MySQL表的增删查改
文章目录
- CREATE
- Retrieve
- Update
- Delete
-
- 截断表
- 插入查询的数据
- 聚合函数
- group by
CURD:create() retrieve updata delete
CREATE
增加数据
insert
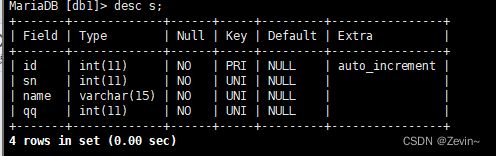
create table if not exists s(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> sn int not null unique comment'学生的学号',
-> name varchar(20) unique ,
-> qq int not null unique
-> );
正常插入
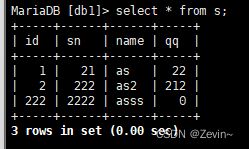
insert into s(id,sn,name,qq) values (1,21,'as',22);
- 单行全列插入,可以省略前面的key,建议不要省略
insert into s values (2,222,'as2',212);
- 插入局部列
insert into s(id,sn,name) values (222,2222,'asss');
- 插入多行数据
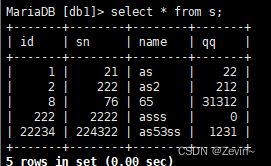
insert into s(id,sn,name,qq) values (22234,224322,'as53ss',1231),(8,76,'65',31312);
插入的数据用,隔开
- 插入的数据和主键出现冲突
出现冲突,就帮助我们修改
insert into s (id,sn,name,qq) values (1,21,'asdasd',127) on duplicate key update sn=1,id=9;
这个会把冲突那个数据修改,
0 row affected;表中有冲突数据,但是冲突数据和update值一样
1 row affected :表中没有冲突数据,数据插入
2 row affected :表中有冲突数据,不求额数据被更新
不存在插入,存在修改即可,替换之前的那些数据
- replace 替换
和刚才的insert替换一样的
没有冲突直接插入
有冲突替换再插入
replace into l(id) value(4);
创造和之前的表一样的结构
like
create table duplicate_tb_bak like duplicate_tb;
Retrieve
查询
select
创建表
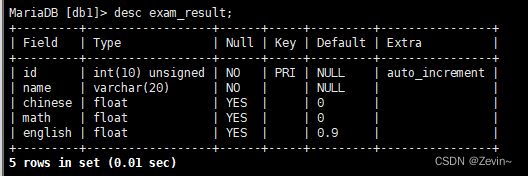
[db1]> create table exam_result(
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> chinese float default 0.0,
-> math float default 0.0,
-> english float default 0.9
-> );
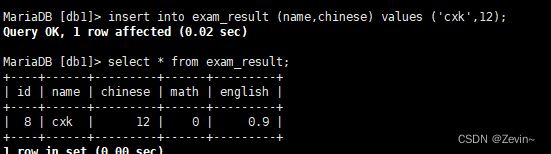
插入数据
[db1]> insert into exam_result (name,chinese,math,english) values
-> ('tsz',67,98,56),
-> ('swk',87,78,77),
-> ('cmd',88,98,99),
-> ('lxd',82,84,67),
-> ('sq',70,73,78),
-> ('sgm',75,65,30);
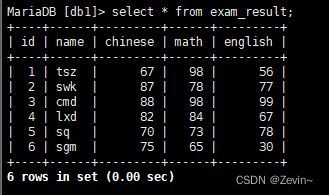
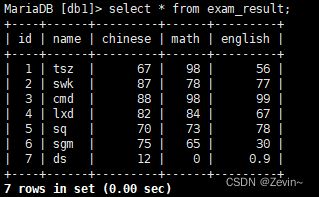
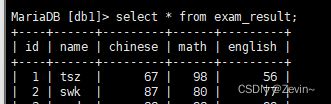
- 全列查询
通常情况下,不建议使用* 进行全列查询
select * from exam_result;
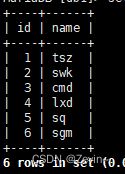
select id,name from exam_result;
select english,id,name from exam_result;
