机器学习sklearn-多项式回归
目录
线性关系
线性模型和非线性模型
利用线性回归解决非线性问题
多项式回归
线性模型
线性关系
首先, ” 线性 “ 这个词用于描述不同事物时有着不同的含义。我们最常使用的线性是指 “ 变量之间的线性关系 ( linear relationship) ” ,它表示两个变量之间的关系可以展示为一条直线,即可以使用方程来进行拟合。要探索两个变量之间的关系是否是线性的,最简单的方式就是绘制散点图,如果散点图能够相对均匀地分布在一条直线的两端,则说明这两个变量之间的关系是线性的。
因此,三角函数, 高次函数,指数函数等等图像不为直线的函数所对应的自变量和因变量之间是非线性关系(non-linear relationship)。
从线性关系这个概念出发,我们有了一种说法叫做 “ 线性数据 ” 。通常来说,一组数据由多个特征和标签组成。当这些特征分别与标签存在线性关系的时候,我们就说这一组数据是线性数据。当特征矩阵中任意一个特征与标签之间的关系需要使用三角函数,指数函数等函数来定义,则我们就说这种数据叫做“ 非线性数据 ” 。对于线性和非线性数据,最简单的判别方法就是利用模型来帮助我们—— 如果是做分类则使用逻辑回归,如果做回归则使用线性回归,如果效果好那数据是线性的,效果不好则数据不是线性的。当然,也可以降维后进行绘图,绘制出的图像分布接近一条直线,则数据就是线性的。
当我们在回归中绘制图像时,绘制的是特征与标签的关系图,横坐标是特征,纵坐标是标签,我们的标签是连续型的,所以我们可以通过是否能够使用一条直线来拟合图像判断数据究竟属于线性还是非线性。
然而在分类中,我们绘制的是数据分布图,横坐标是其中一个特征,纵坐标是另一个特征,标签则是数据点的颜色。因此在分类数据中,我们使用“ 是否线性可分 ” ( linearly separable )这个概念来划分分类数据集。当分类数据的分布上可以使用一条直线来将两类数据分开时,我们就说数据是线性可分的。反之,数据不是线性可分的。
线性模型和非线性模型
作为线性模型的典型代表,我们可以从线性回归的方程中总结出线性模型的特点:其自变量都是一次项 。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
rnd=np.random.RandomState(40)#设置随机数种子
X = rnd.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) #random.uniform,从输入的任意两个整数中取出size个随机数
#生成y的思路:先使用NumPy中的函数生成一个sin函数图像,然后再人为添加噪音
y = np.sin(X) + rnd.normal(size=len(X)) / 3 #random.normal,生成size个服从正态分布的随机数
#使用散点图观察建立的数据集是什么样子
# plt.scatter(X, y,marker='o',c='k',s=20)
# plt.show()
X=X.reshape(-1,1)#将数据升到二维
#使用原始数据进行建模
LinearR = LinearRegression().fit(X, y)
TreeR = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=0).fit(X, y)
#放置画布
fig,ax1=plt.subplots(1)
#创建测试数据:一系列分布在横坐标上的点
line = np.linspace(-3, 3, 1000, endpoint=False).reshape(-1, 1)
#将测试数据代入predict接口,并绘制
ax1.plot(line,LinearR.predict(line),linewidth=2, color='green',label="linear regression")
ax1.plot(line, TreeR.predict(line), linewidth=2, color='red',label="decision tree")
#将原数据上的拟合绘制在图像上
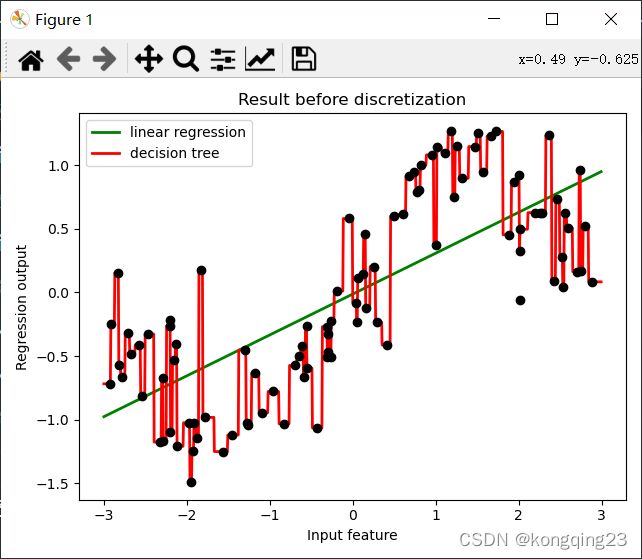
ax1.plot(X[:, 0], y, 'o', c='k')
ax1.legend(loc="best")
ax1.set_ylabel("Regression output")
ax1.set_xlabel("Input feature")
ax1.set_title("Result before discretization")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
从图像上可以看出,线性回归无法拟合出这条带噪音的正弦曲线的真实面貌,只能够模拟出大概的趋势,而决策树却通过建立复杂的模型将几乎每个点都拟合出来了。可见,使用线性回归模型来拟合非线性数据的效果并不好,而决策树这样的模型却拟合得太细致。
线性模型用于拟合线性数据,非线性模型用于拟合非线性数据。但事实上机器学习远远比我们想象的灵活得多,线性模型可以用来拟合非线性数据,而非线性模型也可以用来拟合线性数据,更
神奇的是,有的算法没有模型也可以处理各类数据,而有的模型可以既可以是线性,也可以是非线性模型!
