(一)路径规划算法---Astar实现自定义的全局路径规划插件
Astar实现自定义的全局路径规划插件
文章目录
- Astar实现自定义的全局路径规划插件
-
- 1.插件功能包的建立
- 2. 相关步骤
-
- 2.1 建立工作空间和环境变量的配置
- 2.2 建立功能包
- 2.3 添加源文件与头文件
-
- 2.3.1AstarNode.h头文件
- 2.3.2AstarNode.cpp源文件
- 2.4 插件包进行编译
-
- 2.4.1 CMakeLists.txt改写
- 2.4.2 astar_plugin.xml改写
- 2.4.3 package.xml 改写
- 2.4.4 编译
- 2.5 检验插件包是否建立成功
- 2.6 插件的使用
- 3. 插件执行情况
- 4. 注意事项
本篇代码: astar_plugin
参考链接: https://www.ncnynl.com/archives/201708/1887.html
参考视频: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1JF41137RH?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click
相信看过前几篇关于Astar算法的原理和使用,大家基本对算法本身有了一定了解,那么怎么把自己实现的路径规划放到真实机器人中,让机器人按照你实现的全局路径规划算法进行运动。
ROS具有及其丰富的插件机制,让众多开发者只需关注算法本身的实现,然后通过插件注册机制。本文会一步一步进行插件机制如何使用,并不会过多介绍算法本体。
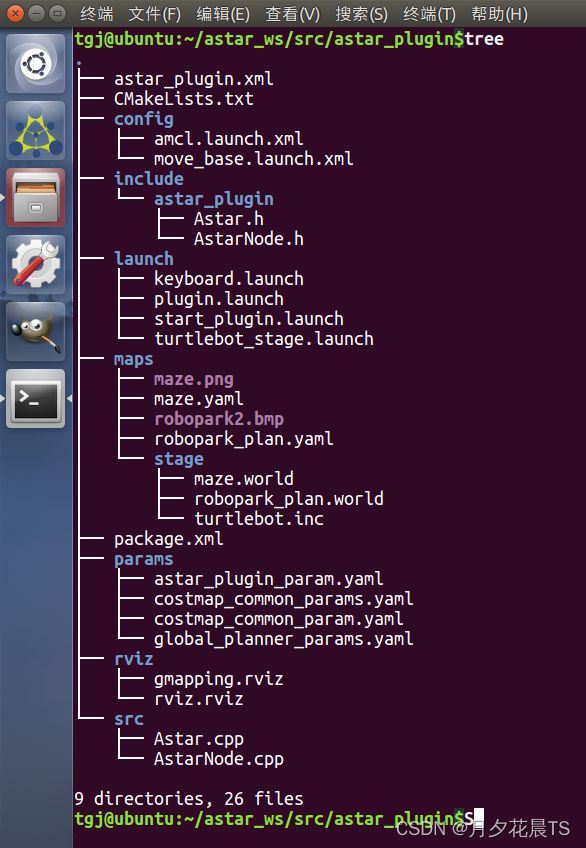
1.插件功能包的建立
相关文件夹和文件说明如下
include:算法本体和插件机制实现的头文件
src:算法本体和插件机制实现的源文件
config:定位和导航的配置文件,测试时使用
params:导航和自身插件所需要的参数设置文件
launch:测试插件的启动文件
rviz:rviz配置文件
maps:测试所需要的仿真地图文件
CMakeLists.txt:编译插件包
package.xml:编译和注册插件包
astar_plugin.xml:插件包的说明
2. 相关步骤
2.1 建立工作空间和环境变量的配置
在根目录下
mkdir -p astar_ws/src
cd astar_ws/src
catkin_init_worksapce
cd ..
catkin_make
配置环境变量
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
在打开的文件下方添加
source ~/astar_ws/devel/setup.bash
最后在配置环境变量
source ~/.bashrc
2.2 建立功能包
cd astar_ws/src
catkin_create_pkg astar_plugin nav_core roscpp rospy std
catkin_make
注意在创建功能包一定需要添加nav_core消息类型
2.3 添加源文件与头文件
include头文件/src源文件包括
Astar.h/Astar.cpp:Astar算法本体文件,就是Astar与C++可视化在RVIZ的二维栅格地图章的算法
AstarNode.h/AstarNode.cpp:插件机制与对外接口函数
2.3.1AstarNode.h头文件
头文件基本框架如下,首先定义一个命名空间Astar_planner,然后定义一个C++类AstarPlannerRos ,该类一定要继承nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner。然后在该类中重写initialize,makePlan方法。
#pragma once
#ifndef __ROS_Astar__
#define __ROS_Astar__
#include 2.3.2AstarNode.cpp源文件
源文件主要对头文件中各函数进行实现,其中比较重要的是
loadRosParamFromNodeHandle:该函数用于加载外部的参数文件,实现源代码与参数解耦。自定义函数
initialize:主要用于地图相关数据的读取,地图数据是一维,其中0表示自由可通行区域,100表示障碍物。并不是自定义的函数,需要重写。
makePlan:进行路径轨迹的生成,通过函数自带的起点start和目标点goal,以及算法本身的调用,最终生成plan路径。并不是自定义的函数,需要重写。
注意:并且makePlan在生成路径点的时候,一定要生成从起点到终点的路径,不能生成从终点到起点的路径(Astar一般都是逆向寻找路径点,默认生成从终点到起点的)。这点一定要注意,本人在这个地方卡了很长时间,编译不报错,运行不报错,就是不生成路径,特别难受。这也是本文代码中for (int i=astarPath.size()-1;i>-1;i–)的原因。如果你的算法本身生成就是从起点到终点的,那么就可以直接进行for循环了。
#include 2.4 插件包进行编译
2.4.1 CMakeLists.txt改写
主要是将AstarNode.cpp编译成libastar_plugin_lib.so动态链接库。
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
project(astar_plugin)
# add_compile_options(-std=c++11)
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
nav_core
roscpp
rospy
std_msgs
)
include_directories(
# include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
include_directories(include/astar_plugin)
add_library(astar_plugin_lib src/AstarNode.cpp src/Astar.cpp)
2.4.2 astar_plugin.xml改写
其中lib/libastar_plugin_lib表示上述生成动态链接库的位置
class 中name按照命名空间/类名,type按照命名空间::类名,base_class_type表示继承的父类。
<library path="lib/libastar_plugin_lib">
<class name="Astar_planner/AstarPlannerRos" type="Astar_planner::AstarPlannerRos" base_class_type="nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner">
<description>This is astar global planner plugin by iroboapp project.description>
class>
library>
2.4.3 package.xml 改写
前面都是一些基本的ros包一些依赖的添加,主要重要的是export中对插件说明文件astar_plugin.xml进行注册。
<package format="2">
<name>astar_pluginname>
<version>0.0.0version>
<description>The astar_plugin packagedescription>
<maintainer email="tgj@todo.todo">tgjmaintainer>
<license>TODOlicense>
<buildtool_depend>catkinbuildtool_depend>
<build_depend>nav_corebuild_depend>
<build_depend>roscppbuild_depend>
<build_depend>rospybuild_depend>
<build_depend>std_msgsbuild_depend>
<build_export_depend>nav_corebuild_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>roscppbuild_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>rospybuild_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>std_msgsbuild_export_depend>
<exec_depend>nav_coreexec_depend>
<exec_depend>roscppexec_depend>
<exec_depend>rospyexec_depend>
<exec_depend>std_msgsexec_depend>
<export>
<nav_core plugin="${prefix}/astar_plugin.xml" />
export>
package>
为了插件包的正常工作,建议将上述三者编译文件路径均放在同一文件中,具体位置见插件功能包的建立。
2.4.4 编译
cd astar_ws/src/astar_plugin
catkin_make
2.5 检验插件包是否建立成功
上述如果编译没问题,那么在终端
rospack plugins --attrib=plugin nav_core
进行astar的插件判断

