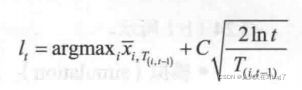Python实现蒙特卡洛树黑白棋完整代码
Python实现的基于蒙特卡洛树搜索的完整代码
最终效果:在控制台输入输出,实现3种玩家(AI或者人类或者随机)的对弈
目录
一、黑白棋简介
二、蒙特卡洛树搜索简介
1.蒙特卡洛树搜索Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS
2.上限置信区间UCB1算法
3.通俗算法思路
4.图示
三、代码实现
前言:
关于代码:黑白棋部分直接来源为浙江大学Mo平台,仅AI模块为原创
由于水平所限,可能会出现一些错误,还请大佬们指正
本文仅做简要的介绍和实现,不涉及数学原理(因为我也不会QAQ)
一、黑白棋简介
黑白棋 (Reversi),也叫苹果棋,翻转棋,是一个经典的策略性游戏
**游戏规则**:
棋局开始时黑棋位于 E4 和 D5 ,白棋位于 D4 和 E5,如图所示。
1. 黑方先行,双方交替下棋。
2. 一步合法的棋步包括:
(1)在一个空格处落下一个棋子,并且翻转对手一个或多个棋子;
(2)新落下的棋子必须落在可夹住对方棋子的位置上,对方被夹住的所有棋子都要翻转过来,可
以是横着夹,竖着夹,或是斜着夹。夹住的位置上必须全部是对手的棋子,不能有空格;
(3)一步棋可以在数个(横向,纵向,对角线)方向上翻棋,任何被夹住的棋子都必须被翻转过来,棋手无权选择不去翻某个棋子。
3. 如果一方没有合法棋步,也就是说不管他下到哪里,都不能至少翻转对手的一个棋子,那他这
轮只能弃权,而由他的对手继续落子直到他有合法棋步可下。
4. 如果一方至少有一步合法棋步可下,他就必须落子,不得弃权。
5. 棋局持续下去,直到棋盘填满或者双方都无合法棋步可下。
6. 如果某一方落子时间超过 1 分钟 或者 连续落子 3 次不合法,则判该方失败。
二、蒙特卡洛树搜索简介
1.蒙特卡洛树搜索Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS
简介:
蒙特卡洛树搜索大概可以被分成四步。选择,扩展,模拟,反向传播。
在开始阶段,搜索树只有一个节点,也就是当前需要做出选择的局面。
搜索树中的每一个节点至少包含:当前局面,访问次数,累计奖励。
1、选择(selection)∶指算法从搜索树的根结点开始,向下递归选择子结点,直至到达叶子结点或者到达具有还未被扩展过的子结点。这个向下递归选择过程可由UCB1算法(公式在后面)来实现。
2、扩展(expansion)∶如果结点L不是一个终止结点(或对抗搜索的终局结点),则随机扩展它的一个未被扩展过的后继边缘结点M。
3、模拟(simulation)∶从结点M出发,模拟扩展搜索树,直到找到一个终止结点。模拟过程使用的策略和采用UCB1 算法实现的选择过程并不相同,前者通常会使用比较简单的策略,例如使用随机策略。
4、反向传播(Back Propagation)∶用模拟所得结果(终止结点的代价或游戏终局分数)回溯更新模拟路径中结点的奖励均值和被访问次数。
2.上限置信区间UCB1算法
具体原理可以查阅其他文章,此处不做赘述。直接给出公式和含义
其中argmax x表示这个节点的平均奖励值,也就是奖励总和(reward)除以访问次数(visits)
C为UCB1的超参数,自定义
t为该节点的父节点的访问次数
T为该节点的访问次数
3.通俗算法思路
(仅限本文黑白棋例子)
选择:从根节点开始,递归选择UCB值最大的一个节点(我们认为没有被扩展的节点UCB值无限大)
扩展:(1)如果当目前节点下的所有节点都已经被访问过了,并且这些节点都不是终止节点,则需要选择一个UCB值最大的节点进行扩展(添加它的子节点并初始化),返回扩展的节点。(2)如果还有节点没有被访问过,就不进行扩展,返回这个没被访问的节点
模拟:从上面已经选择的节点开始,进行一次对局模拟,直到分出胜负或者达到步数限制,返回所得的分值
反向传播:由模拟得到的奖励值,进行由叶节点到根节点的反向路径上的传播,依次更新节点值:原来的节点值加上或者减去新的奖励值(取决于所选的颜色),并且路径上所有节点访问次数+1
最后到达步数上限后,选择搜索树的第一级子节点(根节点的孩子)中UCB值最大的节点,作为下一步行棋
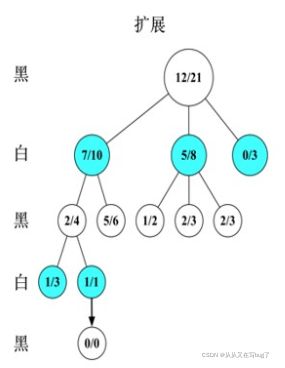
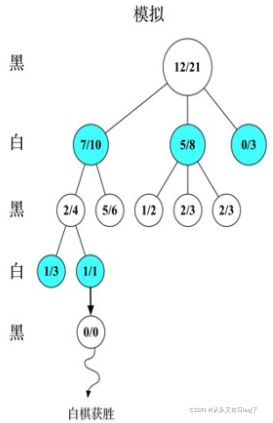
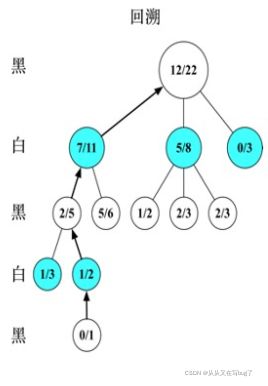
4.图示
假设我们为黑方,图中数值:分值/访问次数
选择:假设初始如下,经过UCB值计算,最终选择了1/1的叶节点(UCB值最大)
扩展:叶节点都被访问过了,需要扩展新的节点,设为0/0
模拟:在新扩展的节点上模拟一次对局,结果白棋胜,记为0分
反向传播:所有路径上的节点分值+0,访问次数+1
三、代码实现
分为Game类,Board类,和三种Player
Game类
# !/usr/bin/Anaconda3/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from func_timeout import func_timeout, FunctionTimedOut
import datetime
from board import Board
from copy import deepcopy
class Game(object):
def __init__(self, black_player, white_player):
self.board = Board() # 棋盘
# 定义棋盘上当前下棋棋手,先默认是 None
self.current_player = None
self.black_player = black_player # 黑棋一方
