NLP-Beginner:自然语言处理入门练习----task 2基于机器学习的文本分类
数据集:http://链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UIrk148uRGWKQBBQp-Q4RQ 提取码:o13v
上方为glove数据集。
任务:
1.熟悉Pytorch,用Pytorch重写《任务一》,实现CNN、RNN的文本分类
2.word embedding 的方式初始化
3.随机embedding的初始化方式
4.用glove 预训练的embedding进行初始化
GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation
一、知识点:
1.word embedding(词嵌入):词嵌入模型即是把每一个词映射到一个高维空间里,每一个词代表着一个高维空间的向量。词嵌入实际上是一类技术,单个词在预定义的向量空间中被表示为实数向量,每个单词都映射到一个向量。举个例子,比如在一个文本中包含“猫”“狗”“爱情”等若干单词,而这若干单词映射到向量空间中,“猫”对应的向量为(0.1 0.2 0.3),“狗”对应的向量为(0.2 0.2 0.4),“爱情”对应的映射为(-0.4 -0.5 -0.2)(本数据仅为示意)。像这种将文本X{x1,x2,x3,x4,x5……xn}映射到多维向量空间Y{y1,y2,y3,y4,y5……yn },这个映射的过程就叫做词嵌入。通过词嵌入这种方式将单词转变为词向量,机器便可对单词进行计算,通过计算不同词向量之间夹角余弦值cos而得出单词之间的相似性。
词嵌入模型的初始化:
(1)随机初始化:给定一个维度d,对于每一个词,随机生成一个d维的向量。这种初始方式非常简单,但是相对可能会产生较劣的初值,也没有一个良好的解释性。
(2)预训练模型初始化(Glove):拿别人已经训练好的模型作为初值,初始化时间会比较长,因为要从别人的词库里面找,但是这种初值无疑要比随机初始化好得多。
特征表示:给定每个词的词向量,可以把一个句子量化成一个ID列表,再变成特征,也就是矩阵,得到句子的特征矩阵X后,便可以把它放到神经网络中。
2.CNN/RNN
- CNN卷积神经网络:一般有3-4层,分别是卷积层,激活层,池化层,全连接层,具有局部连接,权重共享,汇聚等特性的深层前馈神经网络,这里的激活参数选择了ReLU函数,ReLu(x)=max(x,0)。池化层相当于是对特征矩阵/向量提取出一些有用的信息,从而减少特征的规模,不仅减少了计算量,也能去除冗余特征。
- RNN循环神经网络:一般有2-3层,分别是隐藏层,激活曾,全连接层,具有短期记忆能力的神经网络。隐藏层的目的是为了实现记忆功能。
在CNN中,是直接对特征矩阵X进行操作,而在RNN中,是逐个对xi进行操作。
整个流程:句子x通过word embedding得出特征矩阵X在通过神经网络得到类别概率向量p。
3.Dropout(丢弃法)
Dropout (丢弃法) 是指在深度网络的训练中,以一定的概率随机地“临时丢弃”一部分神经元节点。 具体来讲,Dropout 作用于每份小批量训练数据,由于其随机丢弃部分神经元的机制,相当于每次迭代都在训练不同结构的神经网络。简单来讲,就是为了防止模型过拟合,且Dropout层在模型测试时不会有任何影响。
二、实验数据设置
样本个数:约150000;
训练集:测试集: 7:3
alpha:10-3
lh,d:50
ll:最长句子的单词数目
Batch大小:500
三、代码
1.main.py
# -*- coding: GBK -*-
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# coding=gbk
import csv
import random
from feature import Random_embedding,Glove_embedding
from comparison_plot import NN_embedding_plot
# 数据读入
with open('train.tsv') as f :
tsvreader = csv.reader(f,delimiter='\t')
temp = list(tsvreader)
with open('glove.6B.50d.txt','rb') as f: # glove embedding
lines = f.readlines()
# 用Glove创建词典
trained_dict = dict()
n = len(lines) # lines的长度
for i in range(n): # 遍历
line = lines[i].split() # split分割 upper大写
trained_dict[line[0].decode('utf-8').upper()] = [float(line[j]) for j in range(1,51)]
# 初始化
iter_times = 50 # 做50个epoch
alpha = 0.001 # 学习率
# 程序开始
data = temp[1:]
batch_size = 500 # 批大小
# 随机初始化
random.seed(2021) # 随机种子
random_embedding = Random_embedding(data=data ) # 调用feature
random_embedding.get_words() # 找到所有单词,并标记ID
random_embedding.get_id() # 找到每个句子拥有的单词ID
# 预训练模型初始化
random.seed(2021)
glove_embedding = Glove_embedding(data=data,trained_dict=trained_dict)
glove_embedding.get_words() # 找到所有单词并标记ID
glove_embedding.get_id() # 找到每个句子拥有的单词ID
NN_embedding_plot(random_embedding,glove_embedding,alpha,batch_size,iter_times)2.feature.py
# -*- coding: GBK -*-
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# coding=gbk
# 特征提取
import random
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence
import torch
# 将数据按照一定的比例分割为训练集和测试集
def data_split(data,test_rate=0.3):
train = list()
test = list()
for datum in data:
if random.random() > test_rate:
train.append(datum)
else:
test.append(datum)
return train,test
# 随机初始化
class Random_embedding():
def __init__(self,data,test_rate=0.3):
self.dict_words = dict() # 单词->ID的映射
data.sort(key=lambda x:len(x[2].split())) # 按照句子长度排序,短着在前,这样做可以避免后面一个batch内句子长短不一,导致padding过度
self.data = data
self.len_words = 0 # 单词数目(包括padding的ID:0)
self.train,self.test = data_split(data,test_rate=test_rate) # 训练集测试集划分
self.train_y = [int(term[3]) for term in self.train] # 训练集类别
self.test_y = [int(term[3]) for term in self.test] # 测试集类别
self.train_matrix = list() # 训练集的单词ID列表,叠成一个矩阵
self.test_matrix = list() # 测试集的单词ID列表,叠成一个矩阵
