光流的概念以及 Lucas-Kanade 光流法
光流
目标
本节我们将要学习:
• 光流的概念以及 Lucas-Kanade 光流法
• 使用函数 cv2.calcOpticalFlowPyrLK() 对图像中的特征点进行跟踪
光流
由于目标对象或者摄像机的移动造成的图像对象在连续两帧图像中的移动被称为光流。它是一个 2D 向量场,可以用来显示一个点从第一帧图像到第二帧图像之间的移动。如下图所示(Image Courtesy: Wikipedia article on Optical Flow):

上图显示了一个点在连续的五帧图像间的移动。箭头表示光流场向量。光流在很多领域中都很有用:
• 由运动重建结构
• 视频压缩
• Video Stabilization 等
光流是基于一下假设的:
- 在连续的两帧图像之间(目标对象的)像素的灰度值不改变。
- 相邻的像素具有相同的运动
第一帧图像中的像素 I (x,y,t) 在时间 dt 后移动到第二帧图像的(x+dx,y+dy)处。根据第一条假设:灰度值不变。所以我们可以得到:
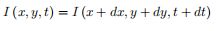
对等号右侧进行泰勒级数展开,消去相同项,两边都除以 dt,得到如下方程:

上边的等式叫做光流方程。其中 f x {{f}_{x}} fx 和 f y {{f}_{y}} fy 是图像梯度,同样 f t {{f}_{t}} ft 是时间方向的梯度。但(u,v)是不知道的。我们不能在一个等式中求解两个未知数。有几个方法可以帮我们解决这个问题,其中的一个是 Lucas-Kanade 法
Lucas-Kanade 法
现在我们要使用第二条假设,邻域内的所有点都有相似的运动。LucasKanade 法就是利用一个 3x3 邻域中的 9 个点具有相同运动的这一点。这样我们就可以找到这 9 个点的光流方程,用它们组成一个具有两个未知数 9 个等式的方程组,这是一个约束条件过多的方程组。一个好的解决方法就是使用最小二乘拟合。下面就是求解结果:

(有没有发现上边的逆矩阵与 Harris 角点检测器非常相似,这说明角点很适合被用来做跟踪)
从使用者的角度来看,想法很简单,我们取跟踪一些点,然后我们就会获得这些点的光流向量。但是还有一些问题。直到现在我们处理的都是很小的运动。如果有大的运动怎么办呢?图像金字塔。我们可以使用图像金字塔的顶层,此时小的运动被移除,大的运动装换成了小的运动,现在再使用 Lucas-Kanade算法,我们就会得到尺度空间上的光流。
OpenCV 中的 Lucas-Kanade 光流
上述所有过程都被 OpenCV 打包成了一个函数:cv2.calcOpticalFlowPyrLK()。
现在我们使用这个函数创建一个小程序来跟踪视频中的一些点。要跟踪那些点呢?我们使用函数 cv2.goodFeatureToTrack() 来确定要跟踪的点。我们首先在视频的第一帧图像中检测一些 Shi-Tomasi 角点,然后我们使用 LucasKanade 算法迭代跟踪这些角点。我们要给函数cv2.calcOpticlaFlowPyrLK()传入前一帧图像和其中的点,以及下一帧图像。函数将返回带有状态数的点,如果状态数是 1,那说明在下一帧图像中找到了这个点(上一帧中角点),如果状态数是 0,就说明没有在下一帧图像中找到这个点。我们再把这些点作为参数传给函数,如此迭代下去实现跟踪。代码如下:
(上面的代码没有对返回角点的正确性进行检查。图像中的一些特征点甚至在丢失以后,光流还会找到一个预期相似的点。所以为了实现稳定的跟踪,我们应该每个一定间隔就要进行一次角点检测。OpenCV 的官方示例中带有这样一个例子,它是每 5 帧进行一个特征点检测。它还对光流点使用反向检测来选取好的点进行跟踪。示例为/samples/python2/lk_track.py)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jan 27 12:28:25 2014
@author: duan
"""
import numpy as np
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('slow.flv')
# params for ShiTomasi corner detection
feature_params = dict( maxCorners = 100,
qualityLevel = 0.3,
minDistance = 7,
blockSize = 7 )
# Parameters for lucas kanade optical flow
#maxLevel 为使用的图像金字塔层数
lk_params = dict( winSize = (15,15),
maxLevel = 2,
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_COUNT, 10, 0.03))
# Create some random colors
color = np.random.randint(0,255,(100,3))
# Take first frame and find corners in it
ret, old_frame = cap.read()
old_gray = cv2.cvtColor(old_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
p0 = cv2.goodFeaturesToTrack(old_gray, mask = None, **feature_params)
# Create a mask image for drawing purposes
mask = np.zeros_like(old_frame)
while(1):
ret,frame = cap.read()
frame_gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# calculate optical flow 能够获取点的新位置
p1, st, err = cv2.calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(old_gray, frame_gray, p0, None, **lk_params)
# Select good points
good_new = p1[st==1]
good_old = p0[st==1]
# draw the tracks
for i,(new,old) in enumerate(zip(good_new,good_old)):
a,b = new.ravel()
c,d = old.ravel()
mask = cv2.line(mask, (a,b),(c,d), color[i].tolist(), 2)
frame = cv2.circle(frame,(a,b),5,color[i].tolist(),-1)
img = cv2.add(frame,mask)
cv2.imshow('frame',img)
k = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xff
if k == 27:
break
# Now update the previous frame and previous points
old_gray = frame_gray.copy()
p0 = good_new.reshape(-1,1,2)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cap.release()
下面是我的到的结果:

