PyTorch笔记 - Attention Is All You Need (2)
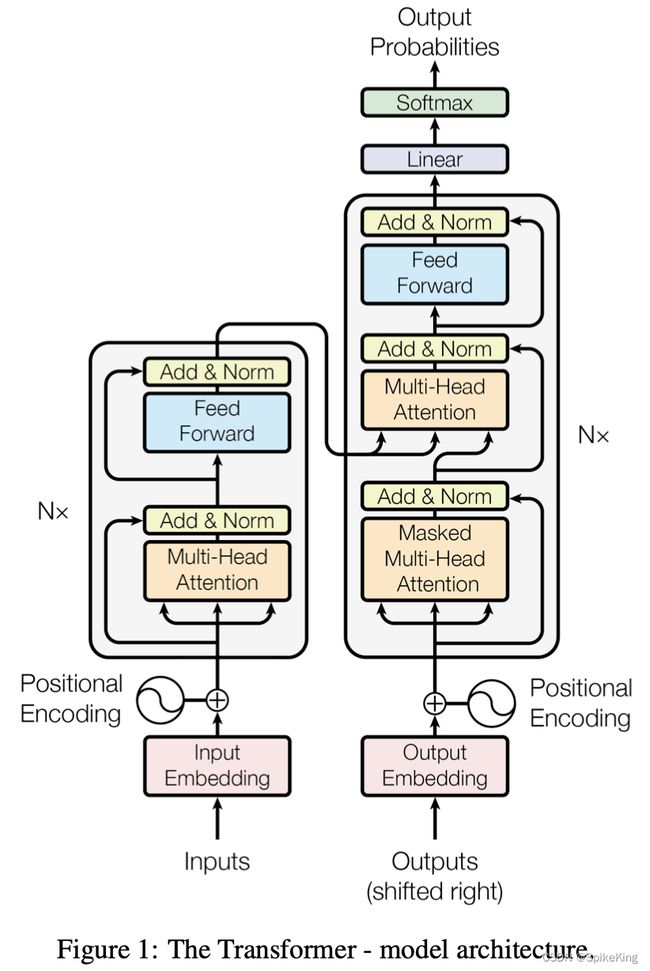
Encoder作为KV、Decoder作为Q
构建WordEmbedding;没有局部假设,需要位置假设,即Position Encoding;序列长度不一致,需要Mask对齐
Masked Multi-Head Attention,序列本身的关联性,自回归模型,保证OutputEmbedding输入不包含未来信息
Transformer难点细节实现,6点:Word Embedding、Position Embedding、Encoder Self-Attention Mask、Intra-Attention Mask、Decoder Self-Attention Mask、Multi-Head Self-Attention
Word Embedding
Torch随机数的种子
torch.manual_seed(42) # torch的随机化种子
Embedding:参考 torch.nn.``Embedding
- torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings, embedding_dim)
构建Word Embedding,源码如下:
import torch
import random
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 关于word embedding 以序列建模为例
# 考虑 source sentence 和 target sentence
# 构建序列,序列的字符以其在词表中的索引的形式表示
batch_size = 2
max_num_src_words = 8 # 单词表的数目
max_num_tgt_words = 8
max_src_seq_len = 5 # 最大序列长度
max_tgt_seq_len = 5
model_dim = 8 # 特征维度大小
# src_len = torch.randint(2, 5, (batch_size,))
# tgt_len = torch.randint(2, 5, (batch_size,))
src_len = torch.Tensor([2, 4]).to(torch.int32) # 第1个句子长度是2,第2个句子长度是4
tgt_len = torch.Tensor([4, 3]).to(torch.int32) # 第1个句子长度是4,第2个句子长度是3
torch.manual_seed(42) # torch的随机化种子
# 单次索引构成的句子
# pad,左侧不pad,即0,右侧pad到最大长度
# torch.stack = torch.cat + torch.unsqueeze
src_seq = torch.stack([F.pad(torch.randint(1, max_num_src_words, (L,)), (0, max_src_seq_len-L)) for L in src_len])
tgt_seq = torch.stack([F.pad(torch.randint(1, max_num_tgt_words, (L,)), (0, max_tgt_seq_len-L)) for L in tgt_len])
print(src_seq, tgt_seq)
print(src_seq.shape, tgt_seq.shape)
# 构造Embeding, max_num_src_words+1, 1表示padding的0
src_embedding_table = nn.Embedding(max_num_src_words+1, model_dim)
tgt_embedding_table = nn.Embedding(max_num_tgt_words+1, model_dim)
src_embedding = src_embedding_table(src_seq) # 调用call或forward
tgt_embedding = tgt_embedding_table(tgt_seq)
print(src_embedding_table.weight.shape)
print(src_embedding_table.weight)
print(src_seq)
print(src_embedding.shape)
print(src_embedding)
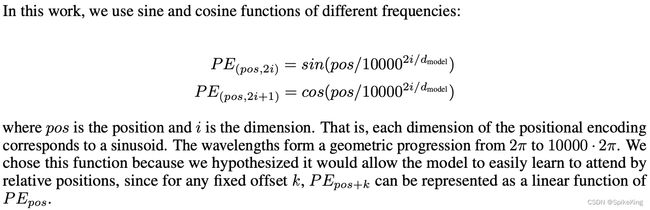
Position Embedding
sinusoid,正弦曲线,两个参数pos和i,pos变量决定行,i变量决定列
# 构造Position Embedding
pos_mat = torch.arange(max_position_len).reshape(-1, 1)
i_mat = torch.arange(0, 8, 2).reshape(1, -1) / model_dim # 最小值是0,最大值是8,间隔是2
i_mat = torch.pow(10000, i_mat)
# 最大词表数max_position_len,数据最大维度model_dim
pe_embedding_table = torch.zeros(max_position_len, model_dim)
pe_embedding_table[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(pos_mat / i_mat) # 赋值偶数列
pe_embedding_table[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(pos_mat / i_mat) # 赋值奇数列
print(pos_mat)
print(i_mat)
print(pe_embedding_table.shape)
print(pe_embedding_table)
pe_embedding = nn.Embedding(max_position_len, model_dim)
pe_embedding.weight = nn.Parameter(pe_embedding_table, requires_grad=False)
