Chapter3 Pytorch与机器学习有关函数(一)
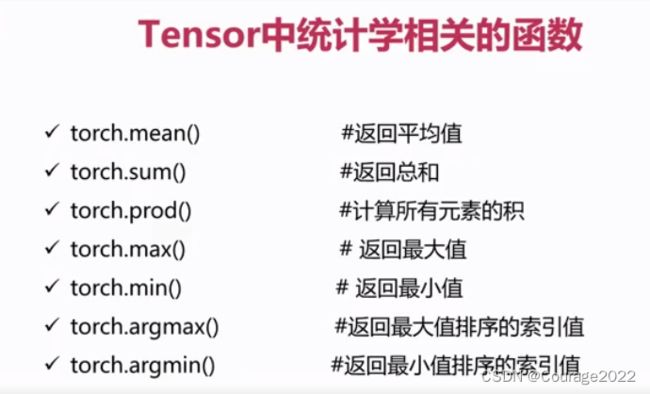
3.1 Tensor中统计学有关的函数
3.1.1 平均值、总和 、累积
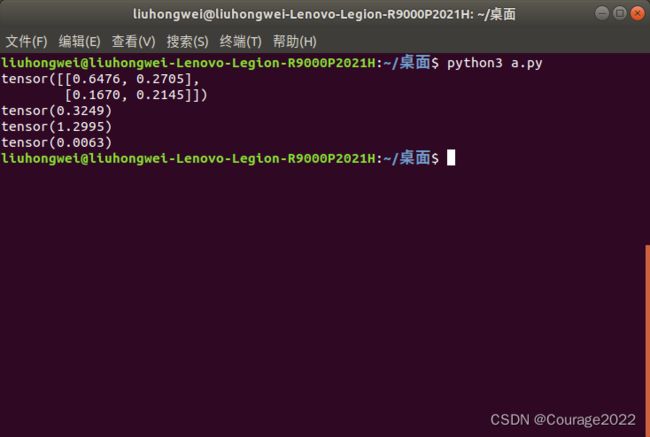
1.测试结果1
import torch a = torch.rand(2, 2) print(a) print(torch.mean(a,)) print(torch.sum(a)) print(torch.prod(a))
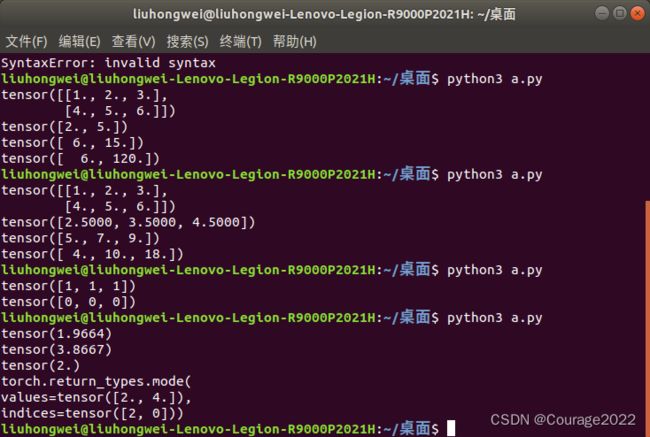
2.测试结果2:![]() 数组对第1维操作
数组对第1维操作
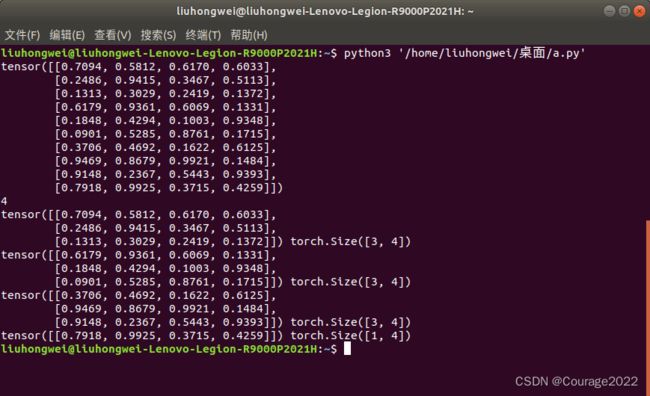
import torch a = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0,3.0],[4.0,5.0,6.0]]) print(a) print(torch.mean(a,dim=1)) print(torch.sum(a,dim=1)) print(torch.prod(a,dim=1))
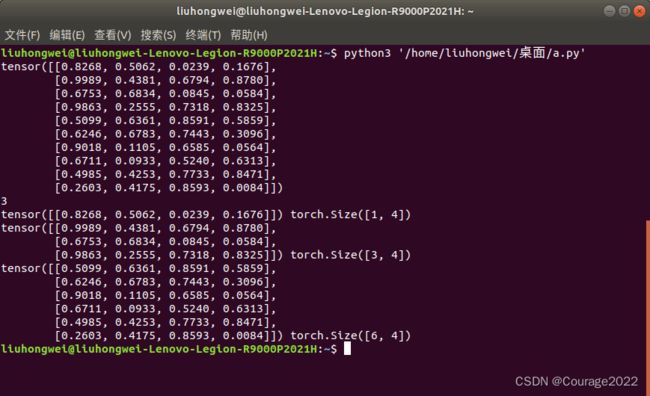
3.测试结果3:![]() 数组对第0维操作
数组对第0维操作
import torch a = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0,3.0],[4.0,5.0,6.0]]) print(a) print(torch.mean(a,dim=0)) print(torch.sum(a,dim=0)) print(torch.prod(a,dim=0))
3.1.2 返回最值排序的索引值
import torch a = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0,3.0],[4.0,5.0,6.0]]) print(torch.argmax(a,dim=0)) print(torch.argmin(a,dim=0))
3.1.3 标准差、方差、中间数、众数
