C++之Map与Set的模拟实现
前言:看这篇博客前首先得看博主关于红黑树的实现:C++之红黑树_cls-evd的博客-CSDN博客
目录
前言:看这篇博客前首先得看博主关于红黑树的实现:C++之红黑树_cls-evd的博客-CSDN博客
一、set与map的源码分析
源码中的set:
编辑源码中的map:编辑源码中的红黑树:编辑
二、map与set的建立
三、红黑树节点的修改
四、红黑树的修改
insert的修改
五、迭代器的实现
迭代器的大框架
begin的实现
end的实现
operator++的实现
operator--的实现
operator[] 的实现(针对于map)
六、红黑树成员函数的实现
拷贝构造的实现
拷贝构造的注意事项
赋值运算符的实现
总结及代码
问题:map/set既然是对红黑树的封装,那么他俩为啥不是适配器?
完整代码
一、set与map的源码分析
map是kv结构,set的key结构,但是它俩的底层都是红黑树,那么我们实现它俩的时候是应该实现一红黑棵树呢?还是应该用两棵树?如果用一棵树该如何控制kv与k呢?但是如果使用两棵树代码又是冗余的,该如何解决呢?基于当前的原因我们可以看一看源码。
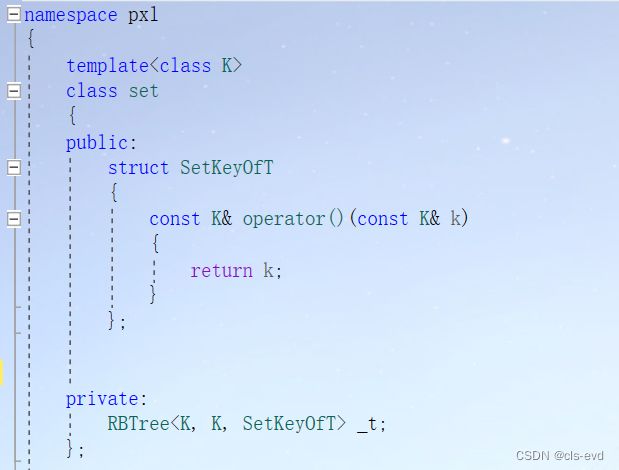
源码中的set:
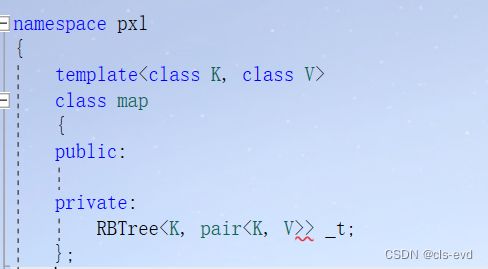
 源码中的map:
源码中的map: 源码中的红黑树:
源码中的红黑树:
源码中是只有一颗红黑树的,它实现两个结构的容器的奥秘就在红黑树的节点
这个容器是set还是map取决于节点里面存的是key还是pair
我们就根据源码的思想进行实现。
二、map与set的建立
三、红黑树节点的修改
template
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode* _left;
RBTreeNode* _right;
RBTreeNode* _parent;
T _data;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED) //红的黑的都无所谓
, _data(data)
{}
}; 四、红黑树的修改
insert的修改
(1)原本我们插入的是pair现在都要换成data,最终目的就是实现复用
(2)同样的insert的比较也就不能使用了,因为现在我们比较的是data。如果data是key没有任何问题,但是如果data是pair我们该如何解决呢?
