AI实验——使用模拟退火局部搜索算法求解一个约束优化问题
一.实验内容
给定集合A,B。A是工料集合,B是产品集合,集合元素都是大于0的实数,代表工料和产品的长度,假设A,B各有m,n个元素,即有m个工料,需制作n个产品
实验要求将B中的每个产品映射到A中的工料,表示该产品由该工料制成,可以多对一映射,也就是一个工料可以制作多个产品
需满足的约束条件是:
![]()
也就是对于每一个工料,用其制作而成的产品长度之和不能超过该工料的长度
需满足的约束优化是:
使得 ![]() 最小
最小
也就是完成所有产品制作用到的工料的长度之和尽可能小
二.实验要求
给定一个输入文件 input.txt,格式举例如下:
4
3.5,6,9.2,10
3
1,2,4.5共4行:
第1行:工料个数 m
第2行:共 m 个值,代表各工料的长度
第3行:待制作产品个数 n
第4行:共 n 个值,代表待制作产品长度
用英文逗号隔开,m和n的最大值为200
编写代码,根据实验内容中的约束条件和约束优化,返回一个解,用以下格式写入输出文件 output.txt
共 n 行,每行3个值,第 i 行的第一个值是 B 中第 i 个产品的长度(从1开始),第二个值是该产品映射到的 A 中工料的下标(从1开始),第三个值是这个工料的长度,每行的值用英文逗号隔开
例如根据上述举例的 input.txt,应得到的 output.txt 格式为:
1,3,9.2
2,3,9.2
4.5,3,9.2三.实验步骤
1.实验思路
使用局部搜索算法求解CSP,初始状态应该每个变量赋值,每一次迭代为一个变量赋一个新的值,问题在于选择哪一个变量,选定变量后为该变量赋哪一个值
下图是一种经典的用局部搜索算法求解CSP的伪代码,该方法变量是随机选择的,选定变量后,选择能使冲突数最少化的那个值进行赋值,赋值完成后无条件更新状态
在本实验中,使用模拟退火搜索算法求解,每一次迭代,变量和变量的赋值的修改都是随机选取的,思路如下:
如果当前状态赋值不满足约束条件:
如果修改后的状态赋值满足约束条件:
更新状态
如果修改后的状态赋值也不满足约束条件:
如果修改后的状态不满足约束的工料个数更少:
更新状态
否则:
以指数下降的概率更新状态
如果当前状态赋值已经满足约束条件:
如果修改后的状态赋值不满足约束条件:
以指数下降的概率更新状态
如果修改后的状态赋值也满足约束条件:
如果修改后的状态赋值用到的工料长度更少:
更新状态
否则:
以指数下降的概率更新状态
总的来说,就是直接接受更好的状态,概率接受更差的状态
其中,以指数下降的概率更新状态是模拟退火算法的核心所在,算法允许接受更坏的状态,以逃离高原
下图是模拟退火搜索算法的伪代码
“以指数下降”通过模拟温度 T 的下降来实现,当 T 下降得足够慢时,算法找到全局最优解得概率逼近于1
2.实验代码
csp_solver.py
具体细节参见注释
import random
import math
from copy import deepcopy
#读取输入文件input.txt信息
outfile = open("test1_input.txt", 'r')
datalines = outfile.readlines()
material_num = eval(datalines[0].rstrip()) #工料数量
materials = [eval(i) for i in datalines[1].rstrip().split(',')] #各工料长度
product_num = eval(datalines[2].rstrip()) #产品数量
products = [eval(i) for i in datalines[3].rstrip().split(',')] #各产品长度
outfile.close()
def Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(assignment): #计算当前赋值下不满足约束的工料个数
global materials, products, material_num
res = 0
for meterial_index in range(material_num):
material_used_sum = 0
for product_index in assignment.keys():
if assignment[product_index] == meterial_index:
material_used_sum += products[product_index]
if material_used_sum > materials[meterial_index]:
res += 1
return res
def Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(assignment): #计算当前赋值下已使用的工料长度之和
global materials, material_num
material_used_length_sum = 0
for material_index in range(material_num):
for material_used_index in assignment.values():
if material_used_index == material_index:
material_used_length_sum += materials[material_index]
break
return material_used_length_sum
#目标赋值应该是在保证Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy的值为0的基础上,Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum的值尽可能小
def Random_Choose_Materials_Index(excluded_index): #从剔除下标为excluded_index的工料之后的所有工料中随机选择一个,返回其下标
global material_num #该函数用于Solve函数每次迭代更新赋值
while True:
chosen_index = random.randint(0, material_num-1)
if chosen_index != excluded_index:
break
return chosen_index
initial_assignment = {} #用字典表示产品和工料的下标映射关系,可以多对一
for product_index in range(product_num): #随机初始化
initial_assignment[product_index] = random.randint(0, material_num-1)
step_count = 0 #记录迭代的次数
def Solve(initial_assignment): #Solve函数:使用模拟退火算法求局部最优解
global products, materials, step_count
current_assignment = initial_assignment #初始赋值
Temperature = 100 #初始温度
while True:
if Temperature < 0.0000000001: #设置结束条件
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment) > 0: #如果仍有不满足的约束,则问题求解失败
print("Problem solving failed!")