import torch a = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0,2.0],[4.0,5.0,6.0]]) print(torch.std(a)) print(torch.var(a)) print(torch.median(a)) print(torch.mode(a))
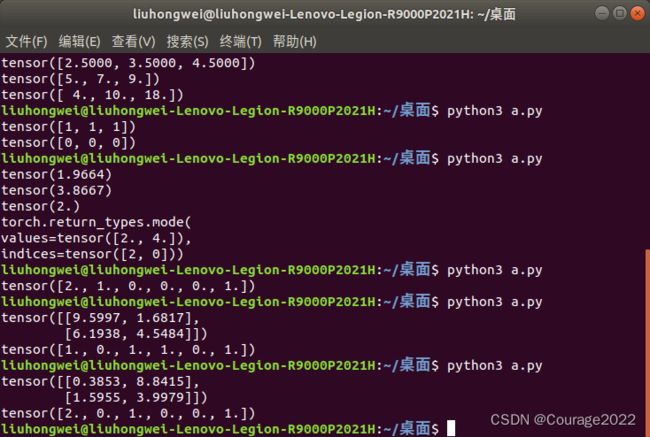
3.1.4 计算input的直方图
import torch a = torch.rand(2,2)*10 print(a) print(torch.histc(a,6,0,0))第二个参数是指将数据分成几个区间,第三个参数第四个参数默认是0表示以a中最小的值作为初始区间,最大的值作为结束区间。演示结果如下图:
3.1.5 返回频数(只支持一位tensor)
import torch a = torch.randint(0,10,[10]) print(a) print(torch.bincount(a))0出现了..次,1出现了..次.....可以用来统计某一样别样本数量
3.1.6 分布函数torch.distributions
3.1.7 tensor中的随机抽样函数
用随机数种子能够保证每次抽样的结果是一样的:
import torch torch.manual_seed(1) mean = torch.rand(1,2) std = torch.rand(1,2) print(torch.normal(mean,std))
3.2 tensor中与线性代数有关函数
3.2.1 tensor中的范数运算
norm:平方和相加开根号
import torch a = torch.tensor([3.0,4.0]) b = torch.tensor([5.0,8.0]) print(a,b) print(torch.dist(a,b,p=1)) print(torch.dist(a,b,p=2)) print(torch.dist(a,b,p=3)) print(torch.norm(a))
3.2.2 tensor与矩阵分解
3.2.2.1 矩阵分解介绍
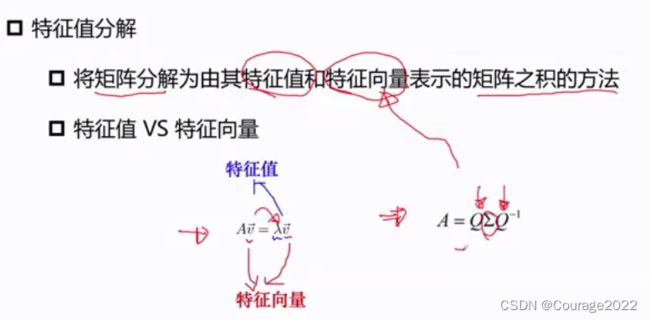
3.2.2.2 EVD分解
考研的时候考过,不细说。
是特征向量矩阵,
是特征值矩阵。要求矩阵满秩。
PCA与特征值分解(主成分分析):通过一个投影矩阵,将原始的
维特征矩阵(n个特征m个样本,即每一个样本表示成n维向量)映射到k维(最终结果为