self.longest = 0 # 记录最长的单词
def get_words(self):
for term in self.data:
s = term[2] # 取出句子
s = s.upper() # 将其转化为大写,避免识别i和I为不同的两个单词
words = s.split()
for word in words: # 一个一个单词进行寻找
if word not in self.dict_words:
self.dict_words[word] = len(self.dict_words) + 1 # padding是第0个,所以要+1
self.len_words = len(self.dict_words) # 单词数目,暂未包括padding的id0
def get_id(self):
for term in self.train: # 训练集
s = term[2]
s = s.upper()
words = s.split()
item = [self.dict_words[word] for word in words] # 找到id列表(未进行padding)
self.longest = max(self.longest,len(item)) # 记录最长的单词
self.train_matrix.append(item)
for term in self.test: # 测试集
s = term[2]
s = s.upper()
words = s.split()
item = [self.dict_words[word] for word in words] # 找到id列表(未进行padding)
self.longest = max(self.longest,len(item))
self.test_matrix.append(item)
self.len_words += 1 # 单词数目,包含padding的id0
class Glove_embedding():
def __init__(self,data,trained_dict,test_rate=0.3):
self.dict_words = dict() # 单词->ID的映射
self.trained_dict = trained_dict # 记录预训练词向量模型
data.sort(key = lambda x:len(x[2].split())) # 按照句子长度排序,短着在前,这样做可以避免后面一个batch内句子长短不一,导致padding过度
self.data = data
self.len_words = 0 # 单词数目(包含padding的id0)
self.train,self.test = data_split(data,test_rate=test_rate) # 测试集和训练集的划分
self.train_y = [int(term[3]) for term in self.train] # 训练集类别
self.test_y = [int(term[3]) for term in self.test] # 测试集类别
self.train_matrix = list()
self.test_matrix = list()
self.longest = 0
self.embedding = list() # 抽取出用到的,即预训练模型的单词
def get_words(self):
self.embedding.append([0] * 50) # 先加padding的词向量
for term in self.data:
s = term[2] # 取出句子
s = s.upper()
words = s.split()
for word in words:
if word not in self.dict_words:
self.dict_words[word] = len(self.dict_words)+1 # padding是第0个所以要加一
if word in self.trained_dict: # 如果预训练模型中有这个单词,直接记录词向量
self.embedding.append(self.trained_dict[word])
else: # 如果预训练模型中没有这个单词,则初始化该词的对应词向量为0向量
self.embedding.append([0]*50)
self.len_words = len(self.dict_words) # 单词数目(暂未包括padding的id0)
def get_id(self):
for term in self.train: # 训练集
s = term[2]
s = s.upper()
words = s.split()
item = [self.dict_words[word] for word in words] # 找到id列表(未进行padding)
self.longest = max(self.longest,len(item)) # 记录最长的单词
self.train_matrix.append(item)
for term in self.test: # 测试集
s = term[2]
s = s.upper()
words = s.split()
item = [self.dict_words[word] for word in words]
self.longest = max(self.longest,len(item))
self.test_matrix.append(item)
self.len_words += 1 # 单词数目(暂未包括padding的id0)
# 自定义数据集的结构
class ClsDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,sentence,emotion):
self.sentence = sentence
self.emotion = emotion
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.sentence[item],self.emotion[item]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.emotion)
# 自定义数据集的内数据返回类型,并进行padding
def collate_fn(batch_data):
sentence,emotion = zip(*batch_data)
sentences = [torch.LongTensor(sent) for sent in sentence] # 把句子变成LongTensor类型
padded_sents = pad_sequence(sentences,batch_first=True,padding_value=0) # 自动padding操作
return torch.LongTensor(padded_sents),torch.LongTensor(emotion)
# 利用dataloader划分batch
def get_batch(x,y,batch_size):
dataset = ClsDataset(x,y)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=False,drop_last=True,collate_fn=collate_fn)
return dataloader
# shuffle是指每个epoch都随机打乱数据再分batch,设置成False,否则之前的顺序会直接打乱
# drop_last是指不利用最后一个不完整的batch(数据大小不能被batch_size整除)3.comparison_plot.py
# -*- coding: GBK -*-
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# coding=gbk
import matplotlib.pyplot
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import optim
from Neural_network import RNN, CNN