return
return current_assignment
step_count += 1
Temperature = Temperature * 0.999 #模拟降温,每次迭代温度变为上次的0.999倍
random_key = random.randint(0, product_num-1) #从当前赋值中随机选择一个产品下标
random_values = Random_Choose_Materials_Index(current_assignment[random_key]) #随机选择将要修改的映射到的工料下标,用到了Random_Choose_Materials_Index函数
next_assignment = deepcopy(current_assignment)
next_assignment[random_key] = random_values
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment): #当前赋值不满足约束
if not Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment): #如果新的赋值满足约束,接受新的赋值
current_assignment = next_assignment
else: #如果新的赋值也不满足约束
delta_E1 = Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment) - Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment)
if delta_E1 < 0: #虽然不满足约束,但新的赋值Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy值更小,接受新的赋值
current_assignment = next_assignment
else: #新的赋值Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy值更大,概率接受新的赋值
probability1 = math.exp(-delta_E1 / Temperature)
if random.random() < probability1:
current_assignment = next_assignment
else:
continue
else: #当前赋值已经满足约束
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment): #如果新的赋值不满足约束,概率接受新的赋值
delta_E2 = Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment) - Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment)
probability2 = math.exp(-delta_E2 / Temperature)
if random.random() < probability2:
current_assignment = next_assignment
else:
continue
else: #如果新的赋值也满足约束
delta_E3 = Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(next_assignment) - Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(current_assignment)
if delta_E3 < 0: #如果新的赋值更优,也就是Calculate_Material_Used_Num的值更小,接受新的赋值
current_assignment = next_assignment
else: #如果新的赋值更差,也就是Calculate_Material_Used_Num的值更大,概率接受新的赋值
probability3 = math.exp(-delta_E3 / Temperature)
if random.random() < probability3:
current_assignment = next_assignment
else:
continue
solution = Solve(initial_assignment)
print("Total length of product: %f" % sum(products))
print("Total length of material used: %f" % Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(solution))
print("The utilization rate of material: %f" % (sum(products) / Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(solution)))
print("The number of iterations: %d" % step_count)
infile = open("test1_output.txt", 'w') #将solution信息写入output.txt
count_written_lines = 0
for product_index in solution.keys():
if count_written_lines == len(solution) - 1: #最后一行不加换行符
infile.write(str(products[product_index]) + ',' + str(solution[product_index]+1) + ',' + str(materials[solution[product_index]]))
count_written_lines += 1
