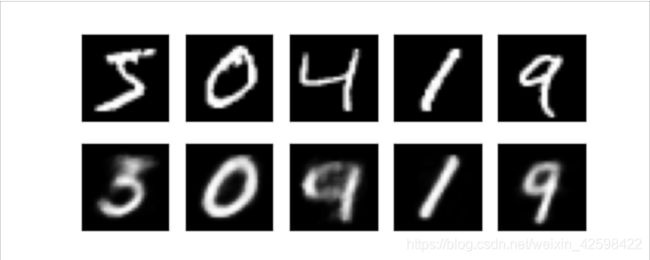莫烦Pytorch入门代码
代码摘自:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
1.torch库与numpy库的数据转换
import torch
import numpy as np
# convert numpy to tensor or vise versa
np_data = np.arange(6).reshape((2, 3))
torch_data = torch.from_numpy(np_data)
tensor2array = torch_data.numpy()
print(
'\nnumpy array:', np_data, # [[0 1 2], [3 4 5]]
'\ntorch tensor:', torch_data, # 0 1 2 \n 3 4 5 [torch.LongTensor of size 2x3]
'\ntensor to array:', tensor2array, # [[0 1 2], [3 4 5]]
)
'''
numpy array: [[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]]
torch tensor: tensor([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]], dtype=torch.int32)
tensor to array: [[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]]
'''
# abs
data = [-1, -2, 1, 2]
tensor = torch.FloatTensor(data) # 32-bit floating point
print(
'\nabs',
'\nnumpy: ', np.abs(data), # [1 2 1 2]
'\ntorch: ', torch.abs(tensor) # [1 2 1 2]
)
'''
abs
numpy: [1 2 1 2]
torch: tensor([1., 2., 1., 2.])
'''
# sin
print(
'\nsin',
'\nnumpy: ', np.sin(data), # [-0.84147098 -0.90929743 0.84147098 0.90929743]
'\ntorch: ', torch.sin(tensor) # [-0.8415 -0.9093 0.8415 0.9093]
)
'''
sin
numpy: [-0.84147098 -0.90929743 0.84147098 0.90929743]
torch: tensor([-0.8415, -0.9093, 0.8415, 0.9093])
'''
# mean
print(
'\nmean',
'\nnumpy: ', np.mean(data), # 0.0
'\ntorch: ', torch.mean(tensor) # 0.0
)
'''
mean
numpy: 0.0
torch: tensor(0.)
'''
# matrix multiplication
data = [[1,2], [3,4]]
tensor = torch.FloatTensor(data) # 32-bit floating point
# correct method
print(
'\nmatrix multiplication (matmul)',
'\nnumpy: ', np.matmul(data, data), # [[7, 10], [15, 22]]
'\ntorch: ', torch.mm(tensor, tensor) # [[7, 10], [15, 22]]
)
'''
matrix multiplication (matmul)
numpy: [[ 7 10]
[15 22]]
torch: tensor([[ 7., 10.],
[15., 22.]])
'''
# incorrect method (错误用法!!!)
data = np.array(data)
print(
'\nmatrix multiplication (dot)',
'\nnumpy: ', data.dot(data), # [[7, 10], [15, 22]]
'\ntorch: ', tensor.dot(tensor) # this will convert tensor to [1,2,3,4], you'll get 30.0
)
'''
RuntimeError: 1D tensors expected, got 2D, 2D tensors at ..\aten\src\TH/generic/THTensorEvenMoreMath.cpp:83
'''
2.variable的使用
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
# Variable in torch is to build a computational graph,
# but this graph is dynamic compared with a static graph in Tensorflow or Theano.
# So torch does not have placeholder, torch can just pass variable to the computational graph.
tensor = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2],[3,4]]) # build a tensor
variable = Variable(tensor, requires_grad=True) # build a variable, usually for compute gradients
print(tensor) # [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2]
print(variable) # [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2]
'''
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]])
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]], requires_grad=True)
'''
# till now the tensor and variable seem the same.
# However, the variable is a part of the graph, it's a part of the auto-gradient.
t_out = torch.mean(tensor*tensor) # x^2
v_out = torch.mean(variable*variable) # x^2
print(t_out)
print(v_out) # 7.5
'''
tensor(7.5000)
tensor(7.5000, grad_fn=)
'''
v_out.backward() # backpropagation from v_out
# v_out = 1/4 * sum(variable*variable)
# the gradients w.r.t the variable, d(v_out)/d(variable) = 1/4*2*variable = variable/2
print(variable.grad)
'''
tensor([[0.5000, 1.0000],
[1.5000, 2.0000]])
'''
print(variable) # this is data in variable format
"""
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]], requires_grad=True)
"""
print(variable.data) # this is data in tensor format
"""
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]])
"""
print(variable.data.numpy()) # numpy format
"""
[[ 1. 2.]
[ 3. 4.]]