self.white_player = white_player # 白棋一方
self.black_player.color = "X"
self.white_player.color = "O"
def switch_player(self, black_player, white_player):
"""
游戏过程中切换玩家
:param black_player: 黑棋
:param white_player: 白棋
:return: 当前玩家
"""
# 如果当前玩家是 None 或者 白棋一方 white_player,则返回 黑棋一方 black_player;
if self.current_player is None:
return black_player
else:
# 如果当前玩家是黑棋一方 black_player 则返回 白棋一方 white_player
if self.current_player == self.black_player:
return white_player
else:
return black_player
def print_winner(self, winner):
"""
打印赢家
:param winner: [0,1,2] 分别代表黑棋获胜、白棋获胜、平局3种可能。
:return:
"""
print(['黑棋获胜!', '白棋获胜!', '平局'][winner])
def force_loss(self, is_timeout=False, is_board=False, is_legal=False):
"""
落子3个不合符规则和超时则结束游戏,修改棋盘也是输
:param is_timeout: 时间是否超时,默认不超时
:param is_board: 是否修改棋盘
:param is_legal: 落子是否合法
:return: 赢家(0,1),棋子差 0
"""
if self.current_player == self.black_player:
win_color = '白棋 - O'
loss_color = '黑棋 - X'
winner = 1
else:
win_color = '黑棋 - X'
loss_color = '白棋 - O'
winner = 0
if is_timeout:
print('\n{} 思考超过 60s, {} 胜'.format(loss_color, win_color))
if is_legal:
print('\n{} 落子 3 次不符合规则,故 {} 胜'.format(loss_color, win_color))
if is_board:
print('\n{} 擅自改动棋盘判输,故 {} 胜'.format(loss_color, win_color))
diff = 0
return winner, diff
def run(self):
"""
运行游戏
:return:
"""
# 定义统计双方下棋时间
total_time = {"X": 0, "O": 0}
# 定义双方每一步下棋时间
step_time = {"X": 0, "O": 0}
# 初始化胜负结果和棋子差
winner = None
diff = -1
# 游戏开始
print('\n=====开始游戏!=====\n')
# 棋盘初始化
self.board.display(step_time, total_time)
while True:
# 切换当前玩家,如果当前玩家是 None 或者白棋 white_player,则返回黑棋 black_player;
# 否则返回 white_player。
self.current_player = self.switch_player(self.black_player, self.white_player)
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
# 当前玩家对棋盘进行思考后,得到落子位置
# 判断当前下棋方
color = "X" if self.current_player == self.black_player else "O"
# 获取当前下棋方合法落子位置
legal_actions = list(self.board.get_legal_actions(color))
# print("%s合法落子坐标列表:"%color,legal_actions)
if len(legal_actions) == 0:
# 判断游戏是否结束
if self.game_over():
# 游戏结束,双方都没有合法位置
winner, diff = self.board.get_winner() # 得到赢家 0,1,2
break
else:
# 另一方有合法位置,切换下棋方
continue
board = deepcopy(self.board._board)
# legal_actions 不等于 0 则表示当前下棋方有合法落子位置
try:
for i in range(0, 3):
# 获取落子位置
action = func_timeout(60, self.current_player.get_move,
kwargs={'board': self.board})
# 如果 action 是 Q 则说明人类想结束比赛
if action == "Q":
# 说明人类想结束游戏,即根据棋子个数定输赢。
break
if action not in legal_actions:
# 判断当前下棋方落子是否符合合法落子,如果不合法,则需要对方重新输入
print("你落子不符合规则,请重新落子!")
continue
else:
# 落子合法则直接 break
break