from feature import get_batch
def NN_embdding(model, train, test, learning_rate, iter_times):
# 定义优化器(求参数)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 损失函数
loss_fun = F.cross_entropy
# 损失值记录
train_loss_record = list()
test_loss_record = list()
long_loss_record = list()
# 准确率记录
train_record = list()
test_record = list()
long_record = list()
# torch.autograd.set_detect_anomaly(True)
# 训练阶段
for iteration in range(iter_times):
model.train() # 重要!!!进入非训练模式
for i, batch in enumerate(train):
x, y = batch # 取一个batch
# y = y.cuda()
pred = model(x) # 计算输出
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度初始化
loss = loss_fun(pred, y) # 损失值计算
loss.backward() # 反向传播梯度
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
model.eval() # 重要!!!进入非训练模式(测试模式)
# 本轮正确率记录
train_acc = list()
test_acc = list()
long_acc = list()
length = 20
# 本轮损失值记录
train_loss = 0
test_loss = 0
long_loss = 0
for i, batch in enumerate(train):
x, y = batch # 取一个batch
# y = y.cuda()
pred = model(x) # 计算输出
loss = loss_fun(pred, y) # 损失值计算
train_loss += loss.item() # 损失值累加
_, y_pre = torch.max(pred, -1)
# 计算本batch准确率
acc = torch.mean((torch.tensor(y_pre == y, dtype=torch.float)))
train_acc.append(acc)
for i, batch in enumerate(test):
x, y = batch # 取一个batch
# y = y.cuda()
pred = model(x) # 计算输出
loss = loss_fun(pred, y) # 损失值计算
test_loss += loss.item() # 损失值累加
_, y_pre = torch.max(pred, -1)
# 计算本batch准确率
acc = torch.mean((torch.tensor(y_pre == y, dtype=torch.float)))
test_acc.append(acc)
if (len(x[0])) > length: # 长句子侦测
long_acc.append(acc)
long_loss += loss.item()
trains_acc = sum(train_acc) / len(train_acc)
tests_acc = sum(test_acc) / len(test_acc)
longs_acc = sum(long_acc) / len(long_acc)
train_loss_record.append(train_loss / len(train_acc))
test_loss_record.append(test_loss / len(test_acc))
long_loss_record.append(long_loss / len(long_acc))
train_record.append(trains_acc)
test_record.append(tests_acc)
long_record.append(longs_acc)
print("---------- Iteration", iteration + 1, "----------")
print("Train loss:", train_loss / len(train_acc))
print("Test loss:", test_loss / len(test_acc))
print("Train accuracy:", trains_acc)
print("Test accuracy:", tests_acc)
print("Long sentence accuracy:", longs_acc)
return train_loss_record, test_loss_record, long_loss_record, train_record, test_record, long_record
def NN_embedding_plot(random_embedding, glove_embedding, learning_rate, batch_size, iter_times):
# 获得训练集和测试集的batch
train_random = get_batch(random_embedding.train_matrix,
random_embedding.train_y, batch_size)
test_random = get_batch(random_embedding.test_matrix,
random_embedding.test_y, batch_size)
train_glove = get_batch(glove_embedding.train_matrix,
glove_embedding.train_y, batch_size)
test_glove = get_batch(random_embedding.test_matrix,
glove_embedding.test_y, batch_size)
# 模型建立
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
random_rnn = RNN(50, 50, random_embedding.len_words)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
random_cnn = CNN(50, random_embedding.len_words, random_embedding.longest)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
glove_rnn = RNN(50, 50, glove_embedding.len_words,
weight=torch.tensor(glove_embedding.embedding, dtype=torch.float))
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
glove_cnn = CNN(50, glove_embedding.len_words, glove_embedding.longest,
weight=torch.tensor(glove_embedding.embedding, dtype=torch.float))
# rnn+random
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
trl_ran_rnn, tel_ran_rnn, lol_ran_rnn, tra_ran_rnn, tes_ran_rnn, lon_ran_rnn = \
NN_embdding(random_rnn, train_random, test_random, learning_rate, iter_times)
