一、准备数据
seq = ["我喜欢你", "我恨你", "我今天很开心", "我最近很沮丧", "我很难过", "我讨厌你", "你非常的勤奋", "我特别懒惰", "我特别痛苦"]
label = [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0] # 0代表消极情感, 1代表积极情感
二、数据处理
- 对数据采用jieba进行分词,将所有句子分词后进行频次排序高频在前,并加入index。由于每一个句子长度不同,加入PAD进行补全,如下所示:
{'我': 1, '你': 2, '很': 3, '特别': 4, '喜欢': 5, '恨': 6, '今天': 7, '开心': 8, '最近': 9, '沮丧': 10, '难过': 11, '讨厌': 12, '非常': 13, '的': 14, '勤奋': 15, '懒惰': 16, '痛苦': 17, 'PAD': 0}
- 然后根据索引将句子进行分词后以此使用索引进行表示,例如:我 \ 喜欢 \ 你 = [1, 4, 2]
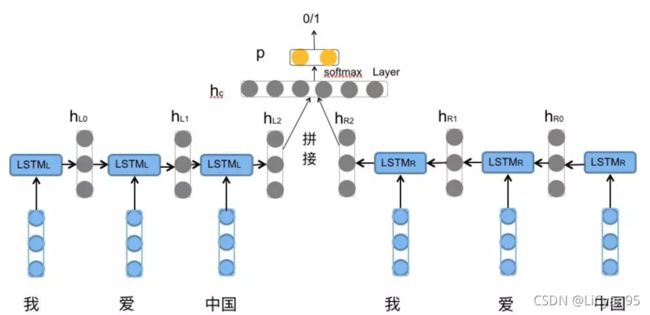
三、模型构建
- 输入采用embedding生成词向量输入
- 最后将正向LSTM和反向LSTM最后一个隐层拼接作为全连接层的输入
- 此模型采用如下所示:
四、具体代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import collections
import torch.utils.data as Data
from torch.autograd import Variable
import jieba
seq = ["我喜欢你", "我恨你", "我今天很开心", "我最近很沮丧", "我很难过", "我讨厌你", "你非常的勤奋", "我特别懒惰", "我特别痛苦"]
label = [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
#分词
seq_cut = []
seq_cut_list = []
for i in seq:
cut_res = list(jieba.cut(i))
seq_cut = seq_cut + cut_res
seq_cut_list.append(cut_res)
word2num = sorted(collections.Counter(seq_cut).items(), key=lambda item: item[1], reverse=True)
# 所有词
vocab = list(set(seq_cut))
# 词对应索引
word2index = {w[0]: i+1 for i, w in enumerate(word2num)}
word2index["PAD"] = 0
# 词典大小
vocab_size = len(word2index)
seq_size = len(seq)
seq_length = max([len(i) for i in seq_cut_list])
batch_size = 3
embedding_size = 3
num_classes = 2
n_hidden = 5
def make_data(seq, label):
inputs = []
for i in seq:
seq_index = [word2index[word] for word in i]
# 补全保持句子长度一致
if len(seq_index) != seq_length:
seq_index = seq_index + [0] * (seq_length-len(seq_index))
inputs.append(seq_index)
targets = [i for i in label]
return inputs, targets
input_batch, target_batch = make_data(seq_cut_list, label)
input_batch, target_batch = Variable(torch.LongTensor(input_batch)), Variable(torch.LongTensor(target_batch))
# dataset = Data.TensorDataset(input_batch, target_batch)
# loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True)
# 建立模型
class BiLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BiLSTM, self).__init__()
self.word_vec = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)
# bidirectional双向LSTM
self.bilstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_size, n_hidden, 1, bidirectional=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(n_hidden * 2, num_classes)
def forward(self, input):
embedding_input = self.word_vec(input)
# 调换第一维和第二维度
embedding_input = embedding_input.permute(1, 0, 2)
output, (h_n, c_n) = self.bilstm(embedding_input)
# 使用正向LSTM与反向LSTM最后一个输出做拼接
encoding1 = torch.cat([h_n[0], h_n[1]], dim=1) # dim=1代表横向拼接
# 使用双向LSTM的输出头尾拼接做文本分类
encoding2 = torch.cat([output[0], output[-1]], dim=1)
fc_out = self.fc(encoding1)
return fc_out
model = BiLSTM()
print(model)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 训练
for epoch in range(5000):
pred = model(input_batch)
loss = criterion(pred, target_batch)
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.6f}'.format(loss))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 测试
test_text = '我今天很痛苦'
# 分词
test_cut = list(jieba.cut(test_text))
# 索引
test_batch, _ = make_data([test_cut], [1])
test_batch = torch.LongTensor(test_batch)
out = model(test_batch)
predict = torch.max(out, 1)[1]
if predict.item() == 0:
print(test_text,"is Bad Mean...")
else:
print(test_text,"is Good Mean!!")