else:
# 落子3次不合法,结束游戏!
winner, diff = self.force_loss(is_legal=True)
break
except FunctionTimedOut:
# 落子超时,结束游戏
winner, diff = self.force_loss(is_timeout=True)
break
# 结束时间
end_time = datetime.datetime.now()
if board != self.board._board:
# 修改棋盘,结束游戏!
winner, diff = self.force_loss(is_board=True)
break
if action == "Q":
# 说明人类想结束游戏,即根据棋子个数定输赢。
winner, diff = self.board.get_winner() # 得到赢家 0,1,2
break
if action is None:
continue
else:
# 统计一步所用的时间
es_time = (end_time - start_time).seconds
if es_time > 60:
# 该步超过60秒则结束比赛。
print('\n{} 思考超过 60s'.format(self.current_player))
winner, diff = self.force_loss(is_timeout=True)
break
# 当前玩家颜色,更新棋局
self.board._move(action, color)
# 统计每种棋子下棋所用总时间
if self.current_player == self.black_player:
# 当前选手是黑棋一方
step_time["X"] = es_time
total_time["X"] += es_time
else:
step_time["O"] = es_time
total_time["O"] += es_time
# 显示当前棋盘
self.board.display(step_time, total_time)
# 判断游戏是否结束
if self.game_over():
# 游戏结束
winner, diff = self.board.get_winner() # 得到赢家 0,1,2
break
print('\n=====游戏结束!=====\n')
self.board.display(step_time, total_time)
self.print_winner(winner)
# 返回'black_win','white_win','draw',棋子数差
if winner is not None and diff > -1:
result = {0: 'black_win', 1: 'white_win', 2: 'draw'}[winner]
return result, diff
def game_over(self):
"""
判断游戏是否结束
:return: True/False 游戏结束/游戏没有结束
"""
# 根据当前棋盘,判断棋局是否终止
# 如果当前选手没有合法下棋的位子,则切换选手;如果另外一个选手也没有合法的下棋位置,则比赛停止。
b_list = list(self.board.get_legal_actions('X'))
w_list = list(self.board.get_legal_actions('O'))
is_over = len(b_list) == 0 and len(w_list) == 0 # 返回值 True/False
return is_over
Board类
#!/usr/bin/Anaconda3/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
class Board(object):
"""
Board 黑白棋棋盘,规格是8*8,黑棋用 X 表示,白棋用 O 表示,未落子时用 . 表示。
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化棋盘状态
"""
self.empty = '.' # 未落子状态
self._board = [[self.empty for _ in range(8)] for _ in range(8)] # 规格:8*8
self._board[3][4] = 'X' # 黑棋棋子
self._board[4][3] = 'X' # 黑棋棋子
self._board[3][3], self._board[4][4] = 'O', 'O' # 白棋棋子
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
添加Board[][] 索引语法
:param index: 下标索引
:return:
"""
return self._board[index]
def display(self, step_time=None, total_time=None):
"""
打印棋盘
:param step_time: 每一步的耗时, 比如:{"X":1,"O":0},默认值是None
:param total_time: 总耗时, 比如:{"X":1,"O":0},默认值是None
:return:
"""
board = self._board
# print(step_time,total_time)
# 打印列名
print(' ', ' '.join(list('ABCDEFGH')))
# 打印行名和棋盘
for i in range(8):
# print(board)
print(str(i + 1), ' '.join(board[i]))
if (not step_time) or (not total_time):