# cnn+random
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
trl_ran_cnn, tel_ran_cnn, lol_ran_cnn, tra_ran_cnn, tes_ran_cnn, lon_ran_cnn = \
NN_embdding(random_cnn, train_random, test_random, learning_rate, iter_times)
# rnn+glove
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
trl_glo_rnn, tel_glo_rnn, lol_glo_rnn, tra_glo_rnn, tes_glo_rnn, lon_glo_rnn = \
NN_embdding(glove_rnn, train_glove, test_glove, learning_rate, iter_times)
# cnn+glove
torch.manual_seed(2021)
torch.manual_seed(2021)
trl_glo_cnn, tel_glo_cnn, lol_glo_cnn, tra_glo_cnn, tes_glo_cnn, lon_glo_cnn = \
NN_embdding(glove_cnn, train_glove, test_glove, learning_rate, iter_times)
# 画图部分
x = list(range(1, iter_times + 1))
matplotlib.pyplot.subplot(2, 2, 1)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, trl_ran_rnn, 'r--', label='RNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, trl_ran_cnn, 'g--', label='CNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, trl_glo_rnn, 'b--', label='RNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, trl_glo_cnn, 'y--', label='CNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.legend()
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(fontsize=10)
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Train Loss")
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel("Iterations")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel("Loss")
matplotlib.pyplot.subplot(2, 2, 2)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tel_ran_rnn, 'r--', label='RNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tel_ran_cnn, 'g--', label='CNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tel_glo_rnn, 'b--', label='RNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tel_glo_cnn, 'y--', label='CNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.legend()
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(fontsize=10)
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Test Loss")
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel("Iterations")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel("Loss")
matplotlib.pyplot.subplot(2, 2, 3)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tra_ran_rnn, 'r--', label='RNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tra_ran_cnn, 'g--', label='CNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tra_glo_rnn, 'b--', label='RNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tra_glo_cnn, 'y--', label='CNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.legend()
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(fontsize=10)
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Train Accuracy")
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel("Iterations")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel("Accuracy")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylim(0, 1)
matplotlib.pyplot.subplot(2, 2, 4)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tes_ran_rnn, 'r--', label='RNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tes_ran_cnn, 'g--', label='CNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tes_glo_rnn, 'b--', label='RNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, tes_glo_cnn, 'y--', label='CNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.legend()
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(fontsize=10)
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Test Accuracy")
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel("Iterations")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel("Accuracy")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylim(0, 1)
