OBB方向包围盒算法实现
如何进行2D旋转矩形的碰撞检测,可以使用一种叫OBB的检测算法(Oriented bounding box)方向包围盒。这个算法是基于SAT(Separating Axis Theorem)分离轴定律的。而OBB不仅仅是计算矩形的碰撞检测,而是一种算法模型。简单解释一下概念,包围盒和分离轴定律。
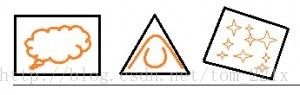
包围盒:是根据物体的集合形状,来决定盒子的大小和方向,这样可以选择最紧凑的盒子来代表物体。见下图
黑色的就是包围盒,可以是凸多边形,最贴近检测物体即可。
分离轴定律:两个凸多边形物体,如果我们能找到一个轴,使得两个在物体在该轴上的投影互不重叠,则这两个物体之间没有碰撞发生,该轴为Separating Axis
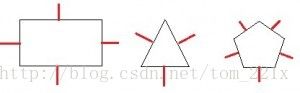
那么用一般去检测那些轴呢,垂直于多边形每条边的轴。如下图:
所以,分离轴定律变成,两个多边形在所有轴上的投影都发生重叠,则判定为碰撞;否则,没有发生碰撞。
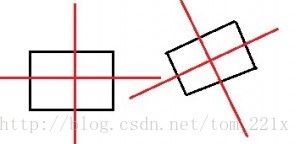
下面,我只考虑矩形的情况,如何检测分离轴。
很明显,矩形4条边,有4条检测轴,那么2个矩形就有8个。但是矩形有2个轴是重复的,所以只需要检测2条轴就可以了,既是矩形的两条互相垂直的边所在的轴。
如上图,判断碰撞,我们需要判断2个矩形在4个轴上的投影是否重叠。这里有2种可能的方式。第一种,把每个矩形的4个顶点投影到一个轴上,这样算出4个顶点最长的连线距离,以后同样对待第二个矩形,最后判断2个矩形投影距离是否重叠。
第二种方式,把2个矩形的半径距离投影到轴上,以后把2个矩形的中心点连线投影到轴上,以后判断2个矩形的中心连线投影,和2个矩形的半径投影之和的大小。本文使用这种方式。
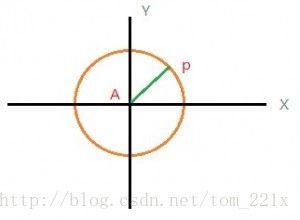
这里用到一些向量的数学知识。如下图:
P点为矩形在X轴上的投影点,矩形在垂直轴上的投影点为原点。这里也能看出来,点P所在的矩形轴, 在X轴上的投影长度为OP,如果矩形逆时针绕远点O旋转,OP在X轴上的投影长度变小,直到为0,OP垂直于X轴。也就是,OP在X轴上的投影长度的最大与最小值。这也解释了,为什么我们选择检测轴为垂直于多边形边的轴,因为在这些轴上我们能取到极值,中间的那些轴就没必要检测了。
如何表示轴,我们需要用向量,正确的使用单位向量,能够简化模型,降低思考的难度。如下图:
假设P点的坐标为(px, py), 那么向量P就是(px, py),点P在X轴上的投影点Q坐标是(qx, qy),那么向量Q就是(qx, qy)。我们假设X轴上的单位向量是(1, 0)。那么向量P和X轴上单位向量点乘有:
向量P * X轴单位向量 = |P| * |X轴单位向量| * cosPQ = px * 1 + py * 0 = px
又因为单位向量的长度等于1所以,px就是向量Q的长度。这是非常有意义的,我们就得到一个规律,就是把一个向量点乘一个单位向量,我们得到的是这个向量在这个单位向量上的投影长度。用代码表示为:
[cpp] view plain copy
- /**
- * dot-multiply
- */
- private float dot(float[] axisA, float[] axisB) {
- return Math.abs(axisA[0] * axisB[0] + axisA[1] * axisB[1]);
- }
这里float[] 存放的是一个点的x ,y 坐标。axisB 为单位向量,这个结果就是axisA向量在,单位向量axisB上投影的长度。
下面我们看一下,单位向量如何表示:
单位向量是用单位圆来描述的。假设这个圆的半径为1,那么圆上的任何一个坐标到原点构成的向量都可以看作一个单位向量,并且长度为1。这般,明显的点P就是一个单位向量。点P在单位圆上移动,那么这个单位向量就在旋转,向量P就和角A建立了关系。很明显的得出,cosA 就是向量P的X坐标,sinA 就是向量P的Y坐标。
这样我们就可以得出,单位向量P为(cosA,sinA)。这个模型的意义就是把单位向量P可以看成矩形的条边。如下图:
那么矩形的另一个边对应的单位向量S如何表示呢,向量S和向量P是垂直的,我们可以得出, S(-sinA, cosA), 向量S 点乘 向量P = 0
至此,我们就可以通过一个旋转角度,得到一个矩形的2个检测轴的单位向量。代码如下:
[cpp] view plain copy
- // unit vector of x axis
- private float[] axisX;
- // unit vector of y axis
- private float[] axisY;
- // 0 -360
- private float rotation;
- /**
- * Set axis x and y by rotation
- *
- * @param rotation float 0 - 360
- */
- public OBB setRotation(float rotation) {
- this.rotation = rotation;
- this.axisX[0] = MathUtils.cos(rotation);
- this.axisX[1] = MathUtils.sin(rotation);
- this.axisY[0] = -MathUtils.sin(rotation);
- this.axisY[1] = MathUtils.cos(rotation);
- return this;
- }
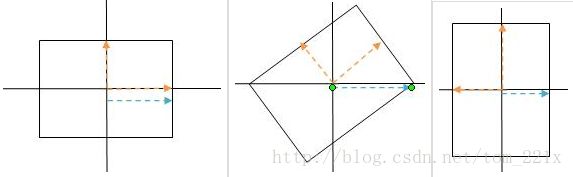
下一步如何计算矩形的半径投影呢,什么又是半径投影呢,看下图:
橙色线段,是矩形的2条检测轴,3张图是矩形旋转的3个特殊位置截图。蓝色线段就是矩形半径投影。其实就是,矩形在X轴上最远处的交点,数学上意义就是2条检测轴的投影之和。
2条检测轴的向量和就是中心点到矩形一个顶点的向量,所以投影半径也是中心点到矩形顶点的向量投影长度。注意向量的方向会影响投影长度。按照中间那幅图,2条检测轴向量和的投影是,2条检测轴投影的差值。如果把其中一个轴,旋转180度,那么2个检测轴和的投影就是,2条轴投影的和值。