# 棋盘初始化时展示的时间
step_time = {"X": 0, "O": 0}
total_time = {"X": 0, "O": 0}
print("统计棋局: 棋子总数 / 每一步耗时 / 总时间 ")
print("黑 棋: " + str(self.count('X')) + ' / ' + str(step_time['X']) + ' / ' + str(
total_time['X']))
print("白 棋: " + str(self.count('O')) + ' / ' + str(step_time['O']) + ' / ' + str(
total_time['O']) + '\n')
else:
# 比赛时展示时间
print("统计棋局: 棋子总数 / 每一步耗时 / 总时间 ")
print("黑 棋: " + str(self.count('X')) + ' / ' + str(step_time['X']) + ' / ' + str(
total_time['X']))
print("白 棋: " + str(self.count('O')) + ' / ' + str(step_time['O']) + ' / ' + str(
total_time['O']) + '\n')
def count(self, color):
"""
统计 color 一方棋子的数量。(O:白棋, X:黑棋, .:未落子状态)
:param color: [O,X,.] 表示棋盘上不同的棋子
:return: 返回 color 棋子在棋盘上的总数
"""
count = 0
for y in range(8):
for x in range(8):
if self._board[x][y] == color:
count += 1
return count
def get_winner(self):
"""
判断黑棋和白旗的输赢,通过棋子的个数进行判断
:return: 0-黑棋赢,1-白旗赢,2-表示平局,黑棋个数和白旗个数相等
"""
# 定义黑白棋子初始的个数
black_count, white_count = 0, 0
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
# 统计黑棋棋子的个数
if self._board[i][j] == 'X':
black_count += 1
# 统计白旗棋子的个数
if self._board[i][j] == 'O':
white_count += 1
if black_count > white_count:
# 黑棋胜
return 0, black_count - white_count
elif black_count < white_count:
# 白棋胜
return 1, white_count - black_count
elif black_count == white_count:
# 表示平局,黑棋个数和白旗个数相等
return 2, 0
def _move(self, action, color):
"""
落子并获取反转棋子的坐标
:param action: 落子的坐标 可以是 D3 也可以是(2,3)
:param color: [O,X,.] 表示棋盘上不同的棋子
:return: 返回反转棋子的坐标列表,落子失败则返回False
"""
# 判断action 是不是字符串,如果是则转化为数字坐标
if isinstance(action, str):
action = self.board_num(action)
fliped = self._can_fliped(action, color)
if fliped:
# 有就反转对方棋子坐标
for flip in fliped:
x, y = self.board_num(flip)
self._board[x][y] = color
# 落子坐标
x, y = action
# 更改棋盘上 action 坐标处的状态,修改之后该位置属于 color[X,O,.]等三状态
self._board[x][y] = color
return fliped
else:
# 没有反转子则落子失败
return False
def backpropagation(self, action, flipped_pos, color):
"""
回溯
:param action: 落子点的坐标
:param flipped_pos: 反转棋子坐标列表
:param color: 棋子的属性,[X,0,.]三种情况
:return:
"""
# 判断action 是不是字符串,如果是则转化为数字坐标
if isinstance(action, str):
action = self.board_num(action)
self._board[action[0]][action[1]] = self.empty
# 如果 color == 'X',则 op_color = 'O';否则 op_color = 'X'
op_color = "O" if color == "X" else "X"
for p in flipped_pos:
# 判断action 是不是字符串,如果是则转化为数字坐标
if isinstance(p, str):
p = self.board_num(p)
self._board[p[0]][p[1]] = op_color
def is_on_board(self, x, y):
"""
判断坐标是否出界
:param x: row 行坐标
:param y: col 列坐标
:return: True or False
"""