else:
infile.write(str(products[product_index]) + ',' + str(solution[product_index]+1) + ',' + str(materials[solution[product_index]]) + '\n')
count_written_lines += 1
infile.close()这里提一个注意点:
产品和工料的映射应该写下标的映射关系,而不是元素(长度)的映射关系,因为有可能出现等长的工料或等长的产品,这样就会造成混乱
四.实验结果
使用如下随机生成 test_input.txt 的程序生成五个测试集进行测试,输入是想要生成的工料个数和产品个数,输出是实验要求中所述的格式的txt文件,可作为csp_solver.py的输入
generate_input_file.py
import random
materials_num = input("Please input number of materials: ")
products_num = input("Please input number of products: ")
infile = open("test1_input.txt", 'w')
infile.write(materials_num + '\n')
for __ in range(int(materials_num) - 1):
if random.random() < 0.1:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(1,10),1)) + ",")
elif random.random() > 0.1 and random.random() < 0.2:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(1,10))) + ",")
elif random.random() > 0.2 and random.random() < 0.6:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(10,20),1)) + ",")
else:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(10,20))) + ",")
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(1,20))) + '\n')
infile.write(products_num +'\n')
for __ in range(int(products_num) - 1):
if random.random() < 0.05:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(16,20),1)) + ",")
elif random.random() > 0.05 and random.random() < 0.1:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(16,20))) + ",")
elif random.random() > 0.1 and random.random() < 0.55:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(1,16),1)) + ",")
else:
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(1,16))) + ",")
infile.write(str(round(random.uniform(1,20))))
infile.close()注:该程序会小概率生成无解的情况,比如生成一个长度为20的产品,但没有长度为20的工料
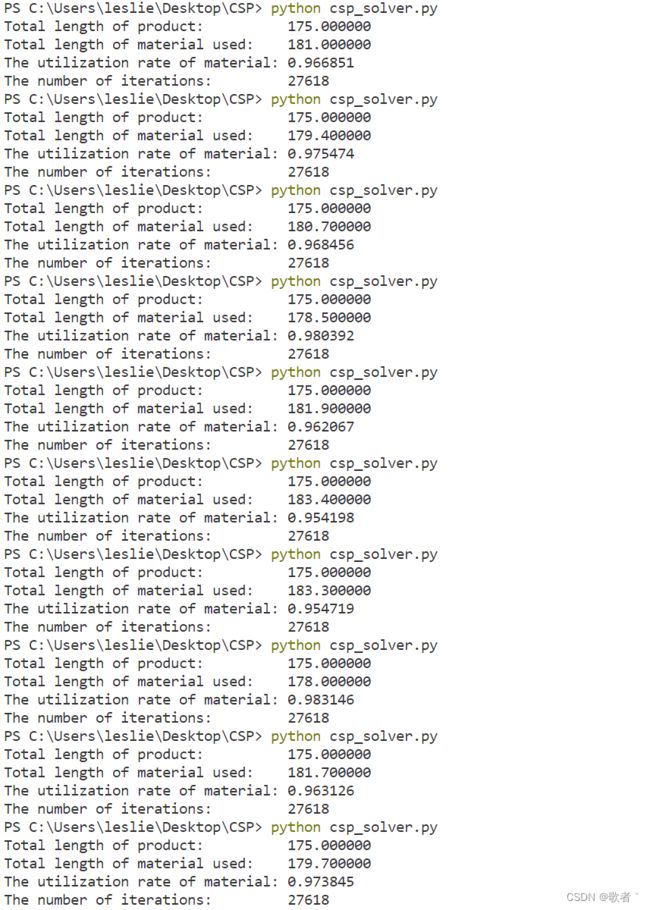
测试一: 40个工料,20个产品
test1_input.txt
40
12,15.4,14,7.9,19.5,13.6,16.8,11.0,19.1,13.7,4.3,10.1,18,13,11,4.1,7.1,11.8,9.8,15.7,12.0,14,16.2,15,1,11.9,4.4,19.6,6,18.9,5.2,14,15.6,11,14.1,18,6,5.0,18,6
20
9,3,5,5.1,10.1,8.9,13.4,17,4,12.6,3,3,7.9,11.2,15.8,18,1,14,6,7测试结果
运行10次结果如下,可以看到会陷入局部最优的情况
test1_output.txt(第以10次测试为例)
9,35,14.1
3,14,13
5,38,5.0
5.1,31,5.2
10.1,9,19.1
8.9,9,19.1
13.4,6,13.6
17,13,18
4,35,14.1
12.6,10,13.7
3,14,13
3,16,4.1
7.9,4,7.9
11.2,18,11.8
15.8,23,16.2
18,39,18
1,16,4.1
14,22,14
6,40,6
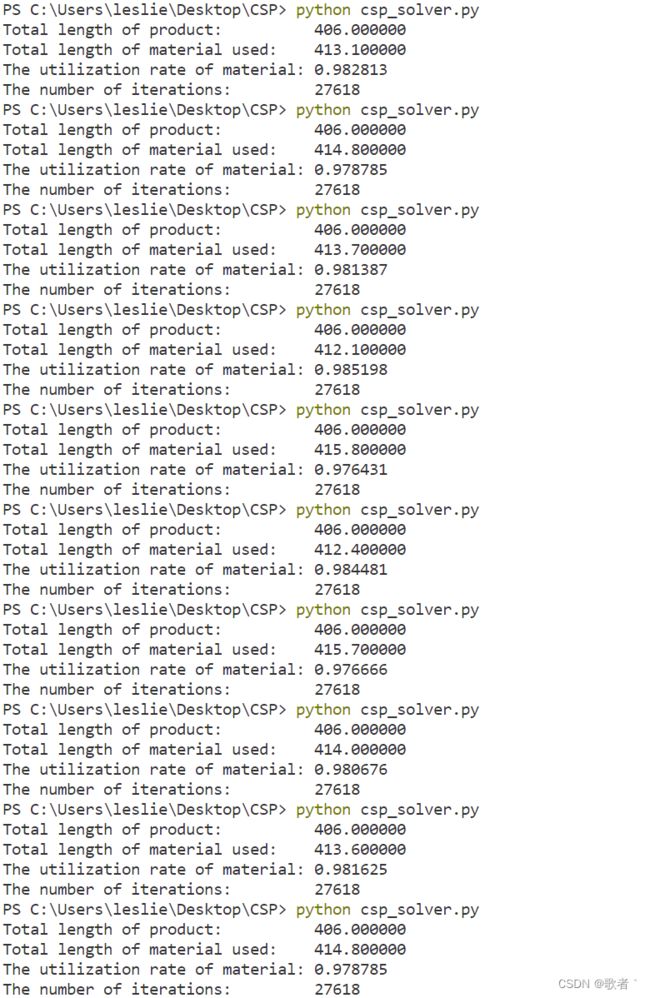
7,14,13测试二:80个工料,35个产品
test2_input.txt
80
16,12.0,17.7,10.2,17.7,17.7,18.4,12,11,19.0,11,10,11,17.9,18,15.1,17,20,12,10,16.4,6.7,11.8,11.0,3.8,9.9,13.9,17,2,18,18.0,5,10,7.8,14.4,19.8,11.5,14,14,15,18,14.9,12,5,16,2.5,13,5.2,2,11.4,12.0,15.2,20,19,13,13.9,18,11,15,12,3.3,15.9,20,15,19.5,8.6,14.4,14.6,11,8.8,8,11.9,4,20,12,19,14,14.0,3,4
