nn.Upsample
写在前面:在PyTorch中有两种上采样/下采样的方法,一种是Upsample,另一种是interpolate
这两个函数的使用方法略有差异,这里仅介绍Upsample
Upsample
torch.nn.Upsample(size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None)
- size - output spatial sizes(int or tuple(int, int))
- scale_factor - multiplier for spatial size(float or tuple(float, float))
- mode - upsampling algorithm: ‘linear’, ‘bilinear’, ‘bicubic’, ‘trilinear’. default:‘nearest’
- align_corners - if True, the corner pixels of the input and output tensors are aligned, and thus preserving the values at those pixels. This only has effect when mode is ‘linear’, ‘bilinear’, or ‘trilinear’. Default: False(这个参数下面会单独讲)
此函数可以上采样或者下采样(但是在PyTorch中下采样推荐interpolate,不过我发现没有区别?)
在上采样/下采样的过程中,只需要给定size或者scale_factor一个值即可,不需要给定所有的值,不然会冲突
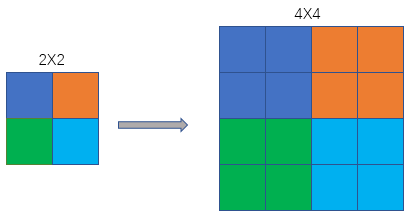
一、nearest
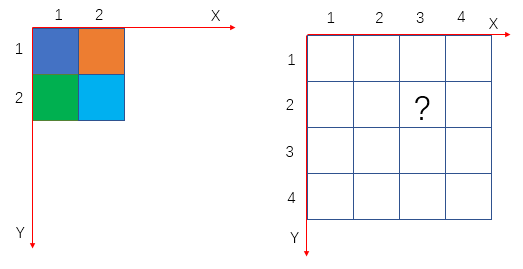
最近邻插值的公式为
s r c X = d e s X ( s r c W / d e s W ) s r c Y = d e s Y ( s r c H / d e s H ) srcX = desX(srcW/desW) \\ srcY = desY(srcH/desH) srcX=desX(srcW/desW)srcY=desY(srcH/desH)
上采样
举个例子,假设放大倍数为2,那么 s r c = d e s × 0.5 src=des\times 0.5 src=des×0.5,对于下图,坐标(3,2)处的颜色应为原来坐标系 ( 3 × 0.5 , 2 × 0.5 ) = ( 1.5 , 1 ) (3\times 0.5, 2\times 0.5)=(1.5, 1) (3×0.5,2×0.5)=(1.5,1)也就是(2, 1)对应橙色
下采样
下采样和上采样的处理过程完全相同
代码示例
input = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(1, 1, 2, 2)
sample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
print(input)
print(sample(input))
'''
tensor([[[[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]]]])
tensor([[[[1., 1., 2., 2.],
[1., 1., 2., 2.],
[3., 3., 4., 4.],
[3., 3., 4., 4.]]]])
'''
二、bilinear
双线性插值
代码示例
input = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(1, 1, 2, 2)
sample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
sample2 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
print(input)
print(sample(input))
print(sample2(input))
'''
tensor([[[[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]]]])
tensor([[[[1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 2.0000],
[1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 2.5000],
[2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 3.5000],
[3.0000, 3.2500, 3.7500, 4.0000]]]])
tensor([[[[1.0000, 1.3333, 1.6667, 2.0000],
[1.6667, 2.0000, 2.3333, 2.6667],
[2.3333, 2.6667, 3.0000, 3.3333],
[3.0000, 3.3333, 3.6667, 4.0000]]]])
'''
关于align_corners参数的用法:给出PyTorch论坛的讨论链接。下面是相应的图解
Here is a simple illustration I made showing how a 4x4 image is upsampled to 8x8.
- When align_corners=True, pixels are regarded as a grid of points. Points at the corners are aligned.
- When align_corners=False, pixels are regarded as 1x1 areas. Area boundaries, rather than their centers, are aligned.
注意事项
在最近的使用中,程序报了如下错误
UserWarning: The default behavior for interpolate/upsample with float scale_factor changed in 1.6.0 to align with other frameworks/libraries, and now uses scale_factor directly, instead of relying on the computed output size. If you wish to restore the old behavior, please set recompute_scale_factor=True. See the documentation of nn.Upsample for details.
这个错误来源于,当我的Upsample中scale_factor为整数时不会报错,为分数时就会报错,这个解决方案是不对scale_factor进行赋值,只对size进行赋值,错误就消失了
代码示例
input = torch.arange(1, 13, dtype=torch.float32).view(1, 3, 2, 2)
# sample = nn.Upsample(size=(5), mode='nearest') # 使用这行,错误消失
sample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2.5, mode='nearest') # 报错:如下
print(input)
print(sample(input))
'''
tensor([[[[ 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4.]],
[[ 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8.]],
[[ 9., 10.],
[11., 12.]]]])
/home/wangyh/anaconda3/envs/torch/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py:3103: UserWarning: The default behavior for interpolate/upsample with float scale_factor changed in 1.6.0 to align with other frameworks/libraries, and now uses scale_factor directly, instead of relying on the computed output size. If you wish to restore the old behavior, please set recompute_scale_factor=True. See the documentation of nn.Upsample for details.
warnings.warn("The default behavior for interpolate/upsample with float scale_factor changed "
tensor([[[[ 1., 1., 1., 2., 2.],
[ 1., 1., 1., 2., 2.],
[ 1., 1., 1., 2., 2.],
[ 3., 3., 3., 4., 4.],
[ 3., 3., 3., 4., 4.]],
[[ 5., 5., 5., 6., 6.],
[ 5., 5., 5., 6., 6.],
[ 5., 5., 5., 6., 6.],
[ 7., 7., 7., 8., 8.],
[ 7., 7., 7., 8., 8.]],
[[ 9., 9., 9., 10., 10.],
[ 9., 9., 9., 10., 10.],
[ 9., 9., 9., 10., 10.],
[11., 11., 11., 12., 12.],
[11., 11., 11., 12., 12.]]]])
'''
还有另一种方法,根据报错内容,我们找到Upsample的文档介绍,其中有一句为,If you want downsampling/general resizing, you should use interpolate().,也就是说当我们采用下采样的时候,scale factor为0.5这时候要用interpolate函数,由此我们进入到interpolate函数的文档中,我们再次找到一个提示信息When scale_factor is specified, if recompute_scale_factor=True, scale_factor is used to compute the output_size which will then be used to infer new scales for the interpolation. The default behavior for recompute_scale_factor changed to False in 1.6.0, and scale_factor is used in the interpolation calculation.,此时如果我们下采样的话需要将scale factor设为0.5,同时加上recompute_scale_factor=True即可