return x >= 0 and x <= 7 and y >= 0 and y <= 7
def _can_fliped(self, action, color):
"""
检测落子是否合法,如果不合法,返回 False,否则返回反转子的坐标列表
:param action: 下子位置
:param color: [X,0,.] 棋子状态
:return: False or 反转对方棋子的坐标列表
"""
# 判断action 是不是字符串,如果是则转化为数字坐标
if isinstance(action, str):
action = self.board_num(action)
xstart, ystart = action
# 如果该位置已经有棋子或者出界,返回 False
if not self.is_on_board(xstart, ystart) or self._board[xstart][ystart] != self.empty:
return False
# 临时将color放到指定位置
self._board[xstart][ystart] = color
# 棋手
op_color = "O" if color == "X" else "X"
# 要被翻转的棋子
flipped_pos = []
flipped_pos_board = []
for xdirection, ydirection in [[0, 1], [1, 1], [1, 0], [1, -1], [0, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, 0],
[-1, 1]]:
x, y = xstart, ystart
x += xdirection
y += ydirection
# 如果(x,y)在棋盘上,而且为对方棋子,则在这个方向上继续前进,否则循环下一个角度。
if self.is_on_board(x, y) and self._board[x][y] == op_color:
x += xdirection
y += ydirection
# 进一步判断点(x,y)是否在棋盘上,如果不在棋盘上,继续循环下一个角度,如果在棋盘上,则进行while循环。
if not self.is_on_board(x, y):
continue
# 一直走到出界或不是对方棋子的位置
while self._board[x][y] == op_color:
# 如果一直是对方的棋子,则点(x,y)一直循环,直至点(x,y)出界或者不是对方的棋子。
x += xdirection
y += ydirection
# 点(x,y)出界了和不是对方棋子
if not self.is_on_board(x, y):
break
# 出界了,则没有棋子要翻转OXXXXX
if not self.is_on_board(x, y):
continue
# 是自己的棋子OXXXXXXO
if self._board[x][y] == color:
while True:
x -= xdirection
y -= ydirection
# 回到了起点则结束
if x == xstart and y == ystart:
break
# 需要翻转的棋子
flipped_pos.append([x, y])
# 将前面临时放上的棋子去掉,即还原棋盘
self._board[xstart][ystart] = self.empty # restore the empty space
# 没有要被翻转的棋子,则走法非法。返回 False
if len(flipped_pos) == 0:
return False
for fp in flipped_pos:
flipped_pos_board.append(self.num_board(fp))
# 走法正常,返回翻转棋子的棋盘坐标
return flipped_pos_board
def get_legal_actions(self, color):
"""
按照黑白棋的规则获取棋子的合法走法
:param color: 不同颜色的棋子,X-黑棋,O-白棋
:return: 生成合法的落子坐标,用list()方法可以获取所有的合法坐标
"""
# 表示棋盘坐标点的8个不同方向坐标,比如方向坐标[0][1]则表示坐标点的正上方。
direction = [(-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 1), (1, 1), (1, 0), (1, -1), (0, -1), (-1, -1)]
op_color = "O" if color == "X" else "X"
# 统计 op_color 一方邻近的未落子状态的位置
op_color_near_points = []
board = self._board
for i in range(8):
# i 是行数,从0开始,j是列数,也是从0开始
for j in range(8):
# 判断棋盘[i][j]位子棋子的属性,如果是op_color,则继续进行下一步操作,
# 否则继续循环获取下一个坐标棋子的属性
if board[i][j] == op_color:
# dx,dy 分别表示[i][j]坐标在行、列方向上的步长,direction 表示方向坐标
for dx, dy in direction:
x, y = i + dx, j + dy
# 表示x、y坐标值在合理范围,棋盘坐标点board[x][y]为未落子状态,
# 而且(x,y)不在op_color_near_points 中,统计对方未落子状态位置的列表才可以添加该坐标点
if 0 <= x <= 7 and 0 <= y <= 7 and board[x][y] == self.empty and (