OpenCV 中的稠密光流
Lucas-Kanade 法是计算一些特征点的光流(我们上面的例子使用的是Shi-Tomasi 算法检测到的角点)。OpenCV 还提供了一种计算稠密光流的方法。它会图像中的所有点的光流。这是基于 Gunner_Farneback 的算法(2003 年)。
下面的例子就是使用上面的算法计算稠密光流。结果是一个带有光流向量(u,v)的双通道数组。通过计算我们能得到光流的大小和方向。我们使用颜色对结果进行编码以便于更好的观察。方向对应于 H(Hue)通道,大小对应于 V(Value)通道。代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jan 27 12:28:46 2014
@author: duan
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("vtest.avi")
ret, frame1 = cap.read()
prvs = cv2.cvtColor(frame1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
hsv = np.zeros_like(frame1)
hsv[...,1] = 255
while(1):
ret, frame2 = cap.read()
next = cv2.cvtColor(frame2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#cv2.calcOpticalFlowFarneback(prev, next, pyr_scale, levels, winsize, iterations, poly_n,
#poly_sigma, flags[)
#pyr_scale – parameter, specifying the image scale (<1) to build pyramids for each image;
#pyr_scale=0.5 means a classical pyramid, where each next layer is twice smaller than the
#previous one.
#poly_n – size of the pixel neighborhood used to find polynomial expansion in each pixel;
#typically poly_n =5 or 7.
#poly_sigma – standard deviation of the Gaussian that is used to smooth derivatives used
#as a basis for the polynomial expansion; for poly_n=5, you can set poly_sigma=1.1, for
#poly_n=7, a good value would be poly_sigma=1.5.
#flag 可选 0 或 1,0 计算快,1 慢但准确
flow = cv2.calcOpticalFlowFarneback(prvs,next, None, 0.5, 3, 15, 3, 5, 1.2, 0)
#cv2.cartToPolar Calculates the magnitude and angle of 2D vectors.
mag, ang = cv2.cartToPolar(flow[...,0], flow[...,1])
hsv[...,0] = ang*180/np.pi/2
hsv[...,2] = cv2.normalize(mag,None,0,255,cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(hsv,cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
cv2.imshow('frame2',rgb)
k = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xff
if k == 27:
break
elif k == ord('s'):
cv2.imwrite('opticalfb.png',frame2)
cv2.imwrite('opticalhsv.png',rgb)
prvs = next
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果如下:

OpenCV 的官方示例中有一个更高级的稠密光流/samples/python2/opt_flow.py,去搞定它吧!