非线性模型们几乎都可以在线性可分数据上有不逊于线性模型的表现。同样的,如果我们使用随机森林来拟合一条直线,那随机森林毫无疑问会过拟合,因为线性数据对于非线性模型来说太过简单,很容易就把训练集上的R^2训练得很高,MSE 训练的很低。
但是相反的,线性模型若用来拟合非线性数据或者对非线性可分的数据进行分类,那通常都会表现糟糕。通常如果我们已经发现数据属于非线性数据,或者数据非线性可分的数据,则我们不会选择使用线性模型来进行建模。改善线性模型在非线性数据上的效果的方法之一是进行分箱。
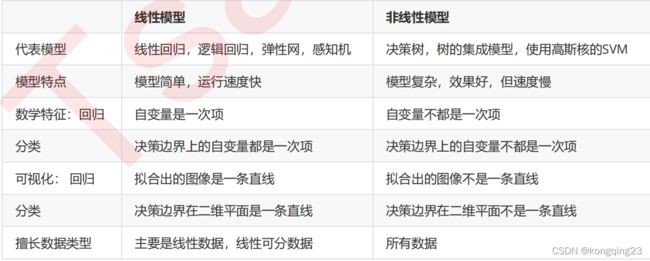
线性模型们的决策边界都是一条条平行的直线,而非线性模型们的决策边界是交互的直线(格子),曲线,环形等等。对于分类模型来说,这是我们判断模型是线性还是非线性的重要评判因
素: 线性模型的决策边界是平行的直线,非线性模型的决策边界是曲线或者交叉的直线 。
模型上如果自变量上的最高次方为1 ,则模型是线性的,但这种方式只适用于回归问题。分类模型中,我们很少讨论模型是否线性,因为我们很少使用线性模型来执行分类任务(逻辑回归是一个特例)。但从上面我们总结出的结果来看,我们可以认为对分类问题而言,如果一个分类模型的决策边界上自变量的最高次方为 1 ,则我们称这个模型是线性模型 。
对于有一些模型来说,他们既可以处理线性模型又可以处理非线性模型,比如说强大的支持向量机。支持向量机的前身是感知机模型,朴实的感知机模型是实打实的线性模型(其决策边界是直线),在线性可分数据上表现优秀,但在非线性可分的数据上基本属于无法使用状态。
但支持向量机就不一样了。支持向量机本身也是处理线性可分数据的,但却可以通过对数据进行升维(将数据转移到高维空间 中),将非线性可分数据变成高维空间中的线性可分数据,然后使用相应的“ 核函数 ” 来求解。当我们选用线性核函数"linear" 的时候,数据没有进行变换,支持向量机中就是线性模型,此时它的决策边界是直线。而当我们选用非线性核函数比如高斯径向基核函数的时候,数据进行了升维变化,此时支持向量机就是非线性模型,此时它的决策边界在二维空间中是曲线。所以这个模型可以在线性和非线性之间自由切换,一切取决于它的核函数。
还有更加特殊的,没有模型的算法,比如最近邻算法 KNN ,这些都是不建模,但是能够直接预测出标签或做出判断的算法。而这些算法,并没有线性非线性之分,单纯的是不建模的算法们。
当我们获取数据时,我们往往希望使用线性模型来对数据进行最初的拟合(线性回归用于回归,逻辑回归用于分类),如果线性模型表现良好,则说明数据本身很可能是线性的或者线性可分的,如果线性模型表现糟糕,那毫无疑问我们会投入决策树,随机森林这些模型的怀抱,就不必浪费时间在线性模型上了。
利用线性回归解决非线性问题
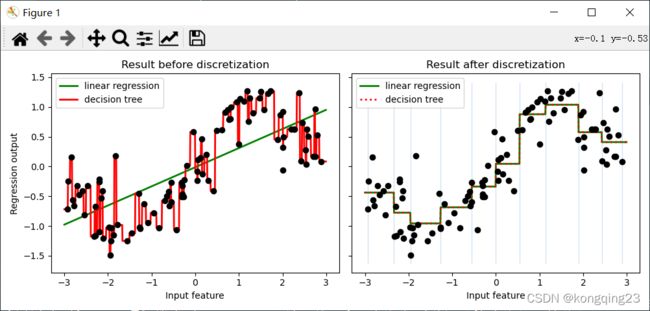
让线性回归在非线性数据上表现提升的核心方法之一是对数据进行分箱,也就是离散化。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer #分箱
rnd=np.random.RandomState(40)#设置随机数种子
X = rnd.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) #random.uniform,从输入的任意两个整数中取出size个随机数
#生成y的思路:先使用NumPy中的函数生成一个sin函数图像,然后再人为添加噪音
y = np.sin(X) + rnd.normal(size=len(X)) / 3 #random.normal,生成size个服从正态分布的随机数
X = X.reshape(-1, 1)
line = np.linspace(-3, 3, 1000, endpoint=False).reshape(-1, 1)#测试集数据
#分箱操作