)上去(通过投影矩阵
来实现映射)来实现降维。
3.2.2.3 SVD分解
由于EVD分解只针对满秩矩阵且必须是方阵,我们引出了SVD分解,对矩阵形状和秩没有要求。
应用:LDA算法中,主要思想是在"新空间"让同类物体的间隔尽可能小,不同类别物体的间隔尽可能大。
描述为同类物体的协方差矩阵,
描述为不同类物体的协方差矩阵。优化目标是对代价函数求最大值。
3.3 pytorch
3.3.1 Tensor的裁减运算
对tensor中元素进行范围性的约束,一是将数据约束在比较小的范围中网络在参数学习中容易稳定,可以实现类似正则化的功能防止过拟合;二是防止梯度离散/梯度爆炸。
import torch a = torch.rand(2,2)*10 print(a) print(a.clamp(1,2)) #将数据处理到1-2之间
3.3.2 tensor的索引与数据筛选
3.2.2.1 torch.where
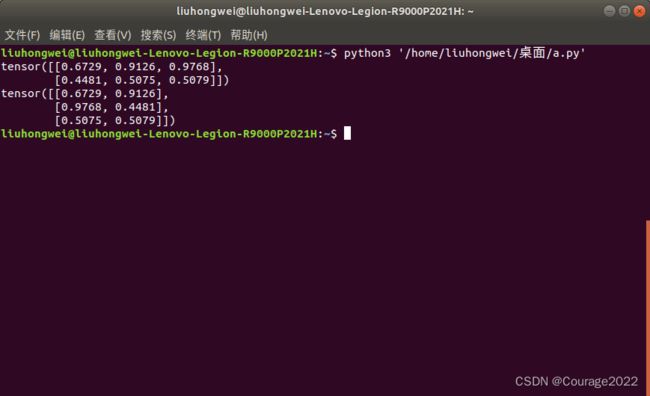
第一个参数是判断条件,如果满足判断条件选择第二个参数的数据,如果不满足选择第三个参数的数据。类似C++中的 a>b?a:b
import torch a = torch.rand(4,4) b = torch.rand(4,4) print(a) print(b) out = torch.where(a>0.5,a,b) print(out)
3.2.2.2 torch.index_select
我们用代码进行分析:
Chapter3 Pytorch与机器学习有关函数(一)我们初始化了一个
的张量,我们取出了第0、3、2行的数据到张量out中。
3.2.2.3 torch.gather
我们用代码进行分析:
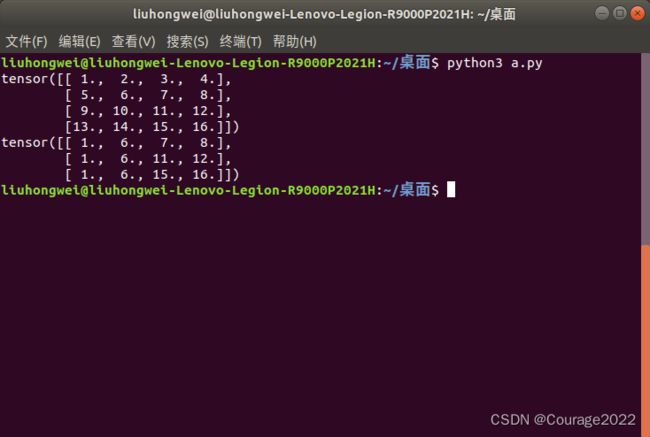
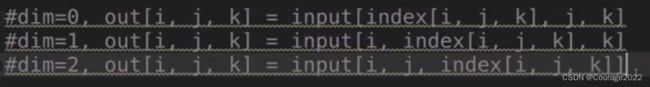
import torch a = torch.linspace(1,16,16).view(4,4) print(a) out = torch.gather(a,dim=0,index=torch.tensor([[0,1,1,1],[0,1,2,2],[0,1,3,3]])) print(out)我们初始化了一个
的张量,分别在第0维上找第 0 1 1 1个数据,即1 6 7 8,然后再取0 1 2 2 个数据......