如果没有发现astar插件,并且编译没有报错,极有可能环境变量没有添加成功。
2.6 插件的使用
全局路径规划插件使用当然在ros中的move_base节点中,添加自定义的全局路径规划器base_global_planner,然后动态加载自定义的该插件算法所用到的一些参数文件astar_plugin_param.yaml。并且注意一点将原先存在的全局路径规划器注释掉。

3. 插件执行情况
再说插件执行情况之前,先简单介绍launch与各个文件夹之间的关系。

启动
roslaunch astar_plugin start_plugin.launch
通过rviz中的2D Nav Goal设置一个目标点,则执行情况如下。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
4. 注意事项
Ubuntn16.04 turtlebot1代功能包安装直接二进制安装
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-turtlebot-*
#其实就是缺啥包安装哪个就行
Ubuntn18.04 由于二进制安装的turtlebot为turtlrbot2,代码并不能通用,因此需要通过源码安装turtlebot,网上有很多方法,但是比较费事,现在推荐一款较方便的方法.ROS Melodic安装、配置和使用turtlebot2(集成众多源代码直接下载
#1.安装依赖包
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-kobuki-*
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-ecl-streams
sudo apt-get install libusb-dev
sudo apt-get install libspnav-dev
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-joystick-drivers
sudo apt-get install bluetooth
sudo apt-get install libbluetooth-dev
sudo apt-get install libcwiid-dev
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-bfl
#2.编译安装,turtlebot_ws为工作空间
git clone https://gitee.com/massif_li/turtlebot_ws.git
cd turtlebot_ws
catkin_make
可能遇到的问题
问题1:Failed to load nodelet [/navigation_velocity_smoother] of type [yocs_velocity_smoother/VelocitySmootherNodelet] even after refreshing the cache: According to the loaded plugin descriptions the class yocs_velocity_smoother/VelocitySmootherNodelet with base class type nodelet::Nodelet does not exist.
解决方法:
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-yocs-velocity-smoother
参考:原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gloria_littlechi/article/details/107402856 、
https://blog.csdn.net/gloria_littlechi/article/details/107402856
问题2:出现ImportError: No module named scipy
解决方法:
sudo apt-get install python-scipy
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41204464/article/details/103575669
问题3:若运行出现amcl、map_server、move_base等包的缺失,则直接通过二进制安装即可
注意:上述代码是自己慢慢摸索出来的,可能会存在一定的bug,但是整体的全局路径规划算法框架基本没有问题,转载请注明出处,谢谢。