"""
3.激励函数
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# fake data
x = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 200) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = Variable(x)
x_np = x.data.numpy() # numpy array for plotting
# following are popular activation functions
y_relu = torch.relu(x).data.numpy()
y_sigmoid = torch.sigmoid(x).data.numpy()
y_tanh = torch.tanh(x).data.numpy()
y_softplus = F.softplus(x).data.numpy() # there's no softplus in torch
# y_softmax = torch.softmax(x, dim=0).data.numpy() softmax is a special kind of activation function, it is about probability
# plt to visualize these activation function
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x_np, y_relu, c='red', label='relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x_np, y_sigmoid, c='red', label='sigmoid')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x_np, y_tanh, c='red', label='tanh')
plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x_np, y_softplus, c='red', label='softplus')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 6))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
# 定义一个神经网路
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
net = Net(n_feature=1, n_hidden=10, n_output=1) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # this is for regression mean squared loss
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(200):
prediction = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target)
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 5 == 0:
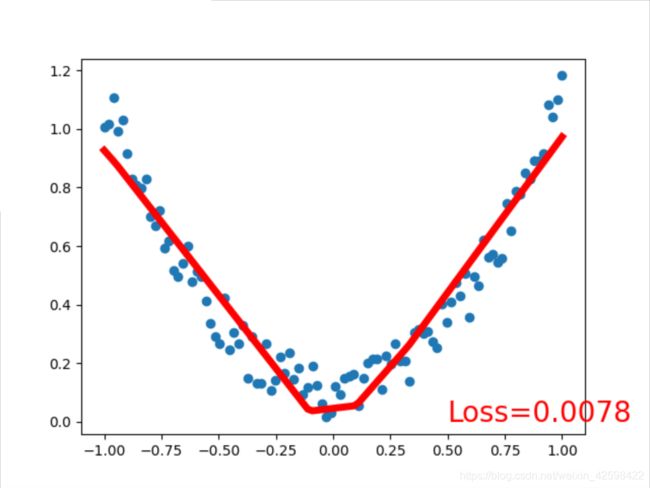
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(0.5, 0, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# make fake data
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
# plt.show()
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.out(x)
return x
net = Net(n_feature=2, n_hidden=10, n_output=2) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.02)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is NOT an one-hotted
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(100):
out = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(out, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target), the target label is NOT one-hotted
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 2 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(out, 1)[1]
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = float((pred_y == target_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(target_y.size)
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 方式一:replace following class code with an easy sequential network
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
net1 = Net(1, 10, 1)
# 方式二:easy and fast way to build your network
net2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
print(net1) # net1 architecture
"""
Net (
(hidden): Linear (1 -> 10)
(predict): Linear (10 -> 1)
)
"""
print(net2) # net2 architecture
"""
Sequential (
(0): Linear (1 -> 10)
(1): ReLU ()
(2): Linear (10 -> 1)
)
"""
7.CNN实现手写数字识别
import os
# third-party library
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 50
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
# Mnist digits dataset
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
)
# plot one example
print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000)
plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray')
plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[0])
plt.show()
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
# pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False)
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.test_data, dim=1).type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.test_labels[:2000]
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1, # input height
out_channels=16, # n_filters
kernel_size=5, # filter size
stride=1, # filter movement/step
padding=2, # if want same width and length of this image after Conv2d, padding=(kernel_size-1)/2 if stride=1
), # output shape (16, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2), # choose max value in 2x2 area, output shape (16, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 14, 14)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2), # output shape (32, 7, 7)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # flatten the output of conv2 to (batch_size, 32 * 7 * 7)
output = self.out(x)
return output, x # return x for visualization
cnn = CNN()
print(cnn) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
# following function (plot_with_labels) is for visualization, can be ignored if not interested
from matplotlib import cm
try: from sklearn.manifold import TSNE; HAS_SK = True
except: HAS_SK = False; print('Please install sklearn for layer visualization')
def plot_with_labels(lowDWeights, labels):
plt.cla()
X, Y = lowDWeights[:, 0], lowDWeights[:, 1]
for x, y, s in zip(X, Y, labels):
c = cm.rainbow(int(255 * s / 9)); plt.text(x, y, s, backgroundcolor=c, fontsize=9)
plt.xlim(X.min(), X.max()); plt.ylim(Y.min(), Y.max()); plt.title('Visualize last layer'); plt.show(); plt.pause(0.01)
plt.ion()
# training and testing
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
output = cnn(b_x)[0] # cnn output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if step % 50 == 0:
test_output, last_layer = cnn(test_x)
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
accuracy = float((pred_y == test_y.data.numpy()).astype(int).sum()) / float(test_y.size(0))
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), '| test accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy)
if HAS_SK:
# Visualization of trained flatten layer (T-SNE)
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000)
plot_only = 500
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(last_layer.data.numpy()[:plot_only, :])
labels = test_y.numpy()[:plot_only]
plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels)
plt.ioff()
# print 10 predictions from test data
test_output, _ = cnn(test_x[:10])
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10].numpy(), 'real number')
'''输出结果:'''
'''
CNN(
(conv1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(conv2): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(out): Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
Please install sklearn for layer visualization
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 2.2968 | test accuracy: 0.14