35
13.4,18.4,14.5,12,9,15.4,15,15,20,9,16.3,6,11.5,17.7,16,4.5,12.9,15.4,4.4,17,4,7.3,5,18,2,19,18,8,10,3,6.3,12,11,12,7测试结果
test2_output.txt(第以10次测试为例)
13.4,27,13.9
18.4,7,18.4
14.5,68,14.6
12,51,12.0
9,20,10
15.4,62,15.9
15,6,17.7
15,64,15
20,63,20
9,26,9.9
16.3,21,16.4
6,65,19.5
11.5,37,11.5
17.7,3,17.7
16,1,16
4.5,78,14.0
12.9,55,13
15.4,45,16
4.4,24,11.0
17,17,17
4,65,19.5
7.3,34,7.8
5,24,11.0
18,30,18
2,6,17.7
19,54,19
18,57,18
8,65,19.5
10,33,10
3,78,14.0
6.3,78,14.0
12,8,12
11,11,11
12,19,12
7,71,8测试三:120个工料,50个产品
test3_input.txt
120
1,19,14.9,18,19,12.3,13,13.8,17.5,5.4,2.0,17,20,19,15,12.0,11,18.1,12,19.0,16,4.9,16,14,17,4,11.7,16,6,17.1,20.0,11,13,17,11.9,15.0,15,16.7,12,14,4.5,3,19.6,4,19,12,20,10.9,13.0,6,10,13.9,18,9,17,4,19.9,14.7,15,14,20,5.7,14,14,4,14,19.1,4,18.9,16.8,9,18,10.5,15.3,6,17.8,18,17.1,13,3,13.5,16.6,5.3,14.1,10.2,17.4,13.9,18.3,11,13,11,3,16,10.2,10,10.4,11.4,15.9,19.0,19.0,18,12,14.9,16,18,11.8,16,6,16,10,15.6,19.8,14.9,12.6,8,19.8,12,14.5,15.3,4
50
4.8,11.2,18.2,17.7,14.2,19,6,9,15,7.0,11,10.2,15,3.7,4.8,4.0,17.0,10,17.5,20,16.9,8,12,6.9,17,6,7,19.4,8,14,9.4,7,13,3,7,13,15.7,10.1,8,5,3.5,8,4.8,13,3.2,15,11,6.3,5,11测试结果
test3_output.txt(第以10次测试为例)
4.8,109,16
11.2,97,11.4
18.2,88,18.3
17.7,76,17.8
14.2,118,14.5
19,20,19.0
6,69,18.9
9,71,9
15,37,15
7.0,54,9
11,32,11
10.2,109,16
15,59,15
3.7,6,12.3
4.8,105,18
4.0,51,10
17.0,55,17
10,45,19
17.5,9,17.5
20,61,20
16.9,25,17
8,110,10
12,19,12
6.9,69,18.9
17,34,17
6,78,17.1
7,98,15.9
19.4,43,19.6
8,78,17.1
14,60,14
9.4,85,10.2
7,45,19
13,7,13
3,78,17.1
7,115,8
13,105,18
15.7,21,16
10.1,94,10.2
8,6,12.3
5,69,18.9
3.5,102,12
8,95,10
4.8,51,10
13,33,13
3.2,102,12
15,36,15.0
11,91,11
6.3,98,15.9
5,102,12
11,89,11测试四:160个产品,70个产品
test4_input.txt
160
18,18.2,16,14.2,13,13,11.8,12.5,10,13,13.5,11,11,13.5,17,18,1.2,12,12.3,14,12.9,15.3,18.8,13.9,12,17,19,11.2,12.7,7.9,1.6,19,3,9,19.0,11.5,7,19,18,16.9,14,15,13.8,4,19,11,11,8,6.0,13,10,8.7,11,3.4,19.6,13,12,18.5,1.8,3.0,19,12,16,18,16,11,10.7,19.4,15,5.6,18,20,19,14.0,19,12,6,1.1,7.1,3,19.9,8,12.0,11.0,17.2,6,9.5,19.1,4,20,15,3.6,12,16,10,11.2,9.0,17,1.7,19,6.0,19.2,4,15,13,5,15,16.4,18.7,16,4,1.0,4.8,16.8,15,10,15,2.0,1.7,16,10.7,6,8,12.8,8.4,8.4,16.5,14,19,12.9,19,10.7,19,19.2,15,20,20,6,6.6,11.3,12.4,11.8,19.7,18.1,12.7,16,6,6.3,16.9,13.4,18,19,19.1,2,11,14,12.0,12.8,7,17
70
19,1.4,10.7,16,13.1,13,7.2,12.5,4,5,19,18,10.1,12.5,9.0,5,12,4,1,15.7,1,1.9,15.6,12.6,1.8,7.5,2,2,2,7.7,5,10,13,5.1,6,10.9,9,1.7,14.5,15.6,14,1.5,12.8,5,8.9,15.2,12.3,2.2,18,15,15,7,13,10,6,13,2.3,9.8,1,6.1,2,17,17,7.3,18,10,20,10,2,2测试结果
test4_output.txt(第以10次测试为例)
19,129,19
1.4,3,16
10.7,67,10.7
16,65,16
