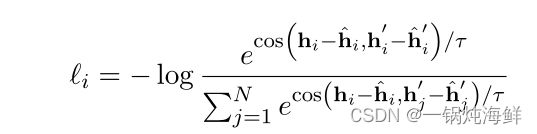PromptBERT: Improving BERT Sentence Embeddings with Prompts
这篇文章用Prompt减少偏差token偏差,传统的BERT输出的向量,在句子语义相似度方面的表现是不好的。作者发现原因主要由两点组成:static token embedding biases和ineffective layers,而不是high cosine similarity of the sentence embedding
NLP名词解释:各向异性(Anisotropic) - 知乎
论文里这一段其实也是他们论文中分析问题主要围绕的中心,这里面static token embedding biases,static token embedding是在bert结构中,输入进block前,通过embedding layer产生的结果,这里强调是静态的embedding,就是embedding metrics中每个token都唯一对应的embedding,是不随句子环境而变化的。(这个是我理解的,论文中没具体说,如果理解有错误请及时提醒我)。那这里产生的biases,其实就是一些外在因素产生的,比如token frequency,分词方法(WordPiece,BPE)会产生很多subwords,英文中字母的大小写,文本中的标签等等…… 这些都会导致embedding的bias。
至于ineffective layers就很好理解了,就是bert中堆叠的block结构,比如bert-base中的12层。作者是说这些结构,对语义相似度的表征这个方面是无效的。
还有他在这里强调原因不是high cosine similarity of the sentence embedding,我觉得是因为之前的文章,大家也都在讨论这个问题,而且把高余弦相似度当成产生bias的原因,这边文章是要区分这两个问题不是一回事。
另外声明他们提出了一种基于prompt生成句向量的一种方法,可以减少上文提到的bias和提升BERT layers的性能。
Prompt Based Contrastive Learning with Template Denoising
这里才是作者的贡献,前面部分基本是说别人的贡献(水了一堆),用了对比学习的思想
既然是对比学习,所以关键在于如何构建正例,作者是思路是用不同的templates去表征同一个句子,就像从不同的view去提取句子embedding,得到的结果互为正例。但这样做有一个问题,得到的句向量中是包含了template的信息的,所以要去做一个denoise的操作。
具体做法是比如对一个句子,先用两个template去表征这个句向量,可以得到 hi 和 hi′ ,然后为了denoise掉template的信息,将这两个template单独的输入进bert,但是输入时需要调整position id,加上句子的长度,就是使用和原来一样的position id,然后可以得到 hi¯ 和 hi¯′ ,再用刚才得到的结果减去这个结果,得到的 hi−hi¯ 和 hi′−hi¯′ 互为正例,就可以用对比学习的loss去优化了,公式如下
对比学习视频
Contrastive Learning(对比学习详解)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
下面是关于Prompt的一个情感分类的项目
import warnings
from datetime import datetime
import time
import torch
import os
from transformers import BertModel, BertConfig, BertModel, BertTokenizerFast, get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup, \
BertForMaskedLM
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data as Data
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# hyperparameters
EPOCH = 200
RANDOM_SEED = 2022
TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE = 32 # 小批训练, 批大小增大时需要提升学习率 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/413656738
TEST_BATCH_SIZE = 96 # 大批测试
EVAL_PERIOD = 20
MODEL_NAME = "bert-large-uncased" # bert-base-chinese
DATA_PATH = "data/Twitter2013"
MASK_POS = 3 # "it was [mask]" 中 [mask] 位置
train_file = "twitter-2013train-A.tsv"
dev_file = "twitter-2013dev-A.tsv"
test_file = "twitter-2013test-A.tsv"
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
writer = SummaryWriter('./tb_log')
'''
'''
pd.options.display.max_columns = None
pd.options.display.max_rows = None
prefix = 'It was [mask]. '
class Bert_Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bert_path, config_file):
super(Bert_Model, self).__init__()
self.bert = BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(bert_path, config=config_file) # 加载预训练模型权重
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask,
token_type_ids) # masked LM 输出的是 mask的值 对应的ids的概率 ,输出 会是词表大小,里面是概率 input_ids:输入文本在词典中的映射id,又称tokens token_type_ids:用来区分一条样本中的第一部分和第二部分,同样用0和1来区分。0表示第一部分,1表示第二部分。常用在句子预测、问答场景下。
# position_ids:在位置embedding中,每个输入序列tokens的位置索引。范围[0,config.max_position_embeddings - 1]。这个目前没有用到,没有研究。
logit = outputs[0] # 池化后的输出 [bs, config.hidden_size]
return logit
# 构建数据集
class MyDataSet(Data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, sen, mask, typ, label):
super(MyDataSet, self).__init__()
self.sen = torch.tensor(sen, dtype=torch.long)
self.mask = torch.tensor(mask, dtype=torch.long)
self.typ = torch.tensor(typ, dtype=torch.long)
self.label = torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
def __len__(self):
return self.sen.shape[0]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.sen[idx], self.mask[idx], self.typ[idx], self.label[idx]
# load data
def load_data(tsvpath):
data = pd.read_csv(tsvpath, sep="\t", header=None, names=["sn", "polarity", "text"])
data = data[data["polarity"] != "neutral"]
yy = data["polarity"].replace({"negative": 0, "positive": 1, "neutral": 2})
# print(data.loc[0:5,[0,1]]) #
# print(data.iloc[0:5,[1,1]]) #
# print(data.iloc[:,1:2]) #
# print(data.iloc[:,2:3]) #
return data.values[:, 2:3].tolist(), yy.tolist() # data.values[:,1:2].tolist()
tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
config = BertConfig.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
model = Bert_Model(bert_path=MODEL_NAME, config_file=config).to(device)
pos_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("good") # 9005
neg_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("bad") # 12139
# get the data and label
def ProcessData(filepath):
x_train, y_train = load_data(DATA_PATH + os.sep + filepath)