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.4375 | test accuracy: 0.83
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.6111 | test accuracy: 0.87
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.2048 | test accuracy: 0.91
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.2585 | test accuracy: 0.93
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0764 | test accuracy: 0.93
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1290 | test accuracy: 0.95
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1609 | test accuracy: 0.96
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0647 | test accuracy: 0.96
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0966 | test accuracy: 0.96
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1824 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0774 | test accuracy: 0.96
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0472 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1196 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1062 | test accuracy: 0.98
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1764 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0414 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0474 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0188 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.3208 | test accuracy: 0.97
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0710 | test accuracy: 0.96
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0863 | test accuracy: 0.98
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.1158 | test accuracy: 0.96
Epoch: 0 | train loss: 0.0737 | test accuracy: 0.97
[7 2 1 0 4 1 4 9 5 9] prediction number
[7 2 1 0 4 1 4 9 5 9] real number
'''
8.RNN分类实现手写数字识别
import torch
from torch import nn
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 64
TIME_STEP = 28 # rnn time step / image height
INPUT_SIZE = 28 # rnn input size / image width
LR = 0.01 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True # set to True if haven't download the data
# Mnist digital dataset
train_data = dsets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, # download it if you don't have it
)
# plot one example
print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000)
plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray')
plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[0])
plt.show()
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
# convert test data into Variable, pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = dsets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
test_x = test_data.test_data.type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255. # shape (2000, 28, 28) value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.test_labels.numpy()[:2000] # covert to numpy array
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM( # if use nn.RNN(), it hardly learns
input_size=INPUT_SIZE,
hidden_size=64, # rnn hidden unit
num_layers=1, # number of rnn layer
batch_first=True, # input & output will has batch size as 1s dimension. e.g. (batch, time_step, input_size)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# x shape (batch, time_step, input_size)
# r_out shape (batch, time_step, output_size)
# h_n shape (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)
# h_c shape (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)
r_out, (h_n, h_c) = self.rnn(x, None) # None represents zero initial hidden state
# choose r_out at the last time step
out = self.out(r_out[:, -1, :])
return out
rnn = RNN()
print(rnn)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
# training and testing
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data
b_x = b_x.view(-1, 28, 28) # reshape x to (batch, time_step, input_size)
output = rnn(b_x) # rnn output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if step % 50 == 0:
test_output = rnn(test_x) # (samples, time_step, input_size)
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
accuracy = float((pred_y == test_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(test_y.size)
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), '| test accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy)
# print 10 predictions from test data
test_output = rnn(test_x[:10].view(-1, 28, 28))
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10], 'real number')
9.RNN回归实现手写数字识别
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
TIME_STEP = 10 # rnn time step
INPUT_SIZE = 1 # rnn input size
LR = 0.02 # learning rate
# show data
steps = np.linspace(0, np.pi*2, 100, dtype=np.float32) # float32 for converting torch FloatTensor
x_np = np.sin(steps)
y_np = np.cos(steps)
plt.plot(steps, y_np, 'r-', label='target (cos)')
plt.plot(steps, x_np, 'b-', label='input (sin)')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.RNN(
input_size=INPUT_SIZE,
hidden_size=32, # rnn hidden unit
num_layers=1, # number of rnn layer
batch_first=True, # input & output will has batch size as 1s dimension. e.g. (batch, time_step, input_size)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32, 1)
def forward(self, x, h_state):
# x (batch, time_step, input_size)
# h_state (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)
# r_out (batch, time_step, hidden_size)
r_out, h_state = self.rnn(x, h_state)
outs = [] # save all predictions
for time_step in range(r_out.size(1)): # calculate output for each time step
outs.append(self.out(r_out[:, time_step, :]))
return torch.stack(outs, dim=1), h_state
# instead, for simplicity, you can replace above codes by follows
# r_out = r_out.view(-1, 32)
# outs = self.out(r_out)
# outs = outs.view(-1, TIME_STEP, 1)
# return outs, h_state
# or even simpler, since nn.Linear can accept inputs of any dimension
# and returns outputs with same dimension except for the last
# outs = self.out(r_out)
# return outs
rnn = RNN()
print(rnn)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
h_state = None # for initial hidden state
plt.figure(1, figsize=(12, 5))
plt.ion() # continuously plot
for step in range(100):
start, end = step * np.pi, (step+1)*np.pi # time range
# use sin predicts cos
steps = np.linspace(start, end, TIME_STEP, dtype=np.float32, endpoint=False) # float32 for converting torch FloatTensor
x_np = np.sin(steps)
y_np = np.cos(steps)
x = torch.from_numpy(x_np[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis]) # shape (batch, time_step, input_size)
y = torch.from_numpy(y_np[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis])