如果维度更高那么gather怎么用呢?
3.2.2.4 torch.masked_select
import torch a = torch.linspace(1,16,16).view(4,4) print(a) mask = torch.gt(a,8) print(mask) out = torch.masked_select(a,mask) print(out)很好理解,不多解释。
3.2.2.5 torch.take
import torch a = torch.linspace(1,16,16).view(4,4) print(a) out = torch.take(a,index = torch.tensor([0,15,13,10])) print(out)很好理解,不多解释。
3.3.3 tensor的组合和拼接
3.3.3.1 torch.cat
import torch a = torch.zeros((2,4)) b = torch.ones((2,4)) out = torch.cat((a,b),dim = 0) print(out)我们看到我们在第0维上进行了拼接,原来是两个
,拼接完成变成了
的张量。
我们再将维度修改成1,查看其运行结果。
3.3.3.2 torch.stack
import torch a = torch.linspace(1,6,6).view(2,3) b = torch.linspace(7,12,6).view(2,3) out = torch.stack((a,b),dim = 0) print(out) print(out.shape)我们来解析一下这个size:
[[[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6.]], [[ 7., 8., 9.], [10., 11., 12.]]]
第一维度就有两个数据:[[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6.]],[[ 7., 8., 9.], [10., 11., 12.]]
第二维度也是两个数据[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6.]
第三维度是三个数据1,2,3
因此这个shape是
的形式。
而a是[ [1,2,3] ,[4,5,6]]的
形式,将a和b看作是两个独立的元素在第0维度进行拼接。
那么如果在第一维度拼接是个什么样的结果呢?
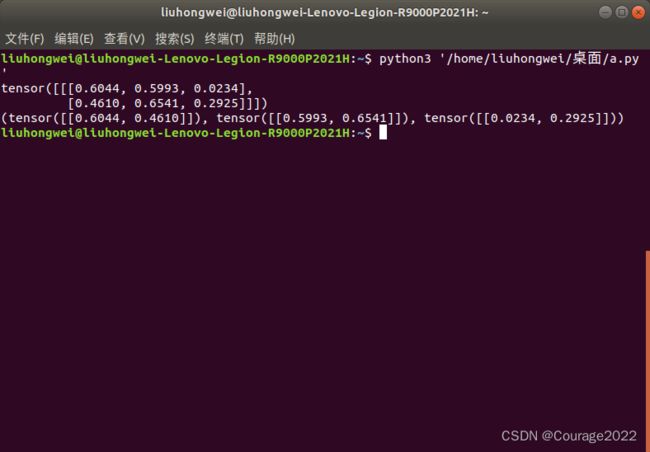
import torch a = torch.linspace(1,6,6).view(2,3) b = torch.linspace(7,12,6).view(2,3) out = torch.stack((a,b),dim = 1) print(out) print(out[:,0,:]) print(out[:,1,:]) print(out.shape)那么如果在第二维度拼接是个什么样的结果呢?