# print(pe_embedding.weight)
# print(src_seq.shape)
# print(pe_embedding.weight.shape)
# src_len是每个句子的长度,最大长度是4,所以位置就是[0, 1, 2, 3]
# 最大长度max(src_len),不能超过max_position_len,保证每个值都可以在Embedding中查找到
print(f'src_len: {src_len}')
src_pos = torch.stack([torch.arange(max(src_len)) for _ in src_len]).to(torch.int32)
src_pe_embedding = pe_embedding(src_pos) # pos index 而不是 word index
print(f'src_pos: {src_pos}')
print(f'src_pe_embedding.shape: {src_pe_embedding.shape}')
print(f'src_pe_embedding: {src_pe_embedding}')
tgt_pos = torch.stack([torch.arange(max(tgt_len)) for _ in tgt_len]).to(torch.int32)
tgt_pe_embedding = pe_embedding(tgt_pos)
Encoder Self-Attention Mask
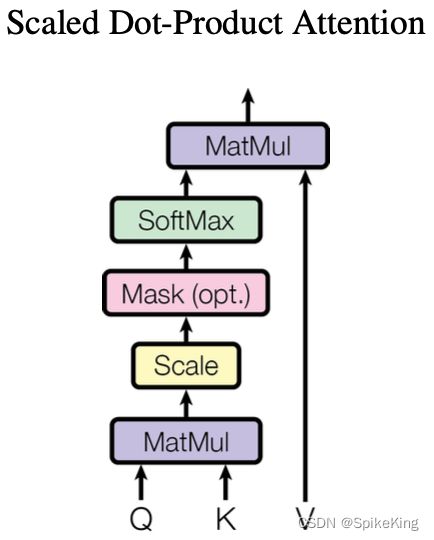
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
Q和K的相似度,Query和Key,两个向量的内积,两两相乘;SoftMax,归一化(0~1),单调,非线性;Scaled,方差为1,均值为0,雅可比矩阵的导数变成非0
Softmax + Scaled,除以根号dk,方差变为1,避免导数为0:
# softmax演示,scaled的重要性
# torch.manual_seed(42) # torch的随机化种子
score = torch.randn(5)
prob = F.softmax(score, -1)
print(score)
print(prob, torch.var(prob))
alpha1 = 0.1
alpha2 = 10
prob1 = F.softmax(score * alpha1, -1)
prob2 = F.softmax(score * alpha2, -1)
print(f"prob1: {prob1}")
print(f"prob2: {prob2}")
def softmax_func(score):
return F.softmax(score, dim=0)
jaco_mat1 = torch.autograd.functional.jacobian(softmax_func, score*alpha1)
jaco_mat2 = torch.autograd.functional.jacobian(softmax_func, score*alpha2)
# 梯度矩阵
print(jaco_mat1)
print(jaco_mat2) # 梯度导数很多为0
关系矩阵:
- 得到有效矩阵,两两相乘
- 取反,置为True or Flase
- 将True的位置,值设置为极小负数,如-1e9
- 执行Softmax,Mask的部分为0,整行mask为均值
# 构造Encoder的Self-Attention Mask
# mask的shape: [batch_size, max_src_len, max_src_len],值为1或-inf
valid_encoder_pos = torch.stack([F.pad(torch.ones(L), (0, max(src_len) - L)) for L in src_len])
print(valid_encoder_pos) # 有效位置是1,无效位置是0,根据batch的最大长度
valid_encoder_pos = torch.unsqueeze(valid_encoder_pos, dim=2) # 增加1维
print(valid_encoder_pos.shape)
# 有效矩阵,值为1,无效pad的值为0
valid_encoder_pos_matrix = torch.bmm(valid_encoder_pos, valid_encoder_pos.transpose(1, 2))
print(f'valid_encoder_pos_matrix.shape: {valid_encoder_pos_matrix.shape}')
print(f'valid_encoder_pos_matrix: \n{valid_encoder_pos_matrix}')
print(f"src_len: {src_len}")
invalid_encoder_pos_matrix = 1 - valid_encoder_pos_matrix
print(f"invalid_mask_encoder_pos_matrix: \n{invalid_mask_encoder_pos_matrix}")
# 转换为True or False的mask
mask_encoder_self_attention = invalid_encoder_pos_matrix.to(torch.bool)
print(mask_encoder_self_attention)
# 测试
score = torch.randn(batch_size, max(src_len), max(src_len))
print(f"score.shape: {score.shape}")
print(f"mask_encoder_self_attention.shape: {mask_encoder_self_attention.shape}")
masked_score = score.masked_fill(mask_encoder_self_attention, -1e9)
print(f"masked_score: \n{masked_score}")
# 4个都mask,则权重相同,都是0.25
prob = F.softmax(masked_score, -1)
print(f"prob: \n{prob}")