prediction, h_state = rnn(x, h_state) # rnn output
# !! next step is important !!
h_state = h_state.data # repack the hidden state, break the connection from last iteration
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # calculate loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
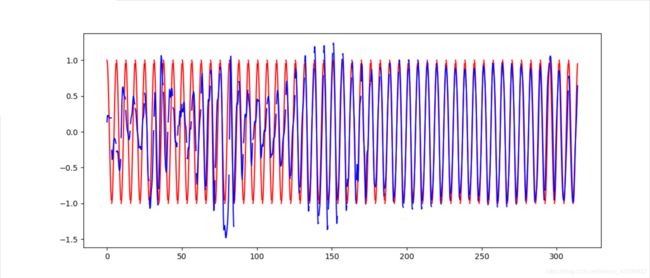
# plotting
plt.plot(steps, y_np.flatten(), 'r-')
plt.plot(steps, prediction.data.numpy().flatten(), 'b-')
plt.draw(); plt.pause(0.05)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
'''
RNN(
(rnn): RNN(1, 32, batch_first=True)
(out): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
'''
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm
import numpy as np
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 10
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR = 0.005 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
N_TEST_IMG = 5
# Mnist digits dataset
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, # download it if you don't have it
)
# plot one example
print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000)
plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[2].numpy(), cmap='gray')
plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[2])
plt.show()
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
class AutoEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(AutoEncoder, self).__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 128),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(128, 64),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(64, 12),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(12, 3), # compress to 3 features which can be visualized in plt
)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(3, 12),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(12, 64),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(64, 128),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(128, 28*28),
nn.Sigmoid(), # compress to a range (0, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return encoded, decoded
autoencoder = AutoEncoder()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(autoencoder.parameters(), lr=LR)
loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
# initialize figure
f, a = plt.subplots(2, N_TEST_IMG, figsize=(5, 2))
plt.ion() # continuously plot
# original data (first row) for viewing
view_data = train_data.train_data[:N_TEST_IMG].view(-1, 28*28).type(torch.FloatTensor)/255.
for i in range(N_TEST_IMG):
a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(view_data.data.numpy()[i], (28, 28)), cmap='gray'); a[0][i].set_xticks(()); a[0][i].set_yticks(())
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (x, b_label) in enumerate(train_loader):
b_x = x.view(-1, 28*28) # batch x, shape (batch, 28*28)
b_y = x.view(-1, 28*28) # batch y, shape (batch, 28*28)
encoded, decoded = autoencoder(b_x)
loss = loss_func(decoded, b_y) # mean square error
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if step % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy())
# plotting decoded image (second row)
_, decoded_data = autoencoder(view_data)
for i in range(N_TEST_IMG):
a[1][i].clear()
a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(decoded_data.data.numpy()[i], (28, 28)), cmap='gray')
a[1][i].set_xticks(()); a[1][i].set_yticks(())
plt.draw(); plt.pause(0.05)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
# visualize in 3D plot
view_data = train_data.train_data[:200].view(-1, 28*28).type(torch.FloatTensor)/255.
encoded_data, _ = autoencoder(view_data)
fig = plt.figure(2); ax = Axes3D(fig)
X, Y, Z = encoded_data.data[:, 0].numpy(), encoded_data.data[:, 1].numpy(), encoded_data.data[:, 2].numpy()
values = train_data.train_labels[:200].numpy()
for x, y, z, s in zip(X, Y, Z, values):
c = cm.rainbow(int(255*s/9)); ax.text(x, y, z, s, backgroundcolor=c)
ax.set_xlim(X.min(), X.max()); ax.set_ylim(Y.min(), Y.max()); ax.set_zlim(Z.min(), Z.max())
plt.show()