import torch a = torch.linspace(1,6,6).view(2,3) b = torch.linspace(7,12,6).view(2,3) out = torch.stack((a,b),dim = 2) print(out) print(out[:,:,0]) print(out[:,:,1]) print(out.shape)
3.3.4 tensor的切片
3.3.4.1 torch.chunk
import torch a = torch.rand((3,4)) print(a) out = torch.chunk(a,2,dim=1) print(out) print(out[0],out[0].shape) print(out[1],out[1].shape)对第一维度进行分割,即
[[0.1813, 0.0810, 0.7142, 0.8603],
[0.2262, 0.8307, 0.2050, 0.7882],
[0.1058, 0.8872, 0.7148, 0.1272]]对大括号里面进行分割,我们一个括号选出两个组成新的张量,构成两个
的张量。
3.3.4.2 torch.split
1.和torch.chunk一样的调用方式
import torch a = torch.rand((3,4)) print(a) out = torch.split(a,2,dim=1) print(out) print(out[0],out[0].shape) print(out[1],out[1].shape)
2.不平均分割
import torch a = torch.rand((10,4)) print(a) out = torch.split(a,3,dim=0) print(len(out)) for t in out: print(t,t.shape)
3.第二种调用方式 :传入list列表,指定我们要切分的尺寸
import torch a = torch.rand((10,4)) print(a) out = torch.split(a,[1,3,6],dim=0) print(len(out)) for t in out: print(t,t.shape)
3.3.5 tensor的变形操作
3.3.5.1 tensor.reshape
import torch a = torch.rand((2,3)) print(a) out = torch.reshape(a,(3,2)) print(out)简单来说,就是进行了简单的排列组合。
3.3.5.2 torch.t
import torch a = torch.rand((2,3)) print(a) out = torch.t(a) print(out)对张量进行矩阵运算。
3.3.5.3 torch.transpose
1.用transpose求转置
将两个维度相互交换:
import torch a = torch.rand((2,3)) print(a) out = torch.transpose(a,0,1) print(out)交换a张量的第0维和第一维,相当于求转置。
2.用transpose实现高维交换
import torch a = torch.rand((1,2,3)) print(a) out = torch.transpose(a,0,1) print(out) print(out.shape)
3.3.5.4 torch.squeeze
去除维度为1的维度。
import torch a = torch.rand((1,2,3)) print(a) out = torch.squeeze(a) print(out) print(out.shape)
3.3.5.5 torch.unsqueeze
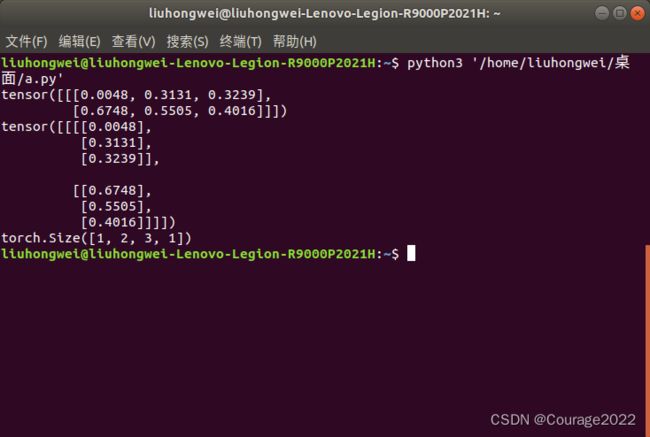
-1表示在最后一个维度进行拓展。
import torch a = torch.rand((1,2,3)) print(a) out = torch.unsqueeze(a,-1) print(out) print(out.shape)
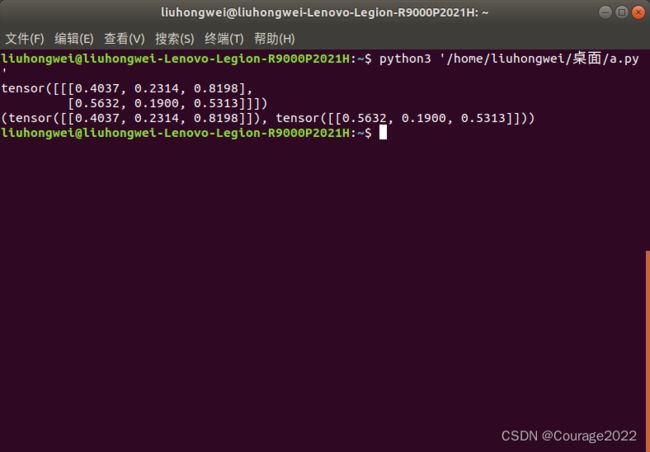
3.3.5.6 torch.unbind
对维度进行删除,类似于tensor切分的过程:我们会拿到元组,和我们切分拿到的元组类似。
import torch a = torch.rand((1,2,3)) print(a) out = torch.unbind(a , dim=1) print(out)tensor([[[0.4037, 0.2314, 0.8198], [0.5632, 0.1900, 0.5313]]])
(tensor([[0.4037, 0.2314, 0.8198]]), tensor([[0.5632, 0.1900, 0.5313]]))