matplotlib.pyplot.tight_layout()
fig = matplotlib.pyplot.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(8, 8, forward=True)
matplotlib.pyplot.savefig('main_plot.jpg')
matplotlib.pyplot.show()
matplotlib.pyplot.subplot(2, 1, 1)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lon_ran_rnn, 'r--', label='RNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lon_ran_cnn, 'g--', label='CNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lon_glo_rnn, 'b--', label='RNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lon_glo_cnn, 'y--', label='CNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.legend()
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(fontsize=10)
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Long Sentence Accuracy")
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel("Iterations")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel("Accuracy")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylim(0, 1)
matplotlib.pyplot.subplot(2, 1, 2)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lol_ran_rnn, 'r--', label='RNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lol_ran_cnn, 'g--', label='CNN+random')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lol_glo_rnn, 'b--', label='RNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, lol_glo_cnn, 'y--', label='CNN+glove')
matplotlib.pyplot.legend()
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(fontsize=10)
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Long Sentence Loss")
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel("Iterations")
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel("Loss")
matplotlib.pyplot.tight_layout()
fig = matplotlib.pyplot.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(8, 8, forward=True)
matplotlib.pyplot.savefig('sub_plot.jpg')
matplotlib.pyplot.show()
4.Neural_network.py
# -*- coding: GBK -*-
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# coding=gbk
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 设计RNN网络
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,len_feature,len_hidden,len_words,typenum=5,weight=None,layer=1,nonlinearity='tanh',batch_first=True,drop_out=0.5):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.len_feature = len_feature # d的大小
self.len_hidden = len_hidden # l_h的大小
self.len_words = len_words # 单词的个数,包含padding
self.layer = layer # 隐藏层层数
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(drop_out) # dropout层
if weight is None: # 随机初始化
x = nn.init.xavier_normal_(torch.Tensor(len_words,len_feature))
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=len_words,embedding_dim=len_feature,_weight=x)
else: # Glove初始化
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=len_words,embedding_dim=len_feature,_weight=weight)
# 用nn.Module的内置函数定义隐藏层
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=len_feature,hidden_size=len_hidden,num_layers=layer,nonlinearity=nonlinearity,batch_first=batch_first,dropout=drop_out)
# 全连接层
self.fc = nn.Linear(len_hidden,typenum)
# softmax层冗余,可以不加
# self.act = nn.softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self,x):
# x:数据,维度为[batch_size,句子长度]
x = torch.LongTensor(x)
batch_size = x.size(0)
# 经过词嵌入后,维度为[batch_size,句子长度,d]
out_put = self.embedding(x) # 词嵌入
out_put = self.dropout(out_put) # dropout层
h0 = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(self.layer,batch_size,self.len_hidden))
# dropout层不变,经过隐藏层后,维度变成[1,batch_size,l_h]
_,hn = self.rnn(out_put,h0) # 隐藏层计算
# 经过全连接后,维度变成[1,batch_size,5]
out_put = self.fc(hn).squeeze(0) # 全连接层
# 挤掉第0维度,返回[batch_size,5]的数据
return out_put
