基于蛙跳算法求解简单调度问题附matlab代码
✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击
智能优化算法 神经网络预测 雷达通信 无线传感器
信号处理 图像处理 路径规划 元胞自动机 无人机 电力系统
⛄ 内容介绍
混合蛙跳算法(Shuffled Frog Leaping Algorithm)是根据青蛙在石块上觅食时的种群分布变化而提出的算法。算法提出于2003年,时间有点久远,但相关的论文并不是特别多,仍有较大的研究和改进空间。
混合蛙跳算法( SFLA) 是一种受自然生物模仿启示而产生的基于群体的协同搜索方法。这种算法模拟青蛙群体寻找食物时,按族群分类进行思想传递的过程,将全局信息交换和局部深度搜索相结合,局部搜索使得思想在局部个体间传递,混合策略使得局部间的思想得到交换。在混合蛙跳算法中,群体( 解集) 由一群具有相同结构的青蛙( 解) 组成。整个群体被分为多个子群,不同的子群被认为是具有不同思想的青蛙的集合。子群中青蛙按照一定策略执行解空间中的局部深度搜索。在已定义的局部搜索迭代次数结束之后,思想在混合过程中进行了交换。局部搜索和混合过程一直持续到定义的收敛条件结束为止。全局信息交换和局部深度搜索的平衡策略使得算法能够跳出局部极值点,向着全局最优的方向进行,这也成为混合蛙跳算法最主要的特点.
⛄ 部分代码
%% Simple Scheduling Problem by Shuffled Frog Leaping Algorithm (SFLA)
% here are 10 jobs or tasks which should be finished in time.
% In "CreateModel.m" file:
% p is process time for jobs
% s is setup time matrix (spaces between boxes in plot)
% d is jobs due
% You can change them.
% q is order of jobs
% ST is start time
% FT is finish time
% z is final cost and Cmax must be equal with it or it is a violation.
%%------------------------------------------------------------------
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% Problem
model=CreateModel();
CostFunction=@(s) MyCost(s,model); % Cost Function
nVar=model.n; % Number of Decision Variables
VarSize=[1 nVar]; % Decision Variables Matrix Size
VarMin=0; % Lower Bound of Variables
VarMax=1; % Upper Bound of Variables
%% SFLA Parameters
MaxIt = 100; % Maximum Number of Iterations
nPopMemeplex = 5; % Memeplex Size
nPopMemeplex = max(nPopMemeplex, nVar+1); % Nelder-Mead Standard
nMemeplex = 5; % Number of Memeplexes
nPop = nMemeplex*nPopMemeplex; % Population Size
I = reshape(1:nPop, nMemeplex, []);
% FLA Parameters
fla_params.q = max(round(0.3*nPopMemeplex), 2); % Number of Parents
fla_params.alpha = 3; % Number of Offsprings
fla_params.beta = 5; % Maximum Number of Iterations
fla_params.sigma = 2; % Step Size
fla_params.CostFunction = CostFunction;
fla_params.VarMin = VarMin;
fla_params.VarMax = VarMax;
%% Initialization
% Empty Individual Template
empty_individual.Position = [];
empty_individual.Cost = [];
empty_individual.Sol = [];
% Initialize Population Array
pop = repmat(empty_individual, nPop, 1);
% Initialize Population Members
for i = 1:nPop
pop(i).Position = unifrnd(VarMin, VarMax, VarSize);
[pop(i).Cost pop(i).Sol] = CostFunction(pop(i).Position);
end
% Sort Population
pop = SortPopulation(pop);
% Update Best Solution Ever Found
BestSol = pop(1);
% Initialize Best Costs Record Array
BestCosts = nan(MaxIt, 1);
%% SFLA Main Loop
for it = 1:MaxIt
fla_params.BestSol = BestSol;
% Initialize Memeplexes Array
Memeplex = cell(nMemeplex, 1);
% Form Memeplexes and Run FLA
for j = 1:nMemeplex
% Memeplex Formation
Memeplex{j} = pop(I(j, :));
% Run FLA
Memeplex{j} = RunFLA(Memeplex{j}, fla_params);
% Insert Updated Memeplex into Population
pop(I(j, :)) = Memeplex{j};
end
% Sort Population
pop = SortPopulation(pop);
% Update Best Solution Ever Found
BestSol = pop(1);
% Store Best Cost Ever Found
BestCosts(it) = BestSol.Cost;
% Show Iteration Information
disp(['Iteration ' num2str(it) ': Best Cost = ' num2str(BestCosts(it))]);
% Plot Best Solution
figure(1);
PlotSolution(BestSol.Sol,model);
end
%% Results
figure;
plot(BestCosts,'k', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('ITR');
ylabel('Cost Value');
ax = gca;
ax.FontSize = 14;
ax.FontWeight='bold';
set(gca,'Color','[0.9 0.8 0.7]')
grid on;
%
BestSol.Sol
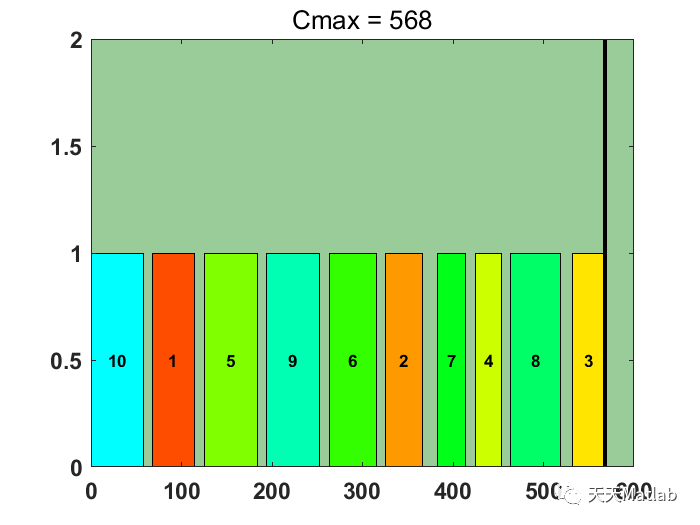
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
[1]贾美琪. 改进蛙跳算法求解变工时排产优化问题[D]. 沈阳建筑大学, 2019.
[2]王一凡. 基于混合蛙跳算法的半主动悬架LQG控制器设计[J]. 时代汽车, 2018(10):5.
⛄ Matlab代码关注
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料