"""
Dependencies:
torch: 0.4
gym: 0.8.1
numpy
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import gym
# Hyper Parameters
BATCH_SIZE = 32
LR = 0.01 # learning rate
EPSILON = 0.9 # greedy policy
GAMMA = 0.9 # reward discount
TARGET_REPLACE_ITER = 100 # target update frequency
MEMORY_CAPACITY = 2000
env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')
env = env.unwrapped
N_ACTIONS = env.action_space.n
N_STATES = env.observation_space.shape[0]
ENV_A_SHAPE = 0 if isinstance(env.action_space.sample(), int) else env.action_space.sample().shape # to confirm the shape
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(N_STATES, 50)
self.fc1.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.1) # initialization
self.out = nn.Linear(50, N_ACTIONS)
self.out.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.1) # initialization
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
actions_value = self.out(x)
return actions_value
class DQN(object):
def __init__(self):
self.eval_net, self.target_net = Net(), Net()
self.learn_step_counter = 0 # for target updating
self.memory_counter = 0 # for storing memory
self.memory = np.zeros((MEMORY_CAPACITY, N_STATES * 2 + 2)) # initialize memory
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.eval_net.parameters(), lr=LR)
self.loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
def choose_action(self, x):
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.FloatTensor(x), 0)
# input only one sample
if np.random.uniform() < EPSILON: # greedy
actions_value = self.eval_net.forward(x)
action = torch.max(actions_value, 1)[1].data.numpy()
action = action[0] if ENV_A_SHAPE == 0 else action.reshape(ENV_A_SHAPE) # return the argmax index
else: # random
action = np.random.randint(0, N_ACTIONS)
action = action if ENV_A_SHAPE == 0 else action.reshape(ENV_A_SHAPE)
return action
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
# replace the old memory with new memory
index = self.memory_counter % MEMORY_CAPACITY
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def learn(self):
# target parameter update
if self.learn_step_counter % TARGET_REPLACE_ITER == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.eval_net.state_dict())
self.learn_step_counter += 1
# sample batch transitions
sample_index = np.random.choice(MEMORY_CAPACITY, BATCH_SIZE)
b_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
b_s = torch.FloatTensor(b_memory[:, :N_STATES])
b_a = torch.LongTensor(b_memory[:, N_STATES:N_STATES+1].astype(int))
b_r = torch.FloatTensor(b_memory[:, N_STATES+1:N_STATES+2])
b_s_ = torch.FloatTensor(b_memory[:, -N_STATES:])
# q_eval w.r.t the action in experience
q_eval = self.eval_net(b_s).gather(1, b_a) # shape (batch, 1)
q_next = self.target_net(b_s_).detach() # detach from graph, don't backpropagate
q_target = b_r + GAMMA * q_next.max(1)[0].view(BATCH_SIZE, 1) # shape (batch, 1)
loss = self.loss_func(q_eval, q_target)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
dqn = DQN()
print('\nCollecting experience...')
for i_episode in range(400):
s = env.reset()
ep_r = 0
while True:
env.render()
a = dqn.choose_action(s)
# take action
s_, r, done, info = env.step(a)
# modify the reward
x, x_dot, theta, theta_dot = s_
r1 = (env.x_threshold - abs(x)) / env.x_threshold - 0.8
r2 = (env.theta_threshold_radians - abs(theta)) / env.theta_threshold_radians - 0.5
r = r1 + r2
dqn.store_transition(s, a, r, s_)
ep_r += r
if dqn.memory_counter > MEMORY_CAPACITY:
dqn.learn()
if done:
print('Ep: ', i_episode,
'| Ep_r: ', round(ep_r, 2))
if done:
break
s = s_
'''
Collecting experience...
Ep: 199 | Ep_r: 1.31
Ep: 200 | Ep_r: 2.17
Ep: 201 | Ep_r: 3.72
Ep: 202 | Ep_r: 2.78
Ep: 203 | Ep_r: 1.89
Ep: 204 | Ep_r: 2.4
Ep: 205 | Ep_r: 0.73
Ep: 206 | Ep_r: 1.53
Ep: 207 | Ep_r: 2.21
Ep: 208 | Ep_r: 1.46
Ep: 209 | Ep_r: 2.28
Ep: 210 | Ep_r: 4.85
Ep: 211 | Ep_r: 1.74
Ep: 212 | Ep_r: 7.58
Ep: 213 | Ep_r: 1.7
Ep: 214 | Ep_r: 3.4
Ep: 215 | Ep_r: 3.12
Ep: 216 | Ep_r: 2.25