13.1,150,13.4
13,105,13
7.2,121,10.7
12.5,8,12.5
4,89,4
5,106,5
19,45,19
18,16,18
10.1,96,11.2
12.5,145,12.7
9.0,115,15
5,37,7
12,57,12
4,3,16
1,2,18.2
15.7,63,16
1,96,11.2
1.9,53,11
15.6,2,18.2
12.6,114,16.8
1.8,114,16.8
7.5,30,7.9
2,110,16
2,37,7
2,11,13.5
7.7,9,10
5,72,20
10,95,10
13,72,20
5.1,11,13.5
6,115,15
10.9,66,11
9,53,11
1.7,72,20
14.5,151,18
15.6,146,16
14,128,14
1.5,151,18
12.8,124,12.8
5,26,17
8.9,34,9
15.2,22,15.3
12.3,19,12.3
2.2,3,16
18,71,18
15,104,15
15,117,15
7,3,16
13,5,13
10,26,17
6,110,16
13,6,13
2.3,114,16.8
9.8,116,10
1,13,11
6.1,11,13.5
2,121,10.7
17,15,17
17,160,17
7.3,110,16
18,1,18
10,13,11
20,137,20
10,51,10
2,151,18
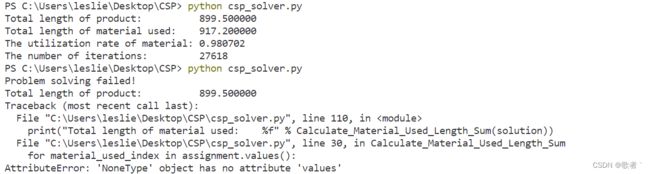
2,9,10测试五:200个工料,90个产品
test5_input.txt
200
14,16.7,19,16.7,9,11.8,10.9,10,4,17,12.5,12.8,6.0,12,14.1,10.2,17.4,16.0,10.5,2.5,16,7,19.3,15,3.2,5.6,2,11,20,16,19.2,19.4,19.4,13,14,17,8.1,9.5,11.4,15,7.8,7,15,15.4,19,7,18,5,16.9,13.6,2,18.4,18.2,15,3,15,14,14.3,5.8,10.8,10,16,16,14,17.9,15.2,19,18,19.4,5,14,8.6,4,9,13.7,7,18,7.3,9,17,13,19.1,10.6,14,4,18.1,15,9,3.9,3,5.6,10.6,6.7,10,16,18,17.0,11,8.4,7,12.1,1,5,17.1,13.5,20,18,19,12.7,12,12,2.2,12.3,10,16,5,17,14,16.8,19,19,16,13,19,2,15.9,12.1,14.4,17.2,13,3,2,13.7,15.4,17.5,10.6,16.1,5,3,14.2,20,16,1.1,14,4,13.8,16.4,17.9,19.2,16.6,19,15,15,13.2,16,2,19,1.2,17,9.4,12,15.9,11.4,20,12,15.8,10.9,10.4,14.0,5.5,16,7.9,17.6,11.5,2,20,17.7,19,8.1,13,17,18,18,17,11,1.6,15.5,14,11,8.8,14,10.5,5.9,19.5,4,5,7.3,1.8,5.9,6
90
19,6.8,9,15,12.0,6,3.4,5,9.5,7,19,6,16.2,13,19.6,12.8,6,5,17,17,12,10,9.7,10,16,11.0,11.5,15.6,12.3,2.9,4.4,2,1.5,4.6,10,5.2,8.0,12,8,14,14.8,16.8,19.1,8.0,2.4,7,4.3,12,6.6,7,15,10,4.2,7,9,19,12.6,7.3,5.1,6,9,2.1,1.5,14.1,12.1,11.8,6,19,4,19.4,7,5.0,15.5,9.0,2,7,17.5,3.3,17,6.0,12.3,12,7,13.0,12,18.4,2,10.3,11,15测试结果
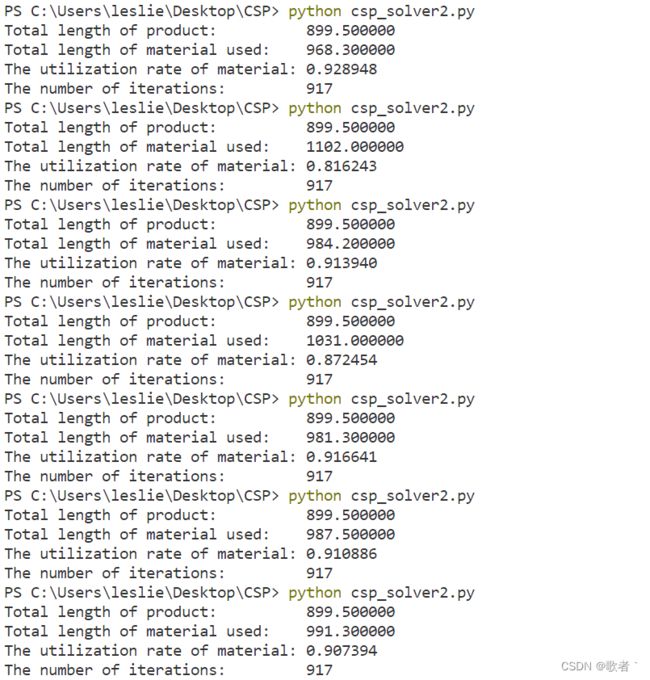
迭代20000多次会出现还不满足约束的情况,这也体现出随着问题规模增大,随机法更新赋值的劣势,增加到40000多次偶尔也会求不出解,但到50000多次就基本不会了
如下图所示
test5_output.txt(第以10次测试为例)
19,45,19
6.8,155,16
9,4,16.7
15,152,15
12.0,161,12
6,200,6
3.4,128,14.4
5,155,16
9.5,80,17
7,171,16
19,121,19
6,72,8.6
16.2,150,16.6
13,34,13
19.6,164,20
12.8,130,13
6,173,17.6
5,81,13
17,181,17
17,184,17
12,14,12
10,31,19.2
9.7,173,17.6
10,61,10
16,62,16
11.0,128,14.4
11.5,174,11.5
15.6,166,15.8
12.3,97,17.0
2.9,37,8.1
4.4,97,17.0
2,72,8.6
1.5,173,17.6
4.6,31,19.2
10,94,10
5.2,189,11
8.0,56,15
12,110,12
8,98,11
14,64,14
14.8,43,15
16.8,119,16.8
19.1,82,19.1
8.0,16,10.2
2.4,155,16
7,78,7.3
4.3,37,8.1
12,165,12
6.6,81,13
7,4,16.7
15,153,15
10,8,10
4.2,31,19.2
7,115,16
9,171,16
19,108,19
12.6,12,12.8
7.3,115,16
5.1,189,11
6,80,17
9,5,9
2.1,24,15
1.5,80,17
14.1,140,14.2
12.1,11,12.5
11.8,6,11.8