# 设计CNN网络
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,len_feature,len_words,longest,typenum=5,weight=None,drop_out=0.5):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.len_feature = len_feature # d的大小
self.len_words = len_words # 单词数目
self.longest = longest # 最长句子单词数目
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(drop_out) # dropout层
if weight is None: # 随机初始化
x = nn.init.xavier_normal(torch.Tensor(len_words,len_feature))
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=len_words,embedding_dim=len_feature,_weight=x)
else: # Glove初始化
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=len_words,embedding_dim=len_feature,_weight=weight)
# Conv2d参数详解:(输入通道数:1,输出通道数:l_l,卷积核大小:(行数,列数))
# padding是指往句子两侧加 0,因为有的句子只有一个单词
# 那么 X 就是 1*50 对 W=2*50 的卷积核根本无法进行卷积操作
# 因此要在X两侧行加0(两侧列不加),(padding=(1,0))变成 3*50
# 又比如 padding=(2,0)变成 5*50
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1,longest,(2,len_feature),padding=(1,0)),nn.ReLU()) # 序列,relu激活函数 第1个卷积核+激活层
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1,longest,(3,len_feature),padding=(1,0)),nn.ReLU()) # 第2个卷积核+激活层
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1,longest,(4,len_feature),padding=(2,0)),nn.ReLU()) # 第3个卷积核+激活层
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1,longest,(5,len_feature),padding=(2,0)),nn.ReLU()) # 第4个卷积核+激活层
# 全连接层
self.fc = nn.Linear(4 * longest,typenum)
def forward(self,x):
# x:数据,维度为[batch_size,句子长度]
x = torch.LongTensor(x)
# 通过词嵌入后,维度为[batch_size,1,句子长度,d]
out_put = self.embedding(x).view(x.shape[0],1,x.shape[1],self.len_feature) # 词嵌入
# dropout后不变,记为x
out_put = self.dropout(out_put) # dropout层
"""X经过2*d卷积后,维度为[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+2-1,1]"""
"""挤掉第三维度(维度从0开始),[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+2-1]记为Y_1"""
"""注意:句子长度+2-1的2是padding造成的行数扩张"""
conv1 = self.conv1(out_put).squeeze(3) # 第1个卷积
"""X经过3*d卷积后,维度为[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+2-2,1]"""
"""挤掉第三维度(维度从0开始),[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+2-2]记为Y_2"""
conv2 = self.conv2(out_put).squeeze(3) # 第2个卷积
"""X经过4*d卷积后,维度为[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+4-3,1]"""
"""挤掉第三维度(维度从0开始),[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+4-3]记为Y_3"""
conv3 = self.conv3(out_put).squeeze(3) # 第3个卷积
"""X经过5*d卷积后,维度为[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+4-4,1]"""
"""挤掉第三维度(维度从0开始),[batch_size,l_l,句子长度+4-4]记为Y_4"""
conv4 = self.conv4(out_put).squeeze(3) # 第4个卷积
"""分别对(Y_1,Y_2,Y_3,Y_4)的第二维(维度从0开始)进行pooling"""
"""得到4个[batch_size,,l_l,1]的向量"""
pool1 = F.max_pool1d(conv1, conv1.shape[2])
pool2 = F.max_pool1d(conv2, conv2.shape[2])
pool3 = F.max_pool1d(conv3, conv3.shape[2])
pool4 = F.max_pool1d(conv4, conv4.shape[2])
# 拼接得到[batch_size,l_l*4,1]的向量
# 挤掉第二维(维度从0开始)为[batch_size,l_l*4]
pool = torch.cat([pool1,pool2,pool3,pool4],1).squeeze(2) # 拼接起来
# 经过全连接层后,维度为[batch_size,5]
out_put = self.fc(pool)
return out_put
四、实验结果
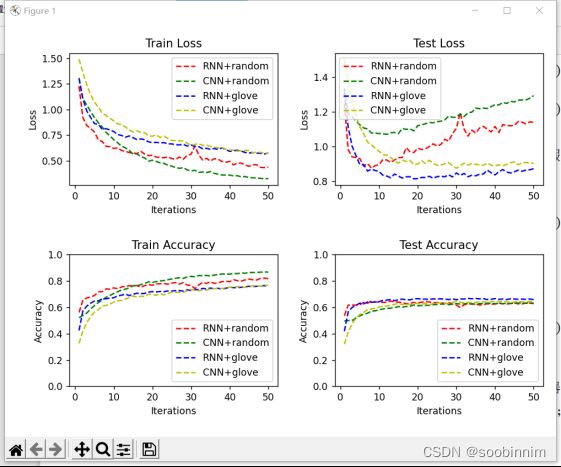
在准确率上,测试集上RNN的准确率比CNN都要高,且测试集的损失值也要比CNN低。比较随机初始化与Glove初始化,在相同的模型下,Glove初始化比随机初始化的效果要好,也就是在测试集上准确率高,损失值小。测试集的准确率在60%左右。
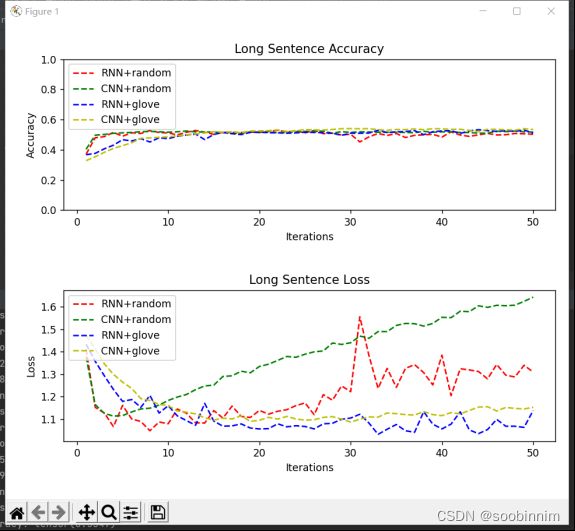
通过上述的结果的显示并不能说明RNN在长句子情感分类方面的优势,因为RNN具有短期记忆,能够处理好词与词之间的关系,以下的结果是在长句子分类上两者的比较,是在测试集中单词数大于20的句子的损失值和正确率。
可以看出,RNN的效果并不比CNN好,无论是CNN还是RNN,长句子的情感分类准确率也只有大概55%左右,比总体的平均正确率低了均10%。
五、总结
这个实验可以使用cuda加速,但是由于我的电脑没有所以就跑得比较慢,只需要在comparison_plot和Neural_network中的一些代码加入.cuda()和.cpu()即可,也可以将代码放入kaggle中用gpu跑或者使用google,我这边也遇到了麻烦所以也没能进行。
在实际神经网络通常是输入一批样本然后得到输出,进行了一个padding操作,即补长,反正数据分batch失败,在实战中先把数据按照句子长度进行了排序,尽量使同一个batch句子长度一致,这样子可以避免零填充,同时设置padding的ID为0。