至此,如果我们把矩形在任意角度的2条轴向量投影到单位向量上,根据前面的单位向量规律。我们就得到了轴向量在单位向量上投影的长度,而单位向量的长度为1,那么我们得到的就是轴向量与单位向量的比例。在用这个比例乘以轴向量的长度,就得到了轴的投影长度,就能求出轴半径的长度了。如图
2个矩形检测过程中,每次以一个矩形的检测轴为坐标系,投影另一个矩形的检测轴。图中,蓝色线段为左边矩形的半径投影,黄色线段为右边矩形检测轴。我们需要把右边2条检测轴投影到蓝色线段所在X轴的单位向量,得到投影比例,以后在乘以2条检测轴的长度,就可以得到右边矩形的半径投影。
红色线段为2个矩形的中心点连心,计算其在X轴的投影长度。比较中心点连线的投影长度与2矩形的半径投影长度之和,如果连线投影大,那么在这条轴上没有碰撞,否则碰撞。半径投影代码如下:
[cpp] view plain copy
- private float halfWidth;
- private float halfHeight;
- /**
- * Get axisX and axisY projection radius distance on axis
- */
- public float getProjectionRadius(float[] axis) {
- // axis, axisX and axisY are unit vector
- // projected axisX to axis
- float projectionAxisX = this.dot(axis, this.axisX);
- // projected axisY to axis
- float projectionAxisY = this.dot(axis, this.axisY);
- return this.halfWidth * projectionAxisX + this.halfHeight * projectionAxisY;
- }
判断2矩形最终是否碰撞,需要依次检测4个分离轴,如果在一个轴上没有碰撞,则2个矩形就没有碰撞。代码如下:
[cpp] view plain copy
- /**
- * OBB is collision with other OBB
- */
- public boolean isCollision(OBB obb) {
- // two OBB center distance vector
- float[] centerDistanceVertor = {
- this.centerPoint[0] - obb.centerPoint[0],
- this.centerPoint[1] - obb.centerPoint[1]
- };
- float[][] axes = {
- this.axisX,
- this.axisY,
- obb.axisX,
- obb.axisY,
- };
- for(int i = 0; i < axes.length; i++) {
- // compare OBB1 radius projection add OBB2 radius projection to centerDistance projection
- if(this.getProjectionRadius(axes[i]) + obb.getProjectionRadius(axes[i])
- <= this.dot(centerDistanceVertor, axes[i])) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
最后,给出OBB完整的代码封装
Java代码:
[java] view plain copy
- /**
- * @author scott.cgi
- * @since 2012-11-19
- *
- * Oriented bounding box
- */
- public class OBB {
- private float[] centerPoint;
- private float halfWidth;
- private float halfHeight;
- // unit vector of x axis
- private float[] axisX;
- // unit vector of y axis
- private float[] axisY;
- // 0 -360
- private float rotation;
- private float scaleX;
- private float scaleY;
- private float offsetAxisPointDistance;
- /**
- * Create default OBB
- *
- * @param x bornCenterX x
- * @param y bornCenterY Y
- * @param halfWidth
- * @param halfHeight
- */
- public OBB(float bornCenterX, float bornCenterY, float halfWidth, float halfHeight) {
- this.halfWidth = halfWidth;
- this.halfHeight = halfHeight;
- this.scaleX = 1.0f;
- this.scaleY = 1.0f;
- this.centerPoint = new float[] {
- bornCenterX,
- bornCenterY
- };
- this.axisX = new float[2];
- this.axisY = new float[2];
- float[] offsetAxisPoint = new float[] {
- bornCenterX - Director.getHalfScreenWidth(),
- bornCenterY - Director.getHalfScreenHeight()
- };
- this.offsetAxisPointDistance = (float) Math.sqrt(this.dot(offsetAxisPoint, offsetAxisPoint));
- this.setRotation(0.0f);