Ep: 217 | Ep_r: 2.35
Ep: 218 | Ep_r: 3.22
Ep: 219 | Ep_r: 5.32
Ep: 220 | Ep_r: 6.1
Ep: 221 | Ep_r: 2.33
Ep: 222 | Ep_r: 8.15
Ep: 223 | Ep_r: 3.26
Ep: 224 | Ep_r: 1.4
Ep: 225 | Ep_r: 4.28
Ep: 226 | Ep_r: 3.43
Ep: 227 | Ep_r: 1.13
Ep: 228 | Ep_r: 2.94
Ep: 229 | Ep_r: 1.83
Ep: 230 | Ep_r: 21.3
Ep: 231 | Ep_r: 2.79
Ep: 232 | Ep_r: 21.15
Ep: 233 | Ep_r: 10.14
Ep: 234 | Ep_r: 9.51
Ep: 235 | Ep_r: 2.37
Ep: 236 | Ep_r: 15.11
Ep: 237 | Ep_r: 42.06
Ep: 238 | Ep_r: 39.99
Ep: 239 | Ep_r: 52.94
Ep: 240 | Ep_r: 86.02
Ep: 241 | Ep_r: 31.62
Ep: 242 | Ep_r: 124.85
'''
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# np.random.seed(1)
# Hyper Parameters
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR_G = 0.0001 # learning rate for generator
LR_D = 0.0001 # learning rate for discriminator
N_IDEAS = 5 # think of this as number of ideas for generating an art work (Generator)
ART_COMPONENTS = 15 # it could be total point G can draw in the canvas
PAINT_POINTS = np.vstack([np.linspace(-1, 1, ART_COMPONENTS) for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE)])
# show our beautiful painting range
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
# plt.legend(loc='upper right')
# plt.show()
def artist_works(): # painting from the famous artist (real target)
a = np.random.uniform(1, 2, size=BATCH_SIZE)[:, np.newaxis]
paintings = a * np.power(PAINT_POINTS, 2) + (a-1)
paintings = torch.from_numpy(paintings).float()
return paintings
G = nn.Sequential( # Generator
nn.Linear(N_IDEAS, 128), # random ideas (could from normal distribution)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, ART_COMPONENTS), # making a painting from these random ideas
)
D = nn.Sequential( # Discriminator
nn.Linear(ART_COMPONENTS, 128), # receive art work either from the famous artist or a newbie like G
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(), # tell the probability that the art work is made by artist
)
opt_D = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=LR_D)
opt_G = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=LR_G)
plt.ion() # something about continuous plotting
for step in range(10000):
artist_paintings = artist_works() # real painting from artist
G_ideas = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, N_IDEAS, requires_grad=True) # random ideas\n
G_paintings = G(G_ideas) # fake painting from G (random ideas)
prob_artist1 = D(G_paintings) # D try to reduce this prob
G_loss = torch.mean(torch.log(1. - prob_artist1))
opt_G.zero_grad()
G_loss.backward()
opt_G.step()
prob_artist0 = D(artist_paintings) # D try to increase this prob
prob_artist1 = D(G_paintings.detach()) # D try to reduce this prob
D_loss = - torch.mean(torch.log(prob_artist0) + torch.log(1. - prob_artist1))
opt_D.zero_grad()
D_loss.backward(retain_graph=True) # reusing computational graph
opt_D.step()
if step % 50 == 0: # plotting
plt.cla()
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], G_paintings.data.numpy()[0], c='#4AD631', lw=3, label='Generated painting',)
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
plt.text(-.5, 2.3, 'D accuracy=%.2f (0.5 for D to converge)' % prob_artist0.data.numpy().mean(), fontdict={'size': 13})
plt.text(-.5, 2, 'D score= %.2f (-1.38 for G to converge)' % -D_loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 13})
plt.ylim((0, 3));plt.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10);plt.draw();plt.pause(0.01)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
GAN网络生成的绿线始终处在蓝线与红线之间。

12.dropout防止过拟合
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
N_SAMPLES = 20
N_HIDDEN = 300
# training data
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, N_SAMPLES), 1)
y = x + 0.3*torch.normal(torch.zeros(N_SAMPLES, 1), torch.ones(N_SAMPLES, 1))
# test data
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, N_SAMPLES), 1)
test_y = test_x + 0.3*torch.normal(torch.zeros(N_SAMPLES, 1), torch.ones(N_SAMPLES, 1))