也可以包含一个不存在的字段,只能是一个可被计算的表达式
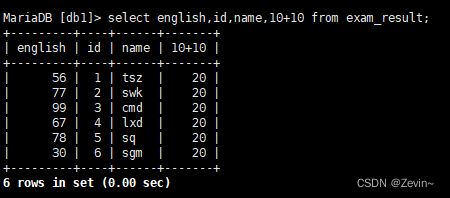
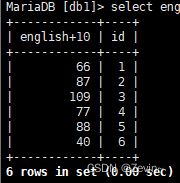
把所有人的id和英语成绩查出来,把英语成绩+10分 ,没有影响原始数据
select english+10 ,id from exam_result;
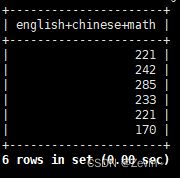
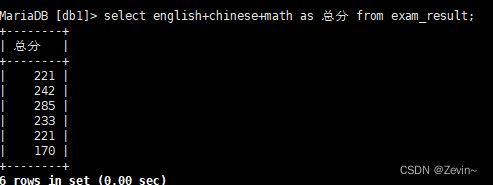
select english+chinese+math from exam_result;
select english+chinese+math as 总分 from exam_result;
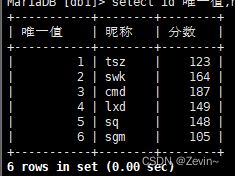
select id 唯一值,name 昵称,english+chinese 分数 from exam_result;
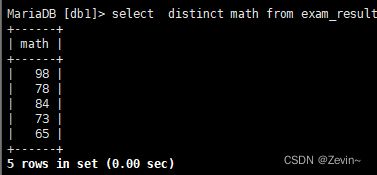
select distinct math from exam_result;
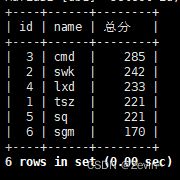
select id,name,chinese+english+math 总分 from exam_result order by 总分;
降序的话desc (descending)
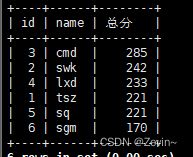
select id,name,chinese+english+math 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 desc;
- where条件
给查询设置条件
比较运算符
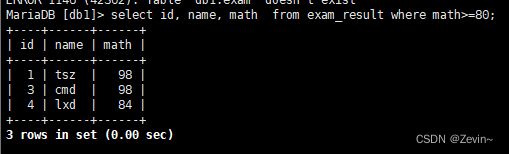
select id, name, math from exam_result where math>=80;
select id, name, math from exam_result where math<=80;
查询=98分的
select id, name, math from exam_result where math=98;
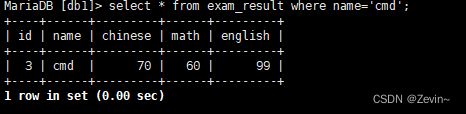
查询字符串
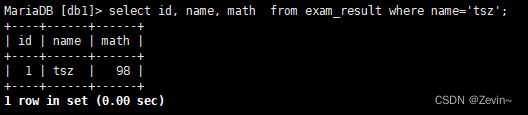
select id, name, math from exam_result where name='tsz';
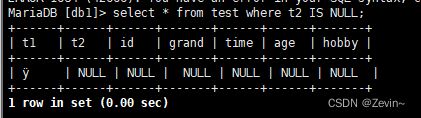
select * from test where t2 IS NULL;
select * from test where t2 IS NOT NULL;
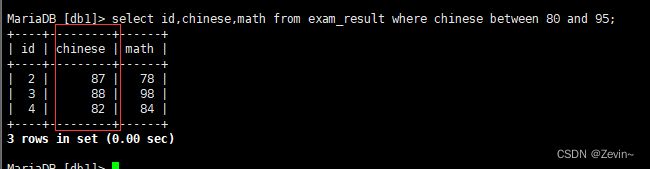
select id,chinese,math from exam_result where chinese between 80 and 95;
[80,95]包含这两个数的
select id,chinese,math from exam_result where chinese >=70 and chinese <=98;
select id,chinese,math from exam_result where chinese =70 or chinese =98;
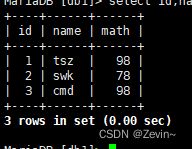
select id,name,math from exam_result where math IN(58,78,98);
查询包含一个字符存在的
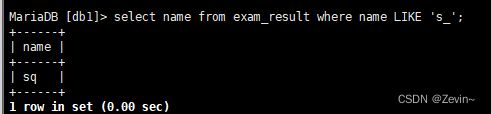
LIKE:模糊匹配,%表示任意多个自读,_表示任意一个字符,后面只能跟一个字符
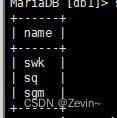
select name from exam_result where name LIKE 's%';