- }
- /**
- * Create default OBB with born in center screen
- *
- * @param halfWidth
- * @param halfHeight
- */
- public OBB(float halfWidth, float halfHeight) {
- this(Director.getHalfScreenWidth(), Director.getHalfScreenHeight(), halfWidth, halfHeight);
- }
- /**
- * Get axisX and axisY projection radius distance on axis
- */
- public float getProjectionRadius(float[] axis) {
- // axis, axisX and axisY are unit vector
- // projected axisX to axis
- float projectionAxisX = this.dot(axis, this.axisX);
- // projected axisY to axis
- float projectionAxisY = this.dot(axis, this.axisY);
- return this.halfWidth * this.scaleX * projectionAxisX + this.halfHeight * this.scaleY * projectionAxisY;
- }
- /**
- * OBB is collision with other OBB
- */
- public boolean isCollision(OBB obb) {
- // two OBB center distance vector
- float[] centerDistanceVertor = {
- this.centerPoint[0] - obb.centerPoint[0],
- this.centerPoint[1] - obb.centerPoint[1]
- };
- float[][] axes = {
- this.axisX,
- this.axisY,
- obb.axisX,
- obb.axisY,
- };
- for(int i = 0; i < axes.length; i++) {
- // compare OBB1 radius projection add OBB2 radius projection to centerDistance projection
- if(this.getProjectionRadius(axes[i]) + obb.getProjectionRadius(axes[i])
- <= this.dot(centerDistanceVertor, axes[i])) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * dot-multiply
- */
- private float dot(float[] axisA, float[] axisB) {
- return Math.abs(axisA[0] * axisB[0] + axisA[1] * axisB[1]);
- }
- /**
- * Set axis x and y by rotation
- *
- * @param rotation float 0 - 360
- */
- public OBB setRotation(float rotation) {
- this.rotation = rotation;
- this.axisX[0] = MathUtils.cos(rotation);
- this.axisX[1] = MathUtils.sin(rotation);
- this.axisY[0] = -MathUtils.sin(rotation);
- this.axisY[1] = MathUtils.cos(rotation);
- this.setCenter(this.centerPoint[0], this.centerPoint[1]);
- return this;
- }
- /**
- * Set OBB center point and will add offsetAxis value
- */
- public OBB setCenter(float x, float y) {
- float offsetX = this.offsetAxisPointDistance * MathUtils.cos(this.rotation);
- float offsetY = this.offsetAxisPointDistance * MathUtils.sin(this.rotation);
- this.centerPoint[0] = x + offsetX;
- this.centerPoint[1] = y + offsetY;
- return this;
- }
- /**
- * Set OBB scale x, y
- */
- public OBB setScale(float scaleX, float scaleY) {
- this.scaleX = scaleX;
- this.scaleY = scaleY;
- return this;
- }
- public float getRotation() {
- return this.rotation;
- }
- public float getCenterX() {
- return this.centerPoint[0];
- }
- public float getCenterY() {
- return this.centerPoint[1];
- }
- public float getHalfWidth() {
- return this.halfWidth * this.scaleX;
- }
- public float getHalfHeight() {
- return this.halfHeight * this.scaleY;