# x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(StrongData,StrongLabel,test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
Inputid = []
Labelid = []
typeid = []
attenmask = []
for i in range(len(x_train)):
text_ = prefix + x_train[i][0]
encode_dict = tokenizer.encode_plus(text_, max_length=60, padding="max_length", truncation=True)
input_ids = encode_dict["input_ids"]
type_ids = encode_dict["token_type_ids"]
atten_mask = encode_dict["attention_mask"]
labelid, inputid = input_ids[:], input_ids[:] #input_ids:输入文本在词典中的映射id
if y_train[i] == 0:
labelid[MASK_POS] = neg_id #bad的标签
labelid[:MASK_POS] = [-1] * len(labelid[:MASK_POS])#0-3
labelid[MASK_POS + 1:] = [-1] * len(labelid[MASK_POS + 1:])
inputid[MASK_POS] = tokenizer.mask_token_id
else:
labelid[MASK_POS] = pos_id#good的标签 #除了MASK_POS其他都是负一
labelid[:MASK_POS] = [-1] * len(labelid[:MASK_POS])
labelid[MASK_POS + 1:] = [-1] * len(labelid[MASK_POS + 1:])
inputid[MASK_POS] = tokenizer.mask_token_id
Labelid.append(labelid)#每句话的标签
Inputid.append(inputid)
typeid.append(type_ids)
attenmask.append(atten_mask)
return Inputid, Labelid, typeid, attenmask
Inputid_train, Labelid_train, typeids_train, inputnmask_train = ProcessData(train_file)
Inputid_dev, Labelid_dev, typeids_dev, inputnmask_dev = ProcessData(dev_file)
Inputid_test, Labelid_test, typeids_test, inputnmask_test = ProcessData(test_file)
train_dataset = Data.DataLoader(MyDataSet(Inputid_train, inputnmask_train, typeids_train, Labelid_train),
TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE, True)
valid_dataset = Data.DataLoader(MyDataSet(Inputid_dev, inputnmask_dev, typeids_dev, Labelid_dev), TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE,
True)
test_dataset = Data.DataLoader(MyDataSet(Inputid_test, inputnmask_test, typeids_test, Labelid_test), TEST_BATCH_SIZE,
True)
train_data_num = len(Inputid_train)
test_data_num = len(Inputid_test)
# print("hello!")
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5, weight_decay=1e-4) # 使用Adam优化器
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=-1)
EPOCH = 200
schedule = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, num_warmup_steps=len(train_dataset),
num_training_steps=EPOCH * len(train_dataset))
print("正在训练中。。。")
totaltime = 0
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
starttime_train = datetime.now()
start = time.time()
correct = 0
train_loss_sum = 0
model.train()
for idx, (ids, att_mask, type, y) in enumerate(train_dataset):
ids, att_mask, type, y = ids.to(device), att_mask.to(device), type.to(device), y.to(device)
out_train = model(ids, att_mask, type)
# print(out_train.view(-1, tokenizer.vocab_size).shape, y.view(-1).shape)
loss = loss_func(out_train.view(-1, tokenizer.vocab_size), y.view(-1)) #X.view(-1)中的-1本意是根据另外一个数来自动调整维度,但是这里只有一个维度,因此就会将X里面的所有维度数据转化成一维的,并且按先后顺序排列。
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
schedule.step()
train_loss_sum += loss.item()
if (idx + 1) % EVAL_PERIOD == 0:
print("Epoch {:04d} | Step {:06d}/{:06d} | Loss {:.4f} | Time {:.0f}".format(
epoch + 1, idx + 1, len(train_dataset), train_loss_sum / (idx + 1), time.time() - start))
writer.add_scalar('loss/train_loss', train_loss_sum / (idx + 1), epoch)
truelabel = y[:, MASK_POS]#保留第一维度所有元素 第二维度保留到MASK_POS维度就看他的标签
out_train_mask = out_train[:, MASK_POS, :] # 第一维度是ids,将该维度所有元素都保留 第二维度是att_mask 只保留到att_mask维度,第三个维度是type
predicted = torch.max(out_train_mask, 1)[1] #torch.max(input,dim)中 input是softmax函数输出的一个Tensor,dim是相应维度(i)中选出最大。
correct += (predicted == truelabel).sum()
correct = float(correct)
acc = float(correct / train_data_num)
eval_loss_sum = 0.0
model.eval()
correct_test = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for ids, att, tpe, y in test_dataset:
ids, att, tpe, y = ids.to(device), att.to(device), tpe.to(device), y.to(device)
out_test = model(ids, att, tpe)
loss_eval = loss_func(out_test.view(-1, tokenizer.vocab_size), y.view(-1))
eval_loss_sum += loss_eval.item()
ttruelabel = y[:, MASK_POS]
tout_train_mask = out_test[:, MASK_POS, :]
predicted_test = torch.max(tout_train_mask.data, 1)[1]
correct_test += (predicted_test == ttruelabel).sum()
correct_test = float(correct_test)
acc_test = float(correct_test / test_data_num)
if epoch % 1 == 0:
out = ("epoch {}, train_loss {}, train_acc {} , eval_loss {} ,acc_test {}"
.format(epoch + 1, train_loss_sum / (len(train_dataset)), acc, eval_loss_sum / (len(test_dataset)),
acc_test))
writer.add_scalar('loss/test_loss', train_loss_sum / (idx + 1), epoch)
print(out)
end = time.time()
print("epoch {} duration:".format(epoch + 1), end - start)
totaltime += end - start
print("total training time: ", totaltime)