select name from exam_result where name LIKE 's_';
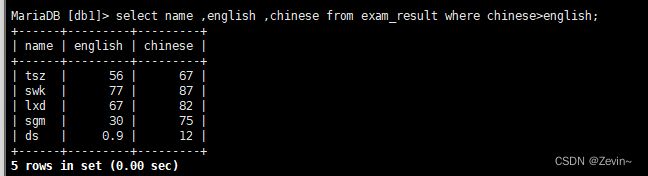
select name ,english ,chinese from exam_result where chinese>english;
- 按照条件赛选数据
- 按照要求计算数据
select一般都是where先执行早于前面的,起别名都是最后操作的,先执行筛选条件的操作
where 子句中不能使用where别名,也不能起一个别名
语文成绩大于80并且不姓’s’
select name,chinese,math,english from exam_result where chinese>80 and name NOT LIKE 's%';
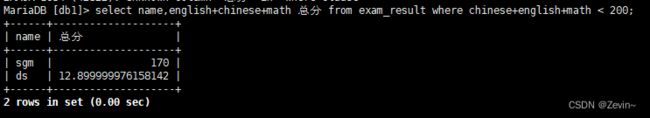
孙某同学,否则要求总成绩>200并且语文成绩<数学成绩并且英语成绩>80
>select id,name, chinese,math,english, english+math+chinese 总分 from exam_result
>where (name like 's_') or
>(english+math+chinese>200 and chinese<math and english>80)
>order by 总分 desc;
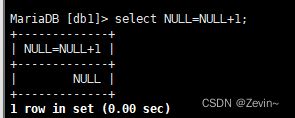
NULL在排序的时候被视作比所有只都小
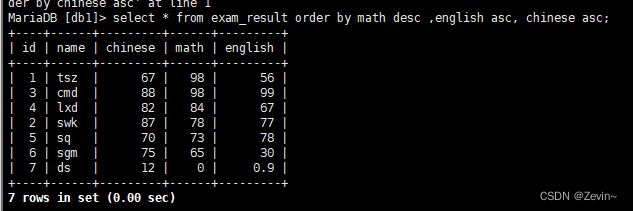
查询同学成绩,按数学降序,英语升序,语文升序
多个条件排序 ,优先按照前面的排序,相同按后面的排序,再相同再按后面的排序
select * from exam_result order by math desc ,english asc, chinese asc;
select name ,english+math+chinese 总分 from exam_result where english +math+chinese >200 order by 总分 desc;
order by 是最后执行的,筛选数据是最先执行的
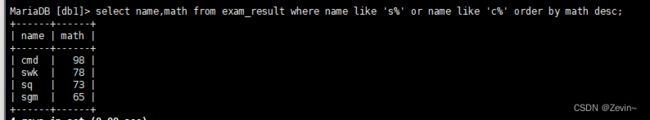
查询姓s的同学或者姓c的同学,结果按照数学成绩排序
select name,math from exam_result where name like 's%' or name like 'c%' order by math desc;
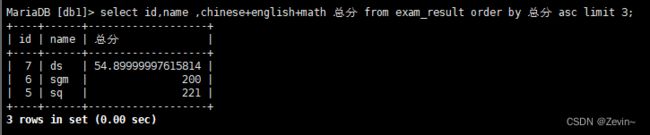
找到总分前三名同学,所有操作都执行了
limit 3,赛选3个,放最后
select name,math+chinese+english 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 desc limit 3;
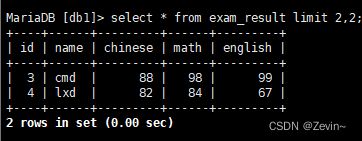
使用limit进行分页limit 2,2从第2条记录往后选两条数据,截取数据库中的一部分
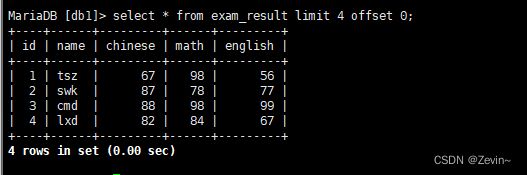
select * from exam_result limit 2,2;
Update
将s同学的成绩改成80分
update exam_result set math=80 where name='swk';
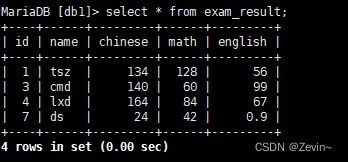
update exam_result set math=60 ,chinese=70 where name='cmd';
先筛选数据
select id,name ,chinese+english+math 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 asc limit 3;
update exam_result set math=math+30 order by math+english+chinese asc limit 3;
update exam_result set chinese=chinese*2;
Delete
删除姓s同学的数据