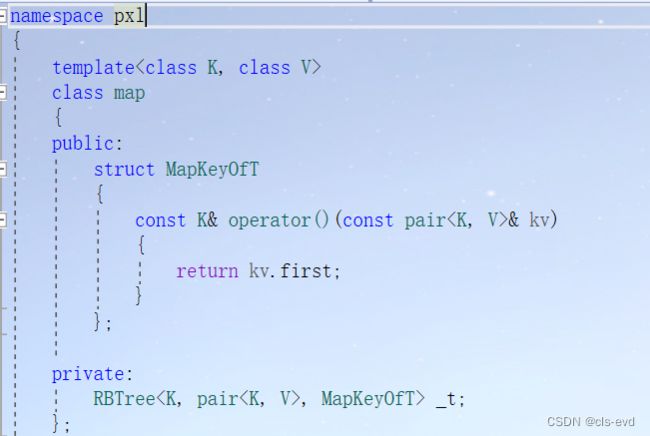
虽然这里不进行修改也不会报错,因为pair本身就支持比较大小,但是pair的比较大小不符合我们的意义 ,pair的小于的定义是first和second有一个小就可以。但是遇到pair我们期望的是只利用pair里面的first比较大小。解决该问题的关键就是源码中红黑树的keyOfValue模板参数。它的作用就是如果你传过来的是key直接返回key,如果你传过来的是pair返回pair的first,由此进行比较,这个模板参数的本质就是一个仿函数。
我们自己实现的叫:keyOfT
相应的map与set建立对应的keyOfT结构体,通过重载()实现返回key或者返回kv.first
红黑树中则通过创建keyOfT的一个对象,这个对象的operator()就可以把他们的值给取出来。
目前为止set与map的插入就实现好了。
五、迭代器的实现
实际上set与map的迭代器就是红黑树的迭代器,所以我们实现出红黑树的迭代器即可。
迭代器的大框架
template
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator Self;
Node* _node;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator ++()
{
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//Self& operator--()
//{
//}
}; 红黑树中就需要typedef一个迭代器
begin的实现
begin就是最左节点
iterator begin()
{
Node* min = _root;
while (min && min->_left) //最左节点
{
min = min->_left;
}
return iterator(min);//构造一个迭代器
}end的实现
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr); //end也就是最后一个数据的下一个位置,这里我们用nullptr替代
}operator++的实现
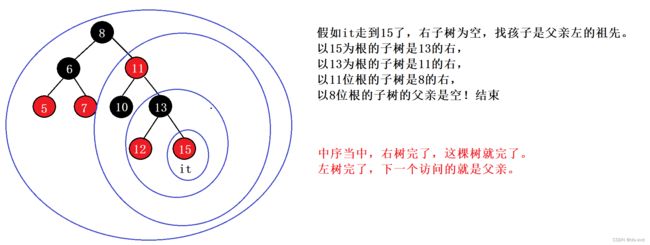
1.如果右子树不为空,中序的下一个就是右子树的最左节点
2.如果右子树是空,说明我所在的子树已经访问完了,如果我是父亲的左边,下一个访问的就是父亲。如果我是父亲的右,说明一中序已经完了,我就要访问我父亲的父亲。
所以我就要沿着根路径,找孩子是父亲左的祖先。直到父亲为空
因为它有三叉链才能这样不借助栈
//前置++
Self& operator ++()
{
if (_node->_right) //访问右子树的最左节点
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right) //parent是进判断根节点的
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
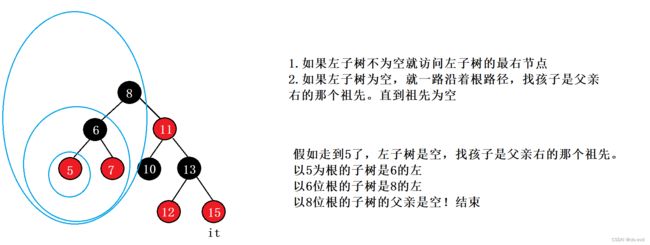
}operator--的实现
Self& operator--()
{
//右根左,左树不为空就访问左树的最右节点,左树为空就去访问祖先里面
if (_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while (max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent&&cur==parent->_left)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}Find的实现
map/set对Find进行一次封装就是find
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return iterator(cur);
}
}
return end();
}operator[] 的实现(针对于map)
首先改造一个插入。将插入的返回值设置为pair,并且跟据相应的规则,如果插入成功返回新插入的节点,如果插入失败返回当前节点。
[ ]的实现:
返回map中的value,ret就是pair
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
auto ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}执行结果:
六、红黑树成员函数的实现
拷贝构造的实现
这里我们没写拷贝构造发现拷贝成功了,是不是就意味着不需要我们再写了呢?