6,13,6.0
19,3,19
4,145,4
19.4,33,19.4
7,22,7
5.0,70,5
15.5,187,15.5
9.0,74,9
2,16,10.2
7,42,7
17.5,177,17.7
3.3,141,20
17,10,17
6.0,56,15
12.3,24,15
12,113,12.3
7,76,7
13.0,180,13
12,101,12.1
18.4,52,18.4
2,98,11
10.3,168,10.4
11,28,11
15,141,20五.拓展
问题
针对测试五中发现的随机法对于大规模数据的劣势,我修改了一下生成初始赋值和更新赋值的方法,如下:
def Get_Initial_Assignment():
while True:
initial_assignment = {} #用字典表示产品和工料的下标映射关系,可以多对一
for product_index in range(product_num): #随机初始化
initial_assignment[product_index] = random.randint(0, material_num-1)
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(initial_assignment) <= material_num / 10:
break
return initial_assignment生成初始赋值的Get_Initial_Assignment函数不停地获取随机初始赋值,直到获取一个不满足约束的工料数在总工料数的1/10以内的赋值,才接受它
def Get_Next_Assignment(current_assignment):
optional_material_index = []
random_product_index = random.randint(0, product_num-1)
for material_index in range(material_num):
if material_index != current_assignment[random_product_index]: #只找改动的
available_remaining_length = materials[material_index] #除去随机选中的产品对应那个工料,记录每一个工料的可用长度
for product_index in current_assignment.keys():
if current_assignment[product_index] == material_index:
available_remaining_length -= products[product_index]
if available_remaining_length >= products[random_product_index]:
optional_material_index.append(material_index)
if len(optional_material_index) > 0: #从可用的工料中随机选一个更新
random_material_index = random.choice(optional_material_index)
else: #如果没有可用的工料,就随机选
random_material_index = Random_Choose_Materials_Index(current_assignment[random_product_index])
next_assignment = deepcopy(current_assignment)
next_assignment[random_product_index] = random_material_index
return next_assignment更新赋值的函数Get_Next_Assignment函数优先选择可用的工料(即剩余长度大于要更新的那个产品长度的工料),这样能基本保证每一次更新赋值不满足约束的工料数不增加
二者结合,应该能大大降低使约束满足的最少迭代次数
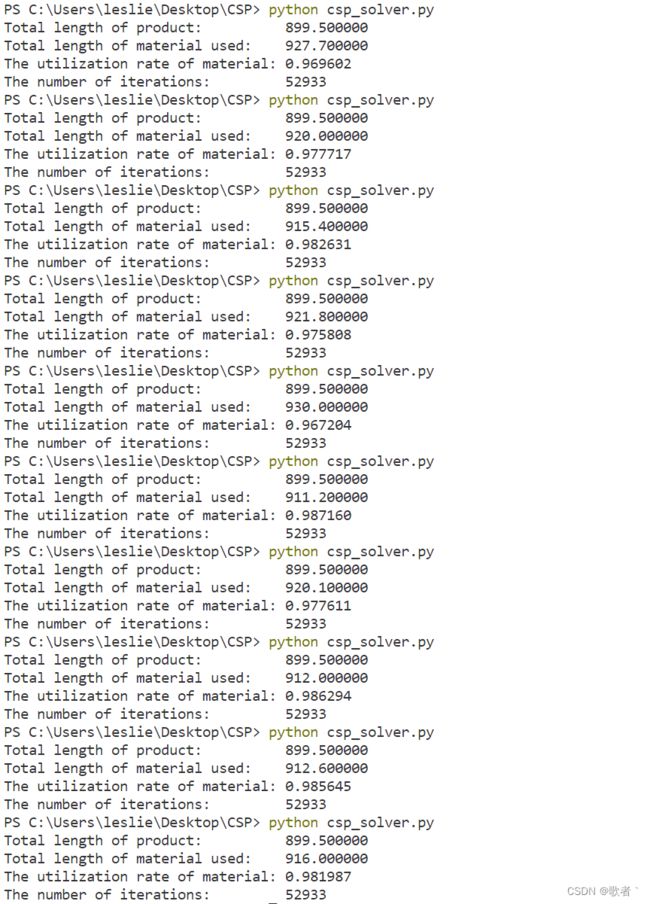
实验验证如下
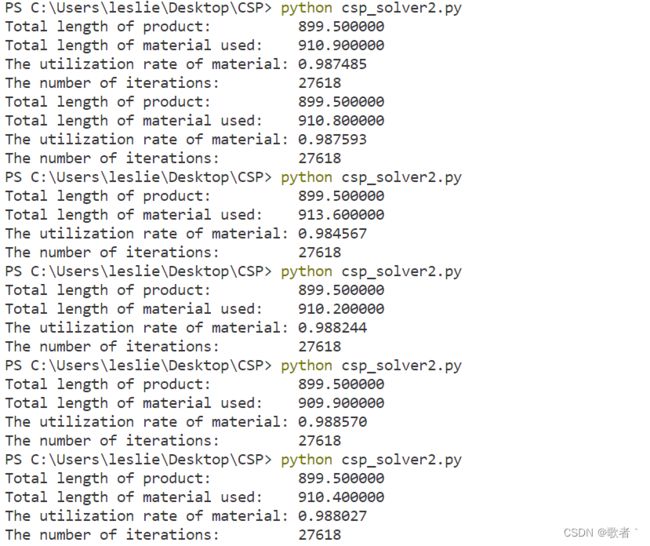
可以看到,只需迭代900次就基本能对测试集五稳定地求解约束满足问题了,只不过约束优化不够好
但随着迭代次数增加,约束优化的效果越来越好,下面用同样的27618次和随机法作比较,可以看到约束优化效果更优,而且波动更小(基本保持在910左右)
但此法也有一个缺点,就是获取满足要求的初始化赋值可能会花费很长时间,这时只需适当降低要求即可(比如将1/10增大到1/5)
附:csp_solver2.py
import random
import math
from copy import deepcopy
#读取输入文件input.txt信息
outfile = open("test5_input.txt", 'r')
datalines = outfile.readlines()
material_num = eval(datalines[0].rstrip()) #工料数量
materials = [eval(i) for i in datalines[1].rstrip().split(',')] #各工料长度
product_num = eval(datalines[2].rstrip()) #产品数量
products = [eval(i) for i in datalines[3].rstrip().split(',')] #各产品长度
outfile.close()
def Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(assignment): #计算当前赋值下不满足约束的工料个数
global materials, products, material_num
res = 0
for meterial_index in range(material_num):