delete from exam_result where name like 's%';
delete from exam_result;
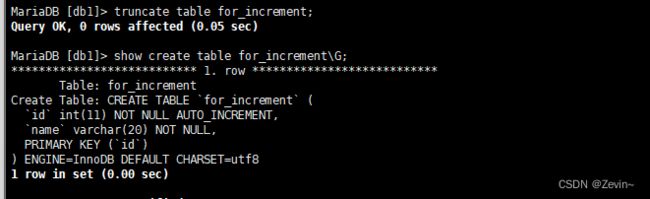
截断表
截断表:清空表,和delete差别就是会把auto_increment进行清零
区别还有
日志:MySQL的日志,需要承担很大的功能要求
- bin log:上下翻动的时候,都能记得住,我们所有的sql操作,mysql服务器就能给我们记录下来,该log可以用来多主机同步,在增量上备份
- redo log:承担MySQL数据持久化,和mysql的crash_safe功能,突然崩溃的时候,避免数据丢失,保持安全()
- undo log:在事务中承担回滚的日志,数据操作回复的功能
delete会更新日志的,truncate不会更新
插入查询的数据
insert 和select可以结合使用
新
insert into duplicate_tb values (100,'aaa'),(200,'bbb'),(200,'bbb'),(300,'ccc');
新键一个备份的表,把它变成duplicate表
create duplicate_tb_bak like duplicate_tb;
把不重复的数据都插到备份的表里面
insert into duplicate_tb_bak select distinct * from duplicate_tb;
但是我们用一个rename,把该表进行修改即可
rename table duplicate_tb to old_duplicate;
聚合函数
按行来记录在一起
将同类别,进行聚合处理
count:计算数据个数
sum:计算数据和
avg:计算数据
max
min
计算exam_result 里面有多少数据
count(*)
select count(*) 人数 from exam_result;
select count(id) from exam_result;
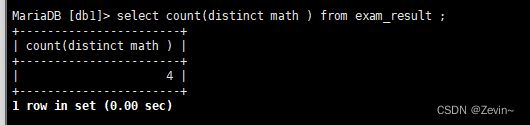
select count(distinct id) from exam_result;
select sum(math) from exam_result;
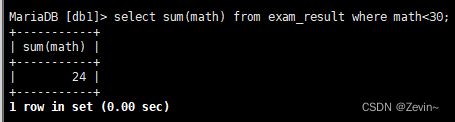
统计数学成绩不及格的人总分
select sum(math) from exam_result where math<30;
group by
按列来进行数据统计分类
先分组,再对select进行数据的赛选统计
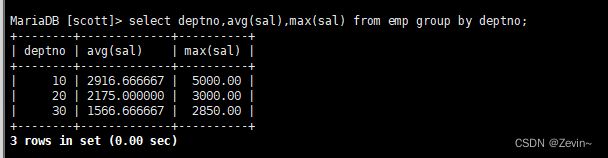
显示每个部门的平均工资
按部门对员工进行分组,分组不是目的,还要对每一组进行聚合求值
select deptno, avg(sal),max(sal) from emp group by deptno;
先执行from emp,后按部门分组,再进行计算
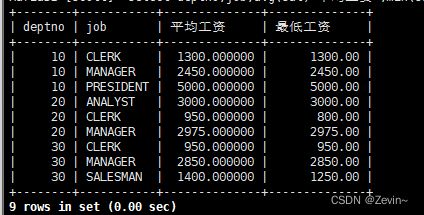
select deptno,avg(sal) 平均工资 ,min(sal) 最低工资 from emp group by deptno,job;
显示平均工资小于2000的部门和它的平均工资
select deptno ,ename,avg(sal) from emp where sal<2000 group by deptno;
having经常和group by进行赛选,相当于where
先分完组,再对数据进行赛选
select deptno ,ename,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno having avg(sal)<2000;
having要先分组,才能有效果,分组之后才能有效果
where和having
根本原因在于,两者的执行次序是不一样的
where是过滤表的数据的
having是过滤分组的数据
两者不冲突
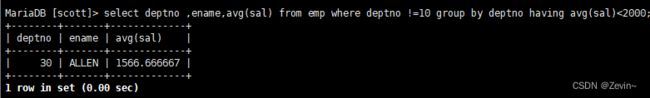
除了10号部门,平均工资小于2000部门和它的工资
select deptno ,ename,avg(sal) from emp where deptno !=10 group by deptno having avg(sal)<2000;