现在是一个浅拷贝,没有在这里崩溃就是因为我们没写析构函数,析构两次才会崩溃的。
当我们实现好红黑树的析构以后,自然而然的也就崩溃了
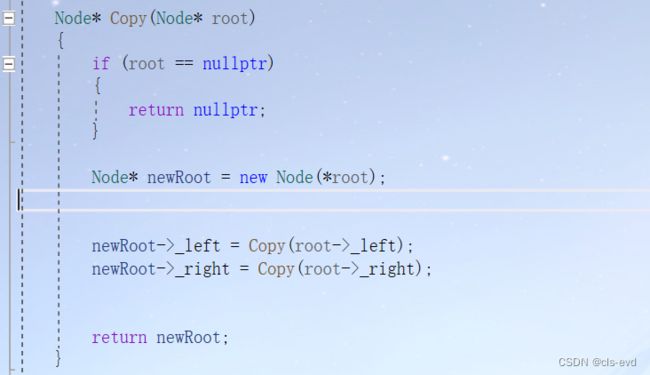
深拷贝实现的思路就是递归的去拷贝,同时要注意我们这里是三叉链要进行链接parent,颜色也需要我们进行拷贝。
RBTree(const RBTree& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_data);
newRoot->_col = root->_col;
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
if (newRoot->_left)
{
newRoot->_left->_parent = newRoot;
}
if (newRoot->_right)
{
newRoot->_right->_parent = newRoot;
}
return newRoot;
} 这下我们的拷贝构造就没有问题了
拷贝构造的注意事项
1.不能去调用红黑树叶子节点的拷贝构造
new这里用的就是拷贝构造,我们的节点没有写拷贝构造会调用默认的,又因为我们节点中定义的全是指针,全是内置类型,都会进行拷贝
结果看似正确,但是实际这棵树已经非常的乱了。
copy这棵树唯独parent没有进行深拷贝还是进行了浅拷贝,因此copy这个数的祖先和s这个数的祖先一模一样,这种问题很难被发现,尤其是当你进行插入的时候,如果你往copy这个树插入节点你就会惊奇的发现新插入的节点居然出现在了s这棵树上。
赋值运算符的实现
RBTree& operator =(RBTree& t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
} empty()接口的实现
红黑树为空返回0,不为空返回1
bool Empty()const
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return false;
return true;
}size()接口的实现
返回红黑树总结点的个数
size_t Size()const
{
return SizeNode(_root);
}
size_t SizeNode(Node* root) const
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
return SizeNode(root->_left) + SizeNode(root->_right) + 1;
}clear()接口的实现
将树中的节点全都清理掉
void Clear()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}总结及代码
map和set就是依靠我们的红黑树实现的,它俩本身就是一个空壳子,就是再对红黑树进行封装。我们同时发现map与set我们都没有进行实现成员函数都用的是默认的成员函数,因为红黑树是set/map里面的自定义类型.eg:我们去调用set/map的构造,但是set/map没有写构造就会调用他们的默认构造函数,默认构造函数对于自定义类型就会去调用红黑树的构造。
总之默认生成的成员函数就会去调用红黑树成员函数。
问题:map/set既然是对红黑树的封装,那么他俩为啥不是适配器?
stack/queue/priority_queue 封装的是deque/vector 他们是适配器,而map/set 封住的是红黑树 他们就不是不是适配器
这里以stack和map为例
关键点就在于这个Container,它是可以进行任意替换的,但是map/set就不存在这样的一个Container,简单来说就是stack的底层能改,但是map的底层是改不了的。所以map/set就不是适配器。
完整代码
RBTree.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode* _left;
RBTreeNode* _right;
RBTreeNode* _parent;
T _data;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED) //红的黑的都无所谓
, _data(data)
{}
};
template
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator Self;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node) //只需要构造函数,迭代器没什么资源要去释放,一个迭代器赋值给另外一个迭代器只需要浅拷贝就可
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() //返回里面的数据
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->() //返回地址
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
//前置++
Self& operator ++()
{
Increament();
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
Increament();
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
DeIncreament();
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
DeIncreament();
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
private:
void Increament()
{
if (_node->_right) //访问右子树的最左节点
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right) //parent是进判断根节点的
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
}
void DeIncreament()
{
//右根左,左树不为空就访问左树的最右节点,左树为空就去访问祖先里面
if (_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while (max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
}
Node* _node; //迭代器就是一个节点的指针
};
//set RBTree
//map RBTree,MapKeyOfT>
template
struct RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode Node;
public:
typedef RBTreeIterator iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* min = _root;
while (min && min->_left) //最左节点
{
min = min->_left;
}
return iterator(min);//构造一个迭代器
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr); //end也就是最后一个数据的下一个位置,这里我们用nullptr替代
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return iterator(cur);
}
}
return end();
}
bool Empty()const
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return false;
return true;
}
size_t Size()const
{
return SizeNode(_root);
}
void Clear()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
RBTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
RBTree(const RBTree& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
RBTree& operator =(RBTree& t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~RBTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
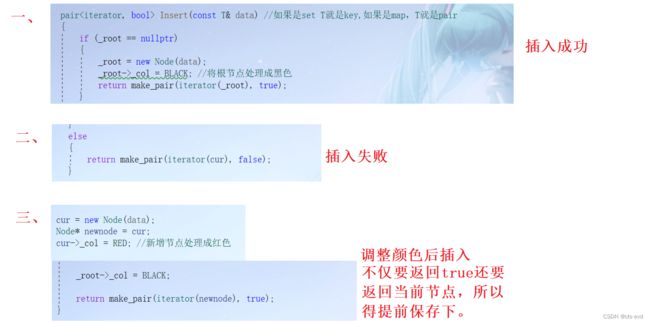
pair Insert(const T& data) //如果是set T就是key,如果是map,T就是pair
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK; //将根节点处理成黑色
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_col = RED; //新增节点处理成红色
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent; //把三叉链链上