x, y) not in op_color_near_points:
op_color_near_points.append((x, y))
l = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
for p in op_color_near_points:
if self._can_fliped(p, color):
# 判断p是不是数字坐标,如果是则返回棋盘坐标
# p = self.board_num(p)
if p[0] in l and p[1] in l:
p = self.num_board(p)
yield p
def board_num(self, action):
"""
棋盘坐标转化为数字坐标
:param action:棋盘坐标,比如A1
:return:数字坐标,比如 A1 --->(0,0)
"""
row, col = str(action[1]).upper(), str(action[0]).upper()
if row in '12345678' and col in 'ABCDEFGH':
# 坐标正确
x, y = '12345678'.index(row), 'ABCDEFGH'.index(col)
return x, y
def num_board(self, action):
"""
数字坐标转化为棋盘坐标
:param action:数字坐标 ,比如(0,0)
:return:棋盘坐标,比如 (0,0)---> A1
"""
row, col = action
l = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
if col in l and row in l:
return chr(ord('A') + col) + str(row + 1)
三个Player(随机玩家,人类玩家,AI玩家)
import math
import random
import sys
from game import Game # 导入黑白棋文件
from copy import deepcopy
class RandomPlayer:
"""
随机玩家, 随机返回一个合法落子位置
"""
def __init__(self, color):
"""
玩家初始化
:param color: 下棋方,'X' - 黑棋,'O' - 白棋
"""
self.color = color
def random_choice(self, board):
"""
从合法落子位置中随机选一个落子位置
:param board: 棋盘
:return: 随机合法落子位置, e.g. 'A1'
"""
# 用 list() 方法获取所有合法落子位置坐标列表
action_list = list(board.get_legal_actions(self.color))
# 如果 action_list 为空,则返回 None,否则从中选取一个随机元素,即合法落子坐标
if len(action_list) == 0:
return None
else:
return random.choice(action_list)
def get_move(self, board):
"""
根据当前棋盘状态获取最佳落子位置
:param board: 棋盘
:return: action 最佳落子位置, e.g. 'A1'
"""
if self.color == 'X':
player_name = '黑棋'
else:
player_name = '白棋'
print("请等一会,对方 {}-{} 正在思考中...".format(player_name, self.color))
action = self.random_choice(board)
return action
class HumanPlayer:
"""
人类玩家
"""
def __init__(self, color):
"""
玩家初始化
:param color: 下棋方,'X' - 黑棋,'O' - 白棋
"""
self.color = color
def get_move(self, board):
"""
根据当前棋盘输入人类合法落子位置
:param board: 棋盘
:return: 人类下棋落子位置
"""
# 如果 self.color 是黑棋 "X",则 player 是 "黑棋",否则是 "白棋"
if self.color == "X":
player = "黑棋"
else:
player = "白棋"
# 人类玩家输入落子位置,如果输入 'Q', 则返回 'Q'并结束比赛。
# 如果人类玩家输入棋盘位置,e.g. 'A1',
# 首先判断输入是否正确,然后再判断是否符合黑白棋规则的落子位置
while True:
action = input(
"请'{}-{}'方输入一个合法的坐标(e.g. 'D3',若不想进行,请务必输入'Q'结束游戏。): ".format(player,
self.color))
# 如果人类玩家输入 Q 则表示想结束比赛
if action == "Q" or action == 'q':
return "Q"
else:
row, col = action[1].upper(), action[0].upper()
# 检查人类输入是否正确
if row in '12345678' and col in 'ABCDEFGH':
# 检查人类输入是否为符合规则的可落子位置
if action in board.get_legal_actions(self.color):
return action
else:
print("你的输入不合法,请重新输入!")