- }
- }
c 代码:
[cpp] view plain copy
- /*
- * OBBRect.h
- *
- * Created on: 2013-2-11
- * Author: scott.cgi
- */
- #ifndef OBBRect_Rect_H_
- #define OBBRect_Rect_H_
- #include
- #include "Mojoc/Graphics/Draw/Rect.h"
- #include "Mojoc/Toolkit/Def/CodeStyle.h"
- #include "Mojoc/Toolkit/Utils/AMathUtils.h"
- #include "Mojoc/Toolkit/Def/StructMember.h"
- #ifdef __cplusplus
- extern "C" {
- #endif
- typedef struct OBBRect OBBRect;
- /**
- * Oriented bounding box in Rect shape
- * Use openGL world coordinate system
- */
- struct OBBRect {
- float centerX;
- float centerY;
- /** Set origin(0,0) when obbRect create */
- float originX;
- float originY;
- /** Clockwise [0 - 360] */
- float rotation;
- float scaleX;
- float scaleY;
- Get(
- /** Unit vector of x axis */
- StructMember(Vector2, xAxis);
- /** Unit vector of y axis */
- StructMember(Vector2, yAxis);
- Rect* rect;
- /** Distance of center point to origin(0, 0 */
- float offsetDistance;
- /** Degree of vector which center point to origin(0, 0 */
- float offsetDegree;
- float halfWidth;
- float halfHeight;
- );
- };
- typedef struct {
- OBBRect* (*create) (Rect* rect);
- void (*init) (Rect* rect, Out(OBBRect* obbRect));
- /**
- * Set obbRect rotation or origin x,y called updateCenter for
- * update obbRect center x,y
- */
- void (*updateCenter)(OBBRect* obbRect);
- /**
- * Set obbRect rotation
- */
- void (*setRotation) (OBBRect* obbRect, float rotation);
- /**
- * OBBRect is collision with other OBBRect
- */
- bool (*isCollision) (OBBRect* obbRect, OBBRect* otherObb);
- /**
- * Get real width with scaleX
- */
- float (*getWidth) (OBBRect* obbRect);
- /**
- * Get real height with scaleY
- */
- float (*getHeight) (OBBRect* obbRect);
- } _AOBBRect;
- extern _AOBBRect AOBBRect;
- #ifdef __cplusplus
- }
- #endif
- #endif /* OBBRect_H_ */
[cpp] view plain copy
- /*
- * OBBRect.c
- *
- * Created on: 2013-2-11
- * Author: scott.cgi
- */
- #include
- #include
- #include "Mojoc/Physics/OBBRect.h"
- #include "Mojoc/Toolkit/Utils/AMathUtils.h"
- #include "Mojoc/Toolkit/Platform/Log.h"
- static void updateCenter(OBBRect* obbRect) {
- obbRect->centerX = obbRect->originX +
- obbRect->offsetDistance * obbRect->scaleX *
- AMathUtils_Cos(obbRect->rotation + obbRect->offsetDegree);
- obbRect->centerY = obbRect->originY +
- obbRect->offsetDistance * obbRect->scaleY *
- AMathUtils_Sin(obbRect->rotation + obbRect->offsetDegree);
- }
- static void setRotation(OBBRect* obbRect, float rotation) {
- obbRect->xAxis->x = AMathUtils_Cos(rotation);
- obbRect->xAxis->y = AMathUtils_Sin(rotation);
- obbRect->yAxis->x = -AMathUtils_Sin(rotation);
- obbRect->yAxis->y = AMathUtils_Cos(rotation);
- obbRect->rotation = rotation;
- }
- /**
- * Get axisX and axisY projection radius distance on unit axis