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
//控制平衡
while (parent&& parent->_col == RED) //父亲存在且为红一定不是根
{
Node* grangfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grangfather->_left) //父亲在g的左
{
Node* uncle = grangfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//情况一:叔叔存在且为红
{
//变色+继续向上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grangfather->_col = RED;
cur = grangfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //情况二+三:叔叔存在/叔叔存在且为黑
{
// g
// p
//c
// g
// p
// c
if (cur == parent->_left) //情况二
{
//单旋
RotateR(grangfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grangfather->_col = RED;
}
else //情况三
{
//双旋
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grangfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grangfather->_col = RED;
}
break; //我这棵树旋转完成了后,每条路径黑节点的个数没变,不会影响其他路径,这棵字树的根已经是黑色了,与情况一不同
}
}
else//parent == grangfather->_right p在g的右
{
Node* uncle = grangfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//情况一:叔叔存在且为红
{
//变色+继续向上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grangfather->_col = RED;
cur = grangfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //情况二+三:叔叔存在/叔叔存在且为黑
{
// g
// p
// c
// g
// p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right) //情况二
{
RotateL(grangfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grangfather->_col = RED;
}
else //情况三
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grangfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grangfather->_col = RED;
}
break; //我这棵树旋转完成了后,每条路径黑节点的个数没变,不会影响其他路径,这棵字树的根已经是黑色了,与情况一不同
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
private:
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_data);
newRoot->_col = root->_col;
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
//增加上三叉连的链接关系
if (newRoot->_left)
{
newRoot->_left->_parent = newRoot;
}
if (newRoot->_right)
{
newRoot->_right->_parent = newRoot;
}
return newRoot;
}
size_t SizeNode(Node* root) const
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
return SizeNode(root->_left) + SizeNode(root->_right) + 1;
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR) //不为空才链接,否则就出现空指针问题
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent; //提前记录一下parent的父亲
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root) //如果是一颗独立的树
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent) //改变parent父亲的链接
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent; //注意三叉链接
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = parent;
}
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
private:
Node* _root; //内置类型
}; MySet.h
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace pxl
{
template
class set
{
public:
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& k)
{
return k;
}
};
typedef typename RBTree::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
bool empty()const
{
return _t.Empty();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _t.Size();
}
void clear()
{
_t.Clear();
}
private:
RBTree _t; //自定义类型,调用它的拷贝构造,但是红黑树的拷贝构造也没写
//红黑树是set/map里面的自定义类型,我们去调用set的构造,但是set没有写构造,就会去调用红黑树的构造
//总之默认生成的成员函数就会去调用红黑树成员函数
};
void test_set()
{
set s;
s.insert(1);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(6);
set::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it <<" ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
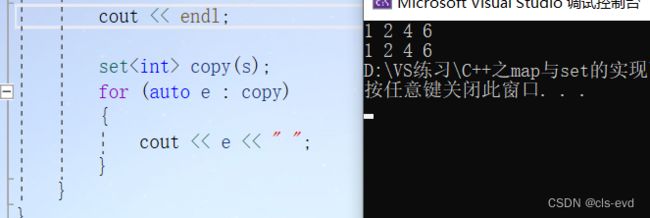
set copy(s);
for (auto e : copy)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}
} MyMap.h
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace pxl
{
template
class map
{
public:
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef typename RBTree, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
//对类模板里面的内嵌类型进行typedef
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair insert(const pair& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
auto ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _t.Empty();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _t.Size();
}
void clear()
{
_t.Clear();
}
private:
RBTree, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_map()
{
map m;
m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 5));
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(8, 8));
m[7];
m[8] = 88;
map::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}