# show data
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy(), c='magenta', s=50, alpha=0.5, label='train')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), c='cyan', s=50, alpha=0.5, label='test')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylim((-2.5, 2.5))
plt.show()
net_overfitting = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, 1),
)
net_dropped = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5), # drop 50% of the neuron
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5), # drop 50% of the neuron
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, 1),
)
print(net_overfitting) # net architecture
print(net_dropped)
optimizer_ofit = torch.optim.Adam(net_overfitting.parameters(), lr=0.01)
optimizer_drop = torch.optim.Adam(net_dropped.parameters(), lr=0.01)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(500):
pred_ofit = net_overfitting(x)
pred_drop = net_dropped(x)
loss_ofit = loss_func(pred_ofit, y)
loss_drop = loss_func(pred_drop, y)
optimizer_ofit.zero_grad()
optimizer_drop.zero_grad()
loss_ofit.backward()
loss_drop.backward()
optimizer_ofit.step()
optimizer_drop.step()
if t % 10 == 0:
# change to eval mode in order to fix drop out effect
net_overfitting.eval()
net_dropped.eval() # parameters for dropout differ from train mode
# plotting
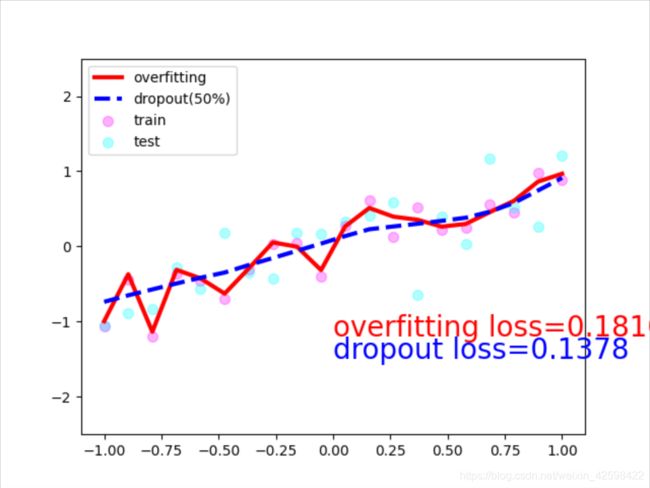
plt.cla()
test_pred_ofit = net_overfitting(test_x)
test_pred_drop = net_dropped(test_x)
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy(), c='magenta', s=50, alpha=0.3, label='train')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), c='cyan', s=50, alpha=0.3, label='test')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), test_pred_ofit.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=3, label='overfitting')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), test_pred_drop.data.numpy(), 'b--', lw=3, label='dropout(50%)')
plt.text(0, -1.2, 'overfitting loss=%.4f' % loss_func(test_pred_ofit, test_y).data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.text(0, -1.5, 'dropout loss=%.4f' % loss_func(test_pred_drop, test_y).data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'blue'})
plt.legend(loc='upper left'); plt.ylim((-2.5, 2.5));plt.pause(0.1)
# change back to train mode
net_overfitting.train()
net_dropped.train()
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
13.batch normalization使得数据被更好的利用
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
import torch.utils.data as Data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# np.random.seed(1)
# Hyper parameters
N_SAMPLES = 2000
BATCH_SIZE = 64
EPOCH = 12
LR = 0.03
N_HIDDEN = 8
ACTIVATION = torch.tanh
B_INIT = -0.2 # use a bad bias constant initializer
# training data
x = np.linspace(-7, 10, N_SAMPLES)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 2, x.shape)
y = np.square(x) - 5 + noise
# test data
test_x = np.linspace(-7, 10, 200)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 2, test_x.shape)
test_y = np.square(test_x) - 5 + noise
train_x, train_y = torch.from_numpy(x).float(), torch.from_numpy(y).float()
test_x = torch.from_numpy(test_x).float()
test_y = torch.from_numpy(test_y).float()
train_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(train_x, train_y)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, num_workers=2,)
# show data
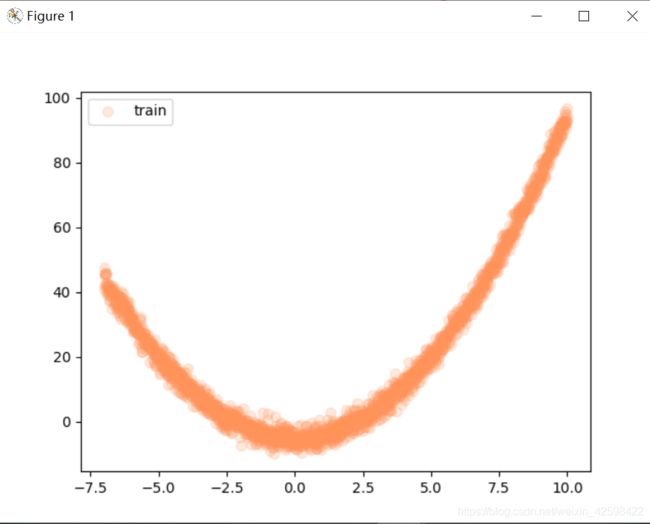
plt.scatter(train_x.numpy(), train_y.numpy(), c='#FF9359', s=50, alpha=0.2, label='train')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_normalization=False):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.do_bn = batch_normalization
self.fcs = []
self.bns = []
self.bn_input = nn.BatchNorm1d(1, momentum=0.5) # for input data
for i in range(N_HIDDEN): # build hidden layers and BN layers
input_size = 1 if i == 0 else 10
fc = nn.Linear(input_size, 10)
setattr(self, 'fc%i' % i, fc) # IMPORTANT set layer to the Module
self._set_init(fc) # parameters initialization
self.fcs.append(fc)
if self.do_bn:
bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(10, momentum=0.5)
setattr(self, 'bn%i' % i, bn) # IMPORTANT set layer to the Module
self.bns.append(bn)
self.predict = nn.Linear(10, 1) # output layer
self._set_init(self.predict) # parameters initialization
def _set_init(self, layer):
init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0., std=.1)
init.constant_(layer.bias, B_INIT)
def forward(self, x):
pre_activation = [x]
if self.do_bn: x = self.bn_input(x) # input batch normalization
layer_input = [x]
for i in range(N_HIDDEN):
x = self.fcs[i](x)
pre_activation.append(x)
if self.do_bn: x = self.bns[i](x) # batch normalization
x = ACTIVATION(x)
layer_input.append(x)
out = self.predict(x)
return out, layer_input, pre_activation
nets = [Net(batch_normalization=False), Net(batch_normalization=True)]
# print(*nets) # print net architecture
opts = [torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=LR) for net in nets]
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
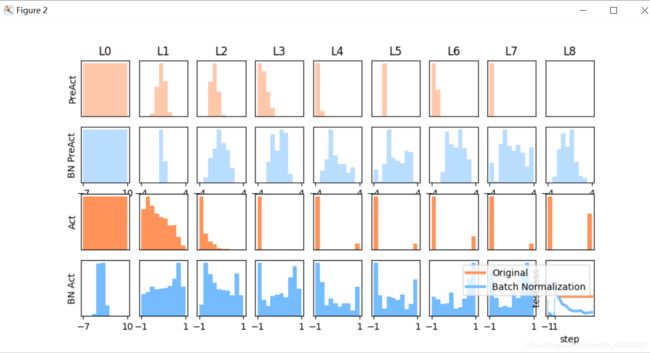
def plot_histogram(l_in, l_in_bn, pre_ac, pre_ac_bn):
for i, (ax_pa, ax_pa_bn, ax, ax_bn) in enumerate(zip(axs[0, :], axs[1, :], axs[2, :], axs[3, :])):
[a.clear() for a in [ax_pa, ax_pa_bn, ax, ax_bn]]
if i == 0:
p_range = (-7, 10);the_range = (-7, 10)
else:
p_range = (-4, 4);the_range = (-1, 1)
ax_pa.set_title('L' + str(i))
ax_pa.hist(pre_ac[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=p_range, color='#FF9359', alpha=0.5);ax_pa_bn.hist(pre_ac_bn[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=p_range, color='#74BCFF', alpha=0.5)
ax.hist(l_in[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=the_range, color='#FF9359');ax_bn.hist(l_in_bn[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=the_range, color='#74BCFF')
for a in [ax_pa, ax, ax_pa_bn, ax_bn]: a.set_yticks(());a.set_xticks(())
ax_pa_bn.set_xticks(p_range);ax_bn.set_xticks(the_range)
axs[0, 0].set_ylabel('PreAct');axs[1, 0].set_ylabel('BN PreAct');axs[2, 0].set_ylabel('Act');axs[3, 0].set_ylabel('BN Act')
plt.pause(0.01)
if __name__ == "__main__":
f, axs = plt.subplots(4, N_HIDDEN + 1, figsize=(10, 5))
plt.ion() # something about plotting
plt.show()
# training
losses = [[], []] # recode loss for two networks
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
print('Epoch: ', epoch)
layer_inputs, pre_acts = [], []
for net, l in zip(nets, losses):
net.eval() # set eval mode to fix moving_mean and moving_var
pred, layer_input, pre_act = net(test_x)
l.append(loss_func(pred, test_y).data.item())
layer_inputs.append(layer_input)
pre_acts.append(pre_act)
net.train() # free moving_mean and moving_var
plot_histogram(*layer_inputs, *pre_acts) # plot histogram
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader):
for net, opt in zip(nets, opts): # train for each network
pred, _, _ = net(b_x)
loss = loss_func(pred, b_y)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step() # it will also learns the parameters in Batch Normalization
plt.ioff()
# plot training loss
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(losses[0], c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='Original')
plt.plot(losses[1], c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='Batch Normalization')
plt.xlabel('step');plt.ylabel('test loss');plt.ylim((0, 2000));plt.legend(loc='best')
# evaluation
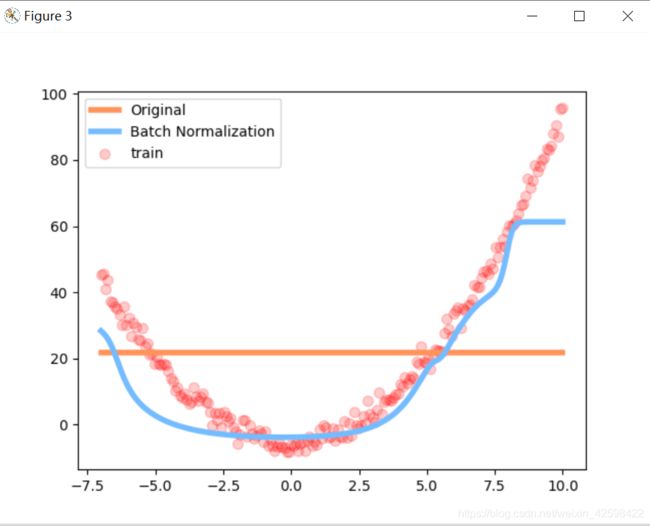
# set net to eval mode to freeze the parameters in batch normalization layers
[net.eval() for net in nets] # set eval mode to fix moving_mean and moving_var
preds = [net(test_x)[0] for net in nets]
plt.figure(3)
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), preds[0].data.numpy(), c='#FF9359', lw=4, label='Original')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), preds[1].data.numpy(), c='#74BCFF', lw=4, label='Batch Normalization')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), c='r', s=50, alpha=0.2, label='train')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()