- */
- static inline float getProjectionRadius(OBBRect* obbRect, Vector2* axis) {
- // axis, axisX and axisY are unit vector
- // projected axisX to axis
- float projectionAxisX = AMathUtils_DotMultiply2(axis->x, axis->y, obbRect->xAxis->x, obbRect->xAxis->y);
- // projected axisY to axis
- float projectionAxisY = AMathUtils_DotMultiply2(axis->x, axis->y, obbRect->yAxis->x, obbRect->yAxis->y);
- return obbRect->halfWidth * obbRect->scaleX * projectionAxisX +
- obbRect->halfHeight * obbRect->scaleY * projectionAxisY;
- }
- static bool isCollision(OBBRect* obbRect, OBBRect* otherObb) {
- // two OBBRect center distance vector
- Vector2 distanceVec = {
- obbRect->centerX - otherObb->centerX,
- obbRect->centerY - otherObb->centerY,
- };
- Vector2* axes[] = {
- obbRect->xAxis,
- obbRect->yAxis,
- otherObb->xAxis,
- otherObb->yAxis,
- };
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- // compare OBBRect1 radius projection add OBBRect2 radius projection to centerDistance projection
- if (getProjectionRadius(obbRect, axes[i]) + getProjectionRadius(otherObb, axes[i]) <=
- AMathUtils_DotMultiply2(distanceVec.x, distanceVec.y, axes[i]->x, axes[i]->y)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- static float getWidth(OBBRect* obbRect) {
- return (obbRect->halfWidth * 2) * obbRect->scaleX;
- }
- static float getHeight(OBBRect* obbRect) {
- return (obbRect->halfHeight * 2) * obbRect->scaleY;
- }
- static inline void initOBBRect(OBBRect* obbRect, Rect* rect) {
- obbRect->rect = rect;
- obbRect->halfWidth = (rect->right - rect->left) / 2;
- obbRect->halfHeight = (rect->bottom - rect->top) / 2;
- obbRect->scaleX = 1.0f;
- obbRect->scaleY = 1.0f;
- obbRect->originX = 0.0f;
- obbRect->originY = 0.0f;
- obbRect->centerX = rect->left + obbRect->halfWidth;
- obbRect->centerY = rect->top - obbRect->halfHeight;
- obbRect->offsetDistance = sqrtf(AMathUtils_DotMultiply2(obbRect->centerX, obbRect->centerY, obbRect->centerX, obbRect->centerY));
- obbRect->offsetDegree = AMathUtils_Atan2(obbRect->centerX, obbRect->centerY);
- LogD("centerX = %f, centerY = %f", obbRect->centerX, obbRect->centerY);
- LogD("offsetDistance = %f, offsetDegree = %f",
- obbRect->offsetDistance, obbRect->offsetDegree);
- setRotation(obbRect, 0.0f);
- }
- static OBBRect* create(Rect* rect) {
- OBBRect* obbRect = (OBBRect*) malloc(sizeof(OBBRect));
- initOBBRect(obbRect, rect);
- return obbRect;
- }
- static void init(Rect* rect, Out(OBBRect* obbRect)) {
- initOBBRect(obbRect, rect);
- }
- _AOBBRect AOBBRect = {
- create,
- init,
- updateCenter,
- setRotation,
- isCollision,
- getWidth,
- getHeight,
- };
本文来自 qing101hua 的CSDN 博客 ,全文地址请点击:https://blog.csdn.net/qing101hua/article/details/52997160?utm_source=copy