class Node:
def __init__(self, now_board, parent=None, action=None, color=""):
self.visits = 0 # 访问次数
self.reward = 0.0 # 期望值
self.now_board = now_board # 棋盘状态
self.children = [] # 孩子节点
self.parent = parent # 父节点
self.action = action # 对应动作
self.color = color # 该节点玩家颜色
def get_ucb(self, ucb_param):
if self.visits == 0:
return sys.maxsize # 未访问的节点ucb为无穷大
# UCB公式
explore = math.sqrt(2.0 * math.log(self.parent.visits) / float(self.visits))
now_ucb = self.reward/self.visits + ucb_param * explore
return now_ucb
# 生个孩子
def add_child(self, child_now_board, action, color):
child_node = Node(child_now_board, parent=self, action=action, color=color)
self.children.append(child_node)
# 判断是否完全扩展
def full_expanded(self):
# 有孩子并且所有孩子都访问过了就是完全扩展
if len(self.children) == 0:
return False
for kid in self.children:
if kid.visits == 0:
return False
return True
class AIPlayer:
"""
AI 玩家
"""
def __init__(self, color):
"""
玩家初始化
:param color: 下棋方,'X' - 黑棋,'O' - 白棋
"""
self.max_times = 50 # 最大迭代次数
self.ucb_param = 1 # ucb的参数C
self.color = color
def uct(self, max_times, root):
"""
根据当前棋盘状态获取最佳落子位置
:param max_times: 最大搜索次数
:param root: 根节点
:return: action 最佳落子位置
"""
for i in range(max_times): # 最多模拟max次
selected_node = self.select(root)
leaf_node = self.extend(selected_node)
reward = self.stimulate(leaf_node)
self.backup(leaf_node, reward)
max_node = None # 搜索完成,然后找出最适合的下一步
max_ucb = -sys.maxsize
for child in root.children:
child_ucb = child.get_ucb(self.ucb_param)
if max_ucb < child_ucb:
max_ucb = child_ucb
max_node = child # max_node指向ucb最大的孩子
return max_node.action
def select(self, node):
"""
:param node:某个节点
:return: ucb值最大的叶子
"""
# print(len(node.children))
if len(node.children) == 0: # 叶子,需要扩展
return node
if node.full_expanded(): # 完全扩展,递归选择ucb最大的孩子
max_node = None
max_ucb = -sys.maxsize
for child in node.children:
child_ucb = child.get_ucb(self.ucb_param)
if max_ucb < child_ucb:
max_ucb = child_ucb
max_node = child # max_node指向ucb最大的孩子
return self.select(max_node)
else: # 没有完全扩展就选访问次数为0的孩子
for kid in node.children: # 从左开始遍历
if kid.visits == 0:
return kid
def extend(self, node):
if node.visits == 0: # 自身还没有被访问过,不扩展,直接模拟
return node
else: # 需要扩展,先确定颜色
if node.color == 'X':
new_color = 'O'
else:
new_color = 'X'
for action in list(node.now_board.get_legal_actions(node.color)): # 把所有可行节点加入孩子列表,并初始化
