, channel, stride=1)
self.bn1 = _bn(channel)
self.conv2 = _conv3x3(channel, channel, stride=stride)
self.bn2 = _bn(channel)
self.conv3 = _conv1x1(channel, out_channel, stride=1)
self.bn3 = _bn_last(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.down_sample = False
if stride != 1 or in_channel != out_channel:
self.down_sample = True
self.down_sample_layer = None
if self.down_sample:
self.down_sample_layer = nn.SequentialCell([_conv1x1(in_channel, out_channel, stride),
_bn(out_channel)])
self.add = P.TensorAdd()
def construct(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
# ResNet50未使用带有下采样的残差支路
if self.down_sample:
identity = self.down_sample_layer(identity)
# output为残差支路,identity为short-cut支路
out = self.add(out, identity)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
ResNet类定义如下,传入的参数包括:
- layer_nums:每个stage中ResidualBlock重复次数列表(list)
- in_channels:每个stage输入通道数列表(list)
- out_channels:每个stage输出通道数列表(list)
- strides:每个stage中卷积算子的stride列表(list)
- num_classes:图片分类数(int)
注解:
- 这里的stage不是ResNet真实层数,只是将ResNet分成多个stage,每个stage包含多个ResidualBlock。
- layer_nums、in_channels、out_channels、strides列表的长度必须相同。
- 传入的参数不同则网络结构不同,典型的有ResNet50、ResNet101。其定义可以参考resnet.py文件。学员可以尝试自定义参数设计一个新的网络。
class ResNet(nn.Cell):
"""
ResNet architecture.
Args:
block (Cell): Block for network.
layer_nums (list): Numbers of block in different layers.
in_channels (list): Input channel in each layer.
out_channels (list): Output channel in each layer.
strides (list): Stride size in each layer.
num_classes (int): The number of classes that the training images are belonging to.
Returns:
Tensor, output tensor.
Examples:
>>> ResNet(ResidualBlock,
>>> [3, 4, 6, 3],
>>> [64, 256, 512, 1024],
>>> [256, 512, 1024, 2048],
>>> [1, 2, 2, 2],
>>> 10)
"""
def __init__(self,
block,
layer_nums,
in_channels,
out_channels,
strides,
num_classes):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if not len(layer_nums) == len(in_channels) == len(out_channels) == 4:
raise ValueError("the length of layer_num, in_channels, out_channels list must be 4!")
self.conv1 = _conv7x7(3, 64, stride=2)
self.bn1 = _bn(64)
self.relu = P.ReLU()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode="same")
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block,
layer_nums[0],
in_channel=in_channels[0],
out_channel=out_channels[0],
stride=strides[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block,
layer_nums[1],
in_channel=in_channels[1],
out_channel=out_channels[1],
stride=strides[1])
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block,
layer_nums[2],
in_channel=in_channels[2],
out_channel=out_channels[2],
stride=strides[2])
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block,
layer_nums[3],
in_channel=in_channels[3],
out_channel=out_channels[3],
stride=strides[3])
self.mean = P.ReduceMean(keep_dims=True)
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.end_point = _fc(out_channels[3], num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, block, layer_num, in_channel, out_channel, stride):
"""
Make stage network of ResNet.
Args:
block (Cell): Resnet block.
layer_num (int): Layer number.
in_channel (int): Input channel.
out_channel (int): Output channel.
stride (int): Stride size for the first convolutional layer.
Returns:
SequentialCell, the output layer.
Examples:
>>> _make_layer(ResidualBlock, 3, 128, 256, 2)
"""
layers = []
resnet_block = block(in_channel, out_channel, stride=stride)
layers.append(resnet_block)
for _ in range(1, layer_num):
resnet_block = block(out_channel, out_channel, stride=1)
layers.append(resnet_block)
return nn.SequentialCell(layers)
def construct(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
c1 = self.maxpool(x)
c2 = self.layer1(c1)
c3 = self.layer2(c2)
c4 = self.layer3(c3)
c5 = self.layer4(c4)
out = self.mean(c5, (2, 3))
out = self.flatten(out)
out = self.end_point(out)
return out
ResNet50类定义如下:
def resnet50(class_num=10):
"""
Get ResNet50 neural network.
Args:
class_num (int): Class number.
Returns:
Cell, cell instance of ResNet50 neural network.
Examples:
>>> net = resnet50(10)
"""
return ResNet(ResidualBlock,
[3, 4, 6, 3],
[64, 256, 512, 1024],
[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
[1, 2, 2, 2],
class_num)
适配训练作业(跳过)
创建训练作业时,运行参数会通过脚本传参的方式输入给脚本代码,脚本必须解析传参才能在代码中使用相应参数。如data_url和train_url,分别对应数据存储路径(OBS路径)和训练输出路径(OBS路径)。脚本对传参进行解析后赋值到args变量里,在后续代码里可以使用。
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--data_url', required=True, default=None, help='Location of data.')
parser.add_argument('--train_url', required=True, default=None, help='Location of training outputs.')
parser.add_argument('--num_epochs', type=int, default=90, help='Number of training epochs.')
