【机器学习】人工智能实验一:A*算法求解 8 数码问题(启发式搜索)(纯代码)
这篇文章主要由三个C/C++代码和1个MATLAB代码构成,一方面用于我个人的知识记录,另一方面用于交流学习
一、网上代码修改版:
1、直接上代码:
代码参考于:A*算法(解决八数码问题)
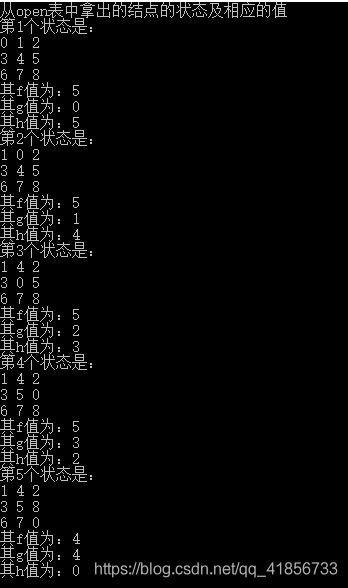
#include2、部分运行结果
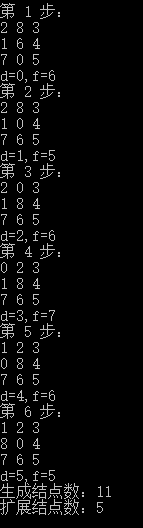
二、他山之石:简略版
这个代码给人的主要启发是:其实照着BFS(广度搜索)的思路直接敲完,核心框架也就出来了
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=3;
int fl=0;//哪种
struct node{
int id,fval,gval,hval;
int faid,x,y;
int state[N][N];
friend bool operator<(node a,node b){
return a.fval>b.fval;
}
}st,ed;
int sta[N][N]={2,8,3,1,6,4,7,0,5};
int eda[N][N]={1,2,3,8,0,4,7,6,5};
//int sta[N][N]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
//int eda[N][N]={1,4,2,3,5,8,6,7,0};
int tar[N*N][2];
int idnum=0;
int nxt[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
int h(node a,int fl){
int num=0,id=1;
if(fl==0){//h(n)
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
// if(i==2&&j==2&&a.state[i][j]==0) continue;
if(a.state[i][j]!=eda[i][j])num++;
id++;
}
}
}
else{//p(n)
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
if(a.state[i][j]==0) continue;
int val=a.state[i][j];
num+=abs(i-tar[val][0])+abs(j-tar[val][1]);
}
}
}
return num;
}
void init(){
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
tar[eda[i][j]][0]=i;
tar[eda[i][j]][1]=j;
if(sta[i][j]==0) st.x=i,st.y=j;
st.state[i][j]=sta[i][j];
ed.state[i][j]=eda[i][j];
}
}
st.id=idnum++;
st.gval=0;
st.hval=h(st,fl);
st.fval=st.hval+st.gval;
st.faid=-1;
}
priority_queue<node> q;//q-open
vector<node> close;
map<string,int> mp,mq;//close open
void Astar(){
string ed1="";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
ed1+=eda[i][j];
q.push(st);
string ss="";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
ss+=sta[i][j];
}
}
mq[ss]=1;
while(!q.empty()){
node nn=q.top();
q.pop();
close.push_back(nn);
ss="";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
ss+=nn.state[i][j];
}
}
if(ss==ed1){
break;
}
mq[ss]=0;
if(mp[ss]) continue;
mp[ss]=1;
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int tx=nn.x+nxt[k][0];
int ty=nn.y+nxt[k][1];
if(tx<0||ty<0||tx>=N||ty>=N)continue;
node tmp=nn;
swap(tmp.state[tx][ty],tmp.state[nn.x][nn.y]);
ss="";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
ss+=tmp.state[i][j];
if(mq[ss]||mp[ss]) continue;
tmp.faid=tmp.id;
tmp.id=idnum++;
tmp.gval++;
tmp.x=tx;
tmp.y=ty;
tmp.hval=h(tmp,fl);
tmp.fval=tmp.gval+tmp.hval;
q.push(tmp);
}
}
}
void out(){
printf("一共扩展多少结点:%d\n",q.size()+close.size());
printf("从初始到目标经历多少结点:%d\n",close.size());
printf("扩展过程:\n");
for(int i=0;i<close.size();i++){
printf("第%d个结点为:\n",i+1);
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
printf("%d ",close[i].state[j][k]);
puts("");
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t,i,j,k;
init();
Astar();
out();
return 0;
}
三、不知道具体出处的代码,粘贴就完事了
1、五百多行的代码即将来袭:
#include 四、MATLBA"实现"
%八数码A*算法程序
function [a1,b1]=shang(a)
[x,y]=find(a==0);
a1=a;