new_board = deepcopy(node.now_board)
new_board._move(action, node.color)
# 新建节点
node.add_child(new_board, action=action, color=new_color)
if len(node.children) == 0:
return node
return node.children[0] # 返回新的孩子列表的第一个,以供下一步模拟
def stimulate(self, node):
"""
:param node:模拟起始点
:return: 模拟结果reward
board.get_winner()会返回胜负关系和获胜子数
考虑胜负关系和获胜的子数,定义获胜积10分,每多赢一个棋子多1分
"""
board = deepcopy(node.now_board)
color = node.color
count = 0
while (not self.game_over(board)) and count < 50: # 游戏没有结束,就模拟下棋
action_list = list(node.now_board.get_legal_actions(color))
if not len(action_list) == 0: # 可以下,就随机下棋
action = random.choice(action_list)
board._move(action, color)
if color == 'X':
color = 'O'
else:
color = 'X'
else: # 不能下,就交换选手
if color == 'X':
color = 'O'
else:
color = 'X'
action_list = list(node.now_board.get_legal_actions(color))
action = random.choice(action_list)
board._move(action, color)
if color == 'X':
color = 'O'
else:
color = 'X'
count = count + 1
# winner:0-黑棋赢,1-白旗赢,2-表示平局
# diff:赢家领先棋子数
winner, diff = board.get_winner()
if winner == 2:
reward = 0
elif winner == 0:
# 这里逻辑是反的,写出了bug...应该是其他地方逻辑也反了一次,负负得正了...实在不想找bug了对不住
reward = 10 + diff
else:
reward = -(10 + diff)
if self.color == 'X':
reward = - reward
return reward
def backup(self, node, reward):
"""
反向传播函数
"""
while node is not None:
node.visits += 1
if node.color == self.color:
node.reward += reward
else:
node.reward -= reward
node = node.parent
return 0
def game_over(self, board):
"""
判断游戏是否结束
:return: True/False 游戏结束/游戏没有结束
"""
# 根据当前棋盘,双方都无处可落子,则终止
b_list = list(board.get_legal_actions('X'))
w_list = list(board.get_legal_actions('O'))
is_over = (len(b_list) == 0 and len(w_list) == 0) # 返回值 True/False
return is_over
def get_move(self, board):
"""
根据当前棋盘状态获取最佳落子位置
:param board: 棋盘
:return: action 最佳落子位置, e.g. 'A1'
"""
if self.color == 'X':
player_name = '黑棋'
else:
player_name = '白棋'
print("请等一会,对方 {}-{} 正在思考中...".format(player_name, self.color))
root = Node(now_board=deepcopy(board), color=self.color)
action = self.uct(self.max_times, root)
return action
# 黑棋初始化
black_player = AIPlayer("X")
# 白棋初始化
white_player = AIPlayer("O")
# 游戏初始化,第一个玩家是黑棋,第二个玩家是白棋
game = Game(black_player, white_player)
# 开始下棋
game.run()
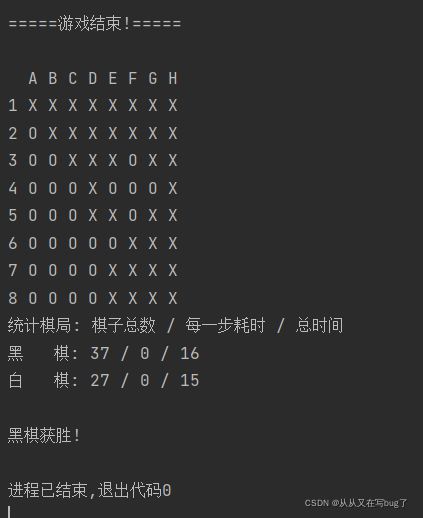
效果图:
算法较为简陋,不过是完成作业罢了,还请大佬们指正。