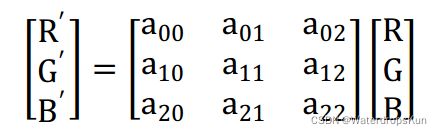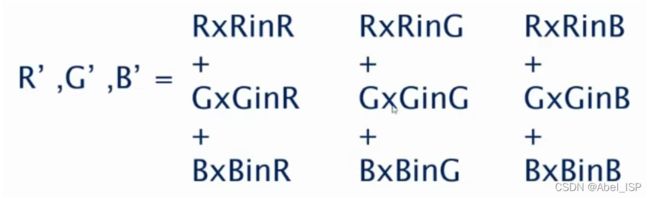ISP之CCM
CCM 标定的原理是,使用 sensor 抓拍到的 24 色卡场景下前 18 个色块的实际颜色信息和其期望值,计算 3x3 的 CCM 矩阵。输入颜色经 CCM 矩阵处理得到的颜色与其期望值差距越小,则 CCM 矩阵就越理想。
海思CCM矩阵:8bit 小数精度。bit 15是符号位,0 表示正数,1表示负数。典型的三组 CCM 为D50,TL84,A 三个光源下的 CCM。典型的五组 CCM为 10K,D65,D50,TL84,A 五个光源下的CCM。优先红、绿、蓝纯色;然后肤色块
采集步骤:(1)标准 X-Rite 24 色卡,照度为 600Lux 均匀光源;(2)调整 AE 目标亮度,最亮灰阶(Block 19)的 G 分量亮度在饱和值的 0.8 倍左右
手动调试CCM步骤:
(1)优先确认颜色问题是由于AWB模块引入还是CCM引入
(2)过灯箱客观指标,确认是否需要重新标定
(3)最后再考虑手动调整CCM
a.一般都是针对单一颜色进行微调整(比如车牌天蓝,想要深蓝;人脸偏红或是偏黄绿),所以单一颜色都会有个当前RGB值,想要调整的目标RGB值,其实调整CCM的目的就是通过CCM使得当前RGB值趋于目标RGB值
b.针对a所述,调整RGB值,调整R:a00、a01、a02(RinR、GinR、BinR);调整G:a10、a11、a12(RinG、GinG、BinG);调整B:a20、a21、a22(RinB、GinB、BinB)。
CCM矩阵色彩校正的方法_一只特立独行的zhu..-CSDN博客_ccm调试
WDR模式下标定CCM,CCM 容易受到 DRC 的影响,容易造成颜色难以矫正:
(1)曝光比手动最大,同时也要调整亮度值,避免长帧过曝,采集长帧的 RAW 数据进行 CCM 的标定。标定过程中可以适当的降低饱和度,不能选择开启 autoGain 功能。
(2)适当减少 DRC 曲线对图像亮度的大幅度提升,这样 DRC 对颜色的改变会较弱。此时,图像的亮度会有所降低达不到想要的亮度,这时,可以用 gamma 对亮度进行适当的提升。这样联调 DRC 和 gamma 模块,可以让整体的颜色调节更准确一些。
(3)对于 WDR 模式,因为大多场景是混合光源场景,容易出现亮处颜色偏色,人脸颜色偏红等问题,除了可以降低饱和度值以外,还可以使用 CA 模块对这些区域适当的降低饱和度。
反gamma后图像和gamma 1.0存在些许差异:
(1)CSC模块
CCM模块代码:
https://github.com/WaterdropsKun/isppipeline_Python/tree/main/lecture14
Python实现ISP pipeline代码:
GitHub - WaterdropsKun/isppipeline_Python: isppipeline_Python
如有帮助,希望帮忙github帮忙点个star
def degamma_hisi(data, clip_range, gamma_txt):
# gamma degamma
hisi_gamma_x = 1024-1
hisi_gamma_y = 4096-1
hisi_degamma_x = 256-1
hisi_degamma_y = 1.0
gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095 = []
degamma_x255_y1 = []
with open(gamma_txt, "r") as f:
for i, line in enumerate(f.readlines()):
line = line.split(',')
gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095 = [float(x) for x in line]
# for j, value in enumerate(line):
# print(j, value)
# x = np.arange(0, 1024+1, 1) # np.arange(start, end+step, step) [start, end] end/step+1
# plt.plot(x, gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095)
# plt.show()
for i in range(hisi_degamma_x+1): # for i in range(0, hisi_degamma_x+1, 1):
for j, value in enumerate(gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095):
if (value / hisi_gamma_y * hisi_degamma_x) >= i:
degamma_x255_y1.append(j/hisi_gamma_x)
break
# x = np.arange(0, hisi_degamma_x+1, 1)
# plt.plot(x, degamma_x255_y1)
# plt.show()
# degamma
data = np.clip(data, clip_range[0], clip_range[1])
data = np.divide(data, clip_range[1])
height = data.shape[0]
weight = data.shape[1]
channels = data.shape[2]
for row in range(height): # 遍历高
for col in range(weight): # 遍历宽
pv0 = data[row, col, 0]
pv1 = data[row, col, 1]
pv2 = data[row, col, 2]
data[row, col, 0] = degamma_x255_y1[int(pv0*255)]
data[row, col, 1] = degamma_x255_y1[int(pv1*255)]
data[row, col, 2] = degamma_x255_y1[int(pv2*255)]
data_show = data.copy()
data_show = np.clip(data_show * clip_range[1], clip_range[0], clip_range[1])
# gbr = rgb[...,[2,0,1]]
# data_show = data_show[..., ::-1]
data_show = data_show[..., [2,1,0]]
cv2.imshow("data", data_show.astype(np.uint8))
cv2.waitKey(0)
return np.clip(data * clip_range[1], clip_range[0], clip_range[1])
def gamma_hisi(data, clip_range, gamma_txt):
# gamma degamma
hisi_gamma_x = 1024-1
hisi_gamma_y = 4096-1
hisi_degamma_x = 256-1
hisi_degamma_y = 1.0
gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095 = []
degamma_x255_y1 = []
with open(gamma_txt, "r") as f:
for i, line in enumerate(f.readlines()):
line = line.split(',')
gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095 = [float(x) for x in line]
# for j, value in enumerate(line):
# print(j, value)
# x = np.arange(0, 1024+1, 1) # np.arange(start, end+step, step) [start, end] end/step+1
# plt.plot(x, gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095)
# plt.show()
for i in range(hisi_degamma_x+1): # for i in range(0, hisi_degamma_x+1, 1):
for j, value in enumerate(gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095):
if (value / hisi_gamma_y * hisi_degamma_x) >= i:
degamma_x255_y1.append(j/hisi_gamma_x)
break
# x = np.arange(0, hisi_degamma_x+1, 1)
# plt.plot(x, degamma_x255_y1)
# plt.show()
# gamma
data = np.clip(data, clip_range[0], clip_range[1])
data = np.divide(data, clip_range[1])
height = data.shape[0]
weight = data.shape[1]
channels = data.shape[2]
for row in range(height): # 遍历高
for col in range(weight): # 遍历宽
pv0 = data[row, col, 0]
pv1 = data[row, col, 1]
pv2 = data[row, col, 2]
data[row, col, 0] = gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095[int(pv0*1023)] / 4095.0
data[row, col, 1] = gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095[int(pv1*1023)] / 4095.0
data[row, col, 2] = gamma_hisi_x1023_y4095[int(pv2*1023)] / 4095.0
data_show = data.copy()
data_show = np.clip(data_show * clip_range[1], clip_range[0], clip_range[1])
# gbr = rgb[...,[2,0,1]]
# data_show = data_show[..., ::-1]
data_show = data_show[..., [2,1,0]]
cv2.imshow("data", data_show.astype(np.uint8))
cv2.waitKey(0)
return np.clip(data * clip_range[1], clip_range[0], clip_range[1])
def CCM_convert(data, CCM, color_space="srgb", clip_range=[0, 255]):
# CCM工作在线性RGB因此需要先进行degamma
if (color_space == "srgb"):
data = color.degamma_srgb(data, clip_range)
data = np.float32(data)
data = np.divide(data, clip_range[1]) # 归一化
elif (color_space == "hisi"):
data = degamma_hisi(data, clip_range, "./gamma_hisi_int.txt")
data = np.float32(data)
data = np.divide(data, clip_range[1]) # 归一化
# matrix multiplication
output = np.empty(np.shape(data), dtype=np.float32)
output[:, :, 0] = data[:, :, 0] * CCM[0,0] + data[:, :, 1] * CCM[0,1] + data[:, :, 2] * CCM[0,2]
output[:, :, 1] = data[:, :, 0] * CCM[1,0] + data[:, :, 1] * CCM[1,1] + data[:, :, 2] * CCM[1,2]
output[:, :, 2] = data[:, :, 0] * CCM[2,0] + data[:, :, 1] * CCM[2,1] + data[:, :, 2] * CCM[2,2]
# gamma
if (color_space == "srgb"):
output = output*clip_range[1]
output = color.gamma_srgb(output, clip_range)
elif (color_space == "hisi"):
output = output*clip_range[1]
output = gamma_hisi(output, clip_range, "./gamma_hisi_int.txt")
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
# CCM = np.array([
# [1.507812, -0.546875, 0.039062],
# [-0.226562, 1.085938, 0.140625],
# [-0.062500, -0.648438, 1.718750],
# ])
CCM = np.array([
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
])
maxvalue = 255
# image = plt.imread('kodim19.png')
image = plt.imread('test02.png')
if (np.max(image) <= 1):
image = image * maxvalue
new_image = CCM_convert(image, CCM, color_space="hisi", clip_range=[0, maxvalue])
color.rgb_show(image / 255)
color.rgb_show(new_image / 255)