material_used_sum = 0
for product_index in assignment.keys():
if assignment[product_index] == meterial_index:
material_used_sum += products[product_index]
if material_used_sum > materials[meterial_index]:
res += 1
return res
def Get_Initial_Assignment():
while True:
initial_assignment = {} #用字典表示产品和工料的下标映射关系,可以多对一
for product_index in range(product_num): #随机初始化
initial_assignment[product_index] = random.randint(0, material_num-1)
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(initial_assignment) <= material_num / 10:
break
return initial_assignment
def Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(assignment): #计算当前赋值下已使用的工料长度
global materials, material_num
material_used_length_sum = 0
for material_index in range(material_num):
for material_used_index in assignment.values():
if material_used_index == material_index:
material_used_length_sum += materials[material_index]
break
return material_used_length_sum
#目标赋值应该是在保证Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy的值为0的基础上,Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum的值尽可能小
def Random_Choose_Materials_Index(excluded_index): #从剔除下标为excluded_index的工料之后的所有工料中随机选择一个,返回其下标
global material_num #该函数用于Solve函数每次迭代更新赋值
while True:
chosen_index = random.randint(0, material_num-1)
if chosen_index != excluded_index:
break
return chosen_index
def Get_Next_Assignment(current_assignment):
optional_material_index = []
random_product_index = random.randint(0, product_num-1)
for material_index in range(material_num):
if material_index != current_assignment[random_product_index]: #只找改动的
available_remaining_length = materials[material_index] #除去随机选中的产品对应那个工料,记录每一个工料的可用长度
for product_index in current_assignment.keys():
if current_assignment[product_index] == material_index:
available_remaining_length -= products[product_index]
if available_remaining_length >= products[random_product_index]:
optional_material_index.append(material_index)
if len(optional_material_index) > 0: #从可用的工料中随机选一个更新
random_material_index = random.choice(optional_material_index)
else: #如果没有可用的工料,就随机选
random_material_index = Random_Choose_Materials_Index(current_assignment[random_product_index])
next_assignment = deepcopy(current_assignment)
next_assignment[random_product_index] = random_material_index
return next_assignment
initial_assignment = Get_Initial_Assignment()
step_count = 0 #记录迭代的次数
def Solve(initial_assignment): #Solve函数:使用模拟退火算法求局部最优解
global products, materials, step_count
current_assignment = initial_assignment #初始赋值
Temperature = 100 #初始温度
while True:
if Temperature < 0.0000000001:
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment) > 0: #如果仍有不满足的约束,则问题求解失败
