基于LSSVM和PSO进行信号预测(Matlab代码实现)
个人主页:研学社的博客
欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️
博主优势:博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
目录
1 概述
2 运行结果
3 参考文献
4 Matlab代码实现
1 概述
LSSVM模型的本质是一个分类机,优化目标是得到最优分类间隔使得模型的拟合误差最小,在区域铁路货运量预测中,其优化目标、约束条件表示为
可以发现,LSS VM优化目标是带约束的等式,其求解仍存在难度,引入拉格朗日函数简化求解过程。通过拉格朗日函数将原始的约束问题转化为无约束问题,在高维空间内有效地运用核函数简化求解过程。
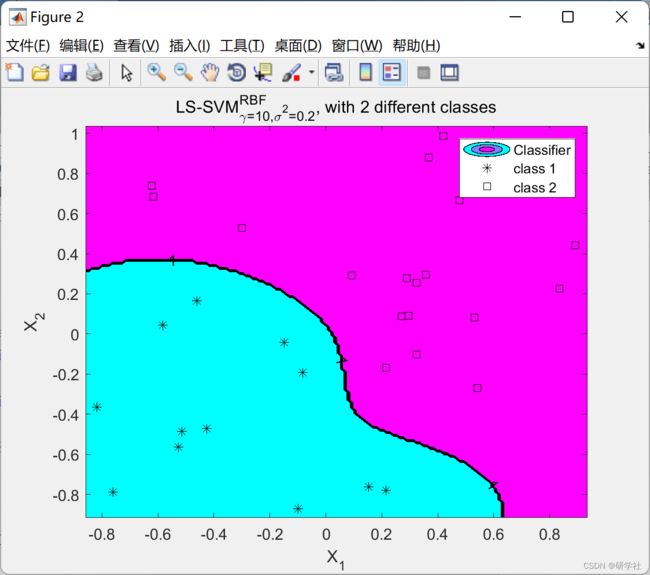
2 运行结果
部分代码:
eval('distfct;','distfct=''codedist_hamming'';');
eval('dist;','dist=2'';');
nb = ceil(log2(m*dist));
codebook =[];
candidates = eps.*ones(nb,1);
while isempty(codebook),
disp(['number of bits ' num2str(nb)]);
if nb>2^(m-1), error('No such code feasable'); end
[codebook,sc] = create_code(candidates, m, dist, distfct,[]);
if isempty(codebook),
nb=nb+1;
candidates = eps.*ones(nb,1);
else
hd=inf;
hdM = 0;
for t1=1:size(codebook,1), for t2=(t1+1):size(codebook,1),
hd = min(hd,feval(distfct,codebook(t1,:), codebook(t2,:)));
hdM = max(hdM,feval(distfct,codebook(t1,:), codebook(t2,:)));
end; end
if hd==0|hdM==size(codebook,2),
candidates = sc;
codebook=[]; disp('retry');
end
end
end
%
% output format, where 'b' stands for binary discriminator
% see also 'code' and 'codelssvm'
scheme = []; for i=1:nb, scheme = [scheme 'b']; end
function [code,shrunkcandidate,rc] = create_code(candidates, m, dist, distfct,foundcand)
%
% recursive called function
%
% base case
if isempty(candidates), code=[]; shrunkcandidate=[]; rc=0; return; end
% pick a candidate
[nb,nc] = size(candidates);
rc=ceil(rand*nc);
acode = candidates(:,rc);
% initate this candidate
% and remove from the candidate list
acode = (acode~=eps).*acode;
aicode = acode +(acode==0).*sign(rand(nb,1)-.5);
if sum(acode==0)==0,
candidates = candidates(:,[1:(rc-1) (rc+1):nc]);
else
while(acode==aicode),
aicode = acode + (acode==0).*sign(rand(nb,1));
end
end
aicode = aicode+(aicode==0).*eps;
acode = acode+(acode==0).*eps;
candidates = shrink(candidates, aicode, dist, distfct);
shrunkcandidate = shrink(acode, aicode, dist, distfct);
% recursion
if m-1>0,
shrunkc = candidates;
fprintf('R;');
[newcode,shrunkcandidate2,cc] = create_code(candidates,m-1, dist, distfct,[foundcand aicode]);
fprintf('O;');
while isempty(newcode),
if isempty(find(shrunkcandidate2)), code=[]; return; end
disp('retry with left candidates');
shrunkc = [shrunkc(:,1:(cc-1)) shrunkcandidate2 shrunkc(:,(cc+1):end)];
[newcode,shrunkcandidate2,cc] = create_code(shrunkc, m, dist, distfct,foundcand);
end
code = [aicode newcode];
else
code = aicode;
end
shrunkcandidate = candidates;
function shrunkcandidates = shrinkr(candidates, aicode, dist, distfct)
% refine candidates according to dist
% and shrink list of candidates
%
% recursive algorithm: TAKE CARE many recursions needed
fprintf('r');
% end of recursion
if isempty(candidates),shrunkcandidates=[]; return; end
if size(candidates,2)==1 &sum(candidates==eps)==0,shrunkcandidates=[]; return; end
% recursive step
cand = candidates(:,1);
if feval(distfct, aicode', cand)
zi = find(cand==eps);
if ~isempty(zi),
ncandn = [cand(1:(zi-1)); -1; cand((zi+1):end)];
ncandp = [cand(1:(zi-1)); 1; cand((zi+1):end)];
candidates = [candidates(:,2:end) ncandp ncandn];
else
candidates = candidates(:,2:end);
end
shrunkcandidates = shrink(candidates,aicode,dist,distfct);
else
shrunkcandidates = [cand shrink(candidates(:,2:end),aicode,dist,distfct)];
end
fprintf('o');
function shrunkcandidates = shrink(candidates, aicode, dist, distfct)
% refine candidates according to dist
% and shrink list of candidates
%
% iteration with dynamical list
%aicode
%candidates
i =1;
nb = size(candidates,2);
while i<=nb,
cand = candidates(:,i);
if feval(distfct, aicode', cand)
if ~isempty(zi),
ncandn = [cand(1:(zi-1)); -1; cand((zi+1):end)];
ncandp = [cand(1:(zi-1)); 1; cand((zi+1):end)];
[candidates(:,[1:(i-1) (i+1):end]) ncandp ncandn];
candidates = [candidates(:,[1:(i-1) (i+1):end]) ncandp ncandn];
else
candidates(:,[1:(i-1) (i+1):end]);
candidates = candidates(:,[1:(i-1) (i+1):end]);
end
else
i=i+1;
end
nb = size(candidates,2);
end
shrunkcandidates = candidates;
3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]Shaojiang Dong,Tianhong Luo,Bearing degradation process prediction based on the PCA and optimized LS-SVMmodel,Measurement,2013.06