enc=KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=10,#分几个箱子
encode='onehot',#采用哑变量方式做离散化
)
X_binned=enc.fit_transform(X)#之后返回一个稀疏矩阵(m,n_bins),m是样本数量,每一列是一个分好的类别
line_binned = enc.transform(line)
LinearR = LinearRegression().fit(X, y)
TreeR = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=0).fit(X, y)
#将两张图像绘制在一起,布置画布
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2
, sharey=True #让两张图共享y轴上的刻度
, figsize=(10, 4))
#在图1中布置在原始数据上建模的结果
ax1.plot(line, LinearR.predict(line), linewidth=2, color='green',
label="linear regression")
ax1.plot(line, TreeR.predict(line), linewidth=2, color='red',
label="decision tree")
ax1.plot(X[:, 0], y, 'o', c='k')
ax1.legend(loc="best")
ax1.set_ylabel("Regression output")
ax1.set_xlabel("Input feature")
ax1.set_title("Result before discretization")
#使用分箱数据进行建模
LinearR_ = LinearRegression().fit(X_binned, y)
TreeR_ = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=0).fit(X_binned, y)
#进行预测,在图2中布置在分箱数据上进行预测的结果
ax2.plot(line #横坐标
, LinearR_.predict(line_binned) #分箱后的特征矩阵的结果
, linewidth=2
, color='green'
, linestyle='-'
, label='linear regression')
ax2.plot(line, TreeR_.predict(line_binned), linewidth=2, color='red',
linestyle=':', label='decision tree')
#绘制和箱宽一致的竖线,可有可无
ax2.vlines(enc.bin_edges_[0] #x轴
, *plt.gca().get_ylim() #y轴的上限和下限
, linewidth=1
, alpha=.2) #将原始数据分布放置在图像上
ax2.plot(X[:, 0], y, 'o', c='k')
ax2.legend(loc="best")
ax2.set_xlabel("Input feature")
ax2.set_title("Result after discretization")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()多项式回归
除了分箱之外,另一种更普遍的用于解决 ” 线性回归只能处理线性数据 “ 问题的手段,就是使用多项式回归对线性回归进行改进。这样的手法是机器学习研究者们从支持向量机中获得的:支持向量机通过升维可以将非线性可分数据转化为线性可分,然后使用核函数在低维空间中进行计算,这是一种“ 高维呈现,低维解释 ” 的思维。那我们为什么不能让线性回归使用类似于升维的转换,将数据由非线性转换为线性,从而为线性回归赋予处理非线性数据的能力呢?