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
MindSpore暂时没有提供直接访问OBS数据的接口,需要通过ModelArts自带的moxing框架与OBS交互。
-
训练开始前,拷贝自己账户下或他人共享的OBS桶内的数据集至执行容器。
import moxing as mox # src_url形如's3://OBS/PATH',为OBS桶中数据集的路径,dst_url为执行容器中的路径 mox.file.copy_parallel(src_url=args.data_url, dst_url='cifar10/') -
如需将训练输出(如模型Checkpoint)从执行容器拷贝至自己的OBS中,请参考:
import moxing as mox # dst_url形如's3://OBS/PATH',将ckpt目录拷贝至OBS后,可在OBS的`args.train_url`目录下看到ckpt目录 mox.file.copy_parallel(src_url='ckpt', dst_url=os.path.join(args.train_url, 'ckpt'))
创建训练作业
可以参考使用常用框架训练模型来创建并启动训练作业(下文给出了操作步骤)。
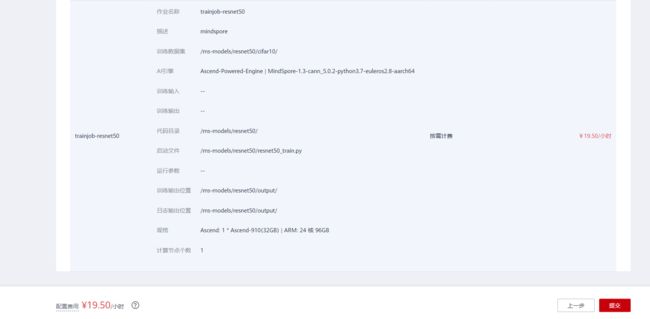
打开ModelArts控制台-训练管理-训练作业,点击“创建”按钮进入训练作业配置页面,创建训练作业的参考配置:
- 算法来源:常用框架->Ascend-Powered-Engine->MindSpore
- 代码目录:选择上述新建的OBS桶中的experiment_3目录
- 启动文件:选择上述新建的OBS桶中的experiment_3目录下的
resnet50_train.py(注意,针对此文件,课程gitee仓库代码在167行有错,多打了一个空格,同时,将120行改为local_data_path = 'cifar10' # your cifar10 path务必修改后重新上传至obs) - 数据来源:数据存储位置->选择上述新建的OBS桶中的experiment_3文件夹下的cifar10目录
- 训练输出位置:选择上述新建的OBS桶中的experiment_3目录并在其中创建output目录
- 作业日志路径:同训练输出位置
- 规格:Ascend:1*Ascend 910
- 其他均为默认
启动并查看训练过程:
- 点击提交以开始训练;
- 在训练作业列表里可以看到刚创建的训练作业,在训练作业页面可以看到版本管理;
- 点击运行中的训练作业,在展开的窗口中可以查看作业配置信息,以及训练过程中的日志,日志会不断刷新,等训练作业完成后也可以下载日志到本地进行查看;
- 在训练日志中可以看到
epoch 90 cost time = 27.328994035720825, train step num: 1562, one step time: 17.496154952446112 ms, train samples per second of cluster: 1829.0等字段,即训练过程的性能数据; - 在训练日志中可以看到
epoch: 90 step 1562, loss is 0.0002547435578890145等字段,即训练过程的loss数据; - 在训练日志里可以看到
Evaluation result: {'acc': 0.9467147435897436}.字段,即训练完成后的验证精度。
epoch 1 cost time = 156.34279108047485, train step num: 1562, one step time: 100.09141554447814 ms, train samples per second of cluster: 319.7
epoch: 1 step 1562, loss is 1.5020508766174316
epoch 2 cost time = 27.33933186531067, train step num: 1562, one step time: 17.502773281248828 ms, train samples per second of cluster: 1828.3
epoch: 2 step 1562, loss is 1.612194299697876
epoch 3 cost time = 27.33275270462036, train step num: 1562, one step time: 17.498561270563613 ms, train samples per second of cluster: 1828.7
epoch: 3 step 1562, loss is 1.0880045890808105
...
...
...
epoch 50 cost time = 27.318379402160645, train step num: 1562, one step time: 17.48935941239478 ms, train samples per second of cluster: 1829.7
epoch: 50 step 1562, loss is 0.028316421434283257
epoch 51 cost time = 27.317234992980957, train step num: 1562, one step time: 17.488626756069756 ms, train samples per second of cluster: 1829.8
epoch: 51 step 1562, loss is 0.09725271165370941
...
...
...
Start run evaluation.
Evaluation result: {'acc': 0.9467147435897436}.
折腾了三个版本,笔者可算是训练成功了。训练大约需要45min。
实验结论
本实验主要介绍使用MindSpore在CIFAR-10数据集上训练ResNet50,了解了以下知识点:
- 使用自定义Callback实现性能监测;
- 使用动态学习率提升训练效果;
- 加载CIFAR-10数据集、数据增强;
- ResNet50模型的结构及其MindSpore实现。