print("Problem solving failed!")
return
return current_assignment
step_count += 1
Temperature = Temperature * 0.999 #模拟降温,每次迭代温度变为上次的0.999倍
next_assignment = Get_Next_Assignment(current_assignment)
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment): #当前赋值不满足约束
if not Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment): #如果新的赋值满足约束,接受新的赋值
current_assignment = next_assignment
else: #如果新的赋值也不满足约束
delta_E1 = Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment) - Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment)
if delta_E1 < 0: #虽然不满足约束,但新的赋值Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy值更小,接受新的赋值
current_assignment = next_assignment
else: #新的赋值Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy值更大,概率接受新的赋值
probability1 = math.exp(-delta_E1 / Temperature)
if random.random() < probability1:
current_assignment = next_assignment
else:
continue
else: #当前赋值已经满足约束
if Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment): #如果新的赋值不满足约束,概率接受新的赋值
delta_E2 = Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(next_assignment) - Calculate_Constraint_Not_Satisfy(current_assignment)
probability2 = math.exp(-delta_E2 / Temperature)
if random.random() < probability2:
current_assignment = next_assignment
else:
continue
else: #如果新的赋值也满足约束
delta_E3 = Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(next_assignment) - Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(current_assignment)
if delta_E3 < 0: #如果新的赋值更优,也就是Calculate_Material_Used_Num的值更小,接受新的赋值
current_assignment = next_assignment
else: #如果新的赋值更差,也就是Calculate_Material_Used_Num的值更大,概率接受新的赋值
probability3 = math.exp(-delta_E3 / Temperature)
if random.random() < probability3:
current_assignment = next_assignment
else:
continue
solution = Solve(initial_assignment)
print("Total length of product: %f" % sum(products))
print("Total length of material used: %f" % Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(solution))
print("The utilization rate of material: %f" % (sum(products) / Calculate_Material_Used_Length_Sum(solution)))
print("The number of iterations: %d" % step_count)
infile = open("test5_output.txt", 'w') #将solution信息写入output.txt
count_written_lines = 0
for product_index in solution.keys():
if count_written_lines == len(solution) - 1: #最后一行不加换行符
infile.write(str(products[product_index]) + ',' + str(solution[product_index]+1) + ',' + str(materials[solution[product_index]]))
count_written_lines += 1
else:
infile.write(str(products[product_index]) + ',' + str(solution[product_index]+1) + ',' + str(materials[solution[product_index]]) + '\n')
count_written_lines += 1
infile.close()