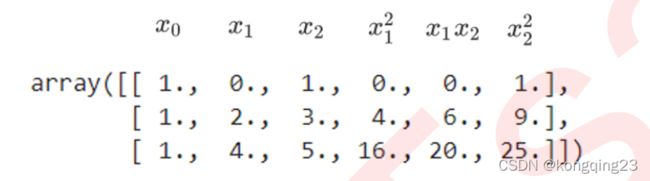
线性模型中的升维工具: 多项式变化 。这是一种通过增加自变量上的次数,而将数据映射到高维空间的方法,只要我们设定一个自变量上的次数(大于1 ),就可以相应地获得数据投影在高方的空间中的结果。这种方法可以非常容易地通过sklearn 中的类 PolynomialFeatures 来实现。
一维的转换公式
二维转换公式
当我们进行多项式转换的时候,多项式会产出到最高次数为止的所有低高次项 。比如如果我们规定多项式的次数为2 ,多项式就会产出所有次数为 1 和次数为 2 的项反馈给我们,相应的如果我们规定多项式的次数为 n ,则多项式会产出所有从次数为1 到次数为 n 的项。
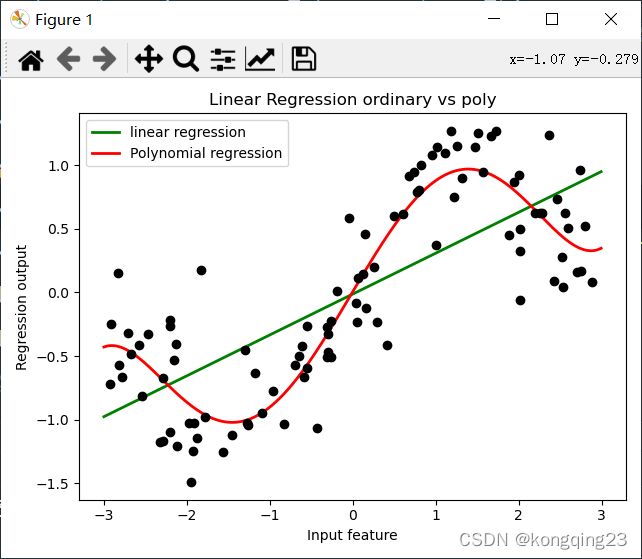
对比多项式处理前后的回归效果
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
d=5#多项式维度
rnd=np.random.RandomState(40)#设置随机数种子
X = rnd.uniform(-3, 3, size=100) #random.uniform,从输入的任意两个整数中取出size个随机数
#生成y的思路:先使用NumPy中的函数生成一个sin函数图像,然后再人为添加噪音
y = np.sin(X) + rnd.normal(size=len(X)) / 3 #random.normal,生成size个服从正态分布的随机数
X = X.reshape(-1, 1)
line = np.linspace(-3, 3, 1000, endpoint=False).reshape(-1, 1)#测试集数据
line_=PolynomialFeatures(degree=d).fit_transform(line)
LinearR = LinearRegression().fit(X, y)
X_=PolynomialFeatures(degree=d).fit_transform(X)#对数据进行多项式处理
LinearR_=LinearRegression().fit(X_, y)
#放置画布
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1) #将测试数据带入predict接口,获得模型的拟合效果并进行绘制
#多项式处理前
ax1.plot(line, LinearR.predict(line), linewidth=2, color='green'
,label="linear regression")
#多项式处理后 训练时使用多项式数据,预测时也应采用多项式数据
ax1.plot(line, LinearR_.predict(line_), linewidth=2, color='red'
,label="Polynomial regression") #将原数据上的拟合绘制在图像上
ax1.plot(X[:, 0], y, 'o', c='k') #其他图形选项
ax1.legend(loc="best")
ax1.set_ylabel("Regression output")
ax1.set_xlabel("Input feature")
ax1.set_title("Linear Regression ordinary vs poly")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
#随后可以试试看较低和较高的次方会发生什么变化
线性模型
狭义线性模型:自变量上不能有高此项,自变量与标签之间不能存在非线性关系。
广义线性模型:只要标签与模型拟合出的 参数之间的关系是线性的 ,模型就是线性的。这是说,只要生成的一系列之间没有相乘或者相除的关系,我们就认为模型是线性的。
就多项式回归本身的性质来说,如果我们考虑狭义线性模型的定义,那它肯定是一种非线性模型没有错 —— 否则如何能够处理非线性数据呢,并且在统计学中我们认为,特征之间若存在精确相关关系或高度相关关系,线性模型的估计就会被“ 扭曲 “ ,从而失真或难以估计准确。多项式正是利用线性回归的这种 ” 扭曲 “ ,为线性模型赋予了处理非线性数据的能力。但如果我们考虑广义线性模型的定义,多项式回归就是一种线性模型,毕竟它的系数之间也没有相乘或者相除。
总结一下, 多项式回归通常被认为是非线性模型,但广义上它是一种特殊的线性模型 ,它能够帮助我们处理非线性数 据,是线性回归的一种进化。