知识蒸馏——pytorch实现
轻量化网络
知识蒸馏可以理解为轻量化网络的一个tricks,轻量化网络是深度学习的一个大的发展趋势,尤其是在移动端,终端边缘计算这种对算力和运算时间有要求的场景中。
轻量化网络可以有以下四种方式实现:
1.压缩已经训练好的模型: 知识蒸馏,权值量化,剪枝,注意力迁移
2.直接训练轻量化网络:SqueezeNet,MobileNet等
3.加速卷积运算:低秩分解
4.硬件部署:Tensorrt,Jetson,Openvino等
知识蒸馏
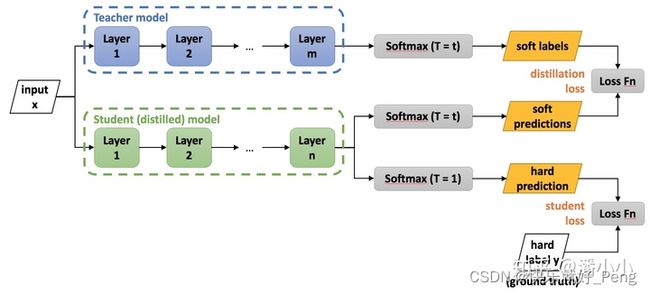
知识蒸馏在轻量化网络方面具有很高的地位。下图是知识蒸馏的实现过程。
导入包
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchinfo import summary
from tqdm import tqdm
#设置随机数种子,便于复现
torch.manual_seed(0)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 使用cudnn加速卷积运算
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
载入MNIST数据集
from torchvision.transforms.transforms import ToTensor
# 载入训练集
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root = 'dataset/',
train = True,
transform = transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
# 生成测试集
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root = 'dataset/',
train = False,
transform = transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
# 生成dataloader
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,batch_size=32,shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset,batch_size=32,shuffle=True)
构建教师模型
class TeacherModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels=1,num_classes=10):
super(TeacherModel,self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784,1200)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1200,1200)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(1200,num_classes)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
def forward(self,x):
x = x.view(-1,784)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
训练教师模型
model = TeacherModel()
model = model.to(device)
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=1e-4)
epochs = 6
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
# 在训练集上训练
for data, targets in tqdm(train_dataloader):
data = data.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
# 前向预测
preds = model(data)
loss = criterion(preds,targets)
# 反向传播,优化权重
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 在测试集上评估性能
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x,y in test_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions==y).sum()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = (num_correct/num_samples).item()
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t Accuracy:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1,acc))
教师模型预测结果
创建学生模型
class StudentModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels=1,num_classes=10):
super(StudentModel,self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784,20)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(20,20)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(20,num_classes)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
def forward(self,x):
x = x.view(-1,784)
x = self.fc1(x)
# x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
# x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
训练学生模型
model = StudentModel()
model = model.to(device)
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=1e-4)
epochs = 6
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
# 在训练集上训练
for data, targets in tqdm(train_dataloader):
data = data.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
# 前向预测
preds = model(data)
loss = criterion(preds,targets)
# 反向传播,优化权重
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 在测试集上评估性能
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x,y in test_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions==y).sum()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = (num_correct/num_samples).item()
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t Accuracy:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1,acc))
学生模型预测结果

学生模型由于比教师模型更加轻量化(教师模型的隐藏层有1200个神经元,学生模型的只有20个神经元),所以性能并不如教师模型
student_model_scratch = model
知识蒸馏训练模型
# 准备预训练好的教师模型
teacher_model.eval()
# 准备新的学生模型
model = StudentModel()
model = model.to(device)
model.train()
# 蒸馏温度
temp = 7
# hard_loss
hard_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# hard_loss权重
alpha = 0.3
# soft_loss
soft_loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='batchmean')
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=1e-4)
epochs = 10
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 训练集上训练模型权重
for data,targets in tqdm(train_dataloader):
data = data.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
# 教师模型预测
with torch.no_grad():
teachers_preds = teacher_model(data)
# 学生模型预测
students_preds = model(data)
# 计算hard_loss
students_loss = hard_loss(students_preds,targets)
# 计算蒸馏后的预测结果及soft_loss
ditillation_loss = soft_loss(
F.softmax(students_preds/temp,dim=1),
F.softmax(teachers_preds/temp,dim=1)
)
# 将hard_loss和soft_loss加权求和
loss = alpha*students_loss+(1-alpha)*ditillation_loss
# 反向传播,优化权重
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 测试集上评估模型性能
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x,y in test_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions==y).sum()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = (num_correct/num_samples).item()
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t Accuracy:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1,acc))
知识蒸馏训练后的预测结果

虽然结果差不多,但是这只是知识蒸馏的一个小的应用,还有就是MNIST数据并不是很多,所以导致差异不明显,但是可以通过这个代码更好的了解知识蒸馏模型。知识蒸馏绝对是轻量化网络的挖坑之作。
