GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations 从廉价的操作中获取更多的特征
论文代码: https://github.com/huawei-noah/ghostnet.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11907
ghostnet是华为在2020年提出的一种网络结构,简单的来说就是利用比较小的计算量来获取特征层的相似的特征图,可以看下面的图,(对ResNet-50中第一个残差组生成的一些特征图进行可视化,其中三个相似的特征图对示例用相同颜色的框进行注释。通过廉价的操作(用扳手表示)转换另一个特征图,可以大致获得这对特征图中的一个。 )
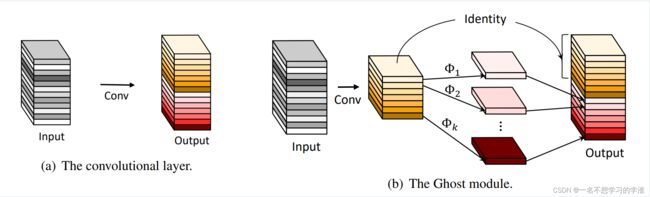
意思就是说,现在很多其他网络结构都是在通过蒸馏等一些方法减小计算量,但是相似的特征图依然存在,并且没有利用好这样的潜在发现,而华为这方面觉的这个相似的特征图是有利用价值的,所以创建了一个网络结构来生成这样的相似特征图,名字叫Ghost模块,你可以将这个模块等价与一个卷积块。如下图可以看的更加清楚:
可以看到,左边是普通的卷积模块,右边是提出的ghost模块,步骤就是,1、利用1x1卷积获得输入特征的必要特征浓缩。2、利用深度可分离卷积获得特征浓缩的相似特征图(Ghost)。3.将两者在通道上进行拼接达到想要的效果。
类似残差网络的残差块,ghost网络也有残差块,如下图,如果步长为1,那么特征图大小不变,如果步长为2,那么特征图大小减半,并且在残差边也会进行相应的卷积操作,以此能够进行相加 操作,这部分大家需要知道的。
下面就是整体的网络结构,当然这里应用了通道注意力机制,和mobilenet的是差不多的,思想就是在特征层的通道中先池化再全连接再全连接再sigmoid()再和输入的通道相乘得到相应的通道注意力机制。注意:在这个整体结构中的exp表示ghostnet每个残差块中的第一个ghost模块的输出通道数。
下面是代码部分,大家可以参考,然后应用到分类或者目标检测任务中,也可以在github中下载。最后祝大家学有所成!
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import torch.nn.functional as F
__all__ = ['ghost_net']#作用和就是在被调用的时候,只能够调用ghost_net这个类
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):#为了变成8 的整数倍,有利于硬件的加持
"""
This function is taken from the original tf repo.
It ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8
It can be seen here:
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/mobilenet/mobilenet.py
"""
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
# class SELayer(nn.Module):
# def __init__(self, channel, reduction=4):
# super(SELayer, self).__init__()
# self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
# self.fc = nn.Sequential(
# nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction),
# nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel), )
#
# def forward(self, x):
# b, c, _, _ = x.size()
# y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
# y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
# y = torch.clamp(y, 0, 1)
# return x * y
class SELayer(nn.Module):#注意力机制
def __init__(self, input_c: int, squeeze_factor: int = 4):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
squeeze_c = _make_divisible(input_c // squeeze_factor, 8)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(input_c, squeeze_c, 1)
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_c, input_c, 1)
def forward(self, x):
scale = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, output_size=(1, 1))
scale = self.fc1(scale)
scale = F.relu(scale, inplace=True)
scale = self.fc2(scale)
scale = F.hardsigmoid(scale, inplace=True)
return scale * x
def depthwise_conv(inp, oup, kernel_size=3, stride=1, relu=False):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, groups=inp, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)
new_channels = self.oup-init_channels
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, hidden_dim, oup, kernel_size, stride, use_se):
super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()
if stride not in [1, 2]:
print("输入的步长错误!")
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# pw
GhostModule(inp, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1, relu=True),
# dw
depthwise_conv(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, stride, relu=False) if stride==2 else nn.Sequential(),
#如果步长为2 就代表是需要进行降低特征图大小
# Squeeze-and-Excite
SELayer(hidden_dim) if use_se else nn.Sequential(),
# pw-linear
GhostModule(hidden_dim, oup, kernel_size=1, relu=False),
)
if stride == 1 and inp == oup:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
else:#由于特征图降低,所以残差边就也需要进行降低特征图大小,这个部分在原论文中的图中不能体现,但是大家必须要知道
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
depthwise_conv(inp, inp, kernel_size, stride, relu=False),
nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x) + self.shortcut(x)
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfgs, num_classes=1000, width_mult=1.):
super(GhostNet, self).__init__()
# setting of inverted residual blocks
self.cfgs = cfgs
# building first layer
output_channel = _make_divisible(16 * width_mult, 4)
layers = [nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, output_channel, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channel),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)]
input_channel = output_channel
# building inverted residual blocks
block = GhostBottleneck
for k, exp_size, c, use_se, s in self.cfgs:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, 4)
hidden_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width_mult, 4)
layers.append(block(input_channel, hidden_channel, output_channel, k, s, use_se))
input_channel = output_channel
self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
# building last several layers
output_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width_mult, 4)
self.squeeze = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channel, output_channel, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channel),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
)
input_channel = output_channel
output_channel = 1280
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_channel, output_channel, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm1d(output_channel),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes),
)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.squeeze(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def ghost_net(**kwargs):
"""
Constructs a GhostNet model
"""
cfgs = [
# k, t, c, SE, s
[3, 16, 16, 0, 1],
[3, 48, 24, 0, 2],
[3, 72, 24, 0, 1],
[5, 72, 40, 1, 2],
[5, 120, 40, 1, 1],
[3, 240, 80, 0, 2],
[3, 200, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 480, 112, 1, 1],
[3, 672, 112, 1, 1],
[5, 672, 160, 1, 2],
[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 1, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 1, 1]
]
return GhostNet(cfgs, **kwargs)
if __name__=='__main__':
model = ghost_net()
model.eval()
print(model)
input = torch.randn(32,3,224,224)
y = model(input)
print(y)