a1(x,y)=a(x-1,y);
a1(x-1,y)=0;
b1=zhao(a1);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [a1,b1]=xia(a)
[x,y]=find(a==0);
a1=a;
a1(x,y)=a(x+1,y);
a1(x+1,y)=0;
b1=zhao(a1);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [a1,b1]=zuo(a)
[x,y]=find(a==0);
a1=a;
a1(x,y)=a(x,y-1);
a1(x,y-1)=0;
b1=zhao(a1);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [a1,b1]=you(a)
[x,y]=find(a==0);
a1=a;
a1(x,y)=a(x,y+1);
a1(x,y+1)=0;
b1=zhao(a1);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function z=panduan(a)
global E;
global I;
I=2;
[x,y]=size(E);
z=1;
for i=1:y
b=E{i};
v=(b-a).^2;
if sum(sum(v))==0
z=0;
break;
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function y=zhao(a)
wan=[1 2 3;8 0 4;7 6 5];
y=0;
b=a-wan;
for i=1:3
for j=1:3
if b(i,j)~=0
y=y+1;
end
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
global E
global I
a=[2 8 3;1 0 4;7 6 5];
b=[1 2 3;8 0 4;7 6 5];
I=1;
E(1)={a};
for i=2:20
q=b-E{i};
if sum(sum(q.^2))
E(i)={kaka(E{i-1})};
celldisp(E(i))
else
break;
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [a1]=kaka(a)
global I;
global E;
c=[2 8 3;1 0 4;7 6 5];
E(1)={c};
[x,y]=find(a==0);
z=9;
if x==1
if y==1
[x1,y1]=xia(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x2,y2]=you(a);
if y2<z
if panduan(x2)
b=x2;
z=y2;
end
end
a1=b;
end
if y==2
[x1,y1]=xia(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x2,y2]=zuo(a);
if y2<z
if panduan(x2)
b=x2;
z=y2;
end
end
[x3,y3]=you(a);
if y3<z
if panduan(x3)
b=x3;
z=y3;
end
end
a1=b;
end
if y==3
[x1,y1]=xia(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x2,y2]=zuo(a);
if y2<z
if panduan(x2)
b=x2;
z=y2;
end
end
a1=b;
end
end
if x==2
if y==1
[x1,y1]=shang(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x2,y2]=xia(a);
if y2<z
if panduan(x2)
b=x2;
z=y2;
end
end
[x3,y3]=you(a);
if y3<z
if panduan(x3)
b=x3;
z=y3;
end
end
a1=b;
end
if y==2
[x1,y1]=shang(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1);
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x2,y2]=xia(a);
if y2<z
if panduan(x2);
b=x2;
z=y2;
end
end
[x3,y3]=zuo(a);
if y3<z
if panduan(x3);
b=x3;
z=y3;
end
end
[x4,y4]=you(a);
if y4<z;
if panduan(x4)
b=x4;
z=y4;
end
end
a1=b;
end
if y==3
[x1,y1]=shang(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x2,y2]=xia(a);
if y2<z
if panduan(x2)
b=x2;
z=y2;
end
end
[x3,y3]=zuo(a);
if y3<z
if panduan(x3)
b=x3;
z=y3;
end
end
a1=b;
end
end
if x==3
if y==1
[x1,y1]=shang(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x4,y4]=you(a);
if y4<z;
if panduan(x4)
b=x4;
z=y4;
end
end
a1=b;
end
if y==2
[x1,y1]=shang(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x3,y3]=zuo(a);
if y3<z
if panduan(x3)
b=x3;
z=y3;
end
end
[x4,y4]=you(a);
if y4<z;
if panduan(x4)
b=x4;
z=y4;
end
end
a1=b;
end
if y==3
[x1,y1]=shang(a);
if y1<z
if panduan(x1)
b=x1;
z=y1;
end
end
[x3,y3]=zuo(a);
if y3<z
if panduan(x3)
b=x3;
z=y3;
end
end
a